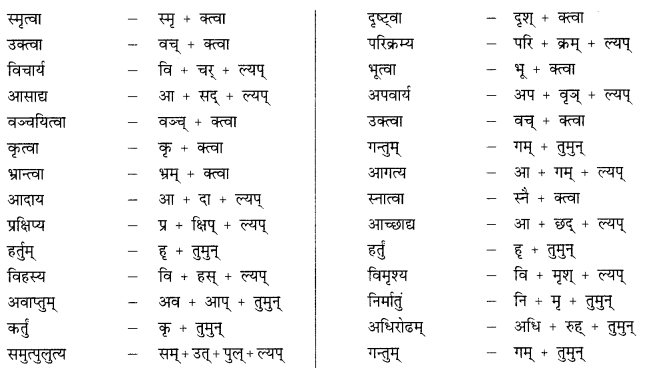
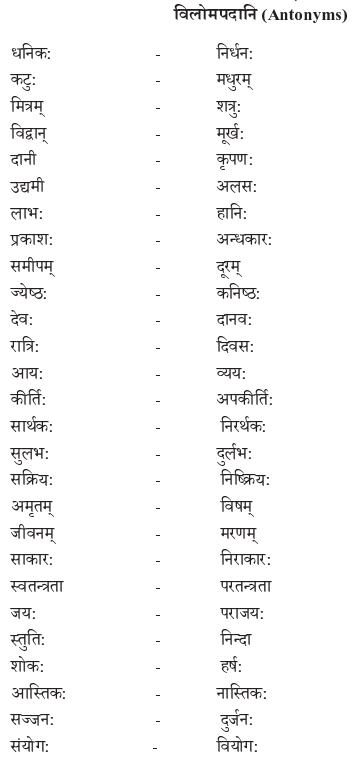
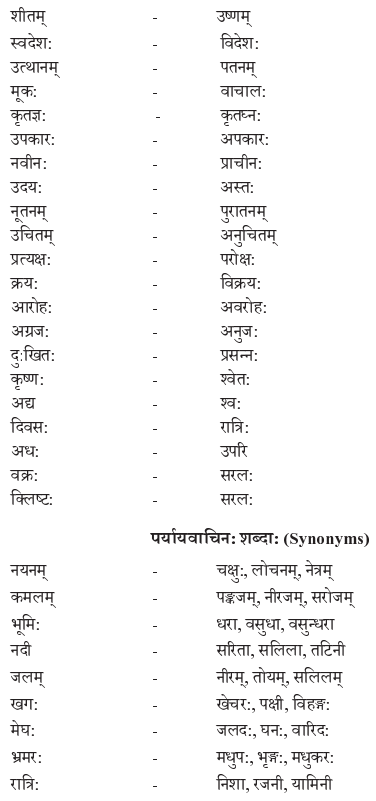
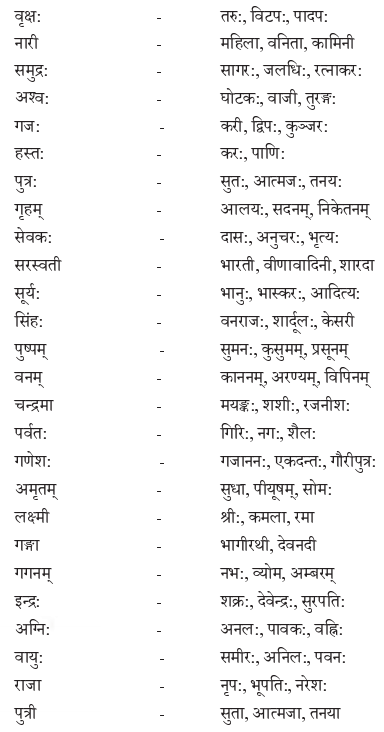
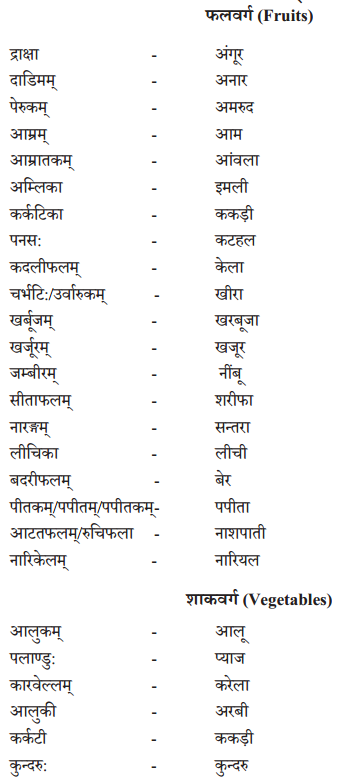
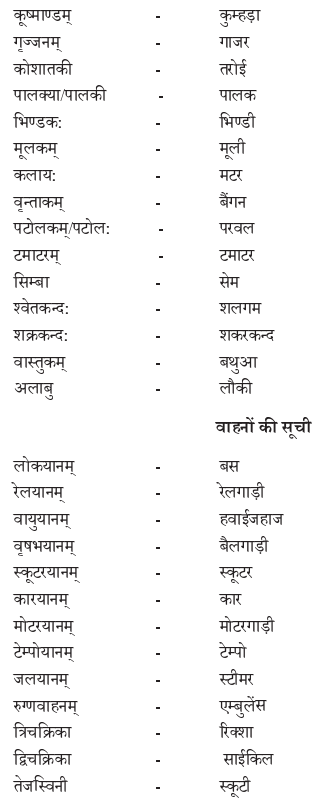
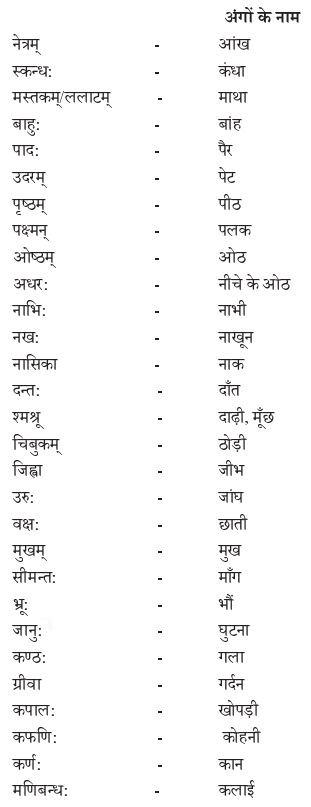
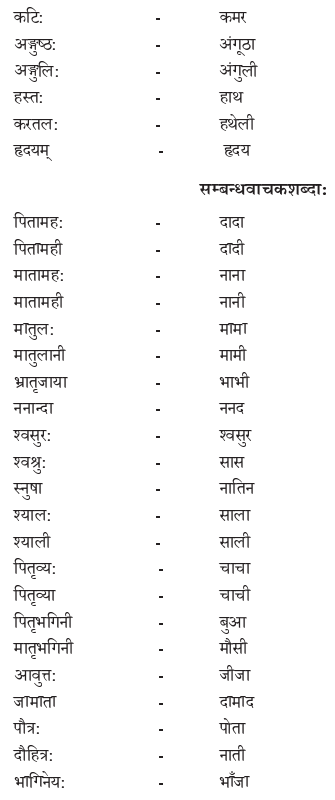
We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit Grammar