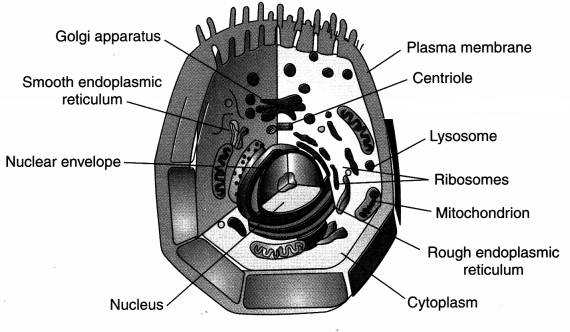
Here we are providing The Letter Extra Questions and Answers Class 10 English Literature Reader, Extra Questions for Class 10 English was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-english/
The Letter Extra Questions and Answers Class 10 English Literature
The Letter Extra Questions and Answers Short Answer Type
The Letter A Question And Answers Class 10 Question 1.
Ali in the story The Letter is a lonely man. How does the writer bring out Ali’s loneliness?
Answer:
Ali lived all alone, passing his days in wait of a letter from his only child Miriam. The writer while describing Ali’s journey to the post office says he walks his lonely way, where except for the occasional bark of a dog, the distant steps of a workman going early to work or the screech of a bird disturbed before its time, the whole town was wrapped in deathly silence.
The Letter Question Answer Class 10 Question 2.
In the story The Letter what are the changes that come over Ali after the marriage of his daughter Miriam?
Answer:
Ali misses his daughter once she goes away. He realises how much he loves her. It also brings to him the realisation that the world is based on love. This makes him give up hunting. He can no longer bear to see the pain of the partridges separated from their parents who have been killed. He patiently waits for his daughter’s letter and goes to the post office daily without bothering about the cold or the heat. He bears the jests and rude remarks of the clerks at the post office.
The Letter Question Answers Class 10 Question 3.
What made Ali a good shikari?
Answer:
Ali had the hunter’s instinct in his blood and bones. A clever shikari, his skill and love for the hunt made it impossible for him to pass a day without hunting. Due to his sharp eyesight, Ali easily spotted the earth brown partridge, almost invisible to others and the cunningly hidden hare crouching in the yellow brown scrub.
Question 4.
“The post office, one of the uninteresting buildings in the world, became his place of pilgrimage.” Who is being referred to here? Why did he come to the post office? Why has the journey been described as a pilgrimage?
Answer:
Coachman Ali is being referred to here. He went daily to the post office waiting for his daughter’s letter. A pilgrimage is a journey, which is often long and difficult, to a special place for religious reasons. Ali’s visits to the post office have been described as a pilgrimage because he went to the post office daily, braving the bitter cold and the heat, with the faith that he would receive his daughter’s letter.
Question 5.
Describe the Postmaster.
Answer:
The Postmaster was a man with a face as sad and as inexpressive as a pumpkin. He did not display any signs of liveliness or excitement. He carried out his job without compassion or feeling. He did not understand Ali’s feelings till his own daughter fell sick.
Question 6.
Why did Ali not come to the post office for several days? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Ali did not come to the post office for several days probably because he was very sick. We can conclude this from the fact that before this for the past five years he had not missed coming to the post office. Moreover, when he came, it was a struggle for him to breathe and on his face were clear signs of the approaching end.
Question 7.
Who did Ali meet on his way back from the post office? What request did he make to him?
Answer:
On his way back from the post office, Ali met one of the post office clerks, a fellow called Lakshmi Das. Ali stopped him and gave him five golden guineas. He told the clerk that he was dying and that day was his very last day. But he had neither seen Miriam nor had he received any letter from her. He told the clerk to keep the money and to keep Miriam’s letter, when it came, on his grave.
Question 8.
What brought about a change in the Postmaster’s attitude?
Answer:
The Postmaster’s attitude changed when his daughter lay ill in another town, and he was anxiously waiting for news of her. This worry and anxiety about her changed the Postmaster. His father’s heart recognised Ali’s yearning for his daughter. The haughty temper of the official left him in his sorrow and anxiety and his human heart was laid bare.
Question 9.
What difference did the Postmaster notice in Ali?
Answer:
Ali was still the meek old man, bent double with age. The tears were wet on his face as they had been when the clerk left him. But his features had been hard then, and now they were softened by lines of kindliness. He lifted his eyes and in them was a light so unearthly that the Postmaster shrank back in fear and astonishment.
Question 10.
Give a short description of Ali.
Answer:
Ali was an old man, bent double with age. He was poor and wore tom clothes. He leant heavily on his stick as he walked. He had sharp eyesight and in his youth he had been a good shikari. His sharp eyes could see the hare even when the dogs failed. He lived alone in the village ever since his daughter, Miriam, had got married and gone away with her husband to Punjab.
