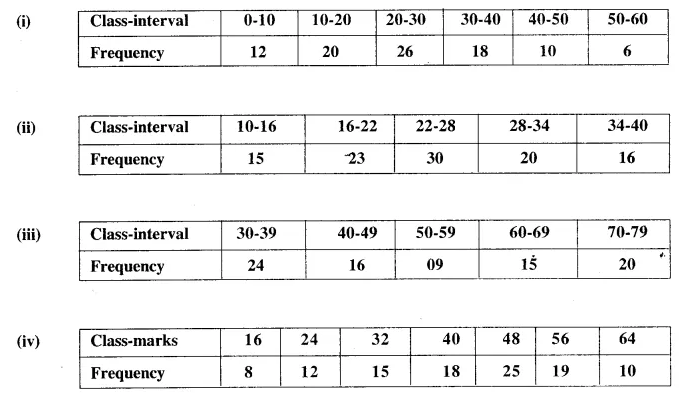
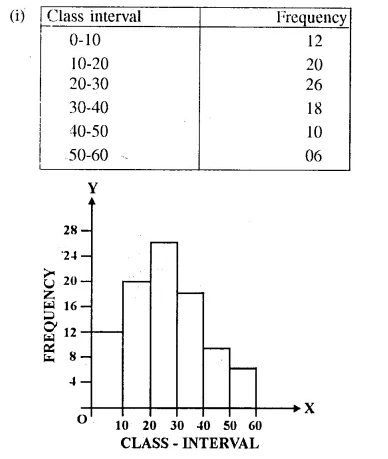
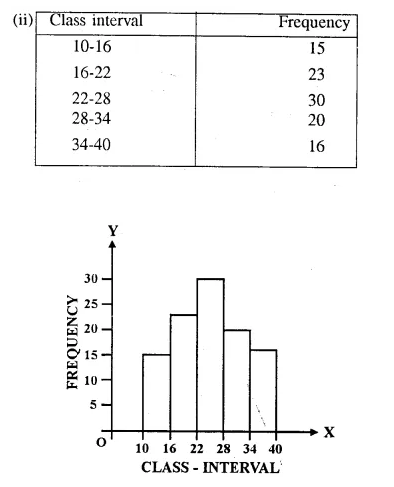
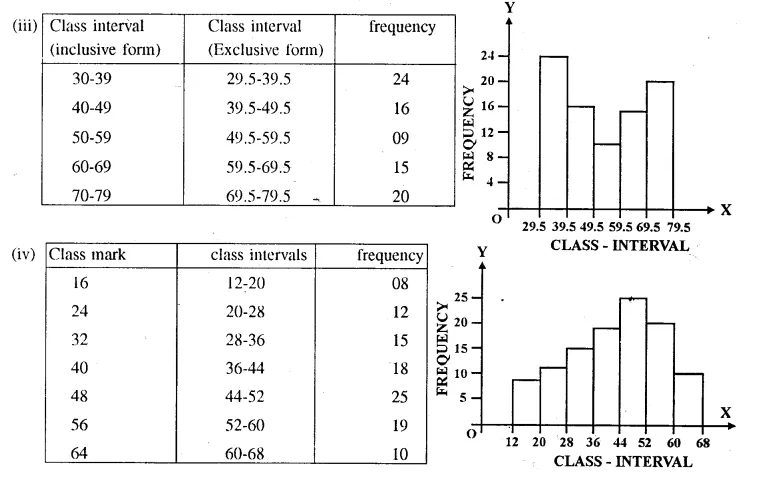
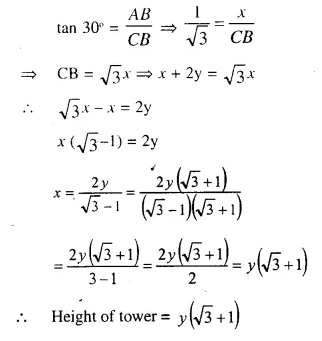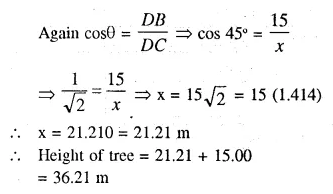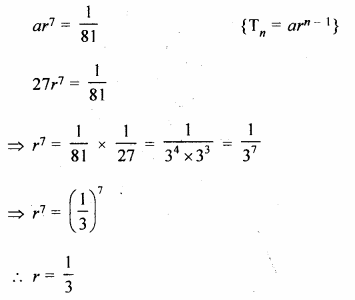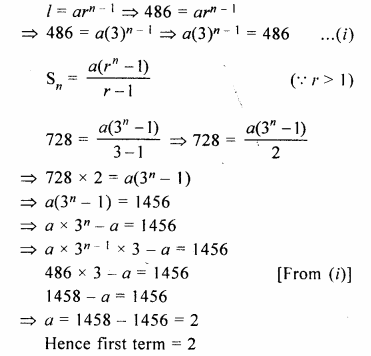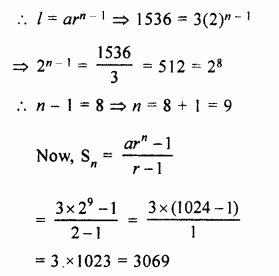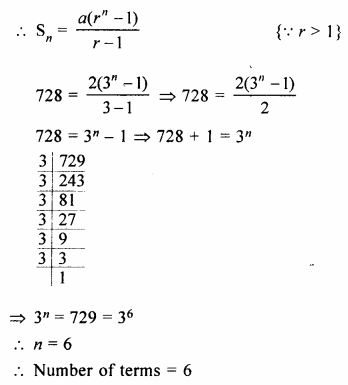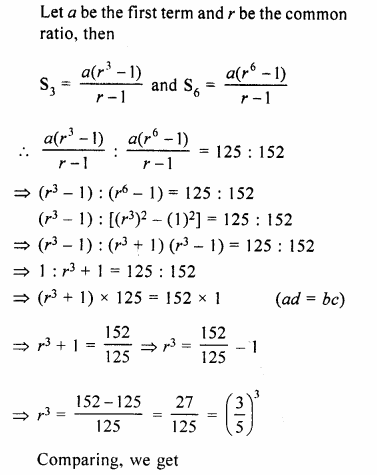HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
These Solutions are part of HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science. Here we have given HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
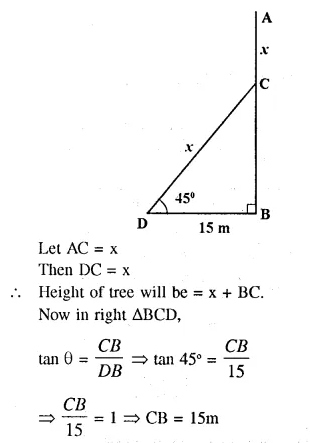
Question 1.
