On this page, you will find Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 6 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Notes Physical and Chemical Changes
Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. The changes around us can be broadly classified as – physical and chemical change.
2. Properties like shape, size, colour, state, etc., of a substance are called its physical properties.
3. A change in which a substance experiences a change in its physical properties is known as physical change.
4. Physical change is generally reversible.
5. A change in which one or more new substances are formed is called a chemical change.
6. Chemical change is generally irreversible.
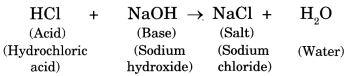
7. The process of formation of red or orange coating on the surface of iron when exposed to air and moisture, consisting chiefly of ferric hydroxide and ferric oxide, is called
8. The process of rusting can be represented by the following equation:
Iron (Fe) + Oxygen (02, from the air) + Water (H20) ➝ Rust (Fe203, Iron oxide)
9. The presence of both oxygen and water (or water vapour) is essential for rusting.
10. The process of depositing a layer of zinc metal on iron is known as It protects iron from rusting.
11. Crystallization is the process of separating pure crystals of a substance from its supersaturated solution on cooling.
Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Notes Important Terms
Chemical change: A change in which the chemical properties of a substance get changed, and new substances are formed is called a chemical change.
Chemical reaction: A chemical change is also known as chemical reaction. In fact, the process involving a chemical change is accompanied by a chemical reaction.
Crystallization: The process of separating pure crystals of a substance from its super-saturated solution is known as crystallization.
Galvanization: The process of depositing a layer of zinc on iron metal is called galvanization.
Physical change: A change in which a substance undergoes a change in its physical properties is called a physical change.
Rusting: A process in which a layer of rust covers the surface of iron is called rusting.