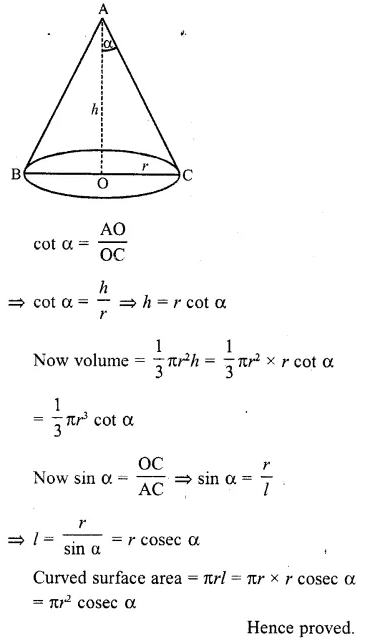
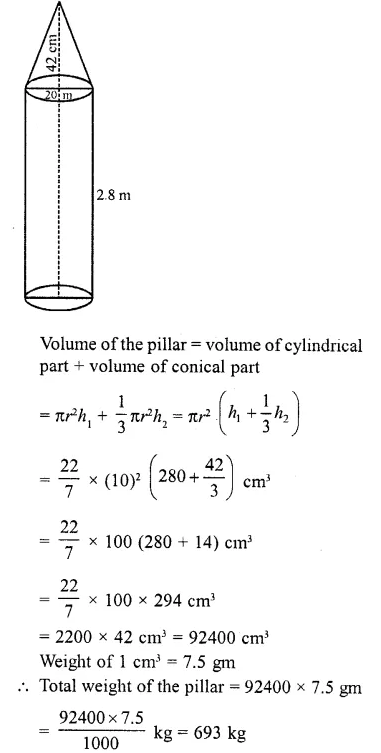
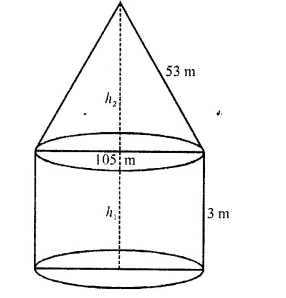
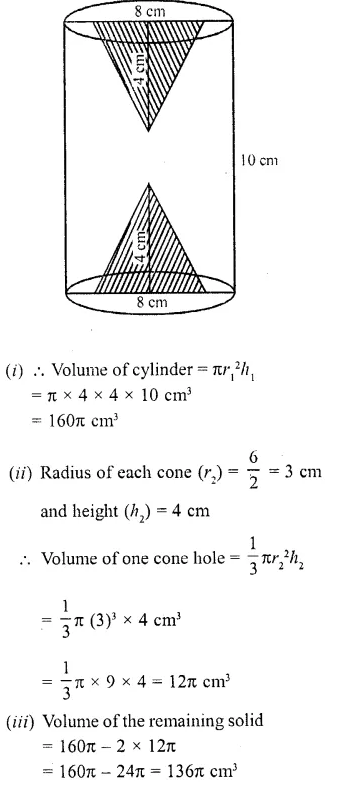
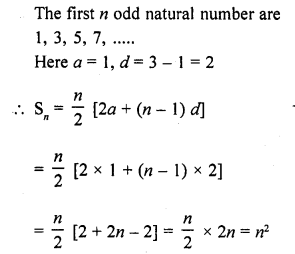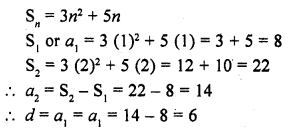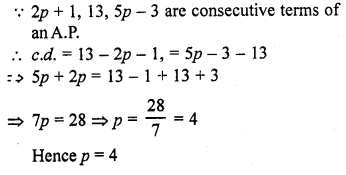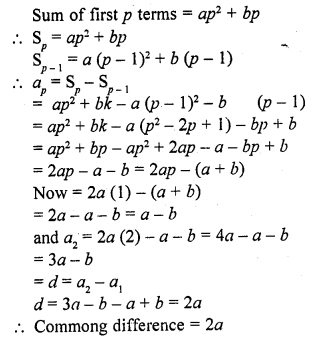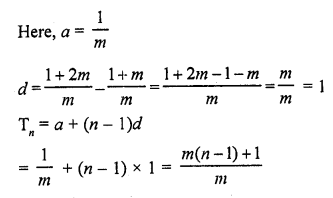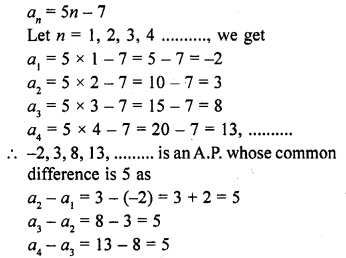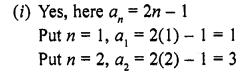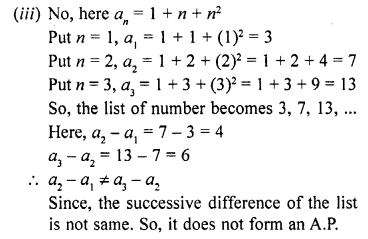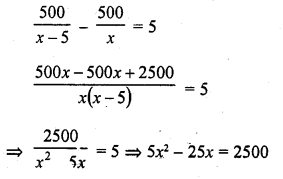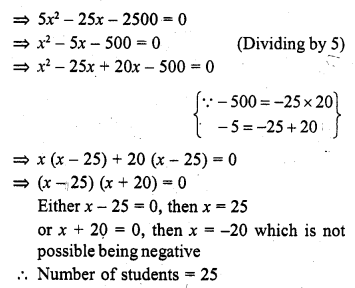RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions MCQS
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions MCQS
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.1
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.2
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.3
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.4
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.5
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Ex 5.6
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions VSAQS
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions MCQS
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following :
Question 1.
