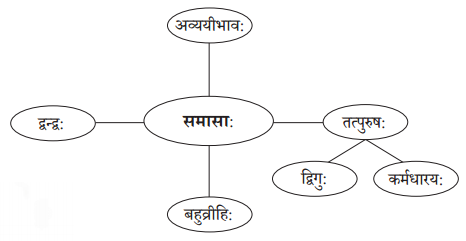
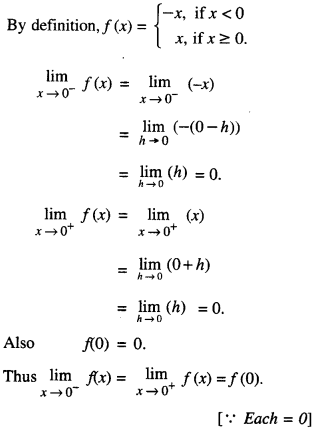
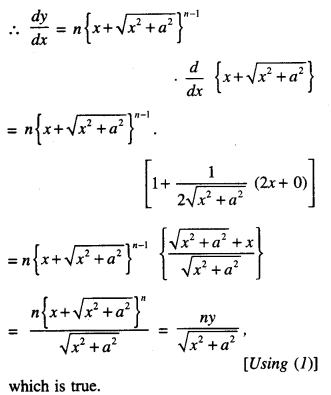
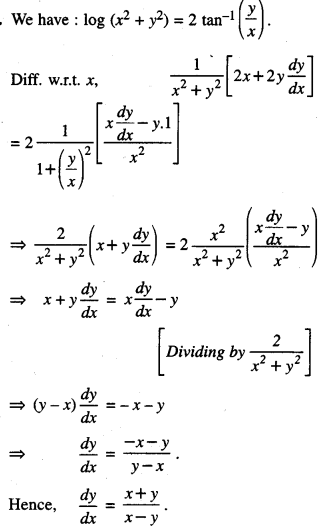
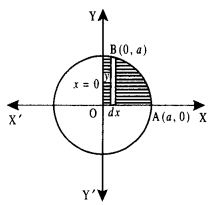
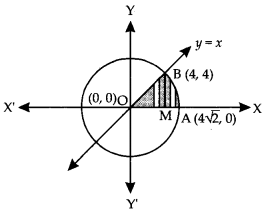
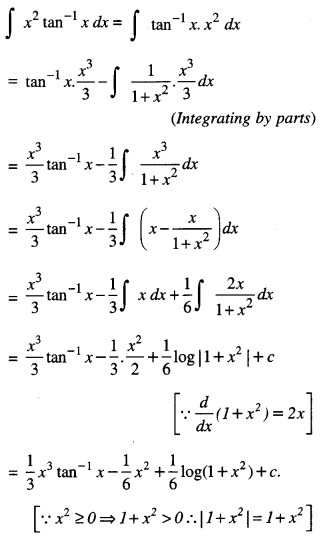
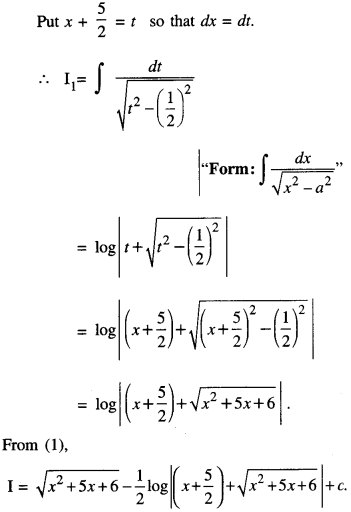
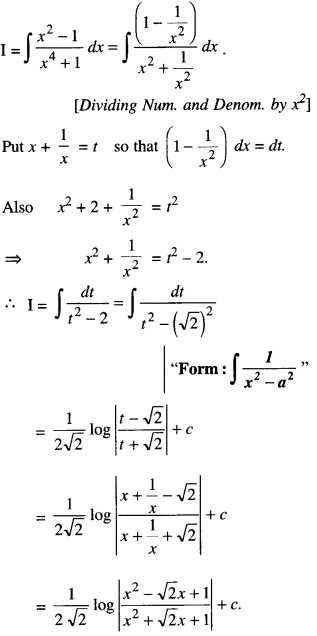
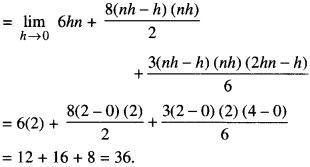
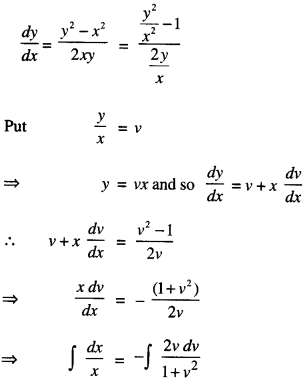
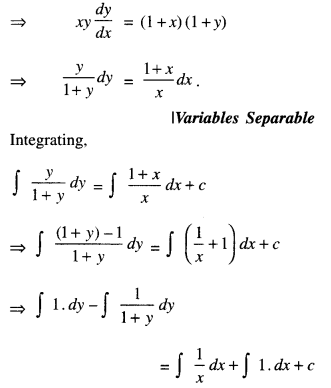
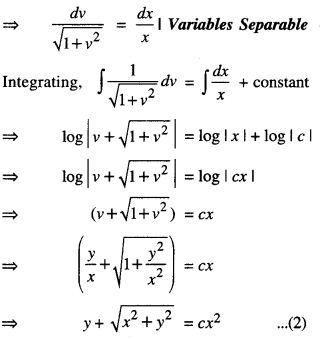
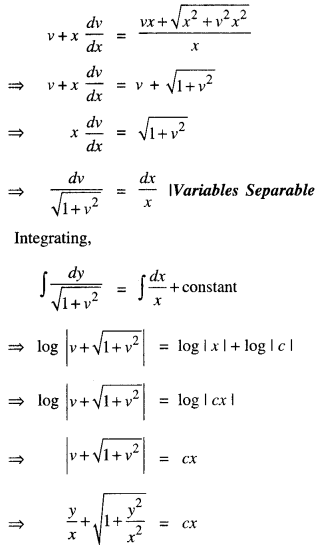
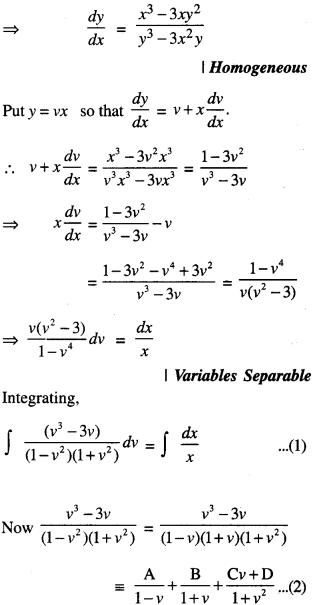
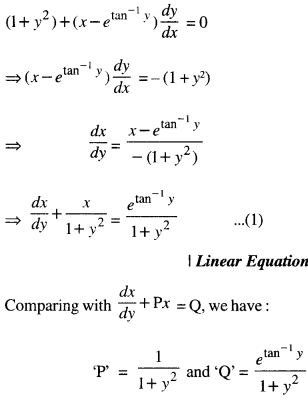
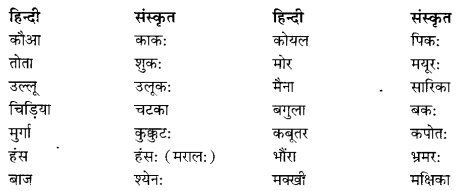
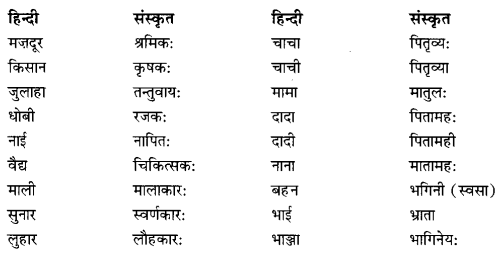
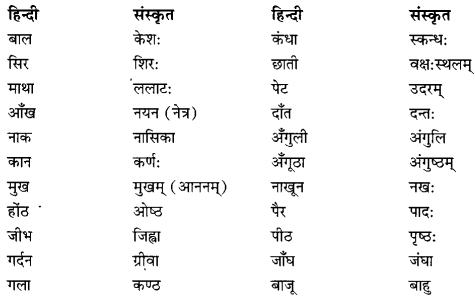
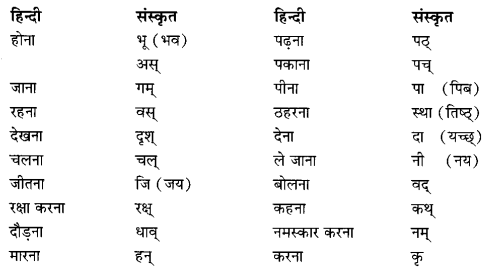
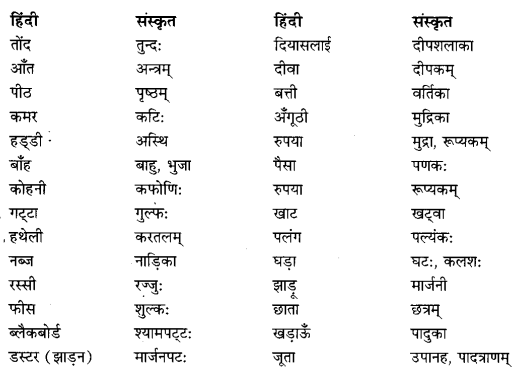
