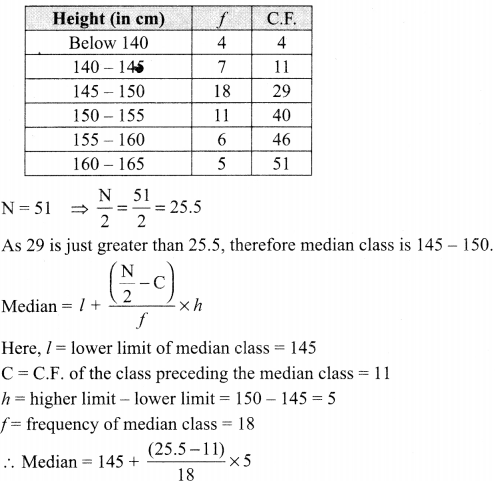
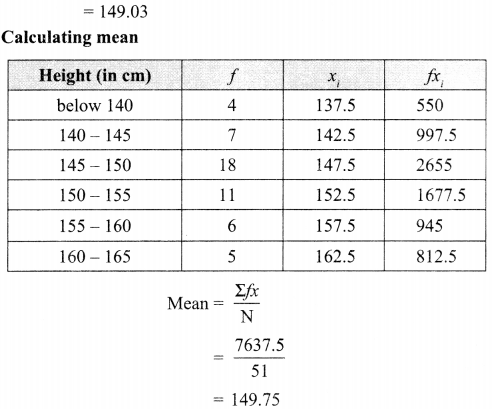
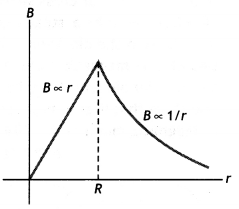
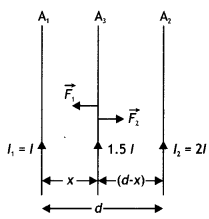
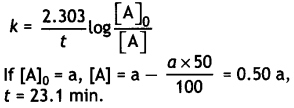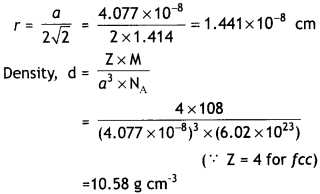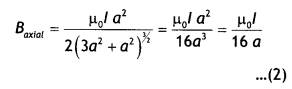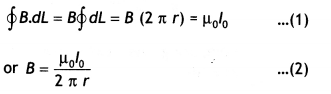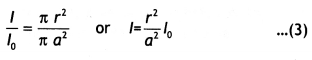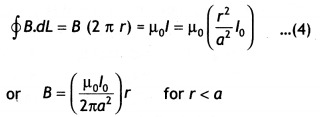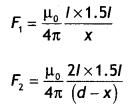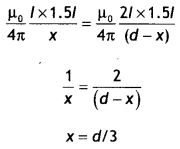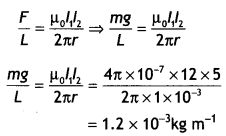Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Important Extra Questions Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Define rate of a reaction. (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
The rate of a reaction is the change of concentration in any one of the reactants or products per unit time.
Question 2.
Define order of a reaction. (CBSE Delhi 2010, CBSE 2011)
Answer:
The sum of the powers of the concentration terms of the reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of that chemical reaction. For example, if rate law expression is
rate = K[A]p[B]q[C]r
Order of reaction = p + q + r
Question 3.
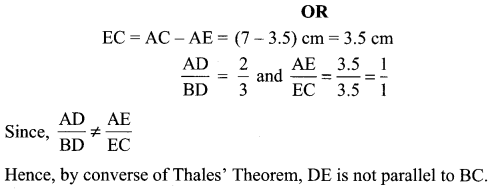
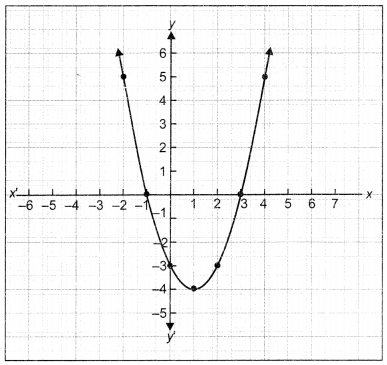
For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is given as
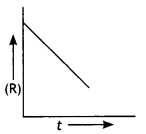
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(i) Zero order reaction
(ii) Slope = – k
Question 4.
Define ‘activation energy’ of a reaction. (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Activation energy is the minimum energy that the reactants must possess for the conversion into the products during their collisions.
It is equal to difference between the threshold energy needed for the reaction and the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
Question 5.
Identify the order of a reaction if the units of its rate constant are:
(i) L-1 mol s-1
(ii) L mol-1 s-1 (CBSE All India 2011)
Answer:
(i) Zero order
(ii) Second order
Question 6.
For a reaction: A + B → P, the rate law is given by, r = k [A]1/2 [B]2 .
What is the order of reaction? (CBSE All India 2013)
Answer:
Order = \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2 = 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) or 2.5.