If 7th and 13th terms of an A.P. be 34 and 64 respectively, then its 18th term is
(a) 87
(b) 88
(c) 89
(d) 90
Solution:
(c) 7th term (a7) = a + 6d = 34
13th term (a13) = a + 12d = 64
Subtracting, 6d = 30 => d = 5
and a + 12 x 5 = 64 => a + 60 = 64 => a = 64 – 60 = 4
18th term (a18) = a + 17d = 4 + 17 x 5 = 4 + 85 = 89
Question 2.
If the sum of p terms of an A.P. is q and the sum of q terms is p, then the sum of (p + q) terms will be
(a) 0
(b) p – q
(c) p + q
(d) – (p + q)
Solution:
(d)
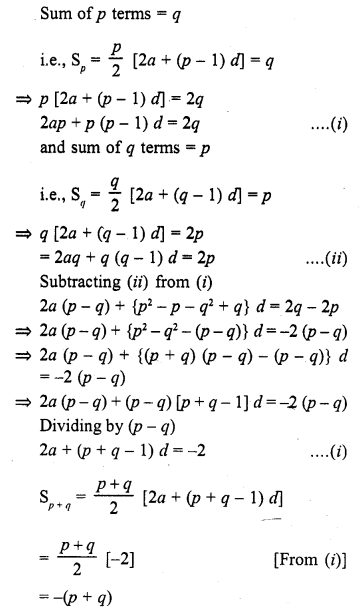
Question 3.
If the sum of n terms of an A.P. be 3n2 + n and its common difference is 6, then its first term is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 4
Solution:
(d)
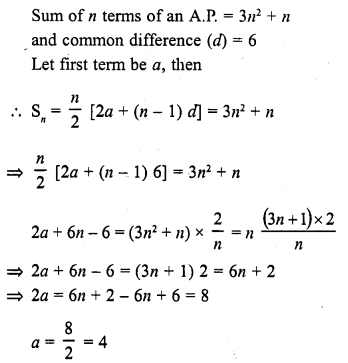
Question 4.
The first and last terms of an A.P. are 1 and 11. If the sum of its terms is 36, then the number of terms will be
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) 8
Solution:
(b) First term of an A.P. (a) = 1
Last term (l) = 11
and sum of its terms = 36
Let n be the number of terms and d be the common difference, then
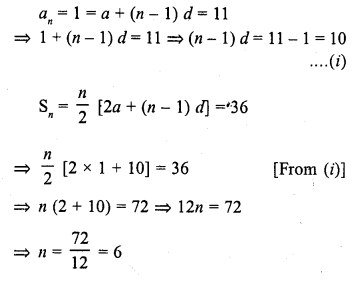
Question 5.
If the sum of n terms of an A.P. is 3n2 + 5n then which of its terms is 164 ?
(a) 26th
(b) 27th
(c) 28th
(d) none of these
Solution:
(b)