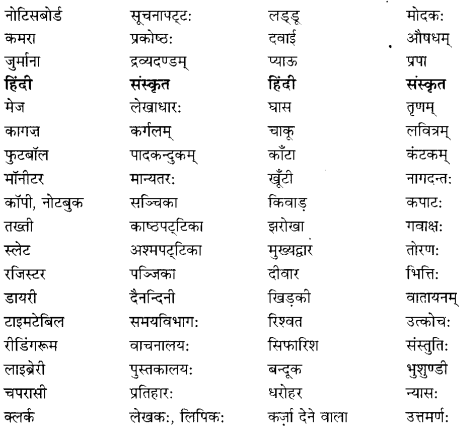
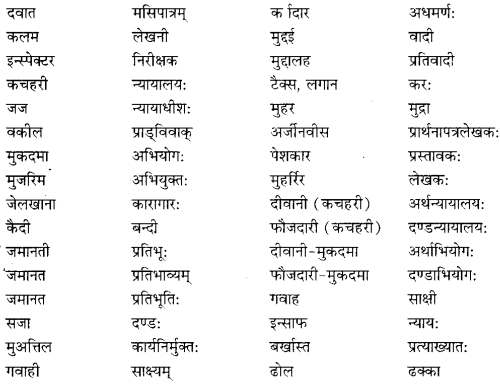
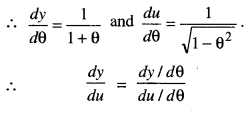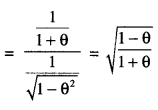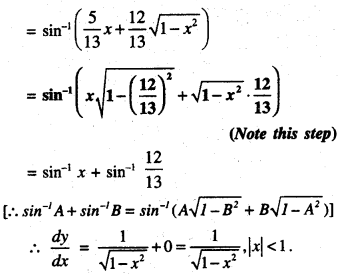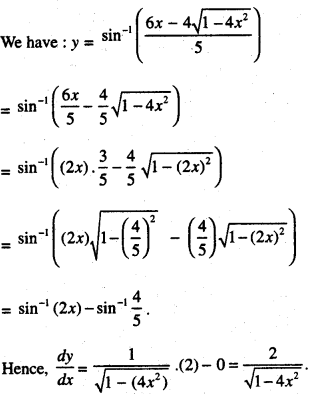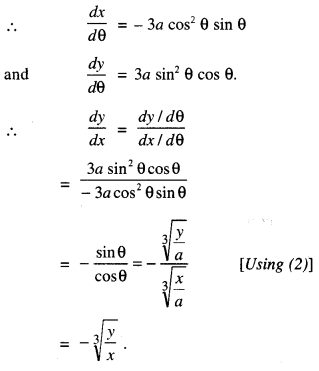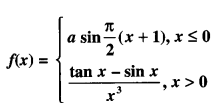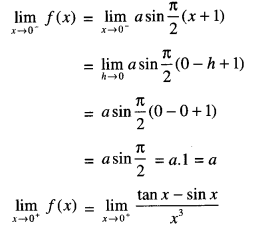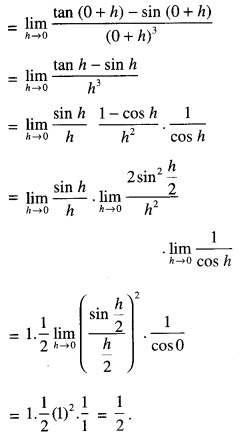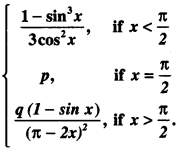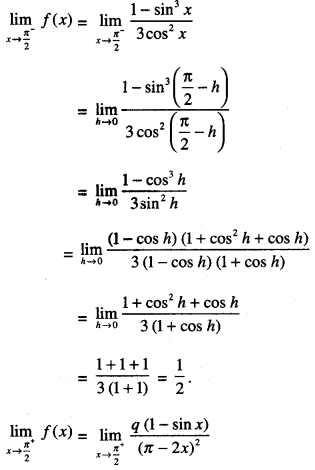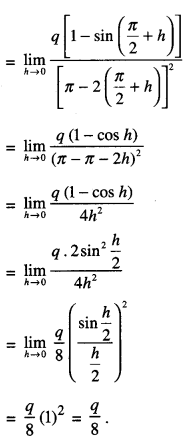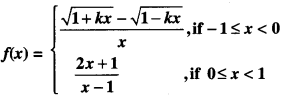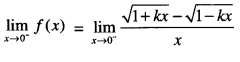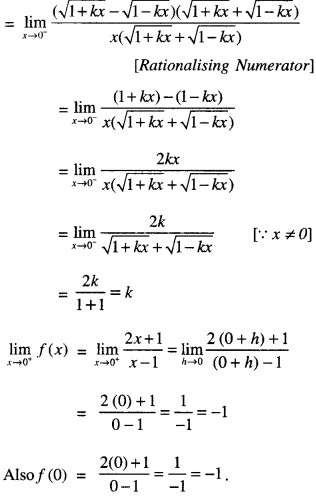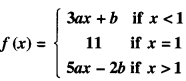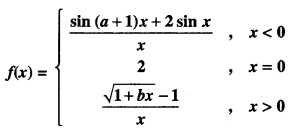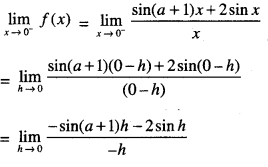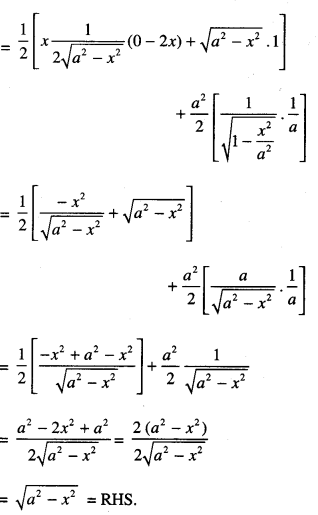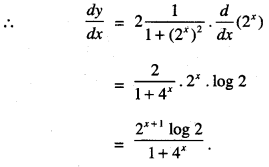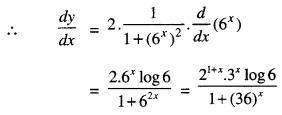