Question 7.
In the Arrhenius equation, what does the factor e-E0/RT correspond to?
(CBSE Sample Paper 2017-18)
Answer:
e-E0/RT corresponds to the fraction of molecules having kinetic energy greater than Ea.
Chemical Kinetics Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
For a reaction,
C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g),
rate = 5.5 × 10-14 [C2H4].
(a) Write the unit of rate constant.
(b) Calculate its half-life (t1/2). (CBSE 2019)
Answer:
(a) Hydrogenation of ethene is an example of first order reaction so the unit of rate constant is s-1 or time-1.
(b) t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{k}=\frac{0.693}{5.5 \times 10^{-14}}\)
= 1.26 × 1013s
(or any other unit of time)
Question 2.
For a reaction
![]()
The proposed mechanism is as given below:
(1) H2O2 + I– → H2O + IO– (slow)
(2) H2O2 + IO– → H2O + I– + O2 (fast)
(i) Write rate law for the reaction.
(ii) Write the overall order of reaction.
(iii) Out of steps (1) and (2), which one is rate-determining step? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(i) Rate = k[H2O2][I–]
(ii) 2
(iii) Step 1 is rate determining.
Question 3.
A reaction is of first order in reactant A and of second order in reactant B. How is the rate of this reaction affected when
(i) the concentration of B alone is increased to three times?
(ii) the concentrations of A as well as B are doubled? (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
The rate law may be expressed as:
Rate = k[A] [B]2
(i) Rate becomes nine times
(ii) Rate becomes eight times.
Question 4.
What do you understand by the rate law and rate constant of a reaction? Identify the order of reaction if the units of its rate constant are:
(i) L-1 mol s-1
(ii) L mol-1 s-1 (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Rate law is the representation of rate of reaction in terms of concentration of the reactants.
Rate constant is the rate of reaction when the concentration of reactants is unity. Order of reaction from rate constants
(i) Zero order
(ii) Second order
Question 5.
A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half? What is the unit of rate constant for such a reaction? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
For a second order reaction,
rate = K[A]2
If the concentration of A is reduced to half, rate will become 1 /4 of the original value.
Units of k.
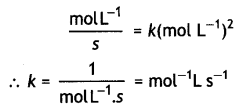
Question 6.
Distinguish between rate expression and rate constant of a reaction. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Rate expression is a mathematical expression which denotes the rate of a reaction in terms of molar concentration of reactants.
Rate constant is the rate of the reaction when the concentration of reactants is unity. It is proportionality constant in the rate law and is independent of initial concentrations of the reactants.
Question 7.
What do you understand by the ‘order of reaction’? Identify the reaction order from each of the following units of reaction rate constant:
(i) L-1 mol s-1
(ii) L mol-1 s-1 (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The sum of the powers of the concentrations of reactants in the rate law expression is called order of a reaction. For example, if rate law expression for a reaction is:
rate = K[A]a[B]a[C]c
then order = a + b + c
(i) Zero order
(ii) Second order
Question 8.
(i) For a reaction A + B → P, the rate law is given by,
r = k[A]1/2 [B]2
What is the order of this reaction?
(ii) A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k = 5.5 × 10-14 s-1. Find the half life of the reaction. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
(i) Order of reaction 1
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 2 = 2.5
(ii) t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{k}=\frac{0.693}{5.5 \times 10^{-14}}\)
= 1.26 × 1013s
Question 9.
Write two differences between ‘order of reaction’ and ‘molecularity of reaction. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
| Order | Molecularity |
| 1. Order is the sum of the powers of the concentration terms in the rate law expression. | 1. Molecularity is the number of reacting species undergoing simultaneous collisions in the elementary or simple reaction. |
| 2. Order of a reaction is determined experimentally and need not be a whole number, i.e. it can have fractional values also. | 2. Molecularity is a theoretical concept and has whole number values only, i.e. 1, 2, 3, etc. |
Question 10.
The rate constant for a reaction of zero order in A is 0.0030 mol L-1s-1. How long will it take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10 M to 0.075 M? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
For a zero order reaction,
k = 0.0030 mol L-1s-1
[A]0 = 0.10 M, [A] = 0.075M

Answer:
Question 11.
The rate of a reaction depends upon the temperature and is quantitatively expressed as k = \(A e^{-E_{a} / R T}\)
(i) If a graph Is plotted between log k and 1/T, write the expression for the slope of the reaction.
(ii) If at under different conditions, Ea1 and Ea2 are the activation energy of two reactions. If Ea1 = 40 J / mol and Ea2 = 80 J / mol which of the two has a larger value of the rate constant? (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
(ii) Arrhenius proposed a quantitative relationship between rate constant
and temperature as k = \(A e^{-E_{a} / R T}\) Taking logarithm,
In k = In A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{R} \times \frac{1}{T}\)
Converting to common logarithm (In X = 2.303 log X), we get
2.303 log k = 2.303 log A – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{\mathrm{RT}}\).