Question 6.
If the sum of it terms of an A.P. is 2n2 + 5n, then its nth term is
(a) 4n – 3
(b) 3n – 4
(c) 4n + 3
(d) 3n + 4
Solution:
(c)

Question 7.
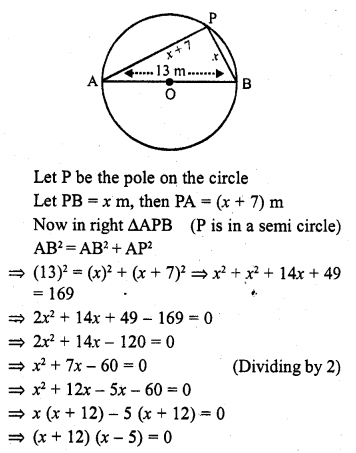
If the sum of three consecutive terms of an increasing A.P. is 51 and the product of the first and third of these terms is 273, then the third term is :
(a) 13
(b) 9
(c) 21
(d) 17
Solution:
(c)

Question 8.
If four numbers in A.P. are such that their sum is 50 and the greatest number is 4 times the least, then the numbers are
(a) 5, 10, 15, 20
(b) 4, 10, 16, 22
(c) 3, 7, 11, 15
(d) None of these
Solution:
(a)
4 numbers are in A.P.
Let the numbers be
a – 3d, a – d, a + d, a + 3d
Where a is the first term and 2d is the common difference
Now their sum = 50
a – 3d + a – d + a + d + a + 3d = 50
and greatest number is 4 times the least number
a + 3d = 4 (a – 3d)
a + 3d = 4a – 12d
4a – a = 3d + 12d
=> 3a = 15d
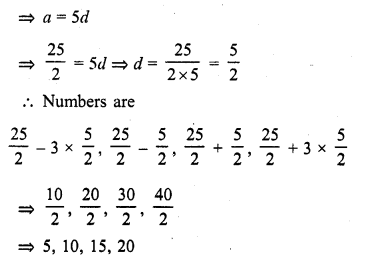
Question 9.
Let S denotes the sum of n terms of an A.P. whose first term is a. If the common difference d is given by d = Sn – k Sn-1 + Sn-2 then k =
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) None of these
Solution:
(b)

Question 10.
The first and last term of an A.P. are a and l respectively. If S is the sum of all the terms of the A.P. and the common difference is given by
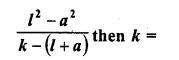
(a) S
(b) 2S
(c) 3S
(d) None of these
Solution:
(b)
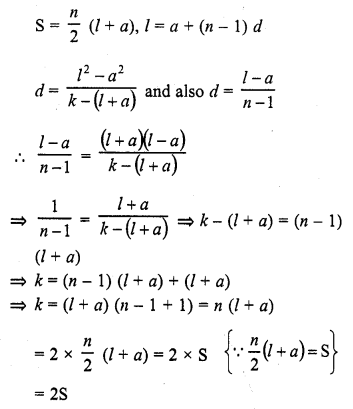
Question 11.
If the sum of first n even natural number is equal to k times the sum of first n odd natural numbers, then k =

Solution:
(d)
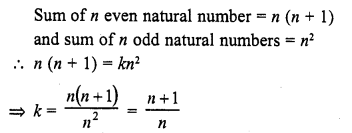
Question 12.
If the first, second and last term of an A.P. are a, b and 2a respectively, its sum is
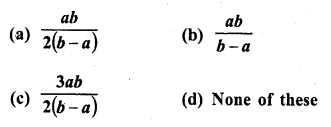
Solution:
(c)

Question 13.
If S1 is the sum of an arithmetic progression of ‘n’ odd number of terms and S2 is the sum of the terms of the
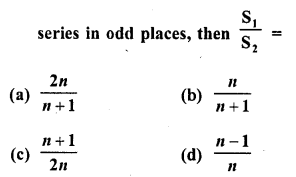
Solution:
(a)
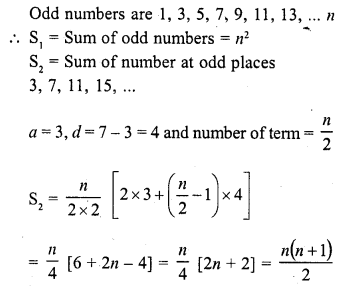
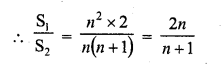
Question 14.
If in an A.P., Sn = n2p and Sm = m2p, where S denotes the sum of r terms of the A.P., then Sp is equal to
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) p3
(b) mnp
(c) p3
(d) (m + n) p2
Solution:
(c)
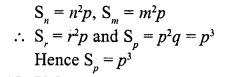
Question 15.
If Sn denote the sum of the first n terms of an A.P. If S2n = 3Sn , then S3n : Sn is equal to
(a) 4
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 10
Solution:
(b)