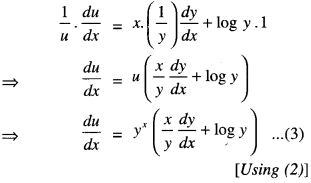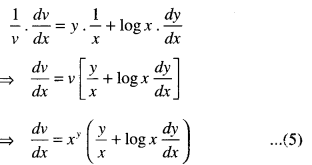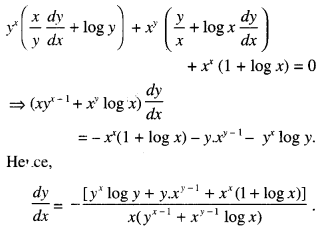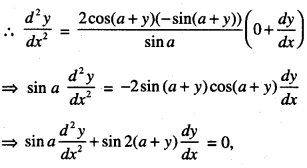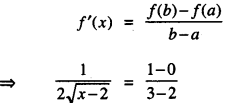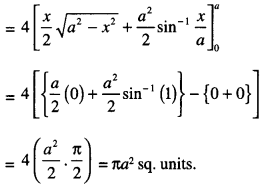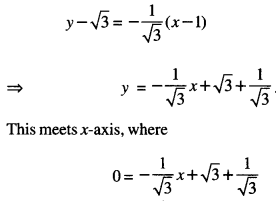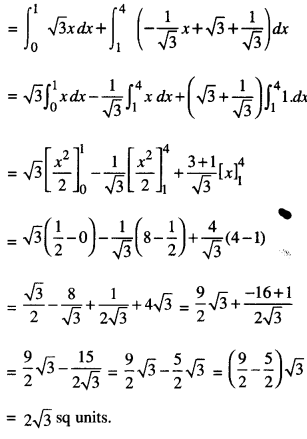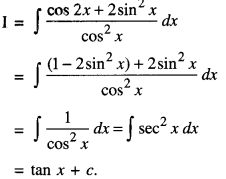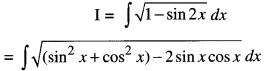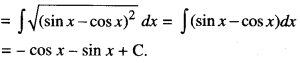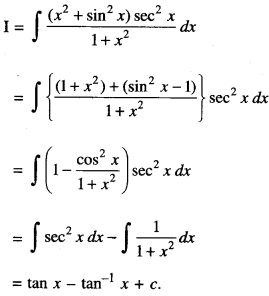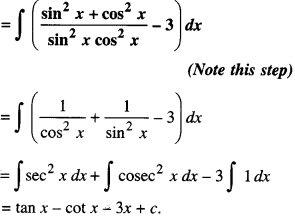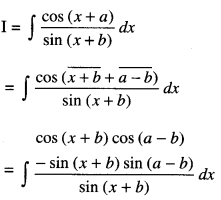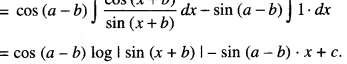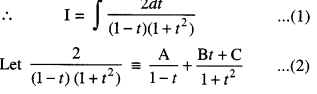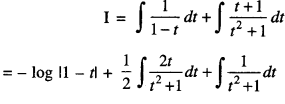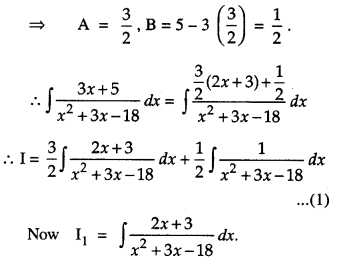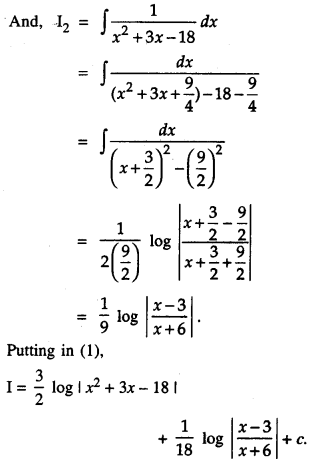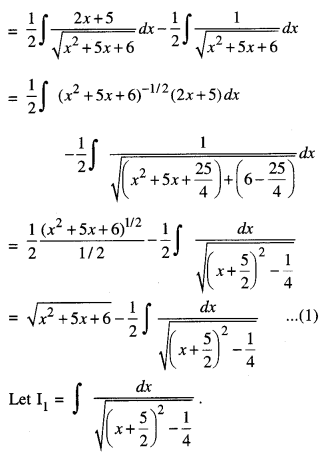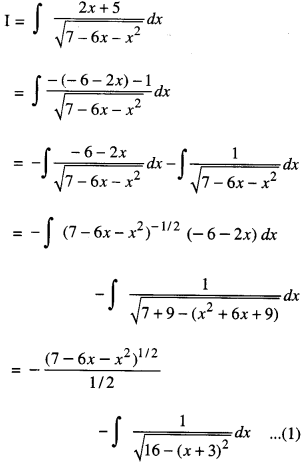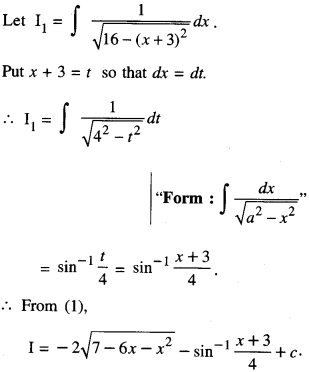