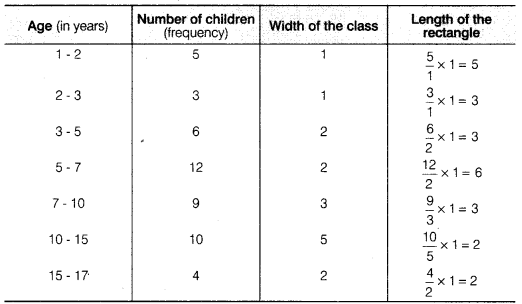
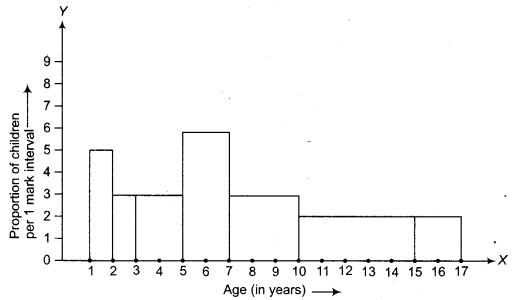
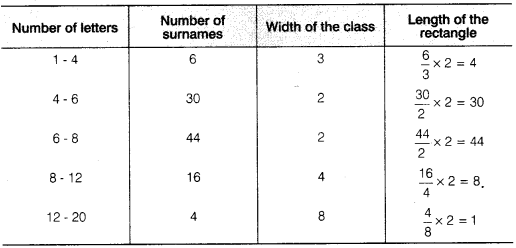
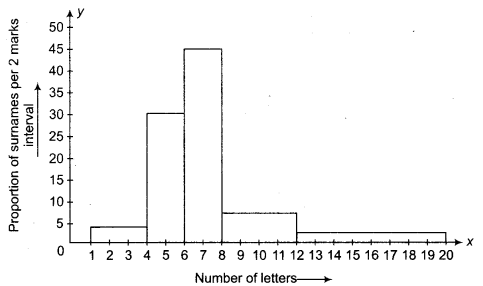
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 7 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 7.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 7
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | X |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 7 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 10 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 7 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 10 Social Science is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions
- The question paper has 27 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
- Marks are indicated against each question.
- Questions from serial number 1 to 7 are very short answer questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Questions from serial number 8 to 18 are 3 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 80 words each.
- Questions from serial number 19 to 25 are 5 marks questions. Answer of these questions should not exceed 100 words each.
- Question number 26 and 27 are map questions of 2 marks from History and 3 marks from Geography. After completion, attach the maps inside the answer book.
QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What was ‘Hosay’?
OR
Who devised Spinning jenny? When?
OR
What do you mean by Chartism and the 10-hour movement?
Question 2.
What were the Biliotheque Bleue’?
OR
Name the earliest Marathi novel? Who wrote it?
Question 3.
Identify any two major alliances which contested in the 2004 Parliamentary Elections of India?
Question 4.
Name the local names of the alluvial soils found in the piedmont plains?
Question 5.
What are renewable resources? Give example.
Question 6.
Define GDP.
Question 7.
What are the functions of money?
Question 8.
Write short note on Rinderpest.
OR
Explain the role of the ‘gomasthas’ and ‘jobbers’ in the history of cotton textile industry of India.
OR
Narrate the information you could draw from the writings of Henry Mayhew on crime in London by the end of 19th century and state the steps taken by the government to check crime.
Question 9.
Why the Roman Catholic Church decide to maintain an Index of Prohibited Books from 1558?
OR
‘Stories in prose were not new to India’. Support your answer with three examples.
Question 10.
How do you differentiate federalism from a Unitary form of government?
Question 11.
“Every social difference does not lead to social division”. Explain with suitable example.
Question 12.
“The leaders of the Sinhala community sought to secure dominance over government by virtue of their majority”. Comment.
Question 13.
Why are dams referred to as multi-purpose river valley projects? Briefly explain these giving two examples of multi-purpose projects.
Question 14.
What is plantation farming? State two characteristics of plantation farming. Also mention two examples of plantation crops.
Question 15.
“Consumers are exploited in the marketplace in various ways”. Discuss with example.
Question 16.
Classify the countries according to the World Bank criterion.
Question 17.
Write a short note on Consumers International.
Question 18.
Define what is trade barrier? Why Indian government put various barriers in foreign trade and investments before 1991?
Question 19.
What marked the beginning of the Civil Disobedience Movement? How was this movement different from the Non-Cooperation Movement?
Question 20.
“The Habsburg Empire that ruled over Austria-Hungary, for example, was a patchwork of many different regions and peoples”. Justify.
OR
Describe any four steps taken by the French for the development of the Mekong Delta Region’.
Question 21.
