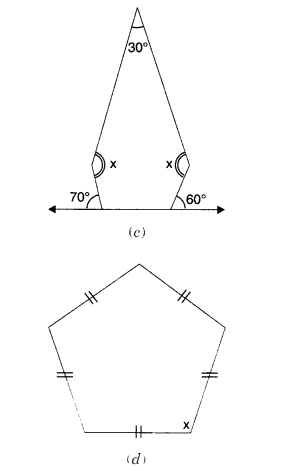
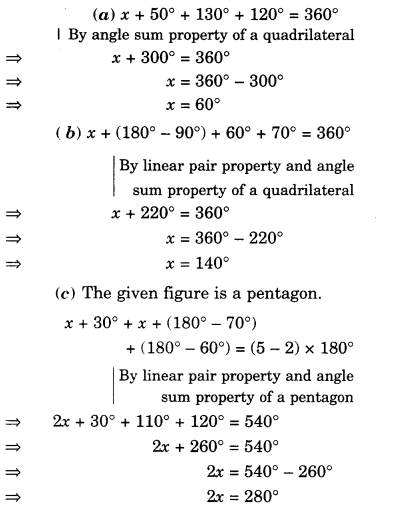
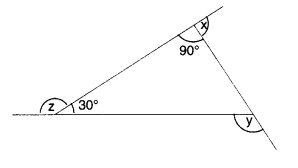
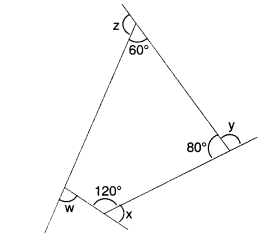
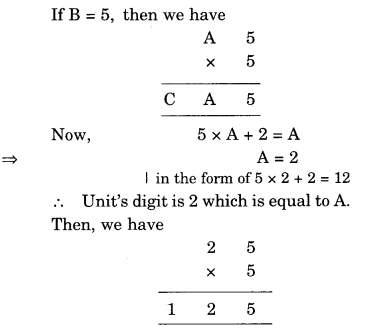
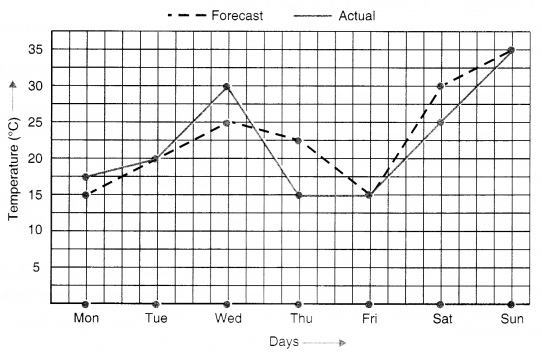
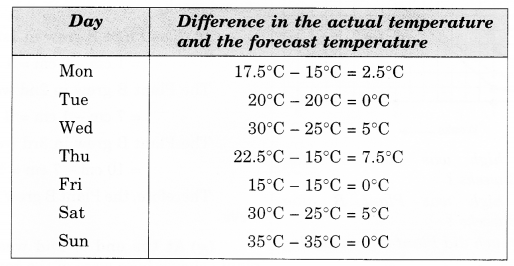
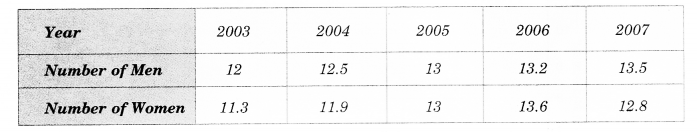
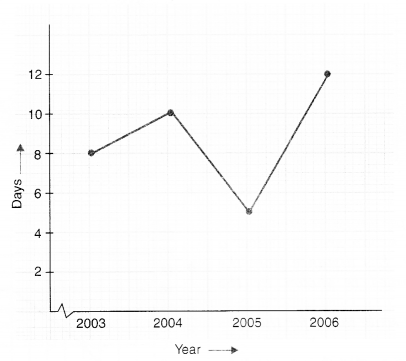
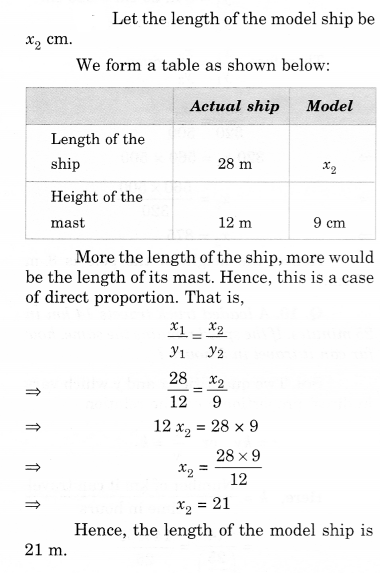
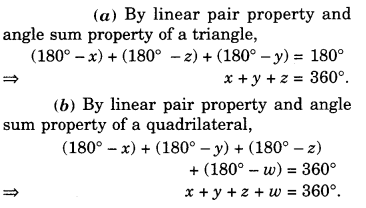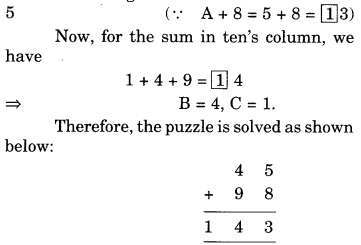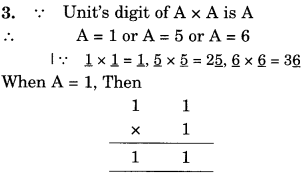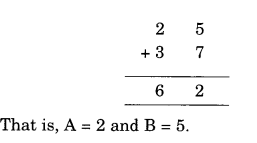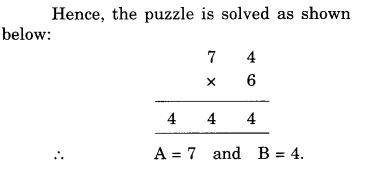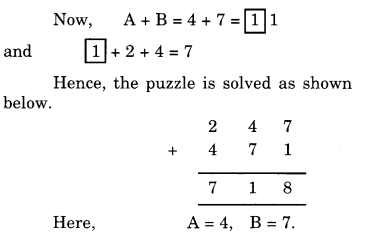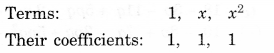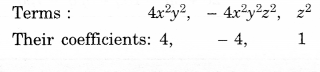