NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.4 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.4.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Exercise | Ex 8.4 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 5 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.4
Question 1.
Express the trigonometric ratios sin A, sec A and tan A in terms of cot A.
Solution:
From trigonometric identity, cosec² A – cot² A = 1, we get
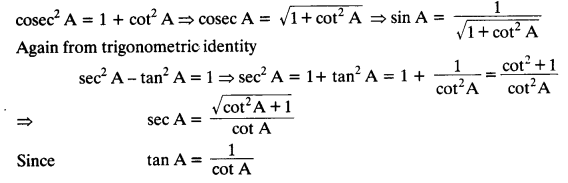
Question 2.
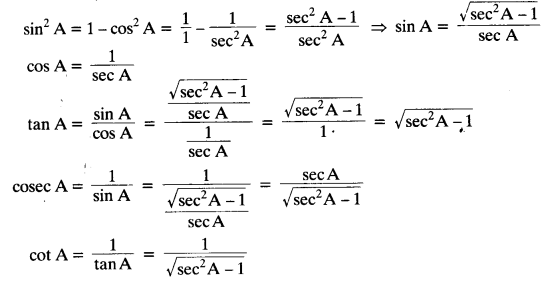
Write all the other trigonometric ratios of ∠A in terms of sec A.
Solution:
Since sin² A + cos² A = 1, therefore
Question 3.
Evaluate:
(i)
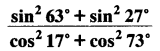
(ii) sin 25° cos 65° + cos 25° sin 65°
Solution:
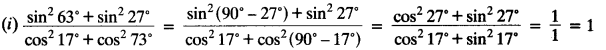
(ii) sin 25° cos 65° + cos 25° sin 65° = sin 25° cos (90° – 25°) + cos 25° sin (90° – 25°)
= sin 25° sin 25° + cos 25° cos 25°
= sin² 25° + cos² 25° = 1
Question 4.
Choose the correct option. Justify your choice.
(i) 9 sec² A – 9 tan² A =
(A) 1
(B) 9
(C) 8
(D) 0
(ii) (1 + tan θ + sec θ) (1 + cot θ – cosec θ ) =
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) -1
(iii) (sec A + tan A) (1 – sin A) =
(A) sec A
(B) sin A
(C) cosec A
(D) cos A
(iv) \(\frac{1+\tan ^{2} A}{1+\cot ^{2} A}\)
(A) sec² A
(B) -1
(C) cot² A
(D) tan² A
Solution:
(i) 9 sec² A – 9 tan² A = 9(sec² A – tan² A) = 9 x 1 = 9
Correct option is (B)
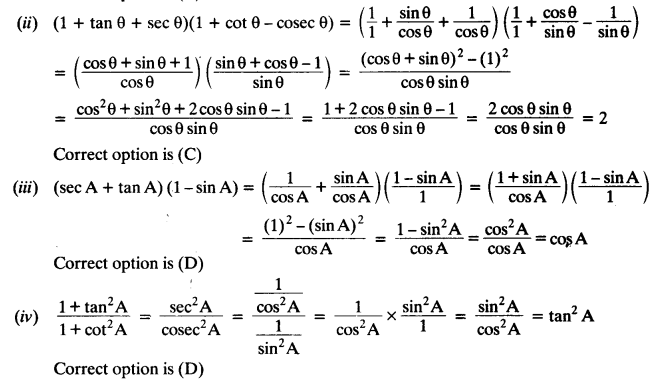
Question 5.
Prove the following identities, where the angles involved are acute angles for which the expressions are defined.
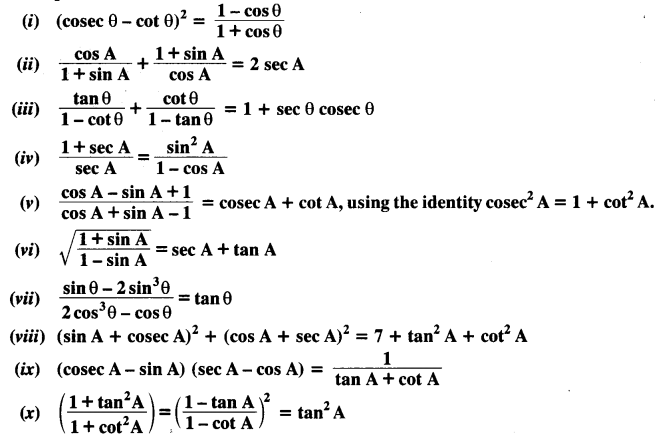
Solution:


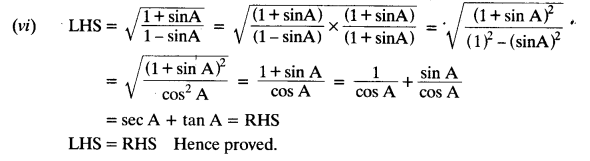
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.4, help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.4, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
 On this page, you will find Data Handling Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 3 Pdf free download. CBSE
On this page, you will find Data Handling Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 3 Pdf free download. CBSE 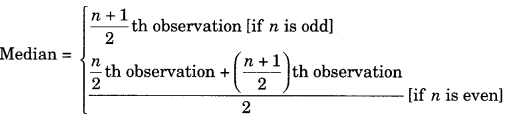
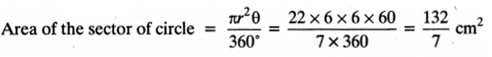
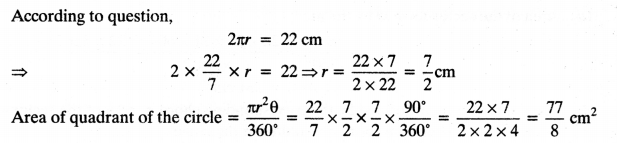



 On this page, you will find Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 2 Pdf free download. CBSE
On this page, you will find Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 2 Pdf free download. CBSE  On this page, you will find Integers Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 1 Pdf free download. CBSE
On this page, you will find Integers Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 1 Pdf free download. CBSE