“Ours is still a male dominated, Patriarchal society. Women face disadvantage, discrimination and oppression in various ways.” Discuss.
Question 22.
Suggest a few broad guidelines that should be kept in mind while devising ways and means for political reforms in India.
Question 23.
What are Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways? What is their major objective? Explain Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways.
Question 24.
When and where the first successful textile mill was established? Explain the three reasons that led to the location of cotton textile industry in Gujarat and Maharashtra initially.
Question 25.
Study the data given in the table and answer the questions that follow :
| Sector | Organised | Unorganised | Total (in million) |
| Primary | 2 | 242 | |
| Secondary | 9 | 54 | 63 |
| Tertiary | 17 | 76 | 93 |
| Total | 28 | ||
| Total in Percentage | 100% |
- Which is the most important sector that provides most jobs to the people?
- What is the number of persons engaged in the unorganised sector?
- Why is this unorganised sector more important? Give one reason.
- Which is the most important organised sector? Give one reason.
Question 26.
Two features A and B are marked on the given political outline map of India:
Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map :
A. The place where Gandhji led the cotton mill workers’ agitation.
B. The place where INC Session took place in 1927
OR
Locate and label on the same map given:
- Champaran-indigo planters’ agitation in 1916.
- Calcutta-INC Session September 1920.
Question 27.
On the given same political outline map of India locate and label/identify the type of soil the following with appropriate symbols:
- Identify the type of soil in the shaded area on map.
- Largest producer of ragi among Indian states,
- Hirakud Dam
ANSWERS
Answer 1.
In Trinidad the annual Muharram procession was transformed into a riotous carnival called ‘Hosay’ (for Imam Hussain) in which workers of all races and religions joined.
OR
Spinning Jenny was devised by James Hargreaves in 1764.
OR
Two political movements of London in the 19th Century were called Chartism (a movement demanding the vote for all adult males) and the 10-hour movement (limiting hours of work in factories).
Answer 2.
In France, were present the ‘Biliotheque Bleue’, which were low-priced small books printed on poor quality paper, and bound in cheap blue covers.
OR
The earliest novel in Marathi was Baba Padmanji’s Yamuna Paryatan (1857).
Answer 3.
Two major alliances in 2004 parliamentary elections- the National Democratic Alliance, the United Progressive Alliance and the Left Front.
Answer 4.
Duars, Chos and Terai.
Answer 5.
Groundwater is an example of renewable resources. These resources are replenished by nature as in the case of crops and plants.
Answer 6.
The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a particular year provides the total production of the sector for that year. And the sum of production in the three sectors gives what is called the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country. It is the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year. GDP shows how big the economy is.
Answer 7.
- Money acts as a medium of exchange in goods and services and in payment of debts.
- Money is used as a measure of value.
- It is a Standard of Demand Payments.
- It acts as store of value.
Answer 8.
(i) A devastating cattle disease, Rinderpest arrived in Africa in the late 1880s. It was carried by infected cattle imported from British Asia to feed the Italian soldiers invading Eritrea in East Africa.
(ii) Entering Africa in the east, rinderpest moved west Tike forest fire’, reaching Africa’s Atlantic coast in 1892. It reached the Cape (Africa’s southernmost tip) five years later. Along the way rinderpest killed 90 per cent of the cattle.
(iii) The loss of cattle destroyed African livelihoods. Planters, mine owners and colonial governments now successfully monopolised what scarce cattle resources remained, to strengthen their power and to force Africans into the labour market. Control over the scarce resource of cattle enabled European colonisers to conquer and subdue Africa.
OR
The ‘gomasthas’: The East India Company tried to eliminate the existing traders and brokers connected with the cloth trade, and establish a more direct control over the weaver. It appointed a paid servant called the gomastha to supervise weavers, collect supplies, and examine the quality of cloth.
Jobber:
(i) Getting jobs was always difficult, even when mills multiplied and the demand for workers increased. The numbers seeking work were always more than the jobs available. Entry into the mills was also restricted. Industrialists usually employed a jobber to get new recruits.
(ii) Very often the jobber was an old and trusted worker. He got people from his village, ensured them jobs, helped them settle in the city and provided them money in times of crisis. The jobber therefore became a person with some authority and power. He began demanding money and gifts for his favour and controlling the lives of workers.
OR
In the mid-nineteenth century, Henry Mayhew wrote about London labour, and compiled long lists of those who made a living from crime.
(i) He listed many of them as ‘criminals’ who were in fact poor people who lived by stealing lead from roofs, food from shops, lumps of coal, and clothes drying on hedges.
(ii) There were others who were more skilled at their trade, expert at their jobs. There were cheats and tricksters, pickpockets and petty thieves crowding the streets of London.
Steps taken:
(i) In an attempt to discipline the population, the authorities imposed high penalties for crime.