Question 16.
In an AP, Sp = q, Sq = p and S denotes the sum of first r terms. Then, Sp+q is equal to
(a) 0
(b) – (p + q)
(c) p + q
(d) pq
Solution:
(c) In an A.P. Sp = q, Sq = p
Sp+q = Sum of (p + q) terms = Sum of p term + Sum of q terms = q + p
Question 17.
If Sn denotes the sum of the first r terms of an A.P. Then, S3n : (S2n – Sn) is
(a) n
(b) 3n
(b) 3
(d) None of these
Solution:
(c)
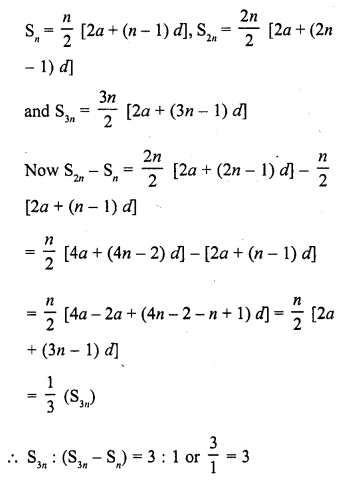
Question 18.
If the first term of an A.P. is 2 and common difference is 4, then the sum of its 40 term is
(a) 3200
(b) 1600
(c) 200
(d) 2800
Solution:
(a)
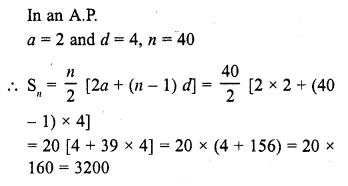
Question 19.
The number of terms of the A.P. 3, 7,11, 15, … to be taken so that the sum is 406 is
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 14
Solution:
(d)
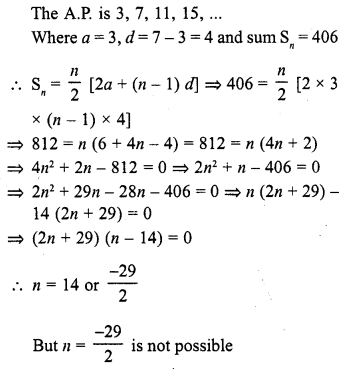
Question 20.
Sum of n terms of the series
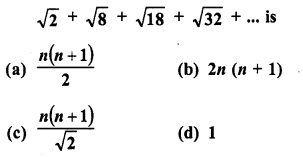
Solution:
(c)
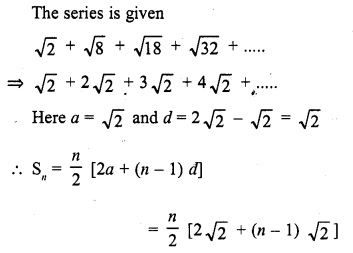
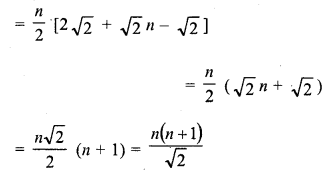
Question 21.
The 9th term of an A.P. is 449 and 449th term is 9. The term which is equal to zero is
(a) 50th
(b) 502th
(c) 508th
(d) None of these
Solution:
(d)

Question 22.
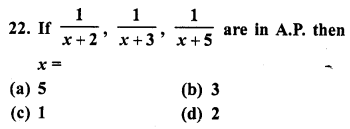
Solution:
(c)
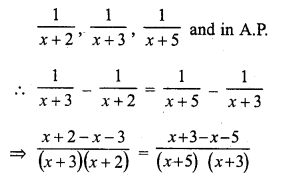
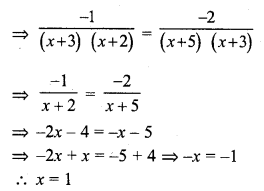
Question 23.

