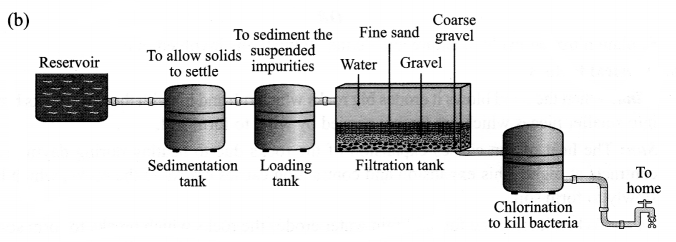
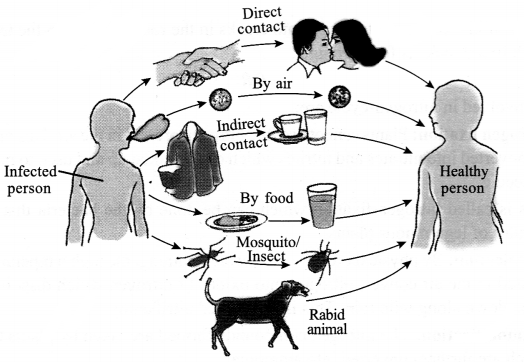
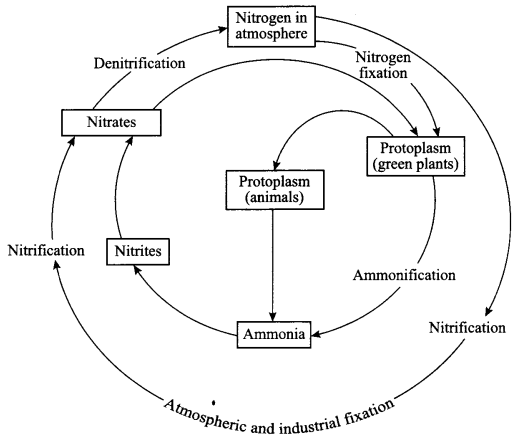
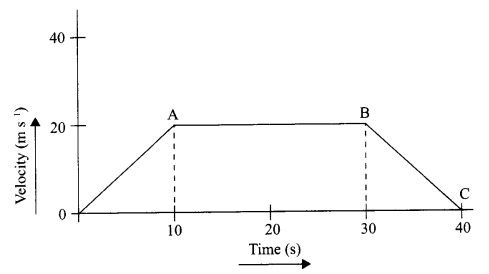
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Paper 7 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Paper 7.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Paper 7
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | IX |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 7 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme, as prescribed by the CBSE, is given here. Paper 7 of Solved CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
(i) The question paper has 27 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Marks are indicated against each question.
(iii) Questions from serial number 1 to 7 are very short answer questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
(iv) Questions from serial number 8 to 18 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
(v) Questions from serial number 19 to 25 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
(vi) Question number 26 and 27 are map questions of 2 marks from History and 3 marks from Geography. After completion, attach the maps inside the answer book.
Questions
Question 1:
In which book was the idea of one person one vote mentioned?
Question 2:
Who were Jadidists?
Question 3:
Which are the two houses of the parliament?
Question 4:
Name the island countries which are our southern neighbors.
Question 5:
Define asset of a country.
Question 6:
What are fair price shops?
Question 7:
Define poverty line.
Question 8:
How was France emerged as republic under Jacobins?
Question 9:
Write a note on Stalin’s collectivization programme.
Question 10:
What are the disadvantages of an electoral competition?
Question 11:
Why do we say that the role of Prime Minister in a coalition government has many constraints?
Question 12:
Name the fundamental rights provided by the Indian Constitution to its citizens?
Question 13:
How was the northern plains of India formed?
Question 14:
Write a note on the peninsular rivers.
Question 15:
How are disguised and seasonal unemployment different?
Question 16:
Explain the term social exclusion.
Question 17:
Mention any three factors of production.
Question 18:
What are the advantages of the Green revolution?
Question 19:
Discuss the consequences of Nazism in Germany.
Question 20:
What is shifting cultivation? Why were the European foresters unwilling to follow it?
OR
Why did the Massai community lost their land?