Dividing each side by 2.303, we get
log k = log A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R T}\)
So, it is clear that increasing the temperature or decreasing the activation energy will result in an increase in the rate of reaction.
(i) Slope = – \(\frac{\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{a}}}{2.303 \mathrm{R}}\)
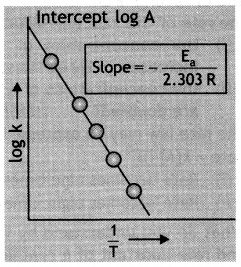
Plot of log k versus 1/T to calculate activation energy.
(ii) k1 > k2
Question 12.
The rate constant for a first order reaction is 60 s-1. How much time will it take to reduce the concentration of the reactant to 1/10th of its initial value?
Answer:
For a first order reaction,

Question 13.
Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
log k = log A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R}\left(\frac{1}{T}\right)\)
where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log k vs. \(\frac{1}{T}\), a straight line with a slope of – 4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction (R = 8.314 JK-1mol-1). (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Slope = –\(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R}\) = -4250K
Ea = – 2.303 × R × Slope
= – 2.303 × 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 × (-4250 K)
= 81375.3 J mol-1 or 81.375 kJ mol-1.
Question 14.
For the reaction
C12H22O11 + H2O → C6H12O6 + C6H12O6
write:
(i) Rate of reaction expression,
(ii) Rate law equation,
(iii) Molecularity,
(iv) Order of reaction (CBSE Sample paper 2011)
Answer:
(i)
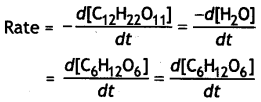
(ii) Rate law equation:
Rate = k[C12H22O11]
(iii) Molecularity = 2
(iv) Order = 1
Question 15.
Consider the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium which is catalysed by iodide ions.
![]()
This reaction takes place in two steps as given below:
Step -1 H2O2 + I– → H2O + IO– (slow)
Step – II H2O2 + IO– → H2O + I– (fast)
(i) Write the rate law expression and determine the order of reaction w.r.t. H2O2.
(ii) What is the molecularity of each individual step? (C8SE Sample paper 2011)
Answer:
(i) Rate = k[H2O2] [I–]
Order w.r.t. H2O2 = 1
(ii) Molecularity: Step I = 2, Step II = 2
Question 16.
For a reaction: A + B → P, the rate law is given as: Rate = k[A][B]2
(i) How is the rate of reaction affected when the concentration of B is doubled?
(ii) What is the order of reaction if A is present in large excess? (CBSE All India 2015)
Answer:
(i) Rate becomes four times
(ii) Order = 2
Question 17.
What is the effect of adding a catalyst on
(i) Activation energy (Ea) and
(ii) Gibbs free energy (∆G) of a reaction? (CBSE All India 2017)
Answer:
(i) Activation energy decreases
(ii) No effect on ∆G because Gibbs free energies of products and reactants remain the same in the presence of catalyst.
Question 18.
For a reaction:
![]()
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k. (CBSE Sample paper 2018)
Answer:
![]()
Rate = k
(i) Order of reaction: Zero order Molecularity = 2 (bi molecular)
(ii) Unit of k = mol L-1 s-1 or atm s-1
Question 19.
Explain the following terms: (CBSE 2014)
(i) Rate constant (k).
(ii) Half life period of a reaction (t1/2).
Answer:
(i) Rate constant is the rate of the reaction
when the molar concentration of each of the reactants is unity. For example, for a reaction,
A + B → AB
Rate of reaction is
Rate = k[A][B]
where k is the rate constant. When
[A] = 1 and [B] = 1
Rate of reaction = k × 1 × 1 = k
It is also catted specific reaction rate and is independent of the initial concentration of the reactants.
(ii) Half life period of a reaction is the time during which the concentration of a reactant Is reduced to half of its initial concentration. In other words, it is the time during which half of the reaction Is completed. It is denoted as t1/2.
Chemical Kinetics Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Show that time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for the completion of 90% reaction. (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
For the first order reaction,
t = \(\frac{2.303}{k} \log \frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]}\)
Let initial concentration, [A0] = a
For 99% completion of reaction, [A]

For 90% completion of reaction,
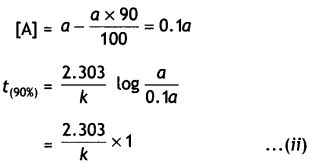
Dividing equation (i) by (ii)
\(\frac{t_{(99 \%)}}{t_{(90 \%)}}\) = 2
or t(99%) = 2 × t(90%)
Question 2.
The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order reaction. If rate constant (k) Is 4 × 10-3 M s-1, how long will it take to reduce the initial concentration of NH3 from 0.1 M to 0.064 M? (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
k = 4 × 10-3M s-1, [A]0 = 0.1 M, [A] = 0.064 M
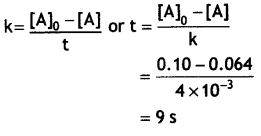
Question 3.