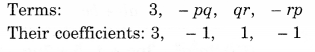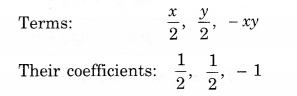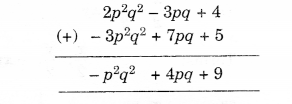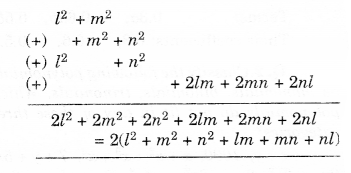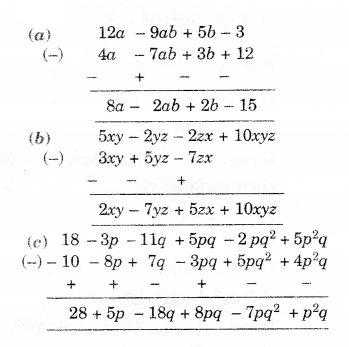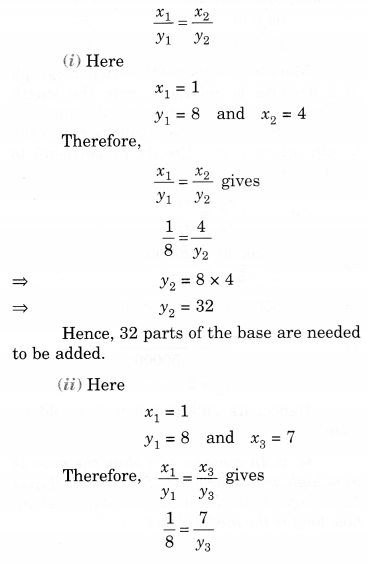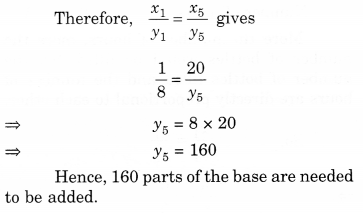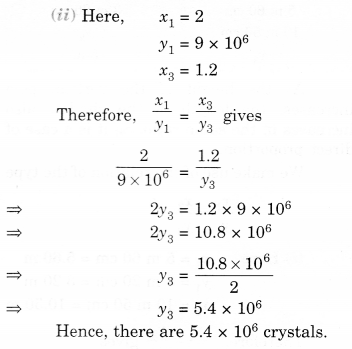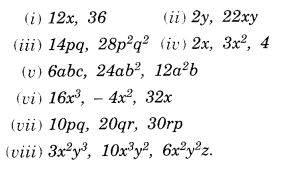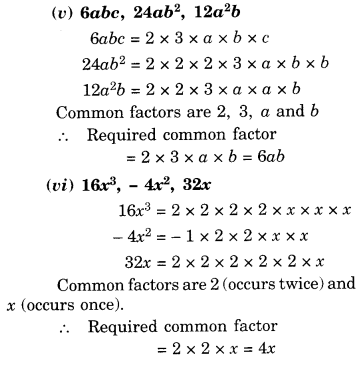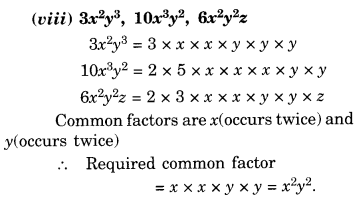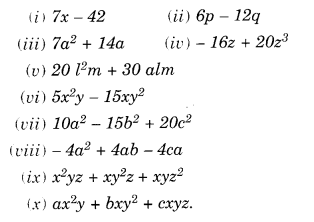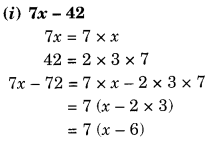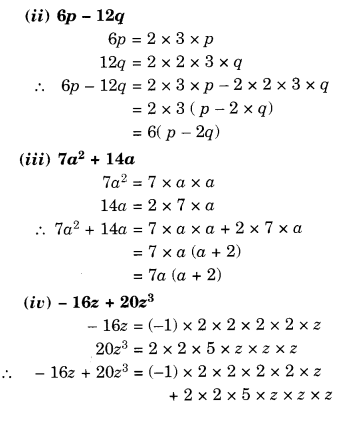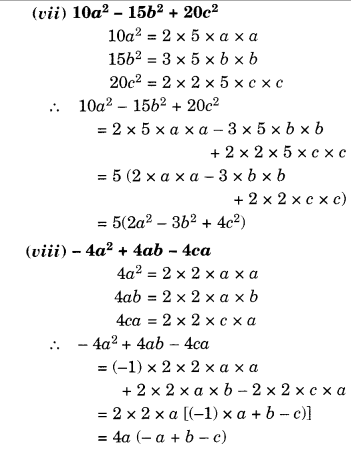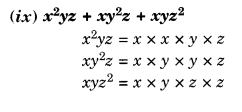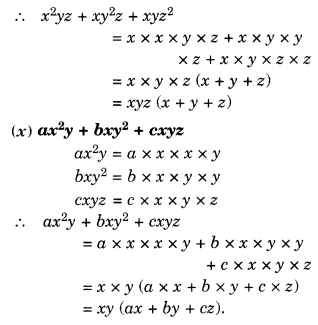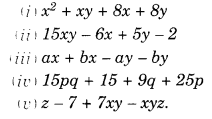