OR
Indian farmers were reluctant to grow opium. Explain.
Question 21:
How are democratic and non- democratic form of government different?
Question 22:
“There is need for constitution in every country”. Comment.
Question 23:
Write a note on the tropical deciduous forests.
Question 24:
Explain the occupational structure of India.
Question 25:
Write any five differences between traditional and modem farming methods.
Question 26:
Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the outline map of world:
(a) One of the central powers of the First World War.
(b) One of the axis powers of the Second World War.
Question 27:
On the given political outline map of India. Locate and label the following features with appropriate symbols:
(a) Western most point of India.
(b) Dachigam wildlife sanctuary.
(c) Wettest place in India.
Answers
Answer 1:
Rousseau mentioned the idea of one person one vote in the book named “The social contract”.
Answer 2:
They were the Muslim reformers in the Russian empire.
Answer 3:
The houses of the parliament are the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha.
Answer 4:
Sri Lanka and the Maldives islands are island countries and our southern neighbours.
Answer 5:
Asset of a country means the working population of a country.
Answer 6:
These are the ration shops opened by the government of India to provide food grains to the poor people at subsidized rate.
Answer 7:
It is an imaginary line based on income and consumption to know that who are poor in the society.
Answer 8:
They were the most radical groups formed in the wake of the French revolution. They were unhappy and angered by the shortage of food grains supply and high prices. As a rgsult they stormed the palace of Tuileries. They killed the king guard’s and made the king hostage for hours. This incident caused election and all the people of 21 years and above got the voting rights. Finally the new convention was formed and France was declared a republic.
Answer 9:
Stalin’s collectivization programme was a step to solve the problem of food shortage. This policy eliminated Kulaks and established state owned farms. The peasants were forced to work in the Kolkhoj. According to this programme policy of deportation and severe punishment was followed.
Answer 10:
The three demerits of the electoral competition are:
- The different parties and candidates use dirty tricks to win the elections.
- These political parties and leaders put allegations on each other.
- Electoral competition causes disunity.
Answer 11:
Yes, it is true to say that the role of Prime Minister in a coalition government has many constraints.
- The Prime Minister cannot take sole decision.
- He has to accommodate different social groups and coalition partners in his party.
- He has to listen the views of all the partners.
Answer 12:
The following are the various fundamental rights provided by the Indian Constitution to its citizens:
- Right to equality
- Right to freedom
- Right against exploitation
- Right to freedom of religion
- Cultural and educational Rights
- Right to constitutional remedies
Answer 13:
When the Indo-Australian plate collided with the Eurasian plate a large depression was formed in between. Gradually this was filled with the sediments deposited by the rivers from the north and south. This resulted in the formation of an extensive flat land called the northern plains of India.
Answer 14:
Three features of the peninsular rivers are:
- The Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, the Kaveri, the Narmada and the Tapi are the important rivers of the peninsular plateau. These rivers originate from the peninsular India.
- These rivers are seasonal in nature.
- These rivers drain into the Bay of Bengal except the Narmada and the Tapi which drain into the Arabian Sea.
Answer 15:
Disguised unemployment: When more than required people are working then the extra people engaged, these are called disguised unemployed. This type of unemployment is found in the agricultural fields. They don’t have job opportunities elsewhere so they are sharing the labour effort with their family members.
Seasonal hunger: It is related to the cycles of food growing and harvesting. People face seasonal hunger in the rural areas because of seasonal nature of agricultural activities.
Answer 16:
The term social exclusion is used to describe those who are excluded from the society on the basis of caste, religion and economic backwardness. They live in the fringes. They don’t enjoy the benefits of the society’ which the upper caste people or rich people enjoy. They are not allowed to come in contact with the upper caste people.
Answer 17:
Basically there are four factors of production- land, labour, physical capital and human capital.
- Land: It is the basic requirement for any kind of production either agricultural or industrial.
- Labour: For production we need cheap and skilled labour. So that cost of production will be low.
- Physical capital: It is of two types- fixed capital and working capital. Fixed capital includes tools and machines whereas working capital includes raw materials and money in hand.