The thermal decomposition of HCO2H is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 × 10-3 s-1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three fourth of initial quantity of HCO2H to decompose. (log 4 = 0.6021) (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
We know that
t = \(\frac{2.303}{k} \log \frac{[A]_{0}}{[A]}\)
If initial conc. of A is a, then
[A] = a – \(\frac{3}{4}\)a = \(\frac{1}{4}\)a
k = 2.4 × 10-3 s-1
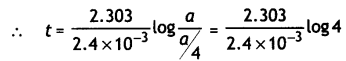
= \(\frac{2.303}{2.4 \times 10^{-3}}\) × 0.6021 = 578 s
Question 4.
For the reaction:
2N0(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g)
the following data were collected. All the measurements were taken at 263 K:
| Experiment No. | Intial [NO] (M) | Intial [Cl2] (M) | Intial rate of Cl2 (M/min) |
| 1 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.60 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 1.20 |
| 3 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 2.40 |
| 4 | 0.25 | 0.25 | ? |
(i) Write the expression for rate law.
(ii) Calculate the value of rate constant and specify its units.
(iii) What is the initial rate of disappearance of Cl2 In exp. 4? (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(i) Rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
(ii) According to experiment 1,
[NO] = 0.15 M; [Cl2] = 0.15 M
Rate = 0.6 M/min.
Rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
0.6 M/min = k(0.15M)2 (0.15 M)
k = 177.8 M-2 min-1
or
= 177.8 mol-2 L2 min-1
Therefore, units of k are M-2 min-1 or mol-2 L2 min-1.
(iii) In experiment 4, [NO] = 0.25 M; [Cl2] = 0.25 M and k = 177.8 M-2 min-1
Rate = k[NO]2 [Cl2]
= 177.8 M-2 min-1 × (0.25 M)2 × 0.25 M
= 2.78 M min-1.
Question 5.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of
SO2Cl2 at a constant volume:
SO2Cl2(g) → SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
| Experiment | Time/s-1 | Total Pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 1 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given: log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010) (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
SO2Cl2 → SO2 + Cl2
At t = 0 s 0.4 atm 0 0
At t = 100 s (0.4 – x) atm x atm x atm
Pt = 0.4 – x + x + x = 0.4 + x
0.7 = 0.4 + x or x = 0.3
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\) log \(\frac{p_{0}}{2 p_{0}-p_{t}}\)
t = 100 s
∴ k = \(\frac{2.303}{100}\) log \(\frac{0.4}{2 \times 0.4-0.7}\)
= \(\frac{2.303}{100}\) log \(\frac{0.4}{0.1}\)
∴ k = \(\frac{2.303}{100}\) × 0.6021 = 1.38 × 10-2 s-1
Question 6.
The rate constant for the first order decomposition of H2O2 is given by the following equation:
log k = 14.2 – \(\frac{1.0 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
Calculate Ea for this reaction and rate constant k if Its half-life period be 200 minutes. (Given: R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1) (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
According to Arrhenius equation,
log k = log A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 \mathrm{RT}}\) …….. (i)
The given equation is
log k = 14.2 – \(\frac{1.0 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{~K}}{\mathrm{~T}}\) ………. (ii)
Comparing eq. (1) and (ii)
\(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 \mathrm{RT}}\) = 1.0 × 104
∴ Ea = 1.0 × 104 × 2.303 × 8.314
= 19.147 × 104 J mol-1
Now t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{k}\)
or k = \(\frac{0.693}{t_{1 / 2}}\)
= \(\frac{0.693}{200 \mathrm{~min}}\) = 3.465 × 10-3 min -1
Question 7.
The rate of a reaction increases four times when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature (R = 8.3 14 JK-1 mol-1). (CBSE All India 2010)
Answer:
T1 = 300 K, T2 = 320 K, R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
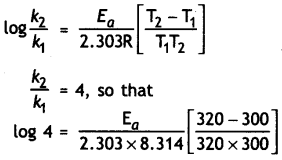
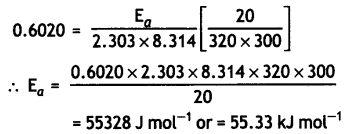
Question 8.
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law, with t1/2 = 3.00 hours. What fraction of sample of sucrose remains after 8 hours? (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
k = \(\frac{0.693}{t_{1 / 2}}\) = \(\frac{0.693}{3.0}\) = 0.231 hr-1
Let initial cone, of sucrose = 1 M
Cone, after 8 hr. = (1 – x) where x is the amount of sucrose decomposed
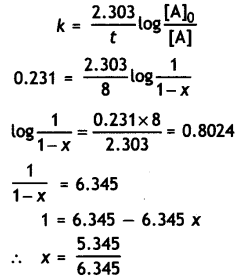
Conc. of sucrose left after 8 hr = 1 – 0.842
= 0.158 M
Question 9.
The rate of a reaction becomes four times when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea) of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
[R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, log 4 = 0.6021] (CBSE All India 2013)
Answer:
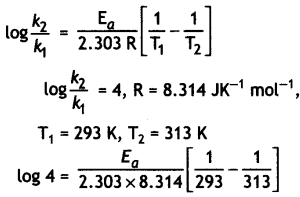

Question 10.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of SO2Cl2 at constant volume.