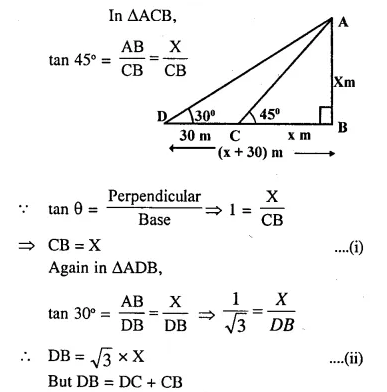
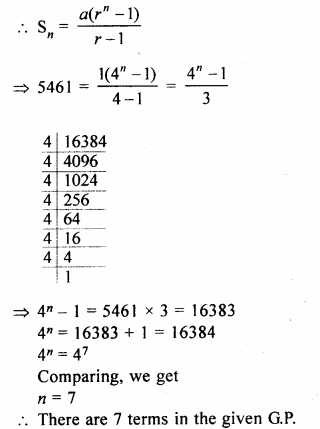
Following model demonstrates the process of thermo-electric production.
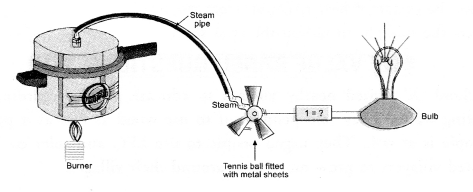
- Identify and label the device marked as 1.
- Why is tennis ball fitted with metal sheets rotated ?
- Name the device, which depends on the principle demonstrated by this model.
- Which form of energy is converted into electrical energy ?
Answer:
- Device 1 is a dynamo.
- Tennis ball fitted with metal sheets rotates due to the force exerted on it by the steam.
- Thermal power plant works on the principle demonstrated by the given model.
- Mechanical energy of tennis ball fitted with metal sheets is converted into electrical energy.
More Resources
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
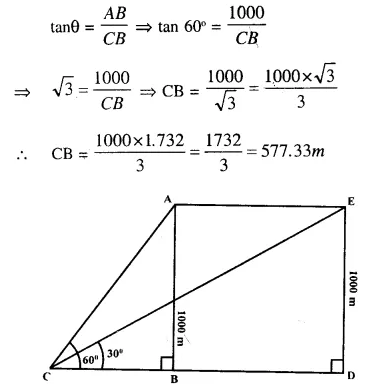
Question 2.
A diagram shown below is a biogas plant.
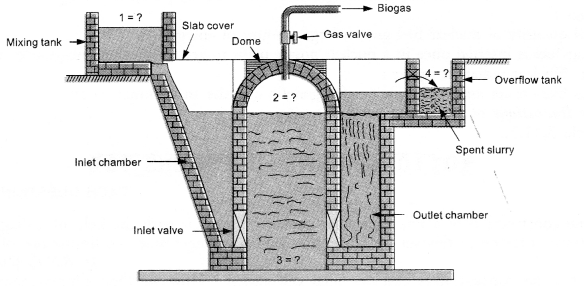
- Identify the parts indicated by question marks and labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the diagram.
- Name the micro organisms responsible for the fermentation of the slurry in the digester.
- Name two chemical elements present in the manure or spent slurry.
Answer:
-
- Slurry of cattle dung and water
- Gas tank containing bio-gas.
- Digester.
- Spent slurry or manure
- Anaerobic micro organisms,
- Nitrogen and phosphorous are present in the manure.
Question 3.
A student constructed a box type solar cooker. He found that it did not work efficiently. What could this be due to ? Give any four possible mistakes in the solar construction and operation of the cooker. What maximum temperature can ordinarily be reached inside a solar cooker ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
He might be committing the following mistakes :
- He might have not blackened the interior of the solar cooker,
- He might be using a plastic cover instead of a glass cover,
- He might have not made it insulated,
- He might have not used black containers. Maximum temperature attained in a solar cooker is about 140° C.
Question 4.
A student has set up a solar cooker in a box by using a black painted aluminium sheet, a black cooking vessel, some glass wool, a glass sheet and a mirror plate. What is the role of each item used in the solar cooker ?
Answer:
Black painted aluminium sheet absorbs heat radiation.
Black cooking vessel also absorbs heat radiation to cook food.
Glass wool prevents the loss of heat.
Glass sheet prevents the escape of heat radiation from the box.
Mirror plate reflects the sunlight to fall on the glass sheet.
Hope given HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.