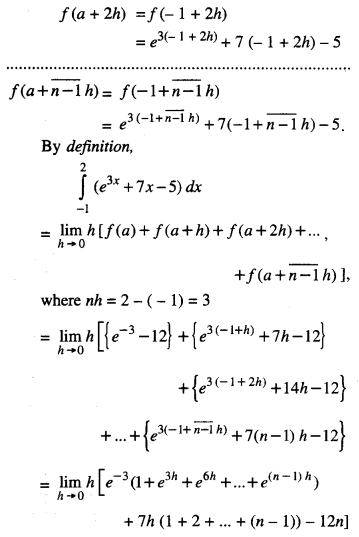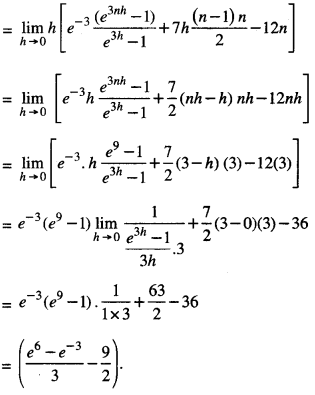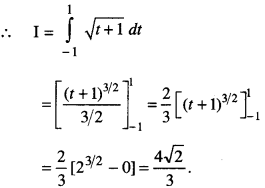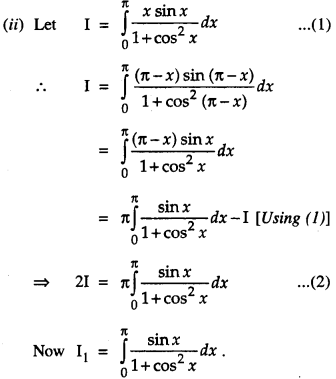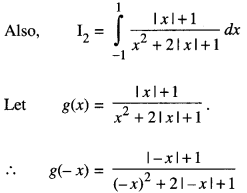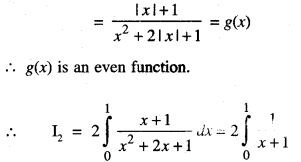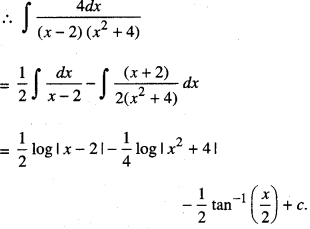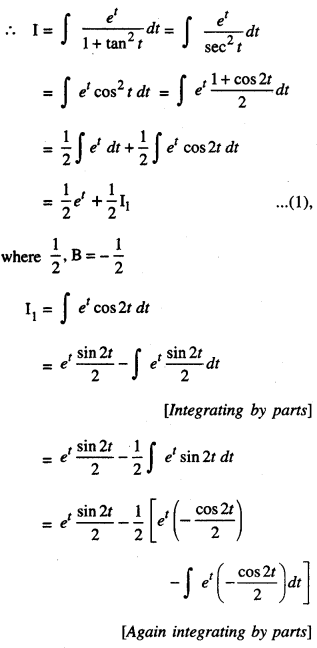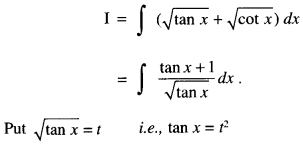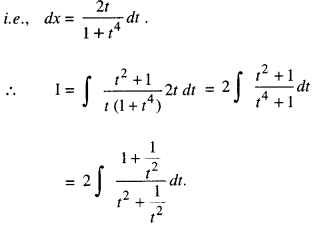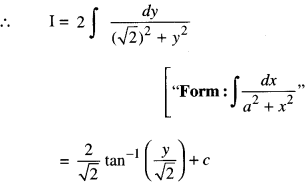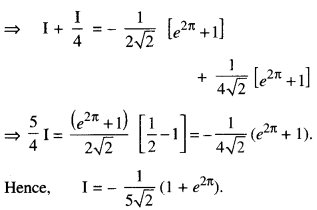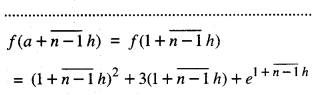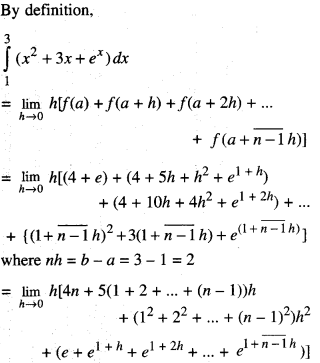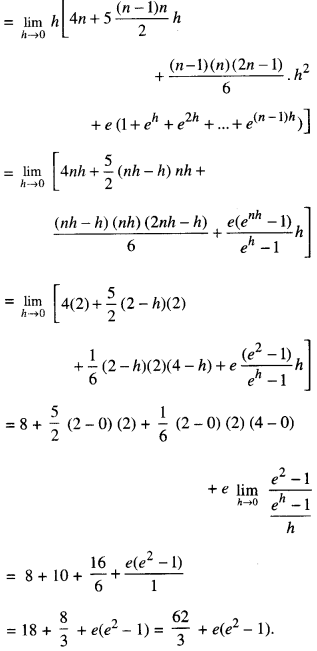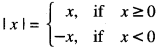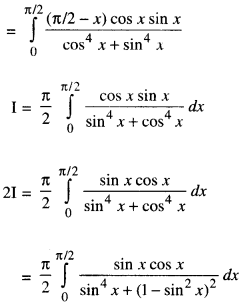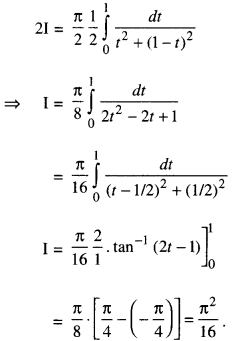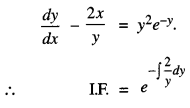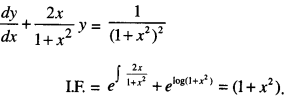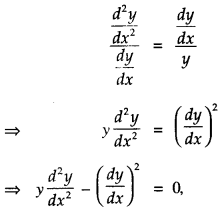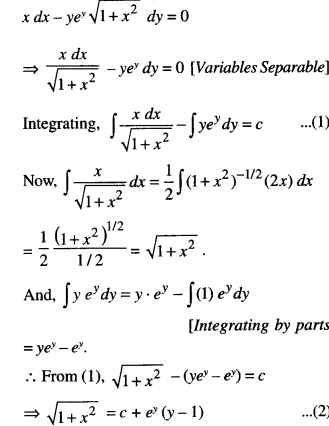