Answer 18:
Green revolution benefitted the Indian agriculture in different ways:
- Green revolution helped in modernizing agriculture.
- It helped in bringing newer ways of production like tools and machines.
- It helped in bringing food security in the country.
Answer 19:
The consequences of Nazism in Germany were as follows:
- Democracy was destroyed and Germany became dictatorial state.
- Economic recovery was given the priority with the aim at full production and full employment.
- Germany left the League of Nations in 1933.
- To control and order the society in their own way special surveillance and security forces were formed.
- An exclusive racial community of pure Aryans was established because they believed in the concept of survival of the fittest.
Answer 20:
Shifting cultivation is a type of cultivation in which the farmers degrade the forest and bum it there only to clear and make a fresh patch of land to be used for cultivation. Seeds are sown with the onset of monsoon and is harvested in the month of October-November. These plots were used for cultivation for few years and then kept fallow for many years for the forest to grow.
In Europe farmers did not want to follow this type of agriculture because they felt that if they will practice this type of cultivation then the land will not be able to produce the type of timber which was needed for railways. The second reason to not practice this type of cultivation was fear of forest fire. They thought that while burning the forest, the flames may spread to other parts of the forests.
OR
The Massai community lost their land due to the following reasons:
- Territorial possessions by the European powers was the basic reason behind losing their grazing land.
- In 1885, Massailand was divided between British Kenya and German Tanganyika.
- The productive grazing lands were allotted for white settlement and the Massai were forced to shift to the arid land.
- The pasturelands were converted into the cultivated lands due to agricultural expansion.
- Large areas of the grazing lands were declared reserved and the Massai people were not allowed to enter there for any business.
OR
Indian farmers were reluctant to grow opium due to the following reasons:
- They had to use their best fertile land to grow opium.
- They were using their fertile land for the crop cultivation.
- It was difficult and time consuming to grow opium.
- They had to pay high rent for the land.
- The opium cultivation was not profitable for them as they were paid low for opium.
Answer 21:
Democratic and non- democratic form of government can be differentiated on the following grounds:
- In the democratic government the elected people rule the country whereas in the non- democratic government people cannot choose their rulers.
- In the democratic government citizens enjoy various freedoms whereas in the non- demociratic government freedom depends on the rulers.
- In the democratic government representatives come in power after free and fair election whereas in the non-democratic government there is no such way to choose their representatives.
- In the democratic government there is political equality whereas in the non-democratic government there is no political equality.
- The democratic government functions according to the constitutional laws whereas the non-democratic government functions according to their will.
Answer 22:
The constitution is needed in a country due to the following reasons:
- To build trust and coordination among the people to live with peace and harmony.
- To specify the formation and the powers of the government.
- To define the duties and responsibilities of different organs of the government.
- To know the rights and duties of the people.
- To protect the minorities and the weaker sections of the society.
Answer 23:
The following are the characteristics of the tropical deciduous forests:
- The tropical deciduous forests are the most widespread in India.
- They also called the monsoon forests.
- They are found in the areas receiving rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm.
- Trees of the tropical deciduous forests shed their leaves in the dry summer for 6 to 8 weeks.
- Lion, tiger, pig, deer and elephants are the common animals of these forests.
Answer 24:
The occupational structure of India:
- It is the distribution of population according to different types of occupation.
- The different occupations can be grouped into three different categories – primary, secondary and tertiary.
- Primary activities includes agriculture related activities, secondary activities includes manufacturing related activities and tertiary activities includes service related activities.
- In India 64% people are engaged in the primary, 13% in the secondary and 20% in the tertiary activities.
- There is a shift taking place from primary to secondary and tertiary.
Answer 25:
The following are the differences between the modem farming and the traditional farming:
- In modem farming latest tools and machines are used whereas in the traditional farming primitive tools are used for farming.
- In modem farming HYV seeds are used whereas in traditional farming simple seeds are used.
- In modem farming chemical fertilisers and pesticides are used whereas in traditional farming natural manures are used.
- Modem farming gives more yield than the traditional farming.
- The land is used more intensively in the modem farming than the traditional farming.
Answer 26:

Answer 27:

We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Paper 7 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Social Science Paper 7, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.