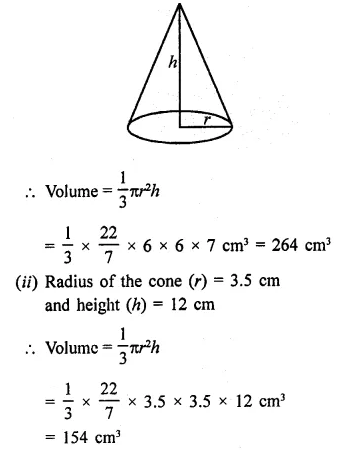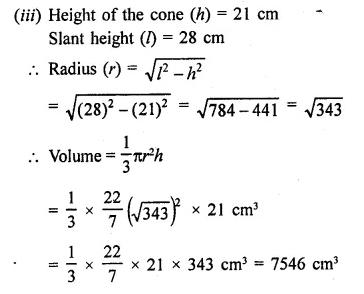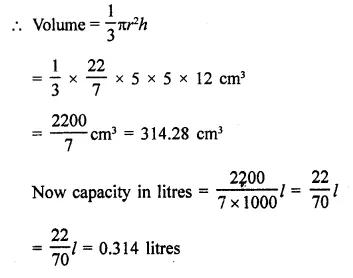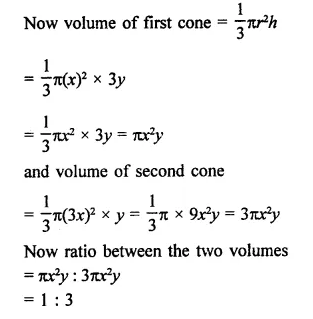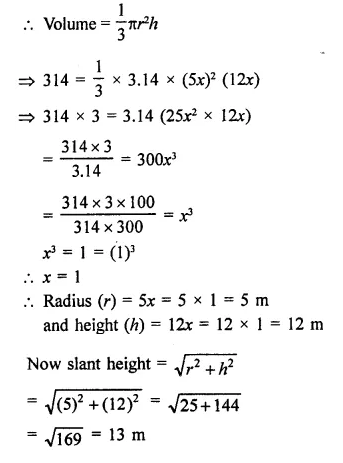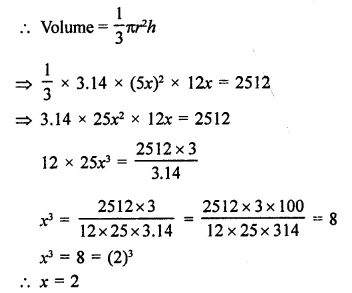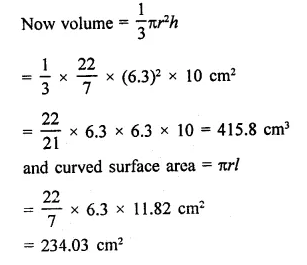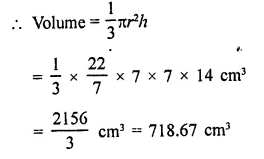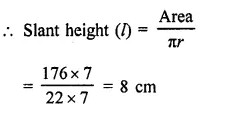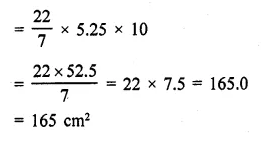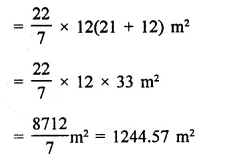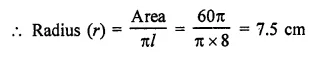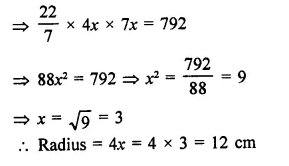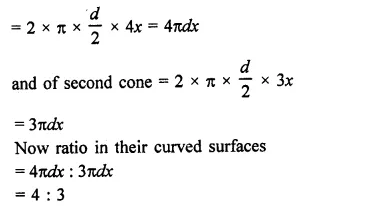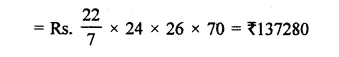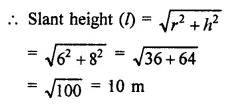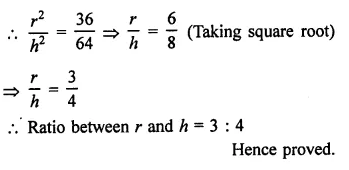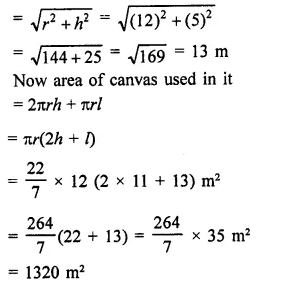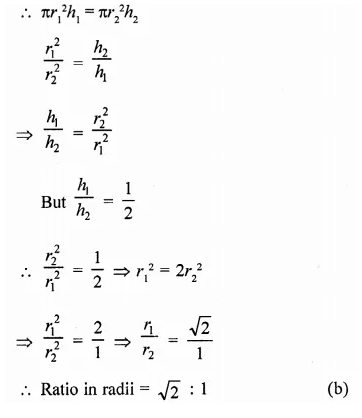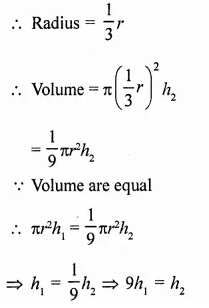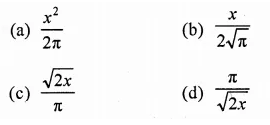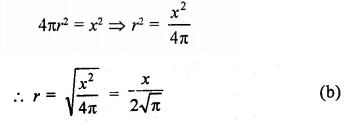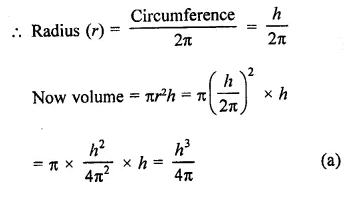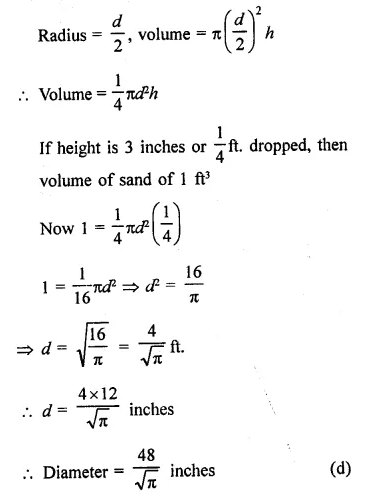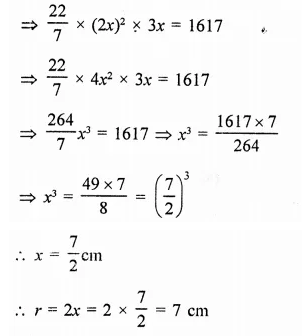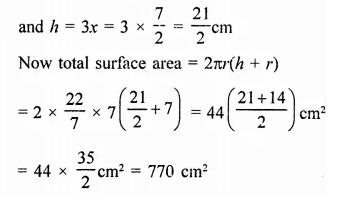RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone VSAQS