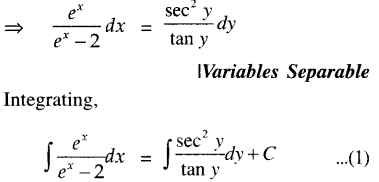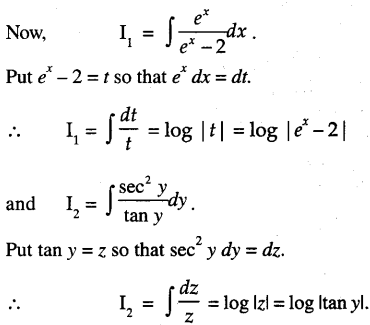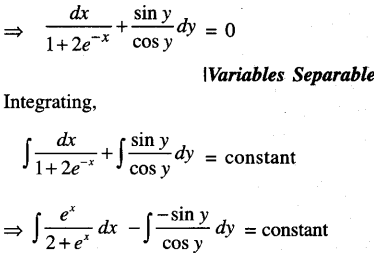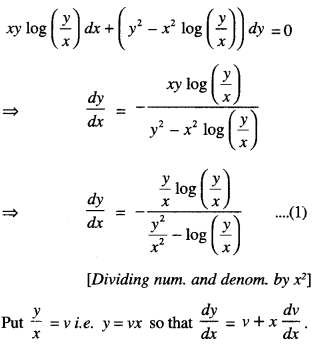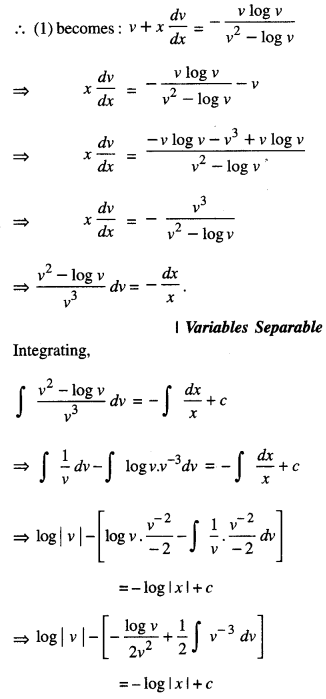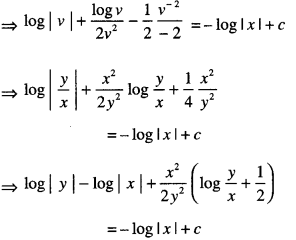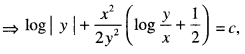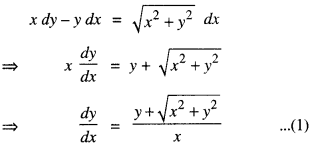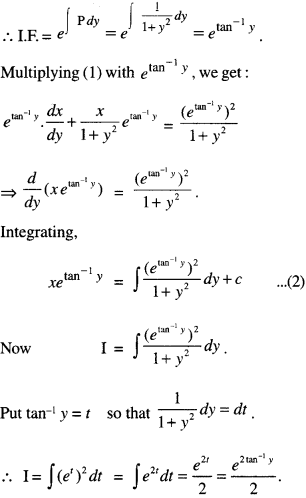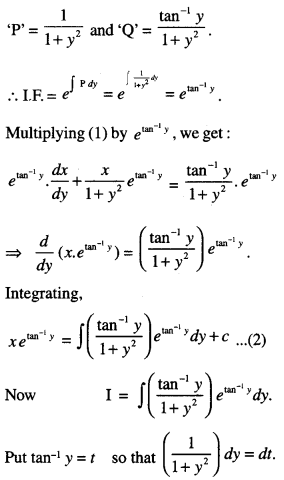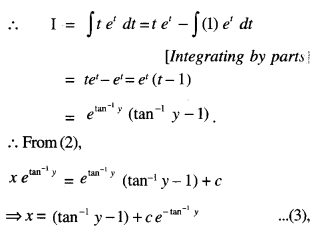We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Sanskrit Abhyasvan Bhav Sanskrit Class 10 Solutions Chapter 7 समासा: Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
Abhyasvan Bhav Sanskrit Class 10 Solutions Chapter 7 समासा:
श्रुतिः – अहं दिनम् दिनम् विद्यायाः आलयम् समयम् अनतिक्रम्य गच्छामि।
अनुकृतिः – अहम् अपि प्रतिदिनं विद्यालयं यथासमयं गच्छामि।
श्रुतिः – किं त्वं जानासि यद् वसुदेवस्य सुतः कः आसीत्?