SO2Cl2(g) → SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
| Experiment | Times/s | Total Pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6 |
Calculate the rate of reaction when total pressure is 0.65 atm. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
For the decomposition of SO2Cl2
SO2Cl2(g) → SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
At t = 0 p0 atm 0 0
At time, t (p0 – x) atm x x
pt = p0 – x + x + x = p0 + x
or x = pt – p0
Now at time t, p(SOCl2) = p0 – x
= P0 – (Pt – P0) = 2 p0 – pt
∴ k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\) log \(\frac{p_{0}}{2 p_{0}-p_{t}}\)
when t = 100 s
k = \(\frac{2.303}{100}\) log \(\frac{0.5}{2 \times 0.5-0.6}\)
= \(\frac{2.303}{100}\) log 1.25 = 2.2316 × 10-3 s-1
When pt = 0.65 atm, i.e. p0 + p = 0.65 atm
p = 0.65 – p0 = 0.65 – 0.50 = 0.15 atm
∴ Pressure of SO2Cl2 at time t = 0.50 – 0.15
= 0.35 atm
Rate = 2.2316 ×10-3 × 0.35
= 7.8 × 10-5 atm s-1
Question 11.
A first order reaction takes 20 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate the time when 75% of the reaction will be completed. {CBSE All India 2017)
Answer:
For the first order reaction:

Question 12.
A first order reaction takes 23.1 minutes for 50% completion. Calculate the time required for 75% completion of this reaction. (log 2 = 0.301, log3 0.4771, log4 = 0.6021) (CBSE All India 2015)
Answer:
For the first order reaction:
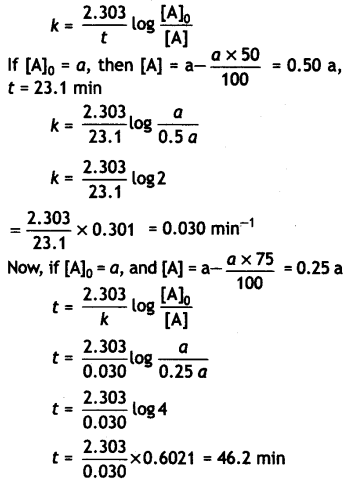
Question 13.
The decomposition of phosphine, PH3, proceeds according to the following equation:
4PH3(g) → P4(g) + 6H2(g)
It is found that the reaction follows the following rate equation:
Rate = k[PH3].
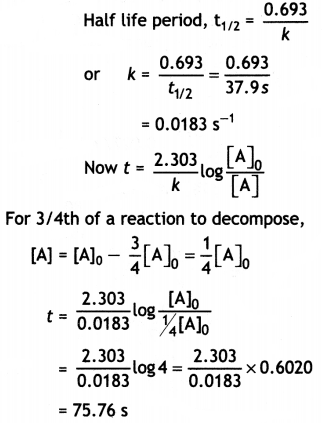
The half-life of PH3 is 37.9 sat 120 C.
(i) How much time is required for 3/4th of PH3 to decompose?
(ii) What fraction of the original sample of PH3 remains behind after 1 minute? (C8SE All India 2010)
Answer:
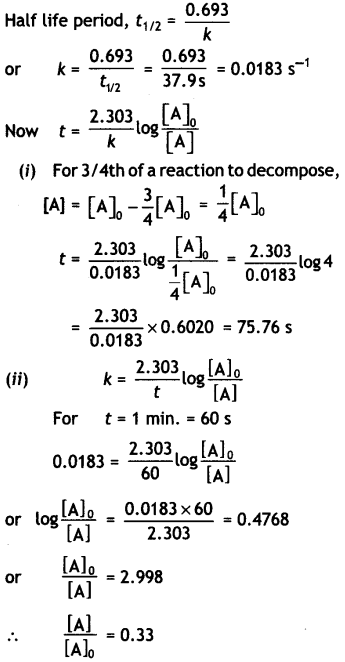
Question 14.
Sucrose decomposes in acid solution into glucose and fructose according to the first order rate law with t1/2 = 3 hrs. Calculate the fraction of sucrose which remains after 8 hrs. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
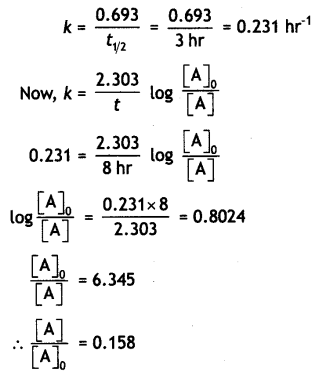
Question 15.
Starting from 10 g of a radioactive element, 0.25 g was left after 5 years. Calculate
(i) Rate constant for the decay of the radioactive element.
Answer:

(ii) The amount left after one year.
