This grammar section explains Online Education English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. Students can also read NCERT Solutions for Class 11 English to get good marks in CBSE Board Exams. https://ncertmcq.com/letter-writing-class-11/
Online Education for Letter Writing Class 11 Format, Examples, Samples, Topics
Letter Writing Class 11
This question requires the student to write letters of the following kinds based on the given input.
(a) business or official letters for making enquiries, registering complaints, asking for and giving information, placing orders and sending replies
(b) letters to the editor (giving suggestions, opinions on an issue of public interest)
(c) application for,a job with a biodata or resume.
(d) letter to the school or college authorities regarding admissions, school issues, requirements/ suitability of courses, etc.
The student is required to write official letters and letters to the editor. The essential requirements of a good letter are:
(a) suitable format
(b) well-organised content, and
(c) appropriate language
Letter Writing Format Class 11
Formal Letters
Formal letters have a variety of purposes. Formal letters are written:
- to ask for/give information
- to apply for a job
- to make inquiries
- to register complaints about inadequate goods or services
- to place orders/send appropriate replies
- to apologise for behaviour
- ‘to solicit new customers for your business
- to redress grievances
- to persuade others
- to make an appeal for help
- to send a recommendation
However, all of these letters have a common goal – to get a response from someone you may or may not know personally.



Letter Writing For Class 11
(c) Application for a job (with biodata)
Job Applications may be written with or without a biodata. This is a formal official letter and has a formal format, language and style. The main body of the letter should contain the following information.
- personal information, e.g., age
- educational/professional qualifications
- experience letter/suitability for the job.
The letter with a biodata will have biodata as an enclosure. Information should be given under-the heading Biodata.
Format same as for the official letter from the sender’s address
Yours faithfully
Signature
(Name in capital letters)
Encl: Biodata
Biodata
Full name: (Given in the question)
Father’s Name: (imaginary)
Date of Birth: According to job needs, imaginary
Address: (Given/imaginary)
Qualifications: According to job requirements, imaginary
Education: Academic
Professional Experience: According to the job, degree, institution, year
- Post, organisation, year
- From junior to a senior position or vice versa
Testimonials (2 or 3 Testimonials)
1. Name
Designation ………………………..
Official Address ……………………
………………………………………..
References (2 References)
Name
Designation ……………………..
Official Address ………………..
Signature …………………………
Content: It is important to organise the content of the letter for clarity and effective communication. The letter should ideally be written in three paragraphs.
The first paragraph is usually a restatement of the subject. It states the purpose of writing the letter and should be of one or two sentences only, e.g.,
1. I would like to draw your attention to the lack of civic amenities in our area.
2. Through the columns of your esteemed newspaper, I would like to draw the attention of the authorities concerned too.
3. This is in response to your advertisement in The Times of India (date) for the post of ………………
The second paragraph makes up the main body of the letter. The problem/subject is stated in detail.
The third paragraph is in the nature of a concluding paragraph. Suggestions, the writer’s expectations from, or request to the addressee may be given.
The letter concludes with best wishes/thanks/request for an early response/regards, etc.
Language: The language in business and official letters is simple and direct. The subject is dealt with in a straightforward manner.
There is greater flexibility in the language and style of a letter to the editor. It is governed by the subject and content of the letter.

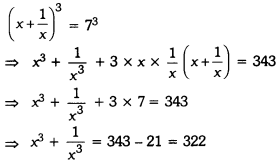
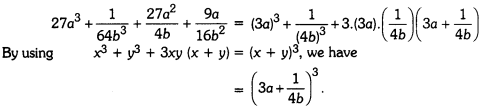
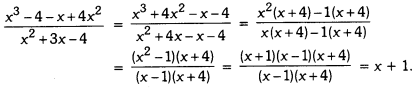
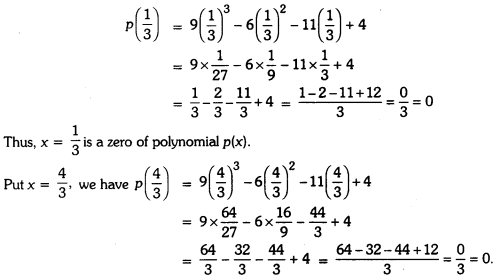




 Online Education Definition: A preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show in what relation the person or thing denoted by it stands in regard to something else.
Online Education Definition: A preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show in what relation the person or thing denoted by it stands in regard to something else.
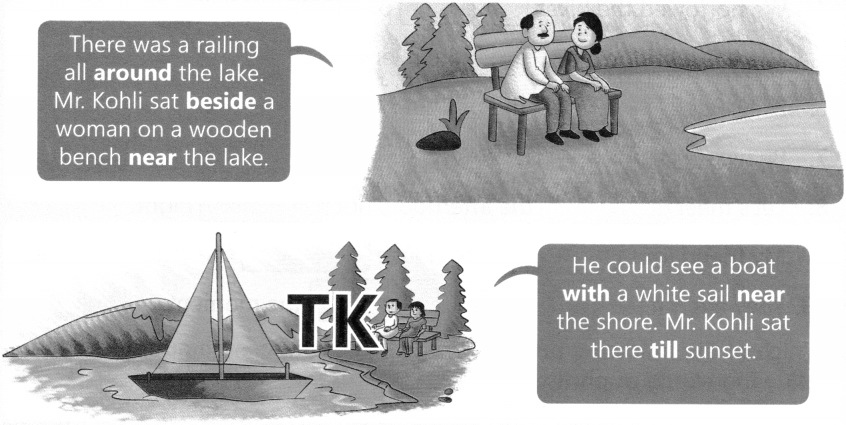


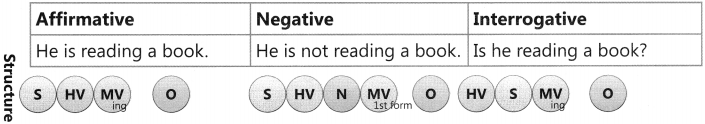
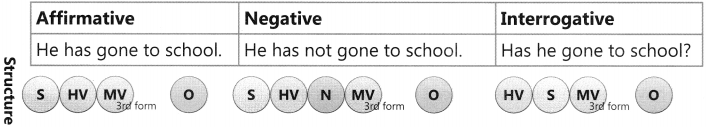
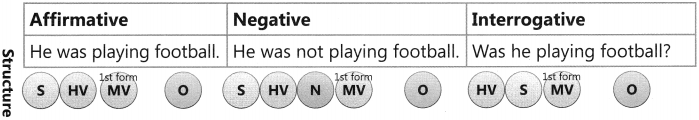
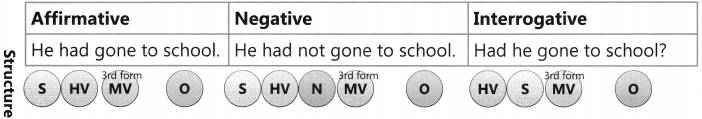
 The Tense of a verb tells us when the action is, was, or will be carried out.
The Tense of a verb tells us when the action is, was, or will be carried out.