अनुकृतिः – जानामि। वसुदेवसुतः श्रीकृष्णः आसीत्।
श्रुतिः – मां पीतः वर्णः रोचते। सः अपि पीतम् अम्बरं धारयति स्म।
अनुकृतिः – सत्यं वदसि। सः पीताम्बरं धारयति स्म अतः सः ‘पीताम्बरः’ इति नाम्ना अपि प्रसिद्धः। मया पठितं यत् कृष्णः च बलरामः च यमुनायाः तटे क्रीडतः स्म।
श्रुतिः – मयापि पठितं यत् कृष्णबलरामौ यमुनातटे क्रीडतः स्म।
उपरिलिखितेषु संवादवाक्येषु श्रुतिः यानि वाक्यानि वदति तेषु रेखाङ्कित-पदानि पृथक् पृथक् सन्ति परन्तु अनुकृतिः यानि वाक्यानि वदति तेषु वाक्येषु तानि एव रेखाङ्कित-पदानि समस्तरूपेण (संक्षिप्तरूपेण) योजयित्वा प्रदर्शितानि सन्ति। यथा शब्दानां पृथक्-पृथक् लेखनं ‘विग्रहः’ कथ्यते तथैव समस्तरूपेण (संक्षिप्तरूपेण) वा लेखनं ‘समासः’ इति कथयते।
समासानां विभाजनं मुख्यतः चतुर्धा भवति-
1. अव्ययीभावः
2. तत्पुरुषः
3. द्वन्द्वः
4. बहुव्रीहिः
(कर्मधारयः द्विगुः चेति तत्पुरुष-समासस्य एव द्वौ भेदी स्तः।)
1. अव्ययीभावः
(क) प्रायः जनाः प्रत्यक्षम् एव सत्यं स्वीकुर्वन्ति।
(ख) तस्मिन् विद्यालये प्रतिमासं परीक्षाः भवन्ति।
(ग) छात्राः यथामति अध्ययनं कुर्वन्ति।
(घ) हरिद्वारे उपङ्गम् अनेके देवालयाः सन्ति।
उल्लिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदेषु चतस्रः विशेषताः सन्ति-
(i) सर्वेषु पदेषु प्रथम/पूर्व-पदम् अव्ययम् उपसर्गो वा अस्ति।
(ii) सर्वाणि पदानि नपुसंकलिङ्गे सन्ति।
(iii) सर्वेषां पदानां प्रयोगः अव्ययवत् भवति।
(iv) एतेषु समस्तपदेषु पूर्वपदम् प्रधानम् अस्ति यतो हि वाक्येषु क्रियापदानि प्रथम/पूर्व पदस्य अनुसारम् अर्थ बोधयन्ति।
इत्थं वयं जानीमः यत् अव्ययीभाव समासः पूर्वपदप्रधानः भवति। अयं समासः सर्वदा नपुसंकलिने तिष्ठति।
एवम् अव्ययीभावसमासं स्पष्टरूपेण विज्ञाय अस्त इतिराणि उदाहरणानि द्रष्टव्यानि-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः |
| 1. | यथामति | मतिम् अनतिक्रम्य |
| 2. | अनुगुणम् | गुणानाम् अनुरूपम् |
| 3. | निर्बाधम् | बाधानाम् अभाव: |
| 4. | अनुरथम् | रथस्य पश्चात् |
| 5. | निर्विघ्नम् | विघ्नानाम् अभाव: |
| 6. | प्रतिमासम् | मासं मासम् इति |
| 7. | उपगुरु | गुरोः समीपम् |
| 8. | अधिहरि | हरौ इति |
| 9. | सपरिवारम् | परिवारेण सह |
| 10. | प्रतिदिनम् | दिन दिने इति |
अभ्यासः
प्रदत्त-तालिकायां समस्तपदं विग्रहं वा लिखत-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः |
| 1. | निर्मलम् | ____________ |
| 2. | ____________ | एकम् एकम् इति |
| 3. | ____________ | दोषाणाम् अभाव: |
| 4. | सव्यवधानम् | ____________ |
| 5. | निरर्थकम् | ____________ |
| 6. | ____________ | चिन्तायाः अभाव: |
| 7. | स्नेहेन सहितम् | ____________ |
| 8. | ____________ | समयम् अनतिक्रम्य |
| 9. | ____________ | गङ्गायाः समीपम् |
| 10. | सहर्षम् | ____________ |
उत्तरम्:
- मलस्य/मलानाम् अभावः
- प्रत्येकम्
- निर्दोषम्
- व्यवधानेन सह
- अर्थस्य अभावः
- निश्चितम्
- सस्नेहम्
- यथासमयम्
- उपगङ्गगम्
- हर्षेण सह
2. तत्पुरुषः
(क) वानराः वृक्षोपरि क्रीडन्ति। (वृक्षस्य उपरि)
(ख) वनराजः उच्चैः गर्जति। (वनस्य राजा)
(ग) संन्यासी पदनिर्लिप्तः भवति। (पदाय निर्लिप्तः)
(घ) रामः शरणागतं विभीषणम् अरक्षत्। (शरणम् आगतम्)
(ङ) चिकित्सकः अग्निदग्धस्य उपचारम् अकरोत्। (अग्निना दग्धस्य)
उल्लिखितेषु उदाहरणेषु वयं पश्यामः यत्-
(i) प्रथम/पूर्वपदेषु द्वितीया, तृतीया, चतुर्थी, षष्ठी चेति भिन्न-भिन्न विभक्तीनां प्रयोगः वर्तते।
(ii) क्रियायाः प्रयोगः द्वितीय/उत्तरपदाय भवति।
अतः यस्मिन् समासे प्रथम/पूर्वपदेषु द्वितीया विभक्तितः सप्तमी विभक्ति-पर्यन्तं विभिन्नविभक्तीनां प्रयोगः भवति सः समासः तत्पुरुषसमासः भवति।
तत्पुरुषसमासस्य इतराणि उदाहरणानि-
| क्रमः | समासः | विग्रहः | उपभेदः |
| 1. | ग्रामगतः | ग्रामं गतः | द्वितीया-तत्पुरुषः |
| 2. | पर्वतारूढः | पर्वतम् आरूढः | द्वितीया-तत्पुरुषः |
| 3. | कालिदासलिखितम् | कालिदासेन लिखितम् | तृतीया-तत्पुरुषः |
| 4. | चक्रहतः | चक्रेण हतः | तृतीया-तत्पुरुषः |
| 5. | यज्ञसामग्री | यज्ञाय सामग्री | चतुर्थी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 6. | निद्राकुलः | निद्रया आकुलः | चतुर्थी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 7. | सिंहभीत: | सिंहात् भीतः | पञ्चमी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 8. | आकाशपतितम् | आकाशात् पतितम् | पञ्चमी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 9. | गृहपतिः | गृहस्य पतिः | षष्ठी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 10. | गौरीशः | गौर्याः ईशः | षष्ठी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 11. | सङ्गीतपटुः | सङ्गीते पटुः | सप्तमी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 12. | चिन्तामग्नः | चिन्तायां मग्नः | सप्तमी-तत्पुरुषः |
| 13. | असत्यम् | न सत्यम् | नञ्-तत्पुरुषः |
| 14. | अनुपकार: | न उपकार: | नञ्-तत्पुरुषः |