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone VSAQS
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone Ex 20.1
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone Ex 20.2
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone MCQS
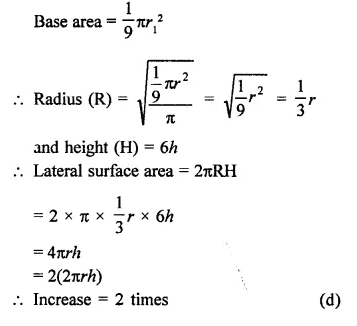
Question 1.
The height of a cone is 15 cm. If its volume is 500π cm3, then find the radius of its base.
Solution:
Volume of cone = 500π cm3
and height (h) = 15 cm
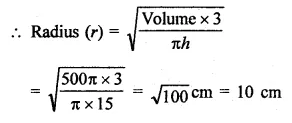
Question 2.
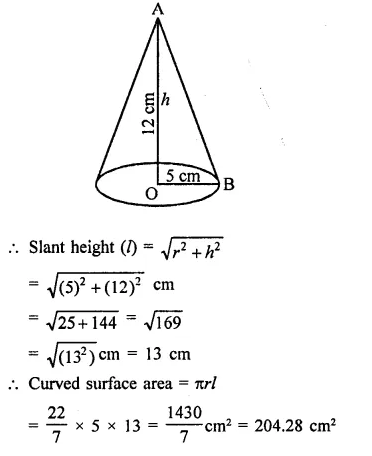
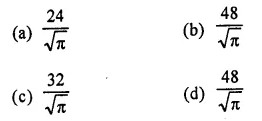
If the volume of a right circular cone of height 9 cm is 48π cm3, find the diameter of its base.
Solution:
Volume of a cone = 48π cm3
Height (h) = 9 cm
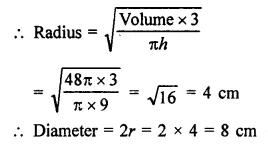
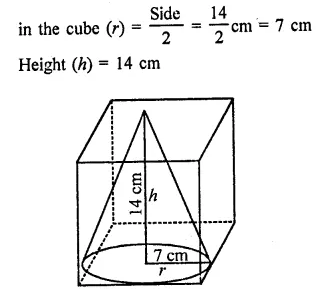
Question 3.