Book अशुद्धि-संशोधनम् Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
Sanskrit Vyakaran Class 10 Solutions अशुद्धि-संशोधनम्
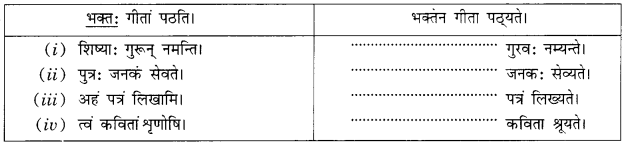
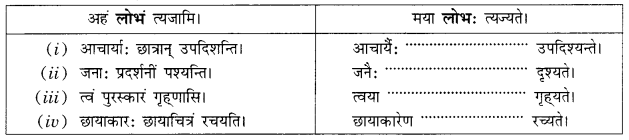
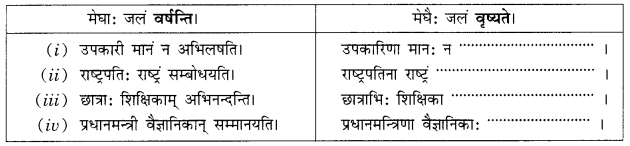
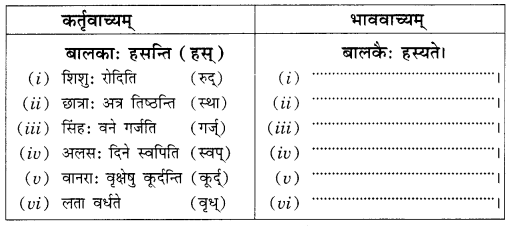
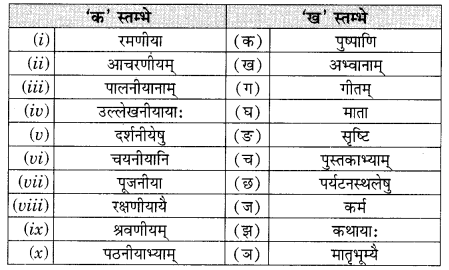
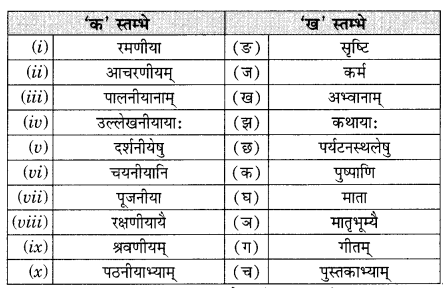
अभ्यास:
प्रश्न 1.