आकाशात् पतितं तोयं यथा गच्छति सारगम्। सर्वदेव नमस्कार: केशवं प्रति गच्छति।
अभ्यासः
अधोलिखितेषु समासं विग्रहं वा कृत्वा लिख्यताम्-
| क्रमः | समासः | विग्रहः |
| 1. | ___________ | न्यायस्य अधीश: |
| 2. | देहविनाश: | ___________ |
| 3. | न मन्त्रः | |
| 4. | अयोग्यः | ___________ |
| 5. | वृक्षोपरि | ___________ |
| 6. | ___________ | निद्रायाः भङ्गस्य दुःखम् |
| 7. | वनराज: | ___________राजा |
| 8. | ___________ | नराणां पतिः |
| 9. | पक्षिकुलम् | ___________ |
| 10. | ___________ | प्रीते: लक्षणम् |
| 11. | निशान्धकारे | ___________ |
| 12. | ___________ | न पक्वम् |
| 13. | मृत्तिकाक्रीडनकम् | ___________ |
| 14. | ___________ | वृद्धेः लाभाः |
| 15. | अधर्मः | ___________ |
उत्तरम्:
- न्यायाधीशः
- देहस्य विनाशः
- अमन्त्रः
- न योग्यः
- वृक्षस्य उपरि
- निद्राभङ्गदुःखम्,
- वनस्य
- नरपतिः
- पक्षिणाम् कुलम् / पक्षीणाम् कुलम्
- प्रीतिलक्षणम्
- निशाया: अन्धकारः, तस्मिन्
- अपक्वम्
- मृत्तिकायाः क्रीडनकम्
- वृद्धिलाभः
- न धर्मः
कर्मधारयः
(विशेषण – विशेष्यौ)
(i) कृष्णसर्पः बिलम् प्राविशत्। (कृष्णः च एषः सर्प: / कृष्णः सर्पः)
(ii) महादेवी करुणां करोतु। (महति च इयं देवी / महती देवी)
(ii) महावृक्षः फलानि ददाति। (महान् च अयं वृक्ष: / महान् वक्षः) (उपमानोपमेयौ (उपमान + उपमेयौ)
(iv) सिंहपुरुष:/पुरुषसिंहः श्री रामः रावणं हतवान्। (सिंह इव पुरुष: / पुरुषः सिंह: इव)
(v) देव्याः कमलनेत्रे दृष्ट्वा भक्तः प्रसन्नः अभवत्। (कमलम् इव नेत्रे)
(vi) तस्याः चन्द्रमुखं दृष्ट्वा सः मोहितः अभवत्। (चन्द्रः इव मुखम्)
उल्लिखितेषु वाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदेषु विशेषणविशेष्ययोः अथवा उपमानोपमेययोः प्रयोगः अस्ति। एतेषु विशेष्यपदम् अथवा उपमेयपदम् एव प्रधानं भवति। उपमानपदस्य पश्चात् ‘इव’ इति अव्ययस्य प्रयोगेण उपमानोपमेय-कर्मधारयसमासस्य विग्रहः भवति। किन्तु विशेषण-विशेष्ययोः प्रथमा-विभक्त्या: प्रयोगेण समासविग्रहः भवति।
अभ्यासः
समस्तपदं विग्रह वा लिखत-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः |
| 1. | _________ | महान् वृक्षः |
| 2. | पुरुषव्याघ्रः | _________ |
| 3. | _________ | महत् कम्पनम् |
| 4. | महाविनाशः | _________ |
| 5. | _________ | रक्तम् उत्पलम् |
| 6. | पीतपुष्पाणि | _________ |
| 7. | _________ | घन इव श्यामः |
| 8. | महोत्सवः | _________ |
| 9. | _________ | विशालः पर्वतः |
| 10. | महागौरी | _________ |
उत्तरम्:
- महावृक्षः
- पुरुषः व्याघ्रः द्व
- महाकम्पनम्
- महान् विनाशः
- रक्तोत्पलम्
- पीतानि पुष्पाणि
- घनश्यामः
- महान् उत्सवः
- विशालपर्वतः
- महती गौरी
द्विगु-समासः
(i) जगत्पालकः त्रिलोकं रक्षति।
(ii) नवरात्रे सः सप्तशतीं पठति।
(ii) दानस्य महत्त्वं चतुर्युगं यावद् भवति।
(iv) दण्डकारण्ये ‘पञ्चवटी‘ इति स्थाने श्रीरामः सीतया लक्ष्मणेन च सह अवसत्।
(v) इयं शताब्दी विज्ञानस्य अस्ति।
उल्लिखितेषु वाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदेषु चतस्रः विशेषताः सन्ति-
(क) एतानि पदानि सङ्ख्याशब्दैः प्रारभन्ते।
(ख) बहुवचनसङ्ख्या प्रयोगे अपि सर्वेषु पदेषु एकवचनस्य प्रयोगः विद्यते।
(ग) समस्तपदानि नपुंसकलिङ्गे अथवा स्त्रीलिङ्गे भवन्ति।
(घ) समस्तपदानि/समूहस्य/समाहारस्य बोधं कारयन्ति।
एतादृशाः समासाः/एतादृशानि समस्तपदानि द्विगुसमासाः कथ्यन्ते।
इत्थं वयं जानीमः यत् द्विगुसमासेषु प्रथमशब्दः सङ्ख्यावाचको भवति। एते समासाः नपुंसकलिङ्गे स्त्रीलिलिङ्गे वा भवन्ति।
समाहार / समूहकारणात् एतेषां समासानां विग्रहः एवं भवति-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः |
| 1. | नवरात्रम् | नवाना रात्रीणां समाहारः |
| 2. | पञ्चवटी | पञ्चानां वटानां समाहारः |
| 3. | चतुर्युगम् / चतुर्युगी | चतुर्णा युगानां समाहार: |
| 4. | त्रिलोकम् / त्रिलोकी | त्रयाणां लोकानां समाहारः |
| 5. | शताब्दम् / शताब्दी | शतस्य अब्दानां समाहार: |
अधोलिखित-तालिकायाम् समस्तपदं विग्रह वा लिख्यन्ताम्-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदानि | विग्रहः |
| 1. | __________ | सप्तानाम् अह्रां समाहारः |
| 2. | पञ्चानां पात्राणां समाहारः | __________ |
| 3. | __________ | त्रयाणां भुवनानां समाहारः |
| 4. | पञ्चरात्रम् | __________ |
| 5. | अष्टाध्यायी | __________ |
उत्तरम्:
- सप्ताहम्
- पञ्चपात्रम्
- त्रिभुवनम्
- पञ्चानां रात्रीणाम् समाहारः
- अष्टाणाम् अध्यायाम् समाहार:
3. द्वन्द्व-समासः
(i) इतरेतरद्वन्द्वः
(क) दशरथस्य चत्वारः पुत्राः रामलक्ष्मणभरतशत्रुघ्नाः आसन्। (रामः च लक्ष्मणः च भरतः च शत्रुघ्नः च)
(ख) रामलक्ष्मी मिथिलाम् अगच्छताम्। (रामः च लक्ष्मणः च)
(ग) मयूरीकुक्कुटौ संवदत:/कुक्कुटमयूयौं संवदतः। (मयूरी च कुक्कुटः च/कुक्कुटः च मयूरी च)
उल्लिखितवाक्येषु चतस्रः विशेषताः सन्ति-
(i) समासेषु शब्दानां सङ्ख्यायाः अनुसार द्विवचन बहुवचन वा प्रयुक्तम्।
