Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Biomolecules Class 11 Biology MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 11 Chapter 9 MCQs On Biomolecules
Biomolecules Class 11 MCQ Question 1.
Feedback inhibition of enzymes is affected by which of the following
(a) enzyme
(b) substrate
(c) end products
(d) intermediate end products
Answer
Answer: (c) end products
Biomolecules MCQs Class 11 Question 2.
An example of competitive inhibition of an enzyme is the inhibition of
(a) succinic dehydrogenase by malonic acid
(b) cytochrome oxidase by cyanide
(c) hexokinase by glucose-6-phosphate
(d) carbonic anhydrase by carbon dioxide
Answer
Answer: (a) succinic dehydrogenase by malonic acid
MCQ On Biomolecules Class 11 Question 3.
Insulin is made up of _______ and _______.
(a) glucose and fructose
(b) glucose and fructose
(c) fructose and mannose
(d) mannose and glucose
Answer
Answer: (b) glucose and fructose
Explanation:
Insulin is a polysaccharide made up of glucose and fructose.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 MCQ Question 4.
Enzymes increase the rate of reaction by
(a) lowering activation energy
(b) increasing activation energy
(c) increasing temperature and pH
(d) decreasing temperature and pH
Answer
Answer: (a) lowering activation energy
Explanation:
Enzymes increase the rate of reaction by decreasing the activation energy.
MCQ Of Biomolecules Class 11 Question 5.
Which of the following statements regarding enzyme inhibition is correct?
(a) Competitive inhibition is seen when a substrate competes with an enzyme for binding to an inhibitor protein
(b) Non-competitive inhibitors often bind to the enzyme irreversibly
(c) Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the enzyme
(d) Non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme can be overcome by adding large amount of substrate
Answer
Answer: (c) Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the enzyme
Class 11 Biomolecules MCQs Question 6.
Which of the following is not a pyrimidine?
(a) Uracil
(b) Cytosine
(c) Guanine
(d) Thymine
Answer
Answer: (c) Guanine
Explanation:
Guanine is a purine.
Biomolecules Class 11 MCQ With Answers Question 7.
Hydrolysis of starch occurs with the help of
(a) Peptidase
(b) Amylase
(c) Sucrose
(d) Lipase
Answer
Answer: (b) Amylase
MCQs Of Biology Class 11 Chapter 9 Question 8.
Assertion: Arachidic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid.
Reason: There are one or more double bonds between carbon atoms in unsaturated fatty acids.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct explanations of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are false
Answer
Answer: (d) Both Assertion and Reason are false
Biomolecules Class 11 MCQs Question 9.
Which of the following influence feedback inhibition of enzyme?
(a) End product
(b) External factors
(c) Enzyme
(d) Substrate
Answer
Answer: (a) End product
MCQ Questions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Question 10.
Which of the following is not a polysaccharide?
(a) Lactose
(b) Starch
(c) Glycogen
(d) Dextrin
Answer
Answer: (a) Lactose
Explanation:
Lactose is a disaccharide made up of glucose and galactose.
Chapter 9 Biology Class 11 MCQs Question 11.
Inulin is made up of _______ and _______.
(a) glucose and fructose
(b) glucose and fructose
(c) fructose and mannose
(d) mannose and glucose
Answer
Answer: (b) glucose and fructose
Explanation:
Inulin is a polysaccharide made up of glucose and fructose.
Class 11 Biology Biomolecules MCQs Question 12.
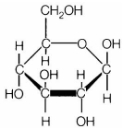
The structure shown above is
(a) mannose
(b) fructose
(c) glucose
(d) galactose
Answer
Answer: (c) glucose
Explanation:
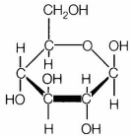
Glucose molecule
MCQ Biomolecules Class 11 Question 13.
A protein having both structural and enzymatic traits is
(a) Collagen
(b) Trypsin
(c) Myosin
(d) Actin
Answer
Answer: (c) Myosin
Ch 9 Bio Class 11 MCQ Question 14.
NADP contains vitamin ______.
(a) B1
(b) B2
(c) B3
(d) B12
Answer
Answer: (c) B3
Explanation:
B3 also named as niacin.
Biology Class 11 Chapter 9 MCQs Question 15.
With reference to enzymes, which one of the following statements is true?
(a) Apoenzyme = Holoenzyme + Coenzyme
(b) Holoenzyme = Apoenzyme + Coenzyme
(c) Coenzyme = Apoenzyme + Holoenzyme
(d) Holoenzyme = Coenzyme – Apoenzyme
Answer
Answer: (b) Holoenzyme = Apoenzyme + Coenzyme
Question 16.
Inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme. Hence blocking the reaction. This is an example of
(a) allosteric inhibition
(b) feedback inhibition
(c) uncompetitive inhibition
(d) competitive inhibition
Answer
Answer: (d) competitive inhibition
Explanation:
When substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme, it completes the reaction.
When inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme, it blocks the reaction.
Question 17.
The fastest enzyme known is
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) carbonic anhydrase
(c) carbonic dehydrogenase
(d) DNA ligase
Answer
Answer: (b) carbonic anhydrase
Explanation:
The fastest enzyme known is carbonic anhydrase. It converts 106 molecules of carbon dioxide molecules per second.
Question 18.
Lecithin is a
(a) polysaccharide
(b) protein
(c) nucleic acid
(d) lipid
Answer
Answer: (d) liquid
Explanation:
Lecithin is a phospholipid.
Question 19.
The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction is called
(a) enzymatic energy
(b) activation energy
(c) substrate energy
(d) initiation energy
Answer
Answer: (b) activation energy
Explanation:
The minimum amount of energy required to initiate a chemical reaction is called activation energy.
Question 20.
Enzymes, vitamins and hormones are common in
(a) Enhancing oxidative metabolism
(b) Being synthesised in the body of organisms
(c) Being proteinaceous
(d) Regulating metabolism
Answer
Answer: (d) Regulating metabolism
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Biology MCQ:
- The Living World Class 11 MCQ
- Biological Classification Class 11 MCQ
- Plant Kingdom Class 11 MCQ
- Animal Kingdom Class 11 MCQ
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 MCQ
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants Class 11 MCQ
- Structural Organisation in Animals Class 11 MCQ
- Cell: The Unit of Life Class 11 MCQ
- Biomolecules Class 11 MCQ
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 MCQ
- Transport in Plants Class 11 MCQ
- Mineral Nutrition Class 11 MCQ
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 MCQ
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 MCQ
- Plant Growth and Development Class 11 MCQ
- Digestion and Absorption Class 11 MCQ
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 MCQ
- Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 MCQ
- Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 MCQ
- Locomotion and Movement Class 11 MCQ
- Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 MCQ
- Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 MCQ