एकः छात्रः अधोलिखितम् अनुच्छेद लिखितवान्। तत्र तेन काश्चन अशुद्धयः कृताः। भवान् तेषां संशोधनं कृत्वा तस्य सहायतां करोतु-
(i) एकः पथिकः ह्यः नगरम् गच्छति।
(ii) तत्र स: बहूनि भवनम् दृष्ट्वा चकितः जातः।
(iii) तस्य मित्रः अपि तत्र तेन सह गतवान्।
(iv) सः अवदत्-अहो विडम्बना! नगरेषु एकतः धनप्रदर्शनम् अपरतः नग्नाः दरिद्राः क्षुधया पीडिताः च स्थ।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अगच्छत्
(ii) भवनानि
(iii) मित्रम्
(iv) सन्ति।
प्रश्न 2.
अस्मिन अनुच्छेदे कानिचित् पदानि पुरुष-वचन-लिङ्ग-लकारदृष्ट्या अशुद्धानि सन्ति। शुद्धीकृत्य समक्षं लिखत-
(i) अहम् पत्रवाहकः अस्ति।
(ii) जनेभ्यः प्रतिदिनम् आगताः पत्राणि वितरामि।
(iii) ते पत्राणि प्राप्य न केवलं निजवृत्तानि अवागच्छत् अपितु साक्षात्कारपत्रम्, नियुक्तिपत्रं, परीक्षाफलम् अपि प्राप्नुवन्ति।
(iv) अहम् स्वकर्म सदा निष्ठया अकरोत्।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अस्मि
(ii) आगतानि
(iii) अवगच्छन्ति
(iv) करोमि।
प्रश्न 3.
एकः छात्रः विहारार्थं जन्त्वागारम् अगच्छत्। ततः आगत्य तस्य वर्णनम् अकरोत्। तत्र च तेन काशचन् अशुद्धयः कृताः। कृपया तासां संशोधनं करोतु-
(i) जन्त्वागारे बहवः सिंहः आसन्।
(ii) तत्र वानराः अपि वृक्षात् वृक्षं कूदते स्म।
(iii) एकः दुष्टः बालकः पाषाण-खण्डान् वानरान् अताडयत्।
(iv) तदैव तत्र रक्षकः आगत्य अवदत्-भौः एतेषु अपि प्राणाः सन्ति अतः एतान् मा ताडयत इति।
उत्तराणि:
(i) सिंहाः
(ii) कूर्दन्ते स्म
(iii) पाषाणखण्डै:
(iv) ताडय।
प्रश्न 4.
अस्मिन् अनुच्छेदे कानिचित् पदानि अशुद्धानि सन्ति तानि शुद्धीकृत्य लिखत-
(i) अहम् एकम् पञ्चाशत् वर्षीया महिला अस्मि।
(ii) अहं किञ्चित् किञ्चित् संस्कृतं अवगच्छति।
(iii) इदानीं यदा बालः अपि-
(iv) संस्कृतभाषा वदन्ति तदा अहम् अति प्रसन्ना भवामि।
उत्तराणि:
(i) एका
(ii) अवगच्छामि
(iii) बालाः
(iv) संस्कृतभाषाम्।
प्रश्न 5.
द्वयोः सख्योः वार्तालापमध्ये काश्चन अशुद्धयः सञ्जाताः। तासां संशोधनं कृत्वा लिखत-
राधिका – अयि लता! अद्य मम विद्यालये वार्षिकोत्सवः अस्ति।
अहम् स्वपितुः सह विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि।
लता – राधिके! किम् तत्र तव मित्राः अपि भविष्यन्ति।
राधिका – आम्र। तत्र अहं पुरस्कारम् अपि लप्स्यते।
लता – शोभनम्, प्रतीक्षस्व तावत्। सञ्जीभूय अहम् अपि आगच्छामि।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अयि लते!
(ii) स्वपित्रा
(iii) मित्राणि
(iv) लप्स्ये।
प्रश्न 6.
अधोलिखित वाक्येषु काश्चन अशुद्धयः रेखांकित कृत्वा तासां संशोधनं कृत्वा पुनः लिखत-
1. (i) जन्तुशालायाम् अनेकाः पशवः बसन्ति।
(ii) मृगानां सह मृगाः चरन्ति।
(iii) धूर्ताः बालकाः पाषाणखण्डान् वानरान् ताडयन्ति।
(iv) केचन बालकाः खगेभ्यः चणकान् यच्छति।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अनेके
(ii) मृगैः
(iii) पाषाणखण्डैः
(iv) यच्छन्ति।
2. (i) अद्य पर्यावरणदिवसः भविष्यति।
(ii) ‘वृक्षाः न छेत्स्यामः’ इति प्रतिज्ञा सर्वैः छात्रैः कृता।
(iii) प्लास्टिकस्यूतानाम् बहिष्कारार्थम् अपि सङ्कल्पः ते कृतः।
(iv) अवकरः जले न क्षेप्तव्यः इत्यपि घोषणां ते कृतवान।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अस्ति
(ii) वृक्षान्
(iii) तैः
(iv) कृतवन्तः।
3. (i) एषा मम विद्यालयः अस्ति।
(ii) इदम् विद्यालये पञ्चाशत् अध्यापकाः अध्यापिकाः च पाठयन्ति।
(iii) किम् त्वत् पार्वे संगणकयन्त्रम् अस्ति?