(ii) Offered work to those who were considered the ‘deserving poor’.
Answer 9.
(i) Print and popular religious literature stimulated many distinctive individual interpretations of faith even among little-educated working people.
(ii) In the sixteenth century, Menocchio, a miller in Italy, began to read books that were available in his locality. He reinterpreted the message of the Bible and formulated a view of God and Creation that enraged the Roman Catholic Church and began its inquisition to repress heretical ideas. Menocchio was hauled up twice and ultimately executed.
(iii) The Roman Church, troubled by such effects of popular readings and questionings of faith, imposed severe controls over publishers and booksellers and began to maintain an Index of Prohibited Books from 1558.
OR
(i) Banabhatta’s Kadambari, written in Sanskrit in the seventh century, is an early example.
(ii) The Panchatantra.
(iii) There was also a long tradition of prose tales of adventure and heroism in Persian and Urdu, known as ‘dastan’.
Answer 10.
Federalism:
- Is a system of government in which power is divided between the central authority and various constituent units of the country. Federation may have government for the entire nation and government at the levels of provinces or states.
- Both these levels of the government enjoy their power independent of the others. Powers of each level is specified in the Constitution.
A unitary government:
- Has one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government.
- The central government can pass orders to the provincial or the local government.
Answer 11.
- Every social difference does not lead to social division. Social differences divide similar people from one another, but they also unite very different people.
- People belonging to different social groups share differences and similarities cutting across the boundaries of their groups
Example: Carlos and Smith were similar in one way (both were African-American) and thus different from Norman who was white. But they were also all similar in other ways – they were all athletes who stood against racial discrimination.
Answer 12.
- The democratically elected government adopted a series of Majoritarian measures to establish Sinhala supremacy.
- In 1956, an Act was passed to recognize Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil.
- The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs.
- A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism.
- All these government measures, coming one after the other, gradually increased the feeling of alienation among the Sri Lankan Tamils.
Answer 13.
Large dams are referred to as multipurpose river valley projects where the many uses of the impounded water are integrated with one another as:
Irrigation, electricity generation, water supply for domestic and industrial uses, flood control, recreation, inland navigation and fish breeding.
(a) In Sutlej-Beas river basin, the Bhakra-Nangal project water is being used both for hydel power production and irrigation.
(b) Similarly, Hirakund project in the Mahanadi basin integrates conservation of water with flood control.
Answer 14.
Plantation farming: In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area.
Characteristics:
- The plantation has an interface of agriculture and industry
- Use large tracts of land and capital intensive inputs with manual labour.
Examples of plantation crops: Tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, banana etc.
Answer 15.
Sometimes traders indulge in unfair trade practices such as when shopkeepers weigh less than what they should or when traders add charges that were not mentioned before, or when adulterated/defective goods are sold.
Answer 16.
(i) In World Development Reports, brought out by the World Bank, this criterion is used in classifying countries.
(ii) Countries with per capita income of US$ 12616 per annum and above in 2012, are called rich countries and those with per capita income of US$ 1035 or less are called low-income countries.
(iii) India comes in the category of low middle income countries because its per capita income in 2012 was just US$ 1530 per annum. The rich countries, excluding countries of Middle East and certain other small countries are generally called developed countries.
Answer 17.
(i) In 1985 United Nations adopted the UN Guidelines for Consumer Protection. This was a tool for nations to adopt measures to protect consumers and for consumer advocacy groups to press their governments to do so.
(ii) At the international level, this has become the foundation for consumer movement.
(iii) Today, Consumers International has become an umbrella body to over 220 member organisations from over 115 countries.
Answer 18.
(i) Tax on imports is an example of trade barrier. It is called a barrier because some restriction has been set up.
(ii) Governments can use trade barriers to increase or decrease (regulate) foreign trade and to decide what kinds of goods and how much of each, should come into the country.
(iii) The Indian government, after Independence, had put barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment. This was considered necessary to protect the producers within from foreign competition.
(iv) Industries were just coming up in the 1950s and 1960s, and competition from imports at that stage would not have allowed these industries to come of only essential items such as machinery, fertilizers, petroleum etc.
Answer 19.
(i) On 6 April Gandhi reached Dandi, and ceremonially violated the law, by picking up a handful of salt. This marked the beginning of the Civil Disobedience Movement.
(ii) People were now asked not only to refuse cooperation with the British, as they had done in 1921-22, but also to break colonial laws. Thousands in different parts of the country broke the salt law, manufactured salt and demonstrated in front of government salt factories.
(iii) As the movement spread, foreign cloth was boycotted, and liquor shops were picketed. Peasants refused to pay revenue and chaukidari taxes, village officials resigned, and in many places forest people violated forest laws – going into Reserved Forests to collect wood and graze cattle.