(ii) वाक्येषु सर्वेषां पदानां सङ्ख्यायाः अनुसार क्रियापदस्य वचनं निर्धारितम् भवति अतः सर्वाणि पदानि प्रधानानि सन्ति।
(iii) समासस्य अन्तिमपदानुसारं समासस्य लिङ्ग निर्धार्यते।
(ii) समाहार द्वन्द्वः
(i) योगिनं शीतोष्णं न बाधते। (शीतं च उष्णं च, तयोः समाहारः)
(ii) सः पुत्रपौत्रं दृष्ट्वा प्रसीदति। (पुत्रः च पौत्रः च, तयोः समाहारः)
(iii) सः दिवारानं प्रसन्नः तिष्ठति (दिवा च रात्रिः च, तयोः समाहारः)
उल्लिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदेषु यद्यपि द्वे एव पदे प्रधाने परन्तु तयोः समाहार / समूहकरणात् एकवचनस्य प्रयोगः अभवत् एवम् एतेषु उदाहरणेषु अधोलिखित-विशेषताः सन्ति-
(i) समस्तपदानि नपुंसकलिङ्गे एकवचने सन्ति।
(ii) द्वयोः पदयोः एकः समहारः भवति।
(iii) एकशेषद्वन्द्वः
पितरौ- माता च पिता च अत्र एकस्य पितृशब्दस्य द्विवचने प्रयोगेण एकशेषद्वन्द्वः समासः कथ्यते। इतरेतरद्वन्द्व समासे ‘मातापितरौ’ इत्यस्य अपि प्रयोगः भवति।
अभ्यासः
अधोलिखिततालिकायां समस्तपदेभ्यः विग्रह विग्रहेभ्यः च समस्तपदानि लिख्यन्ताम्-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः |
| 1. | अग्निसोमो | ___________ |
| 2. | पाणिपादम् | ___________ |
| 3. | ___________ | साता च रामः च |
| 4. | इन्द्रः च वरुणः च | ___________ |
| 5. | ___________ | रमा च शारदा च |
| 6. | ___________ | धर्मः च अर्थः च कामः च मोक्षः च |
| 7. | लतापुष्पम् | ___________ |
| 8. | ___________ | मूषकः च मार्जारः च |
| 9. | अहोरात्रम् | ___________ |
| 10. | ___________ | सुखं च दुःखम् च |
उत्तरम्:
1. अग्निः च सोमः च
2. पाणी च पादौ च तेषां समाहारः
3. सीतारामौ
4. इन्द्रवरुणौ
5. रसाशारदे,
6. धर्मार्थकाममोक्षाः
7. लताः च पुष्पाणि च तेषां समाहारः
8. मूषकमार्जारौ
9. आहश्च रात्रिः च तयोः समाहारः
10. सुखदुःखम्
4. बहुव्रीहिः
(क) चतुर्मुखः ब्रह्मा सृष्टिरचनां करोति। (चत्वारि मुखानि यस्य सः)
(ख) चतुर्भुजः विष्णुः सृष्टेः पालनं करोति। (चतस्रः भुजाः यस्य सः)
(ग) त्रिनेत्रः शिवः जगत् सहरति। (त्रीणि नेत्राणि यस्य सः)
(घ) क्रूरकर्मा जनः आतङ्कवादी भवति। (क्रूरं कर्म यस्य सः)
(ङ) सिंहवाहना दुर्गा महिषासुरस्य वधम् अकरोत्। (सिंहः वाहनं यस्याः सा)
उल्लिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदेषु किमपि पदं प्रधानं नास्ति। अपि तैः पदैः सङ्केतितं किमपि अन्यद् एव पदं प्रधानम् अस्ति। एतेषु समासेषु अधोलिखिताः विशेषताः सन्ति।
(i) द्वे पदे मिलित्वा अन्यपदं सङ्केतयन्ति।
(ii) द्वे पदे यदा परस्परं विशेषणम् विशेष्यं च भवतः तदा ते प्रथमाविभक्तौ समानलिङ्गे च तिष्ठतः।
(iii) विग्रहाय अन्ते यस्य सः/यस्याः सा इत्यादीनां प्रयोगः भवति।
इत्थं वयं जानीमः यद् बहुव्रीहिसमासः अन्यपदप्रधानः भवति। यदा बहुव्रीहिसमासे द्वे पदे एकस्मिन् एव विभक्तौ भवतः तदा समानाधिकरण बहुव्रीहिः भवति। बहुव्रीहिसमासे यदा द्वे पदे पृथक्-पृथक् विभक्तौ भिन्न-लिङ्गे वा तदा व्यधिकरण-बहुव्रीहिः समासः भवति।
अभ्यासः
अधोलिखितसमस्तपदेभ्यः विग्रहाः, विग्रहेभ्यः च समस्तपदानि लिख्यन्ताम्-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदानि | विग्रहः |
| 1. | ___________ | लम्बम् उदरं यस्य सः |
| 2. | पीताम्बरः | ___________ |
| 3. | ___________ | कृतः उपकारः येन सः |
| 4. | प्रत्युपन्नमतिः | ___________ |
| 5. | ___________ | गज इव आननं यस्य सः |
| 6. | चन्द्रमुखी | ___________ |
| 7. | ___________ | चक्रं पाणौ यस्य सः |
| 8. | चन्द्रमौलि: | ___________ |
| 9. | ___________ | बहूनि कमलानि यस्मिन् तत् |
| 10. | ___________ | जितानि इन्द्रियाणि येन सः |
उत्तरम्:
1. लम्बोदरः
2. पीतम् अम्बरं यस्य सः
3. कृतोपकारः
4. प्रत्युत्पन्ना मतिः यस्य सः
5. गजाननः
6. चन्द्रम् इव मुखं यस्याः सा
7. चक्रपाणिः
8. चन्द्रः मौलौ यस्य सः
9. बहुकमलम्
10. जितेन्द्रियः
मिश्रिताभ्यास:
अधोलिखितसमस्तपदेभ्यः विग्रहान् विग्रहेभ्यः च समस्तपदानि निर्माय तेषां नामानि अपि लिख्यन्ताम्-
| क्रमः | समस्तपदम् | विग्रहः | समासनाम |
| 1. | मेघश्यामः | _____________ | _____________ |
| 2. | _____________ | न युक्तम् | _____________ |
| 3. | देहाविनाशाय | _____________ | _____________ |
| 4. | _____________ | नीलं च तत् कमलम् | _____________ |
| 5. | _____________ | हर्षेण मिश्रितम् | _____________ |
| 6. | _____________ | कर्कश: ध्वनिः | _____________ |
| 7. | _____________ | पञ्चानां वटानां समाहारः | _____________ |
| 8. | वनराज | _____________ | _____________ |
| 9. | _____________ | स्थिता प्रज्ञा यस्यः सः | _____________ |
| 10. | _____________ | माता च पिता च | _____________ |
उत्तरम्:
1. मेघः इव श्यामः, कर्मधारयः
2. अयुक्तम्, नञ् तत्पुरुषः
3. देहस्य विनाशाय, षष्ठी तत्पुरुषः
4. नीलकमलम्, कर्मधारयः
5. हर्षमिश्रितम्, तृतीया तत्पुरुषः
6. कर्कशध्वनिः, कर्मधारयः
7. पञ्चवटम् / पञ्चवटी, द्विगुः
8. वनस्य राजा, षष्ठी तत्पुरुषः
9. स्थितप्रज्ञः, बहुव्रीहिः
10. मातापितरौ, इतरेतर द्वन्द्वः