(iv) अद्यत्वे वयं सर्वाणि कार्याणि संगणकयन्त्रेण एव क्रियन्ते।
उत्तराणि:
(i) एषः
(ii) अस्मिन्
(ii) तव
(iv) कुर्मः।
4. (i) सा बालकः भोजनं खादति।
(ii) त्वया सह के गच्छति?
(iii) किं सा श्वः आगच्छत?
(iv) किं त्वम् अपि खादिष्यति?
उत्तराणि:
(i) सः बालकः भोजनं खादति।
(ii) त्वया सह के गच्छन्ति?
(iii) किं सा श्वः आगमिष्यति?
(iv) किं त्वम् अपि खादिष्यसि?
5. (i) सः बालिका अस्ति।
(ii) मया सह मम मित्रम् अपि गच्छन्ति।
(iii) किं त्वम् अपि पठिष्यति?
(iv) सः अपि खादिष्यसि।
उत्तराणि:
(i) सा बालिका अस्ति।
(ii) मया सह मम मित्राणि अपि गच्छन्ति।
(iii) किं त्वम् अपि पठिष्यसि?
(iv) सः अपि खादिष्यति।
6. (i) सः बालकः खादसि।
(ii) त्वं कुत्र गच्छामि।
(iii) किं सा ह्यः आगमिष्यति?
(iv) ताः अत्र फलं खादतः।
उत्तराणि:
(i) खादति
(ii) अहम्
(iii) श्वः
(iv) ते।
7. (i) सा बालकः फलं खादति।
(ii) मया सह ते अपि गच्छति।
(iii) किं सा ह्यः आगमिष्यति?
(iv) किम् अहम् अपि चलिष्यति?
उत्तराणि:
(i) सः बालकः फलं खादति।
(ii) मया सह ते अपि गच्छन्ति।
(iii) किं सा ह्यः आगच्छत्?
(iv) किम् अहम् अपि चलिष्यामि?
8. (i) सः रमा अस्ति।
(ii) त्वया सह तव पिता अपि गच्छन्ति।
(iii) किं त्वं तत्र श्वः गच्छति?
(iv) सः अपि जलं पास्यसि।
उत्तराणि:
(i) सा रमा अस्ति।
(ii) त्वया सह तव पिता अपि गच्छति।
(iii) किं त्वं तत्र श्व: गमिष्यसि?
(iv) सः अपि जलं पास्यति।
प्रश्न 7.
छात्राः कुतुबमीनारं द्रष्टुम् अगच्छन्। एकः छात्रः तस्य वर्णनम् अकरोत्। वर्णने तेन अनेकाः अशुद्धयः कृताः याः रेखाङ्किताः तासां संशोधनं कृत्वा उत्तरपुस्तिकायां लिखत-
(i) कुतुबमीनारे वयं बहून् जनाः अपश्याम।
(ii) तेषु अनेकाः उपरि गच्छन्ति स्म।
(iii) वयम् एकस्य छायायुक्त-वृक्षस्य अधः भोजनं अकुर्वन्।
(iv) माम् कुतुबमीनारः अतीव अरोचत।
उत्तराणि:
(i) कुतुबमीनारे वयं बहून् जनान् अपश्याम।
(ii) तेषु अनेके उपरि गच्छन्ति स्म।
(iii) वयम् एकस्य छायायुक्त-वृक्षस्य अधः भोजनं अकरवाम।
(iv) मह्यम् कुतुबमीनारः अतीव अरोचत।
प्रश्न 8.
अधोदत्तेषु वाक्येषु कानिचित् पदानि रेखाङ्कितानि, तानि पुरुष-वचन-लिङ्ग-लकारदृष्ट्या अशुद्धानि सन्ति। तानि शुद्धीकृत्य पूर्णं वाक्यम् उत्तरपुस्तिकायां लिखत-
(i) अहं पत्रवाहकः अस्ति।
(ii) जनेभ्यः प्रतिदिनम् आगताः पत्राणि वितरामि।
(iii) ते पत्रेषु साक्षात्कारपत्रः, परीक्षाफलं, नियुक्तिपत्रम् अपि आप्नुवन्ति।
(iv) अहं स्वकर्म सदा निष्ठया करोमि।
उत्तराणि:
(i) अहं पत्रवाहकः अस्मि।
(ii) जनेभ्यः प्रतिदिनम् आगतानि पत्राणि वितरामि।
(iii) ते पत्रेषु साक्षात्कारपत्रम्, परीक्षाफलं, नियुक्तिपत्रम् अपि आप्नुवन्ति।
(iv) अहं स्वकर्म सदा निष्ठया करोमि।
प्रश्न 9.
रेखाङ्किपदानां संशोधनं कृत्वां वाक्यानि पुनः उत्तरपुस्तिकायां लिखत-
(i) ते बालिकाः गृहस्य बहिः क्रीडन्ति।
(ii) माता बालिकेभ्यः क्रुध्यन्ति।
उत्तराणि:
(i) ताः बालिकाः गृहात् बहिः क्रीडन्ति।
(ii) माता बालिकाभ्यः क्रुध्यति।
बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्नाः
1. प्रदत्तेषु उत्तरेषु यत् उत्तरम् शुद्धम् अस्ति तत् चीयताम्।
(दिए गए उत्तरों में से जो उत्तर शुद्ध है उसे चुनिए। Choose the appropriate answer from the options given below.)