Answer:
Amount left after 1 year
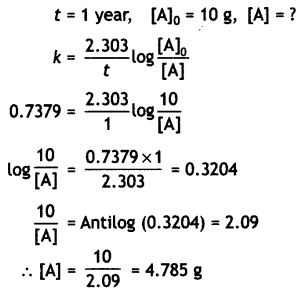
(iii) The time required for half of the element to decay.
Answer:
Time for decay of half of the element
t1/2 = \(\frac{0.693}{k}=\frac{0.693}{0.7379}\) = 0.9392 year
(iv) Average life of the element. (CBSE All India 2011)
Answer:
t = \(\frac{1}{k}=\frac{1}{0.7379}\) = 1.3552 year
Question 16.
In general, It is observed that the rate of a chemical reaction becomes double with every 1o°. rise in temperature. If this generalization holds for a reaction In the temperature range 298 to 308 K, what would be the value of activation energy for this reaction? (R = 8.3 14 JK-1 mol-1) (CBSE Delhi 2000)
Answer:
Arrhenius equation is:
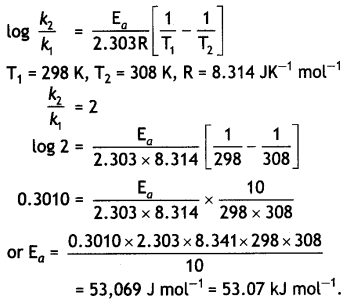
Question 17.
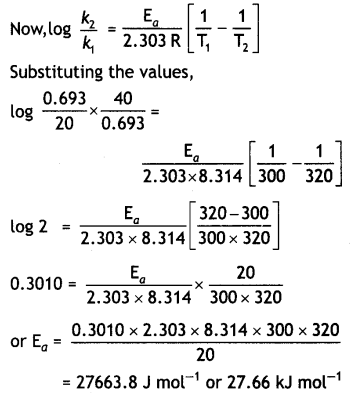
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 40 minutes at 300 K and in 20 minutes at 320 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction.
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021, R = 8.3 14 Jk-1 mol-1) (CBSE All India 2018)
Answer:
Let us first calculate k1 and k1 at temperatures 300 K and 320 K. We know that

Question 18.
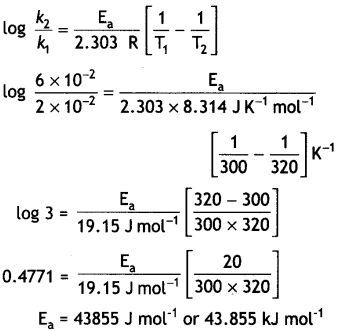
The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 2 × 10-2 to 6 × 10-2 when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the energy of activation. (Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021) (CBSE 2019 C)
Answer:
Question 19.
For the reaction A + B → products, the following initial rates were obtained at various given initial concentrations:
| [A] mol / L | [B] mol / L | Intial rate M/S |
| 1. 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| 2. 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.10 |
| 3. 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.05 |
Determine the half-life period.
OR
A first order reaction is 50% complete In 50 minutes at 300 K and the same reaction is again 50% complete In 25 minutes at 350 K. Calculate activation energy of the reaction. (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
Rate = k [A]x [B]y
0.05 = k [0.1]x [0.1]y …… (i)
0.10 = k [0.2]x [0.1]y ……. (ii)
0.05 = k [0.1]x [0.2]y …….. (iii)
Dividing equation (ii) by (i)
\(\frac{0.10}{0.05}\) = (2)x
x = 1
Dividing equation (iii) by (i)
\(\frac{0.05}{0.05}\) = (2)y
y = 0
Rate = k [A]1 [B]0

Question 20.
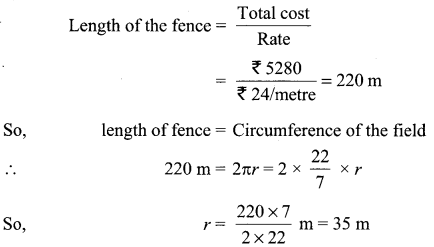
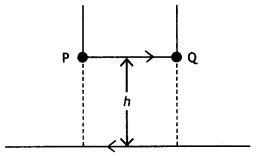
For a certain chemical reaction variation in concentration [A] vs. time (s) plot as shown in given figure:
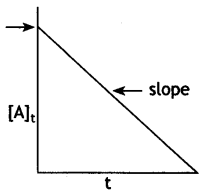
(i) Predict the order of the given reaction?
(ii) What does the slope of the line and intercept indicate?
(iii) What is the unit of rate constant k? (CBSE Sample paper 2018-19)
Answer:
(i) Zero order reaction
(ii) Slope represents k; Intercept represents [R]0
(iii) mol L-1 s-1
Question 21.
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of N2O5(g) at a constant volume:
2N2O5(g) → 2N2O4(g) + O2(g)
| S.NO | Time (sec.) | Total pressure (atm) |
| 1. | 0 | 0.5 |
| 2. | 100 | 0.512 |
Calculate the rate constant.