Solution:
(b) Sn is the sum of first n terms
Last term nth term = Sn – Sn-1
Question 24.
The common difference of an A.P., the sum of whose n terms is Sn, is
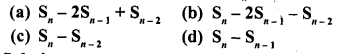
Solution:
(a)
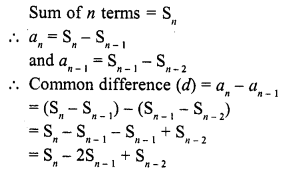
Question 25.

Solution:
(b)
In first A.P. let its first term be a1 and common difference d1
and in second A.P., first term be a2 and common difference d2, then
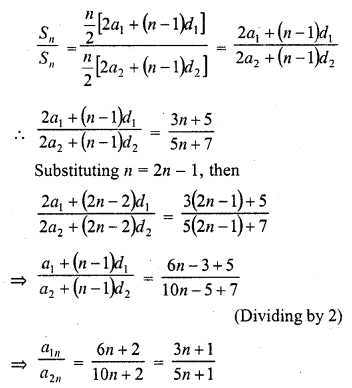
Question 26.

Solution:
(b)

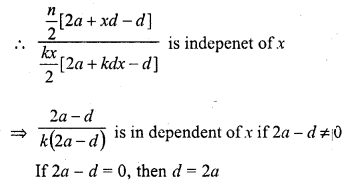
Question 27.
If the first term of an A.P. is a and nth term is b, then its common difference is

Solution:
(b)
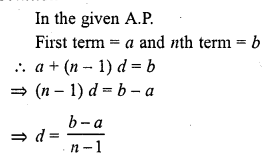
Question 28.
The sum of first n odd natural numbers is
(a) 2n – 1
(b) 2n + 1
(c) n2
(d) n2 – 1
Solution:
(c)
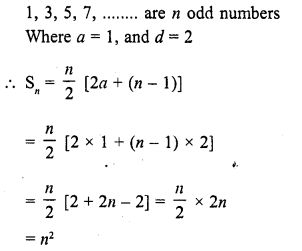
Question 29.
Two A.P.’s have the same common difference. The first term of one of these is 8 and that of the other is 3. The difference between their 30th terms is
(a) 11
(b) 3
(c) 8
(d) 5
Solution:
(d) In two A.P.’s common-difference is same
Let A and a are two A.P. ’s
First term of A is 8 and first term of a is 3
A30 – a30 = 8 + (30 – 1) d – 3 – (30 – 1) d
= 5 + 29d – 29d = 5
Question 30.
If 18, a, b – 3 are in A.P., the a + b =
(a) 19
(b) 7
(c) 11
(d) 15
Solution:
(d) 18, a, b – 3 are in A.P., then a – 18 = -3 – b
=> a + b = -3 + 18 = 15
Question 31.
The sum of n terms of two A.P.’s are in the ratio 5n + 4 : 9n + 6. Then, the ratio of their 18th term is

Solution:
(a)
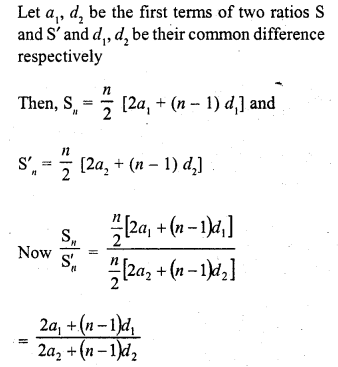

Question 32.
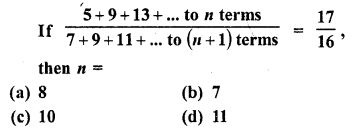
Solution:
(b)