प्रश्न 1.
शुद्धम् पवनः वहति।
(क) शुद्धा
(ख) शुद्धः
(ग) शुद्ध
(घ) शुद्धम्
उत्तराणि:
(ख) शुद्धः
प्रश्न 2.
त्वम् मम मित्रः अस्ति।
(क) मित्रम्
(ख) मित्रे
(ग) मित्राणि
(घ) मित्रेण
उत्तराणि:
(क) मित्रम्
प्रश्न 3.
छात्राः विद्यालयं गच्छति।
(क) गच्छति
(ख) गच्छतः
(ग) गच्छसि
(घ) गच्छन्ति
उत्तराणि:
(घ) गच्छन्ति
प्रश्न 4.
त्वम् पुस्तकं पठामि।
(क) पठति
(ख) पठसि
(ग) पठावः
(घ) पठथः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) पठसि
प्रश्न 5.
गुरवः छात्रेभ्यः विद्यां ददाति।
(क) गुरुः
(ख) गुरुम्
(ग) गुरुणा
(घ) गुरु
उत्तराणि:
(क) गुरुः
प्रश्न 6.
इमे छात्रौ पठतः।
(क) इमाः
(ख) इमानि
(ग) इमौ
(घ) इमम्
उत्तराणि:
(ग) इमौ
प्रश्न 7.
अस्य बालिकायाः गृहं कुत्रास्ति?
(क) अनेन
(ख) अस्याः
(ग) अस्यै
(घ) अस्याम्
उत्तराणि:
(ख) अस्याः
प्रश्न 8.
धर्म: आचरणीयम्।
(क) आचरणीयः
(ख) आचरणीया
(ग) आचरणीयौ
(घ) आचरणीये
उत्तराणि:
(क) आचरणीयः
प्रश्न 9.
वृक्षः परोपकाराय फलन्ति।
(क) वृक्षान्
(ख) वृक्षम्
(ग) वृक्षौ
(घ) वृक्षाः
उत्तराणि:
(घ) वृक्षाः
प्रश्न 10.
अहं पुस्तकं पठति।
(क) पठसि
(ख) पठावः
(ग) पठामि
(घ) पठथः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) पठामि
प्रश्न 11.
ते बालकाः पुस्तकं पठतः।
(क) पठथः
(ख) पठावः
(ग) पठन्ति
(घ) पठामः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) पठन्ति
प्रश्न 12.
यः सत्यं भाषते सः सुखं लभति।
(क) लभसि
(ख) लभते
(ग) लप्स्यते
(घ) लभ्यते
उत्तराणि:
(ख) लभते
प्रश्न 13.
वृक्षे चत्वारि खगाः सन्ति।
(क) चतुरः
(ख) चत्वारि
(ग) चत्वारः
(घ) चतस्रः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) चत्वारः
प्रश्न 14.
रामः विद्यालयं गच्छसि।
(क) गच्छति
(ख) गच्छामि
(ग) गच्छानि
(घ) गच्छथः
उत्तराणि:
(क) गच्छति
प्रश्न 15.
अहम् शास्त्रं पठामः।
(क) पठसि
(ख) पठामि
(ग) पठति
(घ) पठावः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) पठामि
प्रश्न 16.
सत्यः कथयितव्यम्।
(क) सत्येन
(ख) सत्यम्
(ग) सत्यम्
(घ) सत्याय
उत्तराणि:
(ग) सत्यम्
प्रश्न 17.
धर्माचरणेन सुखं लभति।
(क) लभसि
(ख) लभते
(ग) लभ्यते
(घ) लभसे
उत्तराणि:
(ख) लभते
प्रश्न 18.
उद्याने सुन्दराः पुष्पाणि सन्ति।
(क) सुन्दरम्
(ख) सुन्दरः
(ग) सुन्दराणि
(घ) सुन्दरे
उत्तराणि:
(ग) सुन्दराणि
प्रश्न 19.
धनं सुखाय भवथः।
(क) भूयते
(ख) भवति
(ग) भवसि
(घ) भवतः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) भवति
प्रश्न 20.
रामः मम मित्रः अस्ति।
(क) मित्रे
(ख) मित्रा
(ग) मित्रम्
(घ) मित्रौ
उत्तराणि:
(ग) मित्रम्
प्रश्न 21.
क्रोधः न कर्तव्यम्।
(क) कर्तव्यः
(ख) कर्तव्या
(ग) कर्तव्ये
(घ) कर्तव्याः
उत्तराणि:
(क) कर्तव्यः
प्रश्न 22.
इदानीं त्वं किं कुर्वन्ति?
(क) करोमि
(ख) कुर्मः
(ग) करोषि
(घ) कुरुथः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) करोषि
प्रश्न 23.
सः अपि जलं पास्यसि।
(क) पास्यति
(ख) पास्यतः
(ग) पास्यथः
(घ) पास्यन्ति
उत्तराणि:
(क) पास्यति
प्रश्न 24.