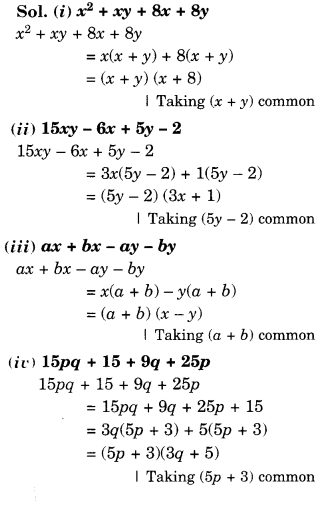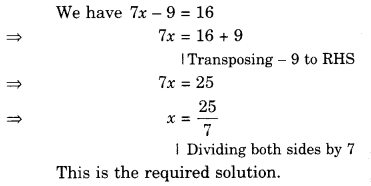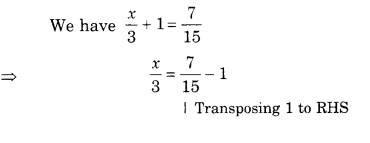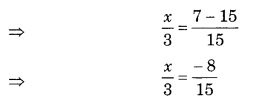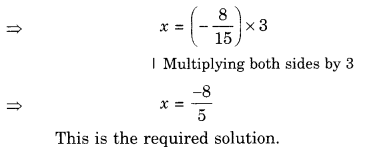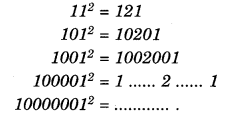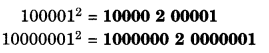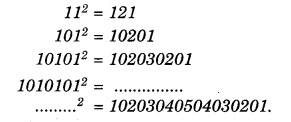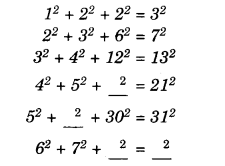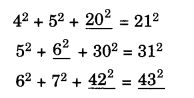NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.1.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 10 |
| Chapter Name | Visualising Solid Shapes |
| Exercise | Ex 10.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 4 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.1
Question 1.