The Letter Extra Questions and Answers Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Tortured by doubt and remorse, the Postmaster sits in the glow of a charcoal sigri that night, waiting for news of his daughter. As the Postmaster, write a diary entry outlining your feelings.
Answer:
20 June 20XX
Today, as I was eagerly going through the mail waiting for my daughter’s letter, my eyes fell upon the letter Coachman Ali had been waiting for. I was shocked on seeing the letter, and my heart was filled with compassion and regret. It was not long ago that Ali had come to me and humbly asked me if I had a letter from his Miriam. I can’t forget how I had reacted. I had rebuked him and told him to go away. I hadn’t seen the pain in his eyes, his tears of helplessness. I hadn’t seen the anguish of the father whose patience had been exhausted even if his faith still held. How all of us had poked fun at him! We had called him a lunatic! How insensitive we were!
My own daughter’s sickness has brought about a major change in me. As I anxiously await news of my daughter, I can understand what poor Ali must have gone through. Now I look at every envelope differently— as though it contains a warm beating heart.
Question 2.
Rebuked by the Postmaster, Ali walks away from the post office with a heavy heart. That night, he writes his diary outlining his feelings about the day’s events and his approaching end. As Ali, write the diary entry.
Answer:
19 June 20XX
It is my love for Miriam that drives me to the post office every day. I miss her and wait for any news from her. I have been waiting at the post office daily for five long years but in vain. The post office employees make fun of me. Today I was rebuked by the Postmaster, maybe they are disturbed by my presence. I will not go there again. I know that my end is near. I will give money to Lakshmi Das to lay Miriam’s letter on my grave. I am sure the letter will come.
Question 3.
Lakshmi Das, a clerk in the post office, writes a letter to his friend describing the events that take place after Ali’s death and his role in the story. Write the letter as Lakshmi Das.
Answer:
2 March, 20XX
Dear Ram Prasad
I wish to recount a strange incident that occurred today involving an old man who died three months ago.
This incident has changed my beliefs and my attitude towards life. The incident inVolves old Coachman Ali. If you remember, I told you of this man whose daughter got married and moved away to Punjab five years ago. He would come every day to the post office to wait for a letter from his daughter.
We often made fun of him. We would call out his name just to see him get up and rush to the door. Yet, he came daily, just the same, in rain and in cold. One day, about three months ago, the Postmaster rebuked him rudely. He said the letter would be delivered to him when it came. Ali left the post office with tears in his eyes. He met me and gave me five golden guineas to lay his daughter’s letter on his grave. Ali died shortly after this.
Today, a letter came from Miriam. When I went to the post office I heard the Postmaster talking to someone. He told me Ali had come to take his letter. He was staring with wide-open eyes at the doorway. Miriam’s letter was lying near the door in the evening we went and kept the letter on Ali’s grave.
Yours sincerely,
Lakshmi Das
Question 4.
A newspaper reporter hears of the Postmaster’s strange encounter with Ali. He writes a report in the newspaper about Ali’s long wait for the letter and his strange appearance at the post office the day he receives a letter from Miriam. As the newspaper reporter, write the article Love Knows
Answer:
No Boundaries.
Heading—LOVE KNOWS NO BOUNDARIES
Byline—by staff reporter
The strength of love, gives courage to face all kinds of situations. Ali’s love for Miriam is reflected in the eagerness with which he waited for her letter. He visited the post office daily, braving the weather, the ridicule of clerks and even the Postmaster’s rebuke. He waited in vain for the letter and died before it arrived. Postmaster saw Ali after his death and spoke to him. In the end, he laid the letter on Ali’s grave. This incident is an example of the power of love.
Question 5.
It is essential to respect everyone’s feelings. Bring out this message with reference to the story
Answer:
The Letter.
The message of the story is that we should always respect everyone’s feelings and take care not to hurt others. Coachman Ali’s daughter got married and left him and then he understood the meaning of love and separation. Since then, he had been regularly visiting the post office, expecting a letter from his daughter Miriam, but returning home empty handed. One day, the post master rebuked him harshly.
Soon, the post master’s daughter fell ill and he was anxious to hear from her. As he waited for his daughter’s letter, he realised his mistake and how he had hurt Ali. He realised the pain of a father waiting for his daughter’s letter. His attitude changed. He now saw the letters as the essential expressions of a human heart, not just pieces of paper. He understood the human worth of a letter.
The Letter Extra Questions and Answers Reference to Context
Read the following passages taken from The Letter and answer the questions:
Question 1.
“Beholding the wooden arch of this building, the old man was filled with the joy that the pilgrim feels when he first sees the goal of his journey. ’’
(a) What building is being referred to here?