कुतुबमीनारे वयं बहून् जनाः अपश्याम।
(क) जनान्
(ख) जनैः
(ग) जनः
(घ) जनम्
उत्तराणि:
(क) जनान्
प्रश्न 25.
तेषु अनेकाः उपरि गच्छन्ति स्म।
(क) अनेकान्
(ख) अनेके
(ग) अनेकः
(घ) अनेकेन
उत्तराणि:
(ख) अनेके
प्रश्न 26.
वयम् एकस्य छायायुक्त-वृक्षस्य अधः भोजनं अकुर्वन्।
(क) अकरवम्
(ख) अकरवाव
(ग) अकरवाम
(घ) अकरोः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) अकरवाम
प्रश्न 27.
माम् कुतुबमीनारः अतीव अरोचत।
(क) मम
(ख) मत्
(ग) मया
(घ) मह्यम्।
उत्तराणि:
(घ) मह्यम्।
प्रश्न 28.
अहं पत्रवाहकः अस्ति।
(क) असि
(ख) अस्मि
(ग) स्थ
(घ) स्तः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) अस्मि
प्रश्न 29.
जनेभ्यः प्रतिदिनम् आगताः पत्राणि वितरामि।
(क) आगतानि
(ख) आगतान्
(ग) आगतेभ्यः
(घ) आगतैः
उत्तराणि:
(क) आगतानि
प्रश्न 30.
ते पत्रेषु साक्षात्कारपत्रः, परीक्षाफलं, नियुक्तिपत्रम् अपि आप्नुवन्ति।
(क) साक्षात्कारपत्रम्
(ख) साक्षात्कारपत्राणि
(ग) साक्षात्कारपत्रैः
(घ) साक्षात्कारपत्रे
उत्तराणि:
(क) साक्षात्कारपत्रम्
प्रश्न 31.
अहं स्वकर्मं सदा निष्ठया करोमि।
(क) स्वकर्मः
(ख) स्वकर्मान्
(ग) स्वकर्मणा
(घ) स्वकर्म
उत्तराणि:
(घ) स्वकर्म
प्रश्न 32.
येन जनाः शिक्षितः भवेयुः।
(क) शिक्षितम्
(ख) शिक्षितान्
(ग) शिक्षिताः
(घ) शिक्षितेन
उत्तराणि:
(ग) शिक्षिताः
प्रश्न 33.
एकस्मिन् ग्रामे द्वे मित्रौ आस्ताम्-रामः च श्यामः च।
(क) मित्रम्
(ख) मित्राणि
(ग) मित्रेण
(घ) मित्रे
उत्तराणि:
(घ) मित्रे
प्रश्न 34.
तयोः रामः बहूनां दीनानां सहायतां कुर्वन्ति स्म।
(क) करोति
(ख) कुरुतः
(ग) करोषि
(घ) करोमि
उत्तराणि:
(क) करोति
प्रश्न 35.
श्यामः च तस्य सह सहयोगं करोति स्म।
(क) तयोः
(ख) तेन
(ग) तस्मै
(घ) तम्
उत्तराणि:
(ख) तेन
प्रश्न 36.
तयोः अपूर्वं मैत्रीं दृष्ट्वा जनाः कथयन्ति स्म-अहो धन्यौ एतौ सुहृदौ।
(क) अपूर्वा
(ख) अपूर्वां
(ग) अपूर्वी
(घ) अपूर्वः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) अपूर्वां
प्रश्न 37.
वयं नित्यम् अग्रजानां चरणौ स्पृशन्ति,
(क) स्पृशति
(ख) स्पृशामि
(ग) स्पृशामः
(घ) स्पृशावः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) स्पृशामः
प्रश्न 38.
तेषाम् आशीर्वादाः अस्मान् रक्षति।
(क) आशीर्वादम्
(ख) आशीर्वादान्
(ग) आशीर्वादौ
(घ) आशीर्वादः
उत्तराणि:
(घ) आशीर्वादः
प्रश्न 39.
ये शिष्यौ गुरुजनानां चरणौ स्पृशन्ति,
(क) शिष्यः
(ख) शिष्याः
(ग) शिष्यान्
(घ) शिष्यौ
उत्तराणि:
(ख) शिष्याः
प्रश्न 40.
तेषाम् आयुः वर्धन्ते।
(क) वर्धते
(ख) वर्धेते
(ग) वर्धे
(घ) वर्धसे
उत्तराणि:
(क) वर्धते
प्रश्न 41.
अहं प्रतिदिनं मातापितरौ प्रणमति।
(क) प्रणमतः
(ख) प्रणमन्ति
(ग) प्रणमामि
(घ) प्रणमामः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) प्रणमामि
प्रश्न 42.
तौ च माम् आशीर्वादं यच्छतः।
(क) मह्यम्
(ख) मत्
(ग) मम
(घ) मयि
उत्तराणि:
(क) मह्यम्
प्रश्न 43.
भवान् सुखी भवन्तु।
(क) भव
(ख) भवत
(ग) भवतु
(घ) भवन्तु
उत्तराणि:
(ग) भवतु
प्रश्न 44.
