RS Aggarwal Class 9 Solutions Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14D
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14D.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14C
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14D
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14E
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14F
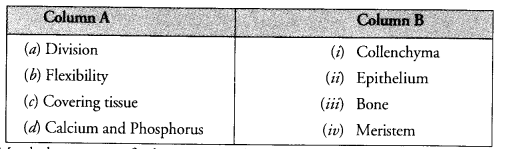
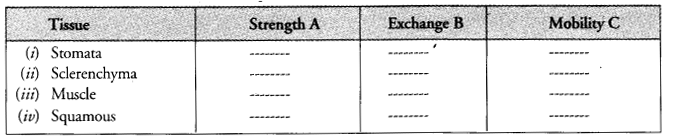
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14G
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14H
Question 1.
Solution:
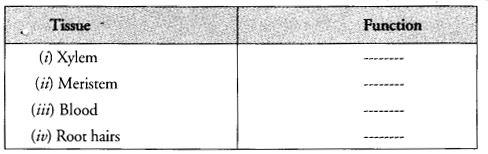
(i) First eight natural numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8 }{ 8 } \) = \(\frac { 36 }{ 8 } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 2 } \) = 4.5
(ii) First ten odd numbers are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 1+3+5+7+9+11+13+15+17+179 }{ 10 } \) = \(\frac { 100 }{ 10 } \) = 10
(iii) First five prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11.
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 2+3+5+7+11 }{ 5 } \) = \(\frac { 28 }{ 5 } \) = 5.6
(iv) First six even numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 2+4+6+8+10+12 }{ 10 } \) = \(\frac { 42 }{ 6 } \) = 7
(v) First seven multiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 5+10+15+20+25+30+35 }{ 7 } \) = \(\frac { 140 }{ 7 } \) = 20
(vi) All the factors of 20 are, 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
∴ Mean = \(\frac { 1+2+4+5+10+20 }{ 6 } \) = \(\frac { 42 }{ 6 } \) = 7
Question 2.
Solution:
No. of families (n) = 10
Sum of children (∑x1) = 2 + 4 + 3 + 4 + 2 + 0 + 3 + 5 + 1 + 6 = 30
∴ Mean \(\left( \overline { x } \right) =\frac { \sum { x1 } }{ n } =\frac { 30 }{ 10 } =3\)
Question 3.
Solution:
Here number of days (n) = 7
Number of books (∑x1) = 105 + 216 + 322 + 167 + 273 + 405 + 346 = 1834
∴ Mean \(\left( \overline { x } \right) =\frac { \sum { x1 } }{ n } =\frac { 1864 }{ 7 } =262 books\)
Question 4.
Solution:
Number of days (n) = 6
Sum of temperature (∑x) = 35.5 + 30.8 + 27.3 + 32.1 + 23.8 + 29.9 = 179.4°F
∴ Mean temperature = \(\frac { \sum { x } }{ n } =\frac { 179.4 }{ 6 } \)=29.9°F
Question 5.
Solution:
Number of students (n) = 12
Sum of marks (∑x) = 64 + 36 + 47 + 23 + 0 + 19 + 81 + 93 + 72 + 35 + 3 + 1 = 474
= \(\frac { \sum { x1 } }{ n } =\frac { 474 }{ 12 } \) = 39.5
Question 6.
Solution:
Here, n = 6