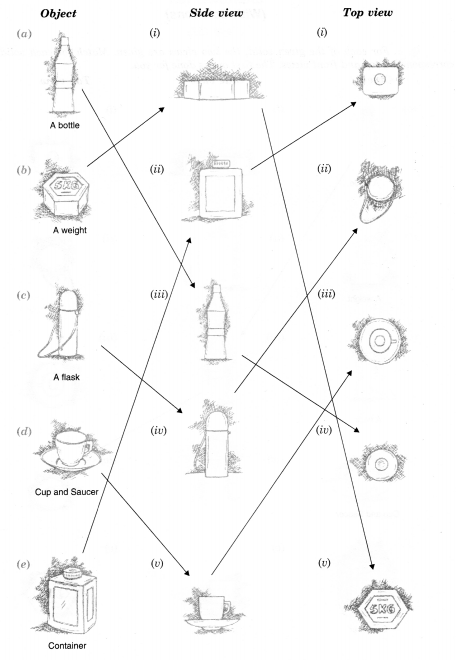
For each of the given solid, the two views are given. Match for each solid the corresponding top and front views. The first one is done for you.
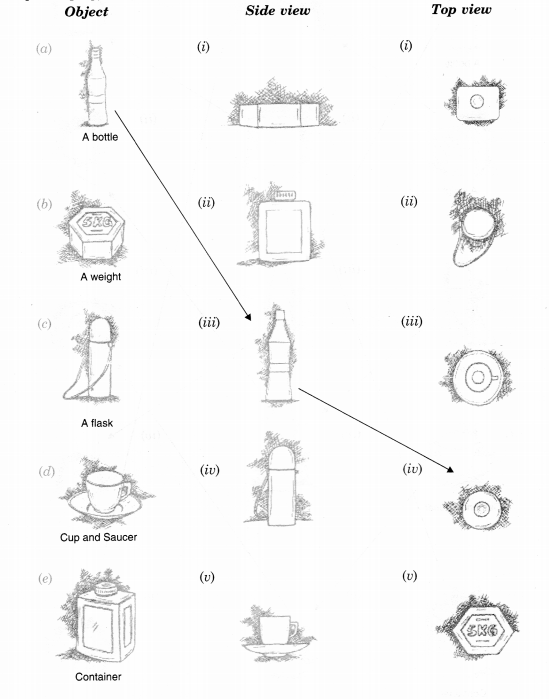
Solution.