सर्वेषां दीनजनस्य सेवां करोतु इति।
(क) दीनजनानाम्
(ख) दीनजनान्
(ग) दीनजनयोः
(घ) दीनजनेभ्यः
उत्तराणि:
(क) दीनजनानाम्
प्रश्न 45.
रात्रौ सर्वे निद्रामग्नाः आसीत्।
(क) आस्ताम्
(ख) आस्त
(ग) आसी:
(घ) आसन्
उत्तराणि:
(घ) आसन्
प्रश्न 46.
एकं शब्दः श्रुतः ढमढम् इति। कश्चित् चौरः भवेत् इति।
(क) एकः
(ख) एकाम्
(ग) एका
(घ) एकया
उत्तराणि:
(क) एकः
प्रश्न 47.
वयं भीतः परन्तु वस्तुतः पाकशालायाम्।
(क) भीतम्
(ख) भीताम्
(ग) भीता
(घ) भीताः
उत्तराणि:
(घ) भीताः
प्रश्न 48.
एकः बिडाली पात्रम् अपातयत्।
(क) एका
(ख) एकाम्
(ग) एकम्
(घ) एक
उत्तराणि:
(क) एका
प्रश्न 49.
वयं प्रतिदिनं भ्रमणाय गच्छन्ति।
(क) गच्छावः
(ख) गच्छामः
(ग) गच्छथ
(घ) गच्छथः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) गच्छामः
प्रश्न 50.
उद्याने अनेकाः जनाः व्यायाम कुर्वन्ति।
(क) अनेकं
(ख) अनेकः
(ग) अनेके
(घ) अनेकान्
उत्तराणि:
(ग) अनेके
प्रश्न 51.
वयं च द्रष्टारः भविष्यामि।
(क) भविष्याव:
(ख) भविष्यामः
(ग) भविष्यन्ति
(घ) भविष्यति
उत्तराणि:
(ख) भविष्यामः
प्रश्न 52.
वृक्षे चतस्त्रः फलानि सन्ति।
(क) चत्वारि
(ख) चत्वारः
(ग) चतुरः
(घ) चतुर्णाम्
उत्तराणि:
(क) चत्वारि
प्रश्न 53.
द्वे बालकौ पठतः।
(क) द्वा
(ख) द्वि
(ग) द्वौ
(घ) द्वयोः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) द्वौ
प्रश्न 54.
वयं श्वः प्रदर्शनी गच्छामः।
(क) गमिष्यावः
(ख) गमिष्यथ:
(ग) गमिष्यामः
(घ) गमिष्यन्ति
उत्तराणि:
(ग) गमिष्यामः
प्रश्न 55.
यूयं तस्मै फलानि यच्छिष्यथ।
(क) दास्यथ
(ख) दास्यथः
(ग) दास्यसि
(घ) दास्यन्ति
उत्तराणि:
(क) दास्यथ
प्रश्न 56.
सा कन्या आयुष्मान् भवतु।
(क) आयुष्मत्
(ख) आयुष्मन्
(ग) आयुष्मती
(घ) आयुष्मतः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) आयुष्मती
2. विकल्पेभ्यः शुद्धम् उत्तरं चित्त्वा रिक्तस्थानानि सम्पूरयत।
(विकल्पों से शुद्ध उत्तर चुनकर खाली स्थान भरें। Fill in the blank by correct words who given below.)
प्रश्न 1.
तस्य _____________ अपि तत्र तेन सह गतवान्। सः अवदत्-
(क) मित्राणि
(ख) मित्रम्
(ग) मित्रे
(घ) मित्रेण
उत्तराणि:
(ख) मित्रम्
प्रश्न 2.
अहो विडम्बना! नगरेषु एकतः धनप्रदर्शनम् अपरतः नग्नाः दरिद्राः क्षुधया पीडिताः च _____________।
(क) स्थः
(ख) अस्मि
(ग) सन्ति
(घ) स्मः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) सन्ति
प्रश्न 3.
अहम् एकः पत्रवाहकः _____________।
(क) अस्मि
(ख) असि
(ग) सन्ति
(घ) स्मः
उत्तराणि:
(क) अस्मि
प्रश्न 4.
जनेभ्यः प्रतिदिनम् _____________ पत्राणि वितरामि।
(क) आगतान्
(ख) आगता
(ग) आगतानि
(घ) आगताः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) आगतानि
प्रश्न 5.
जन्त्वागारे बहवः _____________ आसन्।
(क) सिंहः
(ख) सिंहम्
(ग) सिंहाः
(घ) सिंहान्
उत्तराणि:
(ग) सिंहाः
प्रश्न 6.
तत्र _____________ अपि वृक्षात् वृक्षं कूर्दन्ते स्म।
(क) वानरं
(ख) वानरान्
(ग) वानरैः
(घ) वानराः
उत्तराणि:
(घ) वानराः
प्रश्न 7.
एकः दुष्ट: बालकः _____________ वानरान् अताडयत्।
(क) पाषाण-खण्डैः
(ख) पाषाण-खण्डेभ्यः
(ग) पाषाण-खण्डाः
(घ) पाषाण-खण्डः
उत्तराणि:
(क) पाषाण-खण्डैः
प्रश्न 8.