and arithmetic mean =13
Total sum = 13 x 6 = 78.
But sum of 7 + 9+ 11 + 13 + 21=61
Value of x = 78 – 61 = 17
Hence x = 17 Ans.
Question 7.
Solution:
Let x1, x2, x3, … x24 be the 24 numbers
\(\frac { x1+x2+x3+…..+x24 }{ 24 } =35\)
=> x1 + x2 + x3 +….+ x24 = 35 x 24
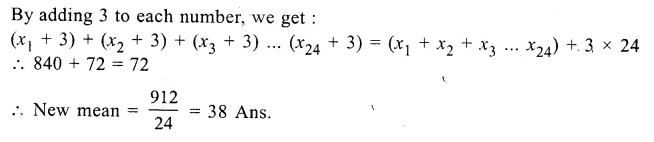
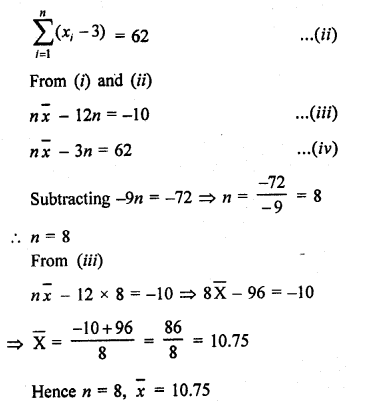
Question 8.
Solution:
Let x1 + x2 + x3……..x20 be the 20 numbers
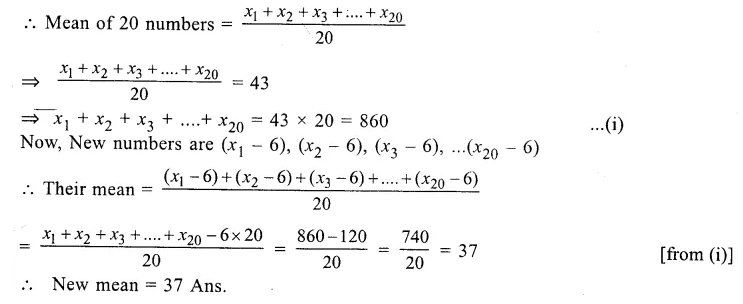
Question 9.
Solution:
Let x1, x2, x3 … x15 be the numbers
Mean = \(\frac { x1+x2+x3+…..+x15 }{ 15 } = 27\)
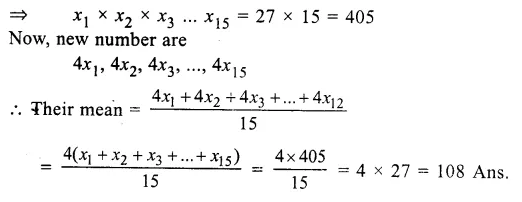
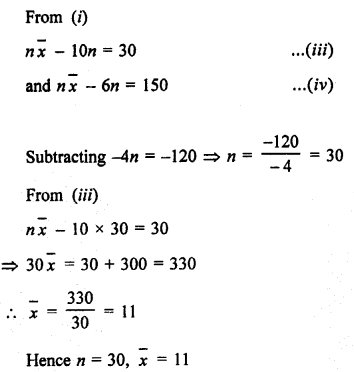
Question 10.
Solution:
Let x1, x2, x3 … x12 be the numbers
Mean = \(\frac { x1+x2+x3+…..+x12 }{ 12 }\) = 40
=> x1+x2+x3+….+x12 = 40 X 12 =480
Now,new numbers are \(\frac { x1 }{ 8 } ,\frac { x2 }{ 8 } ,\frac { x3 }{ 8 } ,..\frac { x12 }{ 8 } \)
Mean = \(\frac { \frac { x1 }{ 8 } +\frac { x2 }{ 8 } +\frac { x3 }{ 8 } +…..+\frac { x12 }{ 8 } }{ 12 } \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 8 } \frac { \left( x1+x2+x3+….x12 \right) }{ 12 } \)
= \(\frac { 480 }{ 8X12 } \) = 5
Mean of new numbers =5
Question 11.
Solution:
Let x1, x2, x3,…..x20 are the numbers
Mean = \(\frac { x1+x2+x3+…x20 }{ 20 }\) = 18
=> x1 + x2 + x3 +….+ x20 = 18 X 20 =360
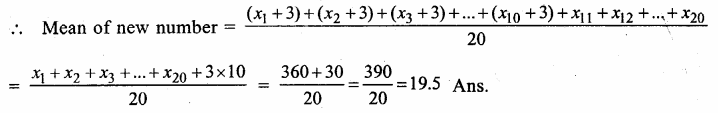
Question 12.
Solution:
Mean weight of 6 boys = 48 kg
Their total weight = 48 x 6 = 288 kg
Weights of 5 boys among them, are 51 kg, 45 kg, 49 kg, 46 kg and 44 kg
Sum of weight of 5 boys = (51 + 45 + 49 + 46 + 44) kg = 235 kg
Weight of 6th boy = 288 kg – 235 kg = 53 kg Ans.
Question 13.
Solution:
Mean of 50 students = 39
Total score = 39 x 50 = 1950
Now correct sum of scores = 1950 – Wrong item + Correct item= 1950 – 23 + 43
= 1950 + 20 = 1970
Correct mean = \(\frac { 1970 }{ 50 } \) = 39.4 Ans.
Question 14.
Solution:
Mean of 100 items = 64
The sum of 100 items = 64 x 100 = 6400
New sum of 100 items = 6400 + 36 + 90 – 26 – 9 = 6526 – 35 = 6491,
Correct mean = \(\frac { 6491 }{ 100 }\) =64.91 = 64.91 Ans.
Question 15.
Solution:
Mean of 6 numbers = 23
Sum of 6 numbers = 23 x 6 = 138
Excluding one number, the mean of remaining 5 numbers = 20
Total of 5 numbers = 20 x 5 = 100
Excluded number = 138 – 100 = 38 Ans.
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 9 Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14D are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.