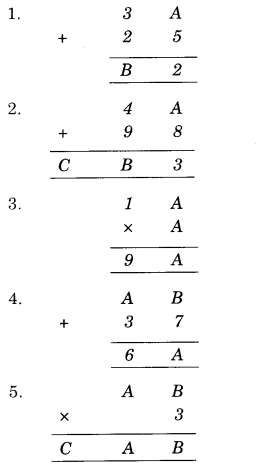
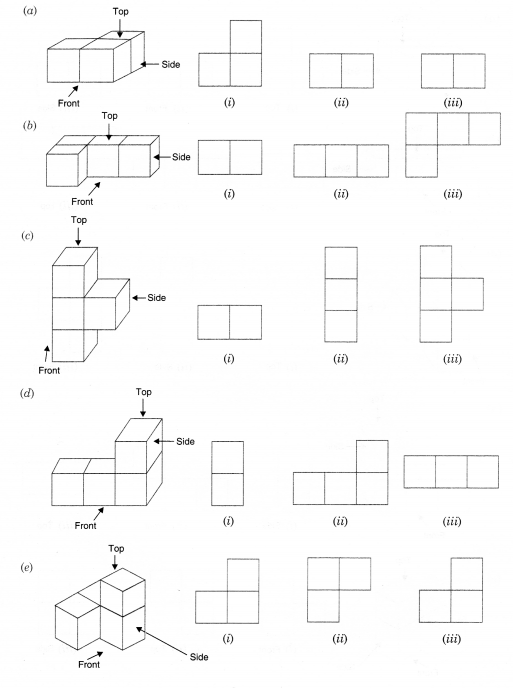
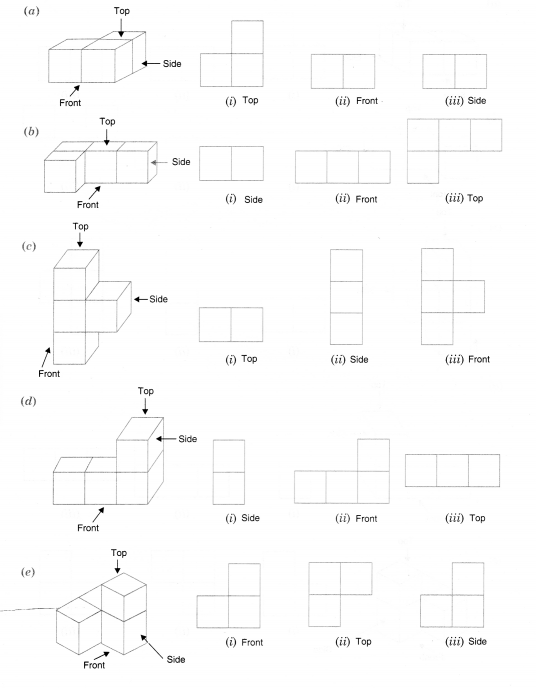
Question 2.
For each of the given solid, the three views are given. Identify for each solid the corresponding top, front and side views.
Solution.
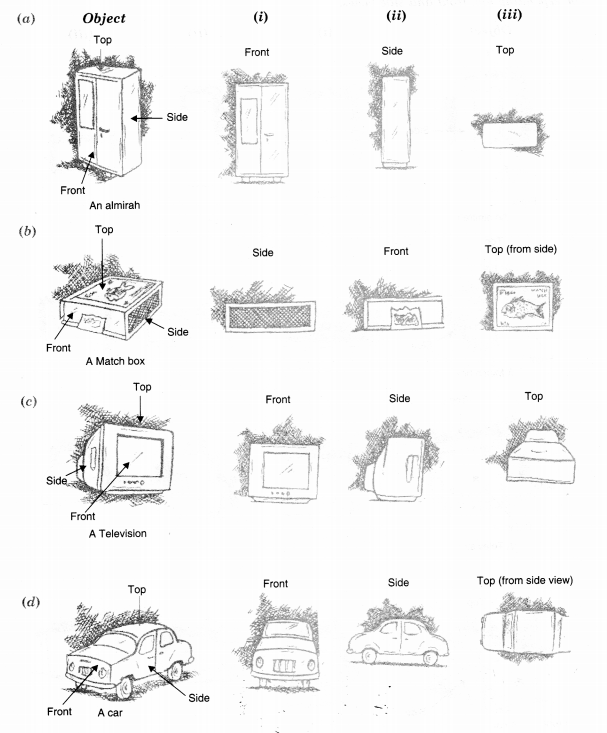
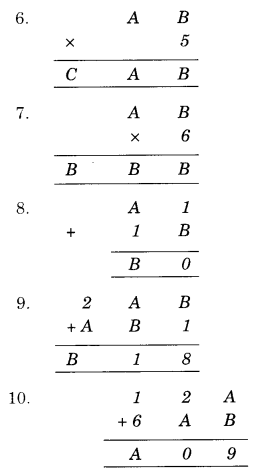
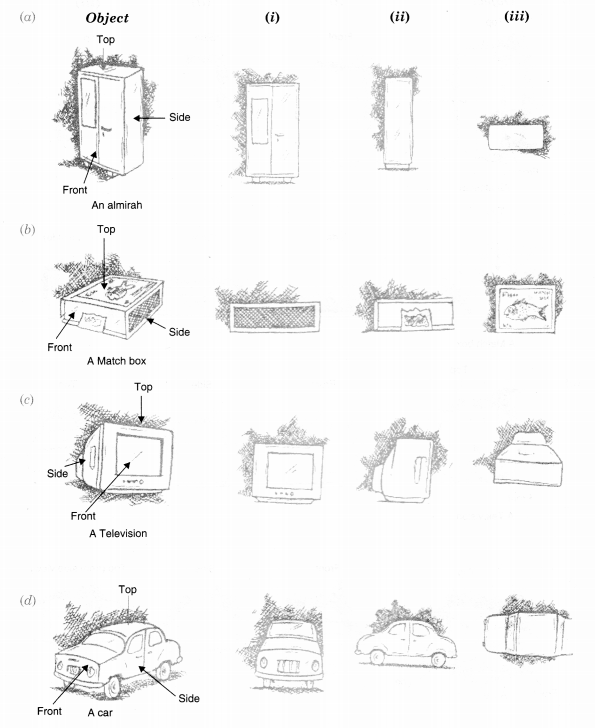
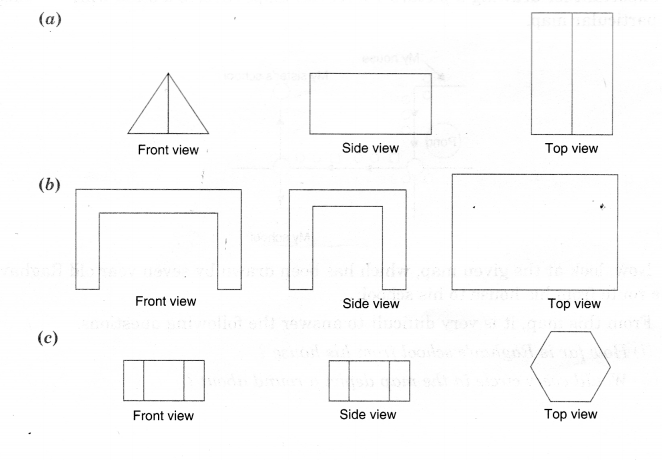
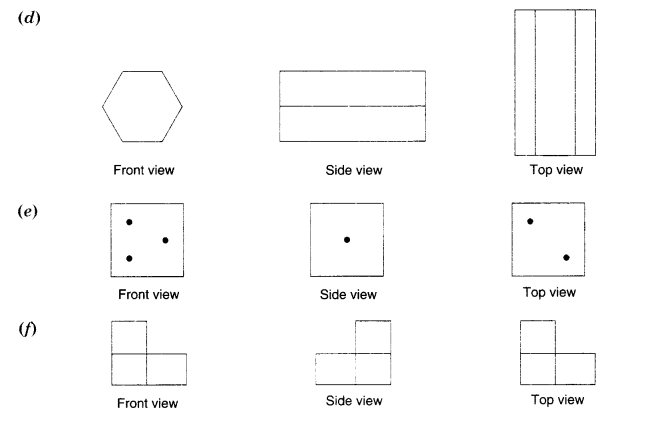