OR
Two reactions of the same order have equal pre-exponential factors but their activation energies differ by 24.9 kJ mol-1. Calculate the ratio between the rate constants of these reactions at 27°C. (Gas constant R 8.314 J K-1 mol-1) (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
2N2O5(g) → 2N2O4(g) + O2(g)
At t = 0 0.5 atm 0 atm 0 atm
At time t 0.5-2x atm 2x atm x atm
Pt = PN2O5 + PN2O5 + PO2
= (0.5 – 2x) + 2x + x = 0.5 + x
x = pt – 0.5
PN2O5 = 0.5 – 2x
= 0.5 – 2(pt – 0.5)
= 1.5 – 2pt
At t = 100s; pt = 0.512 atm
PN2O5 = 1.5 – 2 × 0.512 = 0.47 atm

OR
The Arrhenius equation: k = Ae-Ea/RT
Taking log on both sides:
log k = log A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R T}\)
For reaction (i) log k1 = log A – \(\frac{E_{o}(1)}{2.303 R T}\)
For reaction (ii) log k2 = logA – \(\frac{E_{o}(2)}{2.303 R T}\)
Subtracting (i) from (ii)
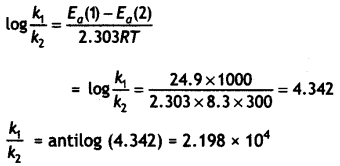
Question 22.
(a) Define order of reaction. How does order of a reaction differ from molecularity for a complex reaction?
Answer:
(a) Order of reaction is the sum of the power to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate law equation. Order of a reaction is applicable for the complex reaction but molecularity has no meaning for the complex reaction. 0.693
(b) A first order reaction is 50% complete in 25 minutes. Calculate the time for 80% completion of the reaction.
Answer:
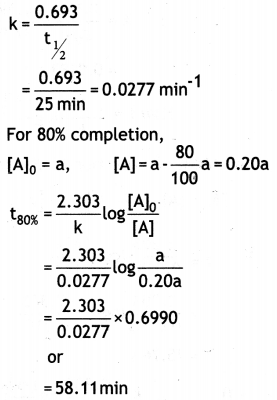
(a) The decomposition of a hydrocarbon has value of rate constant as 2.5 × 104 s-1 at 27 °C. At what temperature would rate constant be 7.5 × 104 s-1 if energy of activation is 19.147 × 103 J mol-1?
Answer:
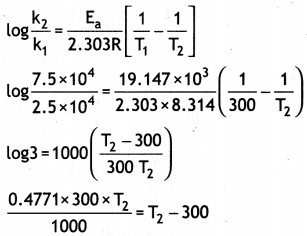
0.1431 T2 = T2 – 300
0.1431 T2 – T2 = 300
0.8569T2 = – 300
T2 = \(\frac{300}{0.8569}\) = 350 k
(b) Write a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order. Give an example of such a reaction.
(Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 5 = 0.6990) (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
A bimolecular reaction is kinetically of first order when one of the reactant is in excess. For example, hydrolysis of methyl acetate.
CH3COOCH3 + H2O (excess) → CH3COOH + CH3OH
Question 23.
Nitrogen pentoxide decomposes according to equation:
2N2O5 (g) →4NO2(g) + O2(g)
The first order reaction was allowed to proceed at 40° C and the data below were collected:
| [N2O5] (M) | Time (min) |
| 0.400 | 0.00 |
| 0.289 | 20.0 |
| 0.209 | 40.0 |
| 0.151 | 60.0 |
| 0.109 | 80.0 |
(i) Calculate the rate constant. Include units with your answer.
Answer:
Since it is a first order reaction,
k = \(\frac{2.303}{t}\) log \(\frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]}\)
k can be calculated as:
at t = 20 min
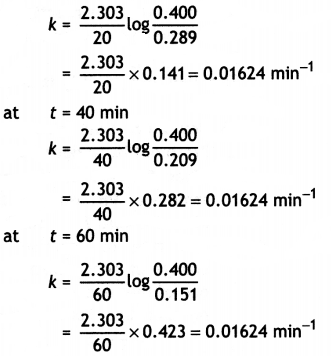

The average value of rate constant,
k = 0.01624 min-1 or = 1.624 × 10-2 min-1
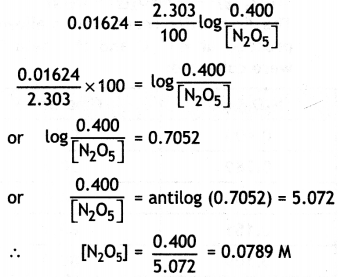
(ii) What will be the concentration of N2O5 after 100 minutes?
Answer:
Concentration of [N2O5] at t = 100 min
(iii) Calculate the initial rate of reaction. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Initial rate of reaction,
rate = k[N2O5]
= 0.01624 × 0.40
= 6.496 × 10-3
Question 24.