Answer 20.
(i) It included the Alpine regions – the Tyrol, Austria and the Sudetenland – as well as Bohemia, where the aristocracy was predominantly German-speaking. It also included the Italian-speaking provinces of Lombardy and Venetia.
(ii) In Hungary, half of the population spoke Magyar while the other half spoke a variety of dialects. In Galicia, the aristocracy spoke Polish.
(iii) Besides these three dominant groups, there also lived within the boundaries of the empire, a mass of subject peasant peoples – Bohemians and Slovaks to the north, Slovenes in Camiola, Croats to the south, and Roumans to the east in Transylvania.
(iv) Such differences did not easily promote a sense of political unity. The only tie binding these diverse groups together was a common allegiance to the emperor.
OR
(i) The French began by building canals and draining lands in the Mekong delta to increase cultivation.
(ii) The vast system of irrigation works – canals and earthworks – built mainly with forced labour, increased rice production and allowed the export of rice to the international market.
(iii) Vietnam exported two-thirds of its rice production and by 1931 had become the third largest exporter of rice in the world.
(iv) This was followed by infrastructure projects to help transport goods for trade, move military garrisons and control the entire region. Construction of a trans-Indo-China rail network that would link the northern and southern parts of Vietnam and China was begun.
Answer 21.
(i) The literacy rate among women is only 54 per cent compared with 76 per cent among men. Similarly, a smaller proportion of girl students go for higher studies. But the girls drop out because parents prefer to spend their resources for their boys’ education rather than spending equally on their sons and daughters.
(ii) The proportion of women among the highly paid and valued jobs is still very small. On an average an Indian woman works one hour more than an average man every day. Yet much of her work is not paid and therefore often not valued.
(iii) The Equal Wages Act provides that equal wages should be paid to equal work. However in almost all areas of work, from sports and cinema, to factories and fields, women are paid less than men, even when both do exactly the same work.
(iv) In many parts of India, parents prefer to have sons and find ways to have the girl child aborted before she is bom. Such sex-selective abortion led to a decline in child sex ratio (number of girl children per thousand boys) in the country to merely 927. This ratio has fallen below 850 or even 800 in some places.
(v) There are reports of various kinds of harassment, exploitation and violence against women. They are not even safe even within their own home from beating, harassment and other forms of domestic violence.
Answer 22.
(i) Reforms through Legal Ways: Law has an important role to play in political reform. Carefully devised changes in law can help to discourage wrong political practices and encourage good ones. Example: A change in rules for LBW decisions helped to reduce negative batting tactics. But no one would ever think that the quality of cricket could be improved mainly through changes in the mles.
(ii) Any legal change must carefully look at what results it will have on politics. Sometimes the results may be counter-productive. Example: Many states have banned people who have more than two children from contesting panchayat elections. This has resulted in denial of democratic opportunity to many poor and women, which was not intended. Another example is RTI.
(iii) Reform through ‘Political Practices’: Democratic reforms are to be brought about principally through political practice. The most important concern should be to increase and improve the quality of political participation by ordinary citizens.
(iv) Reform measures that rely on democratic movements, citizens’ organisations and the media are likely to succeed in reforming political system. The main focus of political reforms should be on ways to strengthen democratic practices.
Answer 23.
(i) The government has launched a major road development project linking Delhi-Kolkata- Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi by six-lane Super Highways.
(ii) The North-South corridors linking Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and East-West Corridor connecting Silcher (Assam) and Porbander (Gujarat) are part of this project.
(iii) The major objective of these Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
(iv) The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) implements and maintains these super highways.
Answer 24.
Successful location: Mumbai, 1854
Factors responsible for location of cotton textile industry in Gujarat and Maharashtra:
(i) Availability of raw cotton: This region predominantly located in the black soil. Therefore, good quality of cotton was easily available.
(ii) Well developed transportation network: This region was well connected with efficient network of roads and railways. It got the benefit of port facilities also.
(iii) Market: There was a huge demand for cotton goods in and around this region. Therefore, this industry concentrated in and around Gujarat and Maharashtra.
Answer 25.
(i) Primary-Agricultural Sector
(ii) 370 million
(iii) Agricultural Sector is most important unorganised sector because the unorganised sector mostly comprises of landless agricultural labourers, small and marginal farmers. Nearly 80 per cent of rural households in India are in small and marginal farmer category. These farmers need to be supported through adequate facility for timely delivery of seeds, agricultural inputs, credit, storage facilities and marketing outlets. Employment is more production is less.
(iv) Tertiary Sector: Employment is less and production is less. Also it produces ‘services’ rather than ‘goods’.
Answer 26.

Answer 27.

We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 7 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Paper 7, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.