Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physical with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 7 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physical Education Term 2 Set 7 with Solutions
General Instructions :
- There are three sections in the Question paper namely Section A, Section B and Section C.
- Section A consists of 9 questions amongst which 7 questions have to be attempted.
Each question carries 2 marks and should have 30-50 words. - Section B consists of 5 questions amongst which 3 questions have to be attempted.
Each question carries 3 marks and should have 80-100 words. - Section C consists of 4 questions amongst which 3 questions have to be attempted.
Each question carries 4 marks and should have 100-150 words.
Maximum Marks : 35
Time : 2 Hours
![]()
Section A
Question 1.
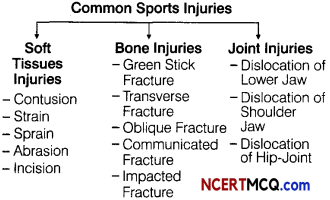
List various causes of bone fracture and joint dislocation? (0.5 x 4)
Answer:
Some causes of bone fractures and joint dislocations are
- Direct hit or strike by any sports equipment
- Sudden or unregulated fall on a hard surface
- Stress or traumatic forceful movement of bones and joints
- Osteoporosis or any other disease that weakens the bones
Question 2.
Explain the procedure of Sukhasana. (0.5 x 4)
Answer:
The procedure of Sukhasana is
- Sit cross-legged on the floor or any other flat surface.
- Bend your knees, and cross your right shin in front of your left shin.
- Move the knees closer until your feet is directly underneath them.
- Place both the palms on your knees, close your eyes and breathe slowly.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the first-aid procedure for minor wounds and cuts. (2)
Answer:
The first aid procedure for minor wounds and cuts is that wash hands or wear sterile disposable gloves and then clean the surface of the cut or the wound with water.
If there is a minor cut, then apply antiseptic cream or lotion to the affected part. If there is bleeding, then cover the wound with cotton or bandage and press to stop bleeding or raise the affected area above the heart level.
Question 4.
Briefly explain how healthy sport environment act as a form of extrinsic motivation. (2)
Answer:
A healthy sports environment acts as an extrinsic motivation in many ways. If the environment has proper temperature, weather conditions, proper humidity along with clean and level sports field, then it acts as a positive reinforcement.
Good quality and smooth running sports equipments along with proper facilities also encourage people to participate in sports.
Question 5.
Explain method of acceleration run for speed development in sportspersons. (2)
Answer:
For acceleration run, sprinter is required to run a specific distance. He starts from stationary position and tries to attain the maximum speed as soon as possible and tries to finish the distance at that speed. These accelerations are repeated 6 to 12 times with sufficient intervals between runs.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you understand by isometric exercises? (2)
Answer:
Isometric term is derived from the words ‘iso’ meaning ‘same’ and ‘metric’ meaning ‘length’. Thus, the word ‘isometric’ refers to the length of the muscle that remains unchanged during workouts.
This happens when there is a tension on a muscle but no movement is made, causing the length of the muscle to remain the same. Therefore, one cannot see any external movement but a muscle is stretched as a lot of pressure is exerted on it.
Question 7.
What is the benefit and contraindication of Trikonasana? (1 + 1)
Answer:
Benefits of Trikonasana is that it stretches and opens the lower back region, groin area, hamstrings, calves, shoulders, chest, arms and spine.
Contraindications of doing Trikonasana is that it should be avoided if a person is suffering from migraine, diarrhoea, neck and back injuries.
Question 8.
What are disability etiquettes? (2)
Answer:
Disability etiquettes are the mannerism or disciplinary guidelines that should be followed Mobility impairment means difficulty in movement. To cope up with this difficulty, wheelchairs, walking sticks and several other things are used.
![]()
Section B
Question 9.
Which asanas are beneficial for curing hypertension? (2)
Answer:
To prevent and cure hypertension, various asanas should be performed that reduces stress and rejuvenate mind and body such as Tadasana, Vajrasana, Pavanamuktasana, Ardha Chakrasana and Bhujangasana.
Question 10.
Mention three ways in which exercises can improve the working of respiratory system. (1 x 3)
Answer:
The respiratory system consists of trachea, bronchi, lungs and air sacs. Exercises can improve the working of respiratory system in the following ways
- Increasing the vital air capacity which is the maximal volume of air forcefully exhaled.
- By doing regular exercises, there is an increase in tidal air capacity of an individual.
- By increasing the size of the alveoli which provides more space for the diffusion of gases oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Question 11.
What does C, E and N stands in OCEAN? Explain them. (1 x 3)
Answer:
OCEAN is a concept given in Big Five personality theory.
C is for Conscientiousness which refers to people having a high degree of reliability and are prompt. These people are organised, systematic and hard working.
E is for Extroversion which refers to people having the traits of energetic, assertive, outgoing, social and talkative. They derive their energy from interacting with other individuals. N is for Neuroticism which relates to ones’ emotional stability and the degree of negative emotions. Such people are moody, tense, anxious and emotionally unstable.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the procedure of Matsyasana? (3)
Answer:
Procedure of Matsyasana is
- Lift your hips and tuck your hands slightly beneath your buttocks, palms facing down. Draw your forearms and elbows in towards your body.