Answer:
The post office is being referred to here.
(b) Why is the old man called a pilgrim?
Answer:
The old man comes to the post office with feelings of faith and love.
(c) Why is the building the goal of his journey?
Answer:
The old man comes to the post office to check if there is a letter for him from his daughter Miriam.
Question 2.
“But for the faith and love that warmed him, he could not have borne the bitter cold. ”
(a) Who is the ‘he’ in this line?
Answer:
The ‘he’ mentioned in this line is Coachman Ali.
(b) Why was he at the post office in the bitter cold?
Answer:
Ali came to the post office daily to wait for a letter from his daughter Miriam, despite the bitter cold and waited there till the letters had been sorted out for delivery’.
(c) What gave Ali the strength to brave the bitter cold?
Answer:
The old man loved his daughter Miriam who had gone off to the Punjab with her husband five years ago. He had faith that she would write to him. This love and faith gave him the strength to bear the bitter winter cold.
Question 3.
“The old man got up, raised his eyes to heaven in gratitude and stepping forward put his hands to the door. ”
(a) Who is the old man?
Answer:
The old man is Coachman Ali.
(b) Why did he raise his eyes to heaven in gratitude?
Answer:
The clerk sorting out the letters had called out his name. Thinking he had got a letter from his daughter Miriam (for which he had been waiting for the past five years), he thanked god and stepped forward to receive the letter.
(c) Why had the clerk called out his name?
Answer:
Every day, regardless of the weather, Ali came and sat on a bench at the post office waiting for his daughter’s letter. The clerk called out his name in jest even though there was no letter for him for the fun of seeing him jump up and come to the door.
Question 4.
“Now he understood the meaning of love and separation. He could no longer enjoy the sportsman’s pleasure and laughter at the bewildered terror of the young partridges bereft of their parents. ”
(a) Who is he?
Answer:
He is Coachman Ali.
(b) Why had he understood the meaning of love and separation now?
Answer:
Ali’s daughter Miriam had gotten married and gone away to the Punjab with her husband and he had not heard from her for the past five years.
(c) How had he reacted to hunting partridges earlier?
Answer:
Earlier, Ali had laughed at the young partridges who had been separated from their parents.
Question 5.
“That day he could not contain his impatience. ”
(a) Who is he?
Answer:
He is Coachman Ali.
(b) Why was he impatient?
Answer:
Ali had been waiting in vain for his daughter’s letter for the past five years. He knew that he was sick and approaching his end. He was impatient to have news of his daughter before he died.
(c) How did he show his impatience?
Answer:
Ali walked up to the Postmaster and asked if he had a letter for him from Miriam rather than waiting quietly.
Question 6.
“He knew at once that this was the letter the old man had been waiting for: it must be from his daughter Miriam. ”
(a) Who is ‘he’?
Answer:
The ‘he’ mentioned here is the Postmaster.
(b) Where was the old man?
Answer:
The old man had died.
(c) Which literary device has been used in these lines?
Answer:
The literary device used here is irony. Ali had waited for five years for a letter from his daughter Miriam and now when the letter arrived, Ali was dead.
Complete the table by explaining the following phrases/sentences in your own words.
| Ph rases/Sentences | Meanings |
| (a) Happy memories light up a life that is nearing its close | Ali was old and approaching death. At this time, recollections of happier times brought joy to his unhappy life. |
| (b) The sounds helped him along his lonely way | Ali was walking down a deserted street early in the morning. The familiar sounds of grinding mills, and the sweet voices of women singing at their work gave him comfort and the courage to walk on. |
| (c) The cold used sleep to extend its sway over all things even as a false friend lulls his chosen victim with caressing smiles | Just as a false friend uses sweet words and false smiles to reassure and lay to rest any suspicion in the heart of his intended victim, the cold weather, too, deceives its victims by . . 9 soothing them into sleep and killing them as they sleep. |
| (d) when the evening of his life was drawing in, he left his old ways and suddenly took a new turn | As he became older and approached the end of his life, Ali gave up his old habits and occupation (hunting animals) and changed his attitude and his lifestyle. |
| (e) The whole universe is built through love and the grief of separation is inescapable | The basis on which the universe revolves is love and if one loves someone, the pain of separation is unavoidable. |
| (f) The postmaster, a man with a face as sad and as inexpressive as a pumpkin, would be seen sitting on his chair inside | The postmaster was an unimpressive person with a sad and vacant look on his face. |
| (g) The haughty temper of the official had quite left him in his sorrow and anxiety, and had laid bare his human heart | The shared grief related to their respective daughters had made the postmaster give up his arrogant attitude. His sorrow and worry aroused compassion and understanding |