तदैव तत्र रक्षकः आगत्य अवदत्-भोः एतेषु अपि प्राणाः सन्ति अतः त्वम् एतान् मा _____________ इति।
(क) ताडय
(ख) ताडयत
(ग) ताडयतु
(घ) ताडयानि
उत्तराणि:
(क) ताडय
प्रश्न 9.
अहम् _____________ पञ्चाशत् वर्षीया महिला अस्मि।
(क) एकम्
(ख) एकाम्
(ग) एकः
(घ) एका
उत्तराणि:
(घ) एका
प्रश्न 10.
अहं किञ्चित् संस्कृतम् _____________।
(क) अवगच्छामि
(ख) अवगच्छति
(ग) अवगच्छसि
(घ) अवगच्छन्ति
उत्तराणि:
(क) अवगच्छामि
प्रश्न 11.
इदानीं यदा _____________ अपि संस्कृतभाषां वदन्ति।
(क) बालः
(ख) बालम्
(ग) बालाः
(घ) बालैः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) बालाः
प्रश्न 12.
तदा अहम् अति _____________ भवामि।
(क) प्रसन्नः
(ख) प्रसन्ना
(ग) प्रसन्न
(घ) प्रसन्नाः
उत्तराणि:
(क) प्रसन्नः
प्रश्न 13.
राधिका-अयि _____________ ‘अद्य मम विद्यालये वार्षिकोत्सवः अस्ति।
(क) लताः!
(ख) लते!
(ग) लताम्!
(घ) लता!
उत्तराणि:
(ख) लते!
प्रश्न 14.
अतः अहम् _____________ सह विद्यालयं गमिष्यामि।
(क) स्वपितुः
(ख) स्वपित्रा
(ग) स्वपितः
(घ) स्वपिता
उत्तराणि:
(ख) स्वपित्रा
प्रश्न 15.
लता-राधिके! किम् तत्र तव _____________ अपि भविष्यन्ति?
(क) मित्रम्
(ख) मित्राः
(ग) मित्राणि
(घ) मित्रैः
उत्तराणि:
(ग) मित्राणि
प्रश्न 16.
राधिका-आम्। तत्र अहं पुरस्कारम् अपि _____________।
(क) लप्स्य ते
(ख) लप्स्यन्ते
(ग) लप्स्य ते
(घ) लप्स्ये
उत्तराणि:
(घ) लप्स्ये
प्रश्न 17.
‘अवकरः जले न क्षेप्तव्यः’ इत्यादि घोषणां ते _____________।
(क) कृतवान्
(ख) कृतवत्
(ग) कृतवती
(घ) कृतवन्तः
उत्तराणि:
(घ) कृतवन्तः
प्रश्न 18.
_____________ मम विद्यालयः अस्ति।
(क) एषा
(ख) एतत्
(ग) एषः
(घ) एते
उत्तराणि:
(ग) एषः
प्रश्न 19.
_____________ विद्यालये पञ्चाशत् अध्यापका: अध्यापिका: च पाठयन्ति।
(क) अयम्
(ख) अस्मिन्
(ग) अस्य
(घ) अस्मात्
उत्तराणि:
(ख) अस्मिन्
प्रश्न 20.
किम् _____________ पार्श्वे संगणकयन्त्रम् अस्ति?
(क) त्वत्
(ख) त्वम्
(ग) तव
(घ) त्वाम्
उत्तराणि:
(ग) तव
प्रश्न 21.
अद्यत्वे वयं सर्वाणि कार्याणि संगणकयन्त्रेण एव _____________।
(क) क्रियन्ते
(ख) कुर्मः
(ग) कुर्वन्ति
(घ) कुरुथ
उत्तराणि:
(ख) कुर्मः
प्रश्न 22.
_____________ बालक: भोजनं खादति।
(क) तत्
(ख) सः
(ग) सा
(घ) तेन
उत्तराणि:
(ख) सः
प्रश्न 23.
त्वया सह के _____________?
(क) गच्छन्ति
(ख) गच्छामः
(ग) गच्छति
(घ) गच्छतः
उत्तराणि:
(क) गच्छन्ति
प्रश्न 24.
_____________ एका योग्या बालिका अस्ति।
(क) तत्
(ख) तेन
(ग) सः
(घ) सा
उत्तराणि:
(घ) सा
प्रश्न 25.
मया सह मम _____________ अपि गच्छन्ति।
(क) मित्राणि
(ख) मित्रम्
(ग) मित्रेण
(घ) मित्रे
उत्तराणि:
(क) मित्राणि
प्रश्न 26.
किं त्वम् अपि _____________?
(क) पठिष्यसि
(ख) पठिष्यति
(ग) पठिष्यथ
(घ) पठिष्यथः
उत्तराणि:
(क) पठिष्यसि
प्रश्न 27.
सः अपि फलानि _____________।
(क) खादिष्यसि
(ख) खादिष्यति।
(ग) खादिष्यामि
(घ) खादिष्यामः
उत्तराणि:
(ख) खादिष्यति।