Question 3.
For each given solid, identify the top view, front view, and side view.
Solution.
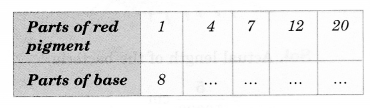
Question 4.
Draw the front view, side view and top view of the given objects,
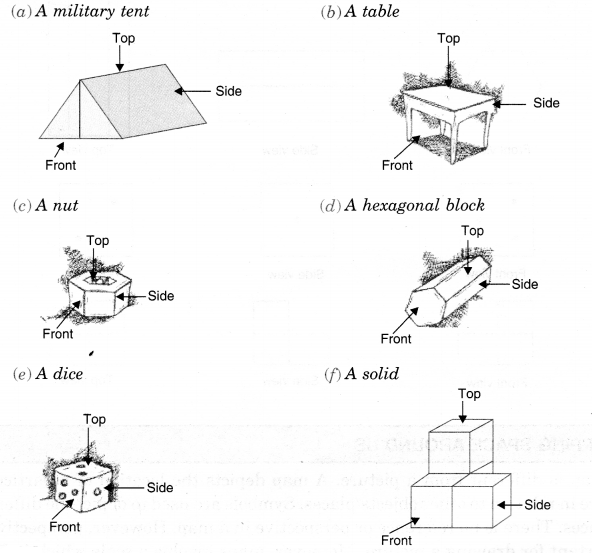
Solution.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.1 help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes Ex 10.1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.