Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Economics Education with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 4 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Economics Term 2 Set 4 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks : 40
General Instructions:
- This is a subjective question paper containing 13 questions.
- This paper contains 5 questions of 2 marks each, 5 questions of 3 marks each and 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- Section A, 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions-Answer them in 30-50 words.
- Section B, 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions-Answer them in 50-80 words.
- Section C, 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions-Answer them in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
![]()
Section – A
(2 Marks Each)
Question 1.
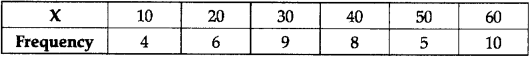
The sum of 100 values is 1,000 and the sum of their square is 10,900. Find the coefficient of variation. (2)
The price of an article which was ₹150 in 2005 increased to ₹300 in 2007. The increase in 2007 on the base year 2005 was 100%. So using 2007 as base year, what should have been the decrease in 2005?
Question 2.
If the points in a scatter diagram tend to cluster in a straight line which makes an angle of 30° with the X-axis, what would you say about the strength of association between X and Y? (2)
Question 3.
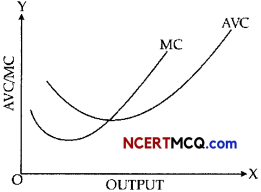
Draw Total Variable Cost, Total Cost and Total Fixed Cost curves in a single diagram. (2)
OR
Price elasticity of supply of a commodity is 1. Its price rises from f 20 to ₹24 per unit and its supply rises by 300 units. Calculate its supply at the original price of ₹20 per unit. (2)
Question 4.
What is the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns? (2)
![]()
Question 5.
Why is the total revenue curve of a price-taking firm an upward-sloping straight line? Why does the curve pass through the origin? (2)
OR
Explain the implications of the feature “homogeneous product” in a perfectly competitive market. (2)
Section – B
(3 Marks Each)
Question 6.
If the salary of a person in the base year is ₹4,000 per annum and the current year salary is ₹6,000, by how much should his salary rise to maintain the same standard of living if the CPI is 400? (3)
Question 7.
Explain the relationship between TR, AR and MR with the help of a table. (3)
OR
Comment on the shape of the MR curve in case the TR curve is a:
(i) Positively sloped straight line passing through the origin.
(ii) Horizontal line.
Read the hypothetical case study and answer the Q. 8 and Q. 9 that follows:
![]()
Law of Supply states that, other things being equal, quantity supplied increases with increase in price and decreases with decrease in price of a commodity.
Assumptions of Law of Supply: The Law of Supply assumes the following as constant:
(i) Price of all related goods
(ii) Prices of input of factors of production
(iii) Technique of production
(iv) Goals of the producer
(v) Policies of the government
(vi) Expectations about the market
Exceptions to the Law of Supply:
Agricultural Produce: The supply of agricultural produce cannot be increased with increase in prices because of limitation of agricultural land and the time involved in producing a fresh crop. Also, it is more season dependent. On the other hand, most of the agricultural produce like fruits and vegetables is perishable in nature. This is why, their supply cannot be reduced with decrease in prices.
Supply of Labour: The supply of labour is an exception to the law of supply. Initially, the supply of labour follows the law of supply, that is, with an increase in wage rate, there is an increase in supply of labour. But beyond a certain wage rate, the labour prefers to have some relaxed hours. The workers can maintain the same standard of living by working for fewer hours at higher wage rates. As a result, beyond that wage rate, the supply of labour starts falling. As a result, the supply curve of labour is backward bending.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain how changes in prices of other products influence the supply of a given product. (3)
Question 9.
The agricultural produce and the labour supply are the exceptions to the supply curve as they do not have an upward rising supply curve, but when the assumption of law of supply is not working it may result in the rightward shift or the leftward shift in the supply curve. State three reasons which can cause it. (3)
Question 10.
Explain the effects of ‘maximum price ceiling’ on the market of a good. Use diagram. (3)
Section – C
(5 Marks Each)
Question 11.
Construct Index Number of price of 2011 from the following data by:
(i) Laspeyre’s Method
(ii) Paasche’s Method
(iii) Fisher’s Method
| Commodity | 2001 | 2011 | ||
| Price | Quantity | Price | Quantity | |
| A | 15 | 40 | 22 | 45 |
| B | 18 | 18 | 21 | 12 |
| C | 28 | 20 | 30 | 25 |
| D | 16 | 25 | 17 | 30 |
![]()
Question 12.
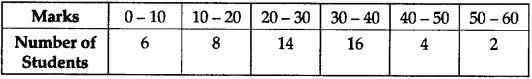
Calculate Standard Deviation for the following distribution. (5)
| Class | Frequencies |
| 20-40 | 3 |
| 40-80 | 6 |
| 80-100 | 20 |
| 100-120 | 12 |
| 120-140 | 9 |
| 50 |
Question 13.
Giving reasons, state whether the following statements are true or false:
(i) When the equilibrium price of a good is less than the market price, there will be competition among the sellers.
Excess supply of a commodity exists when its market price is greater than its equilibrium price. [2 1/2 × 2]
OR
Suppose the value of demand and supply curves of a Commodity-X is given by the following two equations simultaneously:
Qd – 200 – 10p
Qs = 50 + 15p
(i) Find the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity of commodity X.
(ii) Suppose that the price of a factor input used in producing the commodity has changed, resulting in the new supply curve given by the equation:
Qs – 100 + 15p
![]()
Analyse the new equilibrium price and new equilibrium quantity as against the original equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. (5)