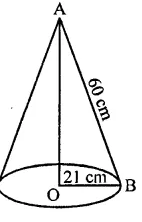
If the height and slant height of a cone are 21 cm and 28 cm respectively. Find its volume.
Solution:
Height of a cone (h) = 21 cm
and slant height (l) = 28 cm
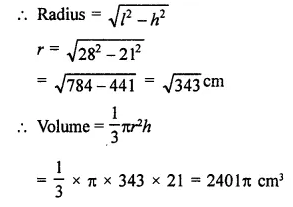
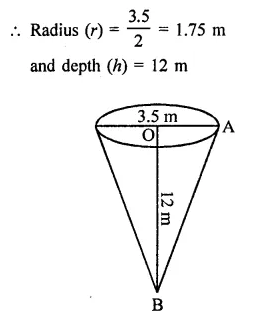
Question 4.
The height of a conical vessel is 3.5 cm. If its capacity is 3.3 litres of milk. Find the diameter of its base.
Solution:
Capacity of conical vessel = 3.3 litres
Volume = 3.3 m3
= 3.3 x 1000 = 3300 cm2
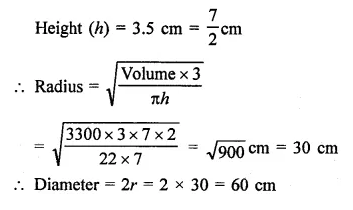
Question 5.
If the radius and slant height of a cone are in the ratio 7 : 13 and its curved surface area is 286 cm2, find its radius.
Solution:
Two ratio in radius and slant height of a cone = 7 : 13
Let radius (r) = 7x
and slant height (1) = 13x
Curved surface area = πrl
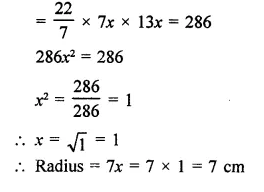
Question 6.
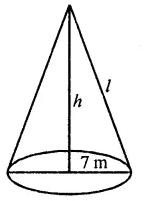
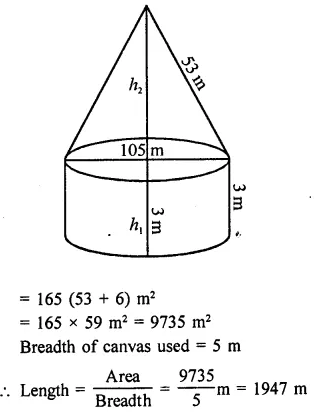
Find the area of canvas required for a conical tent of height 24 m and base radius 7 m.
Solution:
Base radius of the closed cone (r) = 7 cm
and vertical height (h) = 24 cm
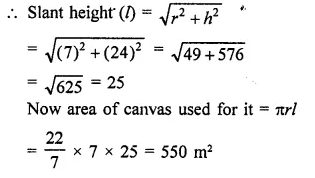
Question 7.
Find the area of metal sheet required in making a closed hollow cone of base radius 7 cm and height 24 cm. making a closed hollow cone of base radius 7 cm and height 24 cm.
Solution:
Base radius of the closed cone (r) = 7 cm
and vertical height (h) = 24 cm
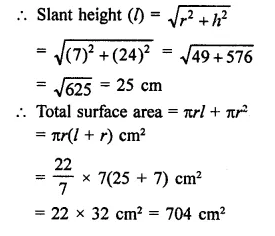
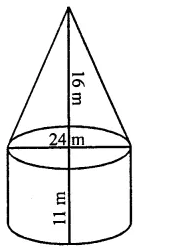
Question 8.
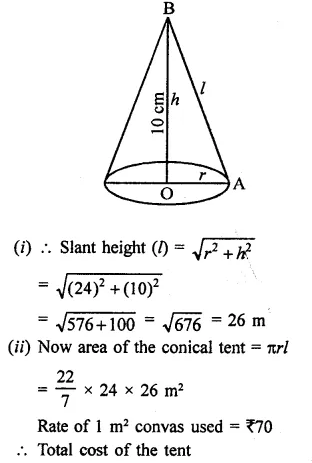
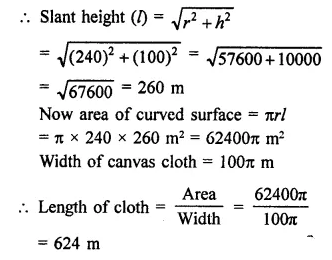
Find the length of cloth used in making a conical pandal of height 100 m and base radius 240 m, if the cloth is 100π m wide.
Solution:
Height of conical pandal (A) = 100 m
Base radius (r) = 240 m
Hope given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 20 Surface Areas and Volume of A Right Circular Cone VSAQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.