On this page, you will find Fibre to Fabric Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 3 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Notes Fibre to Fabric
Fibre to Fabric Class 6 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Clothes are one of our basic needs.
2. Clothes protect us from heat, cold, dirt and dust.
3. The style of clothing differs from place to place.
4. Clothes also differ according to weather conditions.
5. In summer, mostly the cotton clothes of light colours are worn while in winters, mostly woollen clothes like sweaters, caps and gloves are worn.
6. The material that is used to make clothes is called
7. Fabric is woven from various kinds of fibres through various processes with the help of different machines.
8. Fibres are the thread-like structures that are obtained from animals or plants sources or synthesised artificially.
9. Fibre is the basic unit of a fabric.
10. Fabrics are of many types depending on the fibre they are made up of.
11. Fibres are classified on the basis of their origin and are mainly divided into two types: Natural fibres and synthetic fibres.
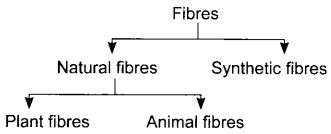
12. Fibres obtained from natural sources are called natural fibres.
13. Cotton, jute, wool, silk, fur, etc., are some of the examples of natural fibres.
14. Natural fibres are further classified into two types- animal fibres and plant fibres.
15. We use fleece of such animals that have special types of hair and fur on their body to make our clothes.
16. For example, wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep, cashmere wool is obtained from cashmere goat, the hair of yak, camel are also used to make woollen clothes.
17. Main plant fibres are cotton, jute, flax, hemp, etc.
18. In addition to these, coconut fibres are also taken in various uses.
19. Fibres that are manufactured artificially in factories using different chemicals are called synthetic fibres. Examples are rayon, terylene, nylon, polyester, etc.
20. Among all the fibres, cotton is produced in the largest quantity in India.
21. Cotton plants are usually grown at places having black soil and warm climate because black soil has capacity to retain water.
22. Cotton is mainly cultivated in Punjab, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
23. The fruits of the cotton plant are known as cotton bolls which are about the size of a lemon.
24. On maturing, these bolls burst open and white fluffy mass is revealed.
25. In this white mass, there are cotton seeds covered with cotton fibres.
26. These white masses of cotton are handpicked from bolls. Then they are passed through various processes.
27. All the fibres are removed from the bolls through a process called
28. Machines are also used for ginning.
29. Jute is the cheapest and most affordable fibre. It is called the ‘golden fibre’.
30. fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant. It is cultivated during the rainy season in India.
31. In India, jute is mainly grown in Bihar, Assam and West Bengal.
32. The jute plant is normally harvested when it is at flowering stage.
33. The stems of the harvested plants are immersed in water for a few days.
34. The stems rot and fibres are separated by hand.
35. All these fibres are first converted into yarns to make fabrics.
36. Spinning is the process of converting fibres into yarn by twisting the fibre using various machines.
37. Spinning is done in the same way as the wicks are made from cotton wool at homes.
38. Spinning can be done both by hands and by machines.
39. Manually, it is done with a hand spindle called takli or on a spinning wheel called
40. Mahatma Gandhi was a great supporter of spinning on the charkha.
41. Once the yarn is obtained, it could be converted into fabric by either of the following two processes- weaving and knitting.
42. Weaving is the process of interlocking two sets of yarns at right angle to each other to form a fabric.
43. Weaving is done on the looms.
44. If looms are manually operated, they are called handlooms and if these are power operated then they are called power looms.
45. The process of making fabric from single yarn is called
46. Knitting can be done either by hands or by machines.
47. Knitting is mostly done for making woollen clothes.
48. In ancient times, people used the bark and big leaves of trees or animal skins and furs to cover themselves.
49. After people began to settle in agricultural communities, they learnt to weave twigs and grass into mats and baskets.
50. The early Indians wore fabrics made out of cotton that grew in the regions near the river Ganga.
51. Flax also a plant that gives natural fibres. In ancient times, cotton as well as flax were cultivated near the river Nile and were used for making fabrics.
52. In those days, stitching was not known. People simply draped the fabrics around different parts of their body.
53. With the invention of sewing needle, people started stitching fabrics to make clothes.
54. Stitched clothes have gone through many variations since this invention.
55. Just as there is a large variety in the food eaten all over the country, a large variety exists also in fabrics and clothing items.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Notes Important Terms
Cotton wool: Cotton wool is obtained from cotton plants. It is made up of thin cotton fibres.
Fabric: The woven materials which are used to make clothes are called fabrics.
Fibre: A long hair-like structure which is the basic unit of a fabric is called fibre.
Knitting: The process of making a piece of fabric from a single yam is called knitting.
Spinning: The process of converting fibres into yarn by twisting the fibre using various machines are called spinning.
Weaving: The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric is called weaving.
Yam: A long strand which are made up of fibre is called yarn.