- With inhale, bend your elbows and press firmly on your forearms and elbows to lift your head and upper body away from the floor.
- Firm your shoulder blades into your back and lift your chest higher towards the ceiling, elongating your spine.
- Bring the crown of your head on the floor.
- Remain in that position with your knees bent.
- Take 5 to 10 deep breaths.
- Slowly return to normal position.
Question 13.
Explain the concept of disorder. (3)
Answer:
Disorder is considered as an ailment that disrupts the normal well-being or health of an individual. It hinders a person’s performance. Disorder may be present by birth or may be acquired during one’s lifetime.
Disorder may be seen ordinary in the beginning but usually grows or spreads with time in an individual. It disrupts the normal functioning of a person. It may not be detected on time as it is present in minor form initially. Sometimes the disorders may go away on their own and sometimes, psychological help is needed to manage them.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the concept of disability. (3)
Answer:
The concept of disability relates to the impairment that may be developmental, physical, cognitive or intellectual. Disability affects the every day activities of a person in many ways. Physical disability limits the functions of the body parts while cognitive and intellectual disability affect the mental functions.
It may be present in an individual by birth or may occur during one’s lifetime but mostly it is present from birth. Disability is considered as a condition that does not permit a person to perform any activity or a movement.
Section C
Question 15.
Explain the procedures of the following. (2 + 2)
(i) Pada Hastasana
(ii) Urdhva Hastasana
Answer:
(i) Procedure of Pada Hastasana is
- Stand in tree pose or Tadasana, hands to the side of the body.
- Bend forward until the fingers or palms of the hands touches the floor, either side of the feet.
- Keep the knees straight and try to touch knees with the forehead and try to contract the abdomen.
- After few minutes, release the hand and slowly straighten the body keeping the neck down.
(ii) Procedure of Urdhva Hastasana is
- Stand in a Tadasana (Tree pose). Then, gently raise your hand upward without bending the shoulders, bring your arms together over your head.
- Expand the elbows completely and reach upwards. Then, slightly slant your head backwards and look at the thumbs.
- Shoulder blades must be pressed firmly on your back.
- Keep your feet together and press your heel firmly against the ground.
![]()
Question 16.
Elaborate the training methods to improve flexibility. (1 x 4)
Answer:
The training methods to improve flexibility are :
Dynamic Stretching It refers to stretching that involves putting muscular effort along with movement at the same time. Walking lunges, kicking action and moving the arm in circular motion are the examples of dynamic stretching.
Static Active Stretching Under this method, the muscles are stretched without moving the limbs and the limbs are held in a position for 30 seconds. Standing on one leg and holding the other leg directly in front for 20-30 seconds is static active stretching.
Static Passive Stretching This also refers to stretching of muscles without moving the limbs. However, an external force is applied to hold the stretch in position.
The external force can be some other parts of your body like hands to hold the stretch, an assistance or an equipment.
Ballistic Stretching It uses the momentum of a moving body or a limb in an attempt to force it beyond its normal range of motion.
This is a stretching or warming up, by bouncing into a stretched position, using the stretched muscles as a spring which pulls you out of the stretched position.
The stretching can be performed rhythmically with a count. At each count, joint is stretched to the maximum limit and then it is again flexed.
![]()
Question 17.
On the basis of nature of activity and duration of activity, what are the types of endurance? (2 + 2)
Answer:
On the basis of nature of activity, the endurance is classified into the following types
- Basic Endurance It is the ability to perform movements in which large number of body muscles are involved, e.g. walking, jogging, slow running, etc.
- General Endurance It is the ability of body to tolerate fatigue satisfactorily caused by different types of activities.
- Specific Endurance It is the ability to resist the fatigue caused by a particular sports activity.
- On the basis of duration of activity, the endurance is classified into following types
- Speed Endurance It is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that last upto 45 seconds.
- Short-term Endurance It is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that range from 45 seconds to 2 minutes.
- Medium-term Endurance It is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that range from 2 minutes to 11 minutes.
- Long-term Endurance It is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that last more than 11 minutes.
Question 18.
How pesticides, medicines or vaccines, lack of education, dangerous working conditions and heredity may cause disability? (0.5 x 5)
Answer:
Pesticides, medicines or vaccines, lack of education, dangerous working conditions and heredity may cause disability in the following ways
Pesticides Chemicals such as lead found in paints or pesticides found in various products can cause disabilities in people and cause birth defects in babies growing in the womb.
Medicines or Vaccines The use of unclean syringes may cause serious diseases like Hepatitis or HIV/AIDS. Improperly stored as well as wrong vaccines may cause allergic reactions, leading to many kinds of disabilities among people.
Lack of Education Lack of education among the people, leads to disability as they are not aware regarding the symptoms of certain diseases and how they can be avoided by using scientific methods or taking precautions.
Dangerous Working Conditions If individuals are working in factories, mines or agricultural fields under improper working conditions, they may be exposed to dangerous machinery, tools or chemicals and wide variety of health hazards.
![]()
Heredity Disabilities may also be inherited from parents to their offspring i.e. passed on from one generation to the other.