(i) Explain the following terms:
(a) Rate of a reaction
Answer:
The rate of reaction is the change of concentration in any one of the reactants or products per unit time. For a reaction, A → B rate may be expressed as
= \(\frac{-d[A]}{d t}\) or \(\frac{d[B]}{d t}\)
(b) Activation energy of a reaction
Answer:
Activation energy is the minimum energy which the reacting molecules should acquire so that they react to give the products. It is also defined as the energy required to form the products.
(ii) The decomposition of phosphine, PH3, proceeds according to the following equation:
4PH3(g) → P4 (g) + 6H2(g)
It Is found that the reaction follows the following rate equation:
Rate = k[PH3]
The half life of PH3 is 37.9 s at 120°C.
(a) How much time is required for 3/4th of PH3 to decompose?
Answer:
(b) What fraction of the original sample of PH3 remains behind after 1 minute? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:

Question 25.
Explain the following terms:
(a) Order of a reaction
Answer:
The sum of the powers of the concentration of reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of the reaction.
For example, if rate law expression for a reaction is:
Rate = k[A]a[B]b[C]c
then order of reaction is
order = a + b + c
(b) Molecularity of a reaction
Answer:
Molecularity is the number of molecules taking part in a reaction. For example, for the reaction:
aA + bB → Product
Molecularity is a + b
(ii) The rate of a reaction Increases four times when the temperature changes from 300 K to 320 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction, assuming that it does not change with temperature (R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1). (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
T1 = 300 k, T2 = 320 k,
R = 8.314 Jk-1 mol-1
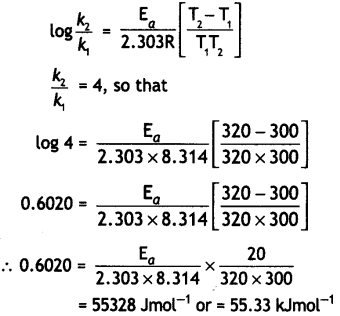
Question 26.
(i) A reaction is second order in A and first order in B.
(a) Write the differential rate equation.
(b) How is the rate affected on Increasing the concentration of A three times?
(C) How is the rate affected when the concentrations of both A and B are doubled?
Answer:
(a) Rate = k[A]2[B]
(b) 9 times
(C) 8 times
(ii) A first order reaction takes 40 minutes for 30% decomposition. Calculate t1/2 for this reaction. (Given log 1.428 = 0.1548)
Answer:
Let initial conc. = a
Conc. after 40 min

OR
(i) For a first order reaction, show that time required for 99% completion is twice the time required for the completion of 90% of reaction.
Answer:
For a first order reaction,
t = \(\frac{2.303}{k}\) log \(\frac{[\mathrm{A}]_{0}}{[\mathrm{~A}]}\)
Let intial concentration, [A]0 = a
For 99% completion of reaction,
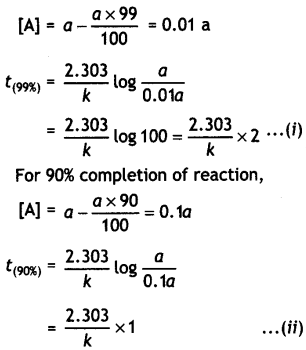
Dividing equation (i) by (ii)
\(\frac{t_{(99 \%)}}{t_{(90 \%)}}\) = 2 or t(99%) = 2 × t(90%)
(ii) Rate constant ‘k’ of a reaction varies with temperature ‘T’ according to the equation:
log k = log A – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R}\left(\frac{1}{T}\right)\)
where Ea is the activation energy. When a graph is plotted for log k vs. \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~T}}\), a straight line with a slope
of – 4250 K is obtained. Calculate ‘Ea’ for the reaction (R = 8.3 14 JK-1 mol-1). (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Slope = – \(\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R}\) = – 4250 k
∴ Ea = 2.303 × 8.314 Jk-1 mol-1 × 4250 k
= 81.375 kJ mol-1
Question 27.
(i) What is rate of reaction? Write two factors that affect the rate of reaction.
Answer:
Rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time. Factors that affect rate of a reaction
(a) Concentration of reactant
(b) Temperature
(ii) The rate constant of a first order reaction increases from 4 × 10-2 to 8 × 10-2 when the temperature changes from 27 °C to 37°C. Calculate the energy of activation (Ea).
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021)
Answer:
log \(\frac{k_{2}}{k_{1}}=\frac{E_{a}}{2.303 R}\left[\frac{T_{2}-T_{1}}{T_{1} T_{2}}\right]\)
k1 = 4 × 10-2,
k2 = 8 × 10-2,
T1 = 273 + 27 = 300 K
T2 = 273 + 37 = 310 K,
R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1

= 53598 J mol-1
= 53.598 KJ mol-1
OR
(i) For a reaction A + B → P, the rate is given by.
Rate = k [A] [B]2
(a) How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of B is doubled?
(b) What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
Answer:
Rate = K[A][B]2
(a) becomes four times
(b) Second order
(ii) A first order reaction takes 23.1 minutes for 50% completion. Calculate the time required for 75% completion of this reaction.
(log 2 = 0.301, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021) (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
For a first order reaction,