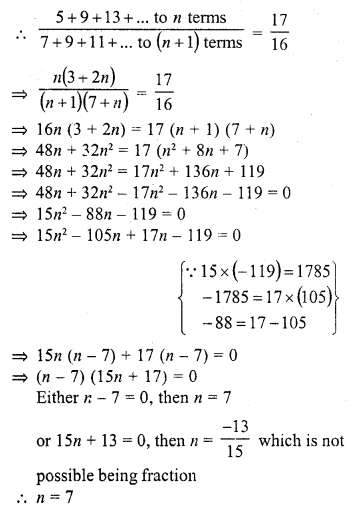
Question 33.
The sum of n terms of an A.P. is 3n2 + 5n, then 164 is its
(a) 24th term
(b) 27th term
(c) 26th term
(d) 25th term
Solution:
(b)
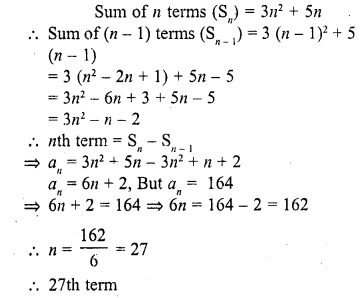
Question 34.
If the nth term of an A.P. is 2n + 1, then the sum of first n terms of the A.P. is
(a) n (n – 2)
(b) n (n + 2)
(c) n (n + 1)
(d) n (n – 1)
Solution:
(b)
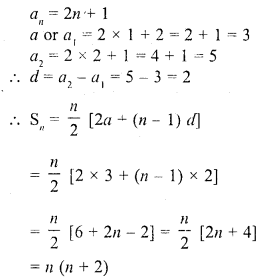
Question 35.
If 18th and 11th term of an A.P. are in the ratio 3 : 2, then its 21st and 5th terms are in the ratio
(a) 3 : 2
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 3
(d) 2 : 3
Solution:
(b)
Question 36.
The sum of first 20 odd natural numbers is
(a) 100
(b) 210
(c) 400
(d) 420 [CBSE 2012]
Solution:
(c)
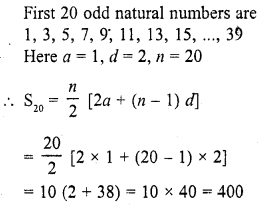
Question 37.
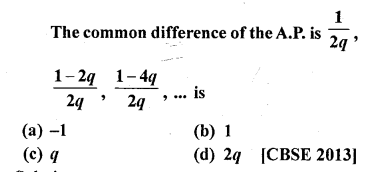
Solution:
(a)
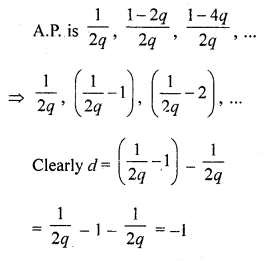
Question 38.
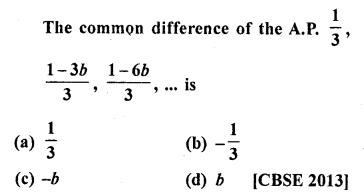
Solution:
(c)
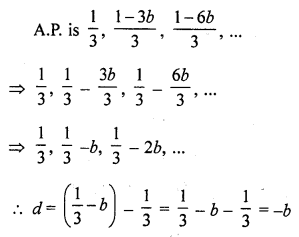
Question 39.
The common difference of the A.P. \(\frac { 1 }{ 2b }\) ,
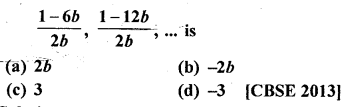
Solution:
(d)
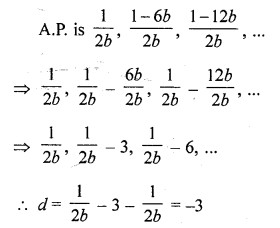
Question 40.
If k, 2k – 1 and 2k + 1 are three consecutive terms of an AP, the value of k is
(a) -2
(b) 3
(c) -3
(d) 6 [CBSE 2014]
Solution:
(b) (2k – 1) – k = (2k + 1) – (2k- 1)
2k – 1 – k = 2
=> k = 3
Question 41.
The next term of the A.P. , √7 , √28, √63, …………
(a) √70
(b) √84
(c) √97
(d) √112 [CBSE 2014]
Solution:
(d)
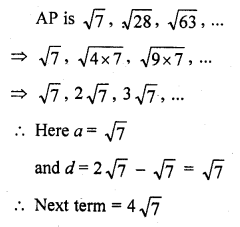
= √(l6 x 7)= √112
Question 42.
The first three terms of an A.P. respectively are 3y – 1, 3y + 5 and 5y + 1. Then, y equals
(a) -3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 2 [CBSE 2014]
Solution:
(c) 2 (3y + 5) = 3y – 1 + 5y + 1
(If a, b, c are in A.P., b – a = c – b=> 2b = a + c)
=> 6y + 10 = 8y
=> 10 = 2y
=> y = 5
Hope given RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions MCQS are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.