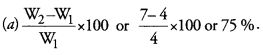
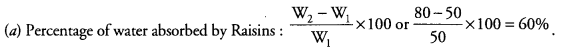
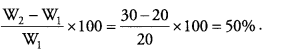
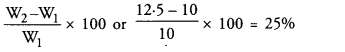



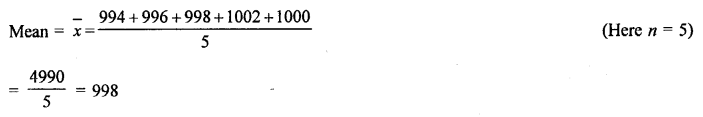
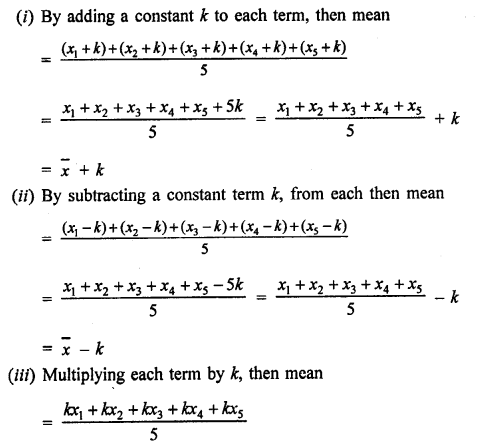
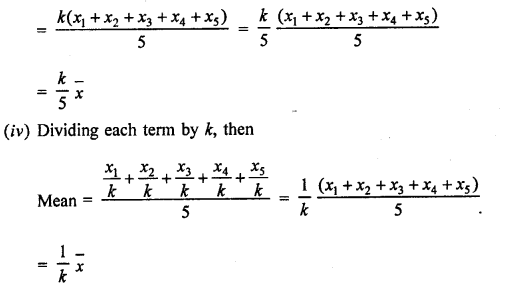

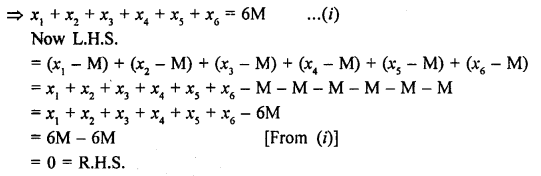

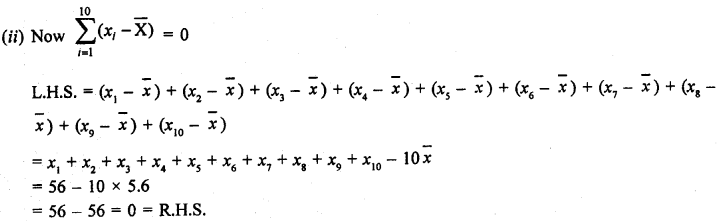
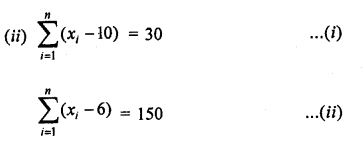


 Answer:
Answer: