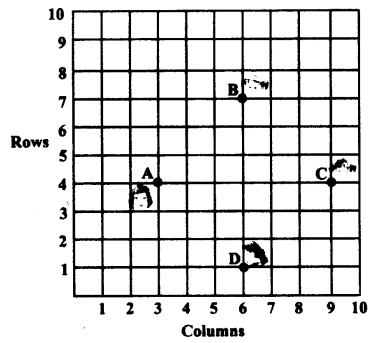
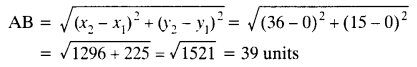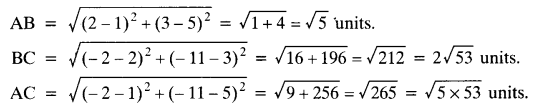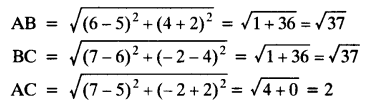Solved CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 2021-2022 Pdf with Solutions: Solving Pre Board CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 with Solutions Answers Pdf Download Term 1 & Term 2 will give students an idea about the question paper pattern, frequently asked questions, and on which topics to emphasize more in a subject. CBSE Sample Papers of Class 11th Term 1 & Term 2 will boost their confidence level, and they will feel optimistic about the board exams.
CBSE Sample Papers Class 11 2022 with Solutions Term 1 & Term 2
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Maths
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Applied Mathematics
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Physics
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 English Core
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Hindi
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Geography
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 History
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Political Science
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Economics
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Accountancy
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Business Studies
- CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Computer Science
We hope these Solved Sample Paper of Class 11 CBSE 2021 2022 Pdf with Solutions Term 1 & Term 2 will help in self-evaluation. Stay tuned for further updates on CBSE Class 11th Sample Papers Term 1 & Term 2 for their exam preparation.