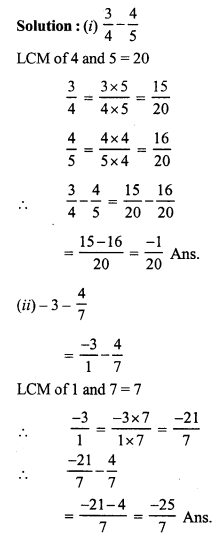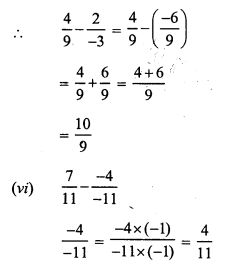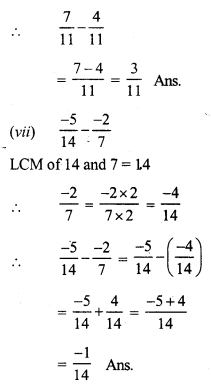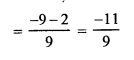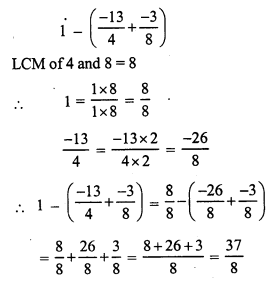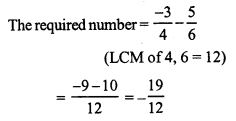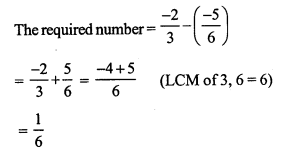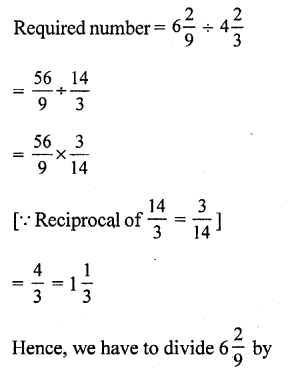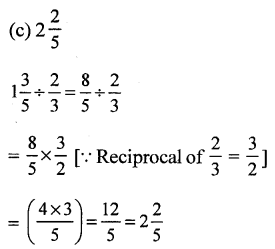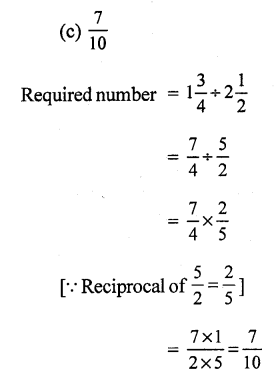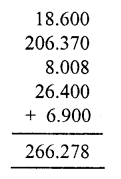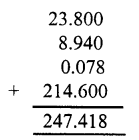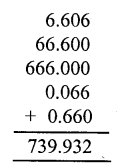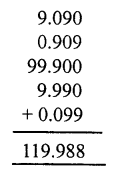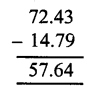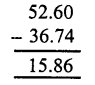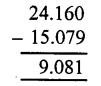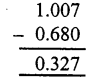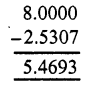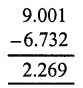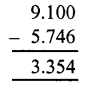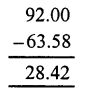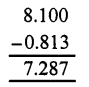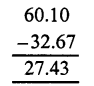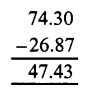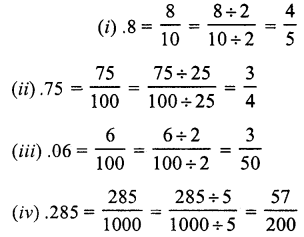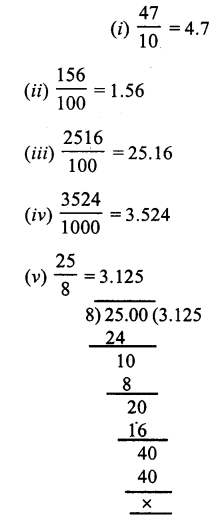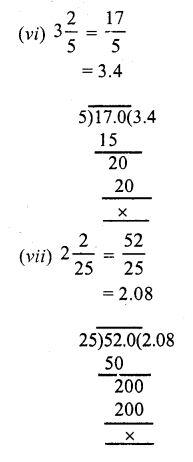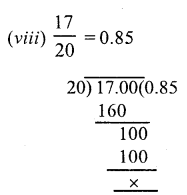RS Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3E
These Solutions are part of RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7. Here we have given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3E.
Other Exercises
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3A
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3B
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3C
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3D
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3E
- RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals CCE Test Paper
OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Mark (✓) against the correct answer in each of the following:
Question 1.
Solution:
(b)
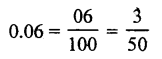
Question 2.
Solution:
(c)
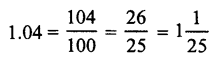
Question 3.
Solution:
(b)
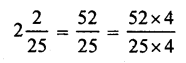
= \(\frac { 208 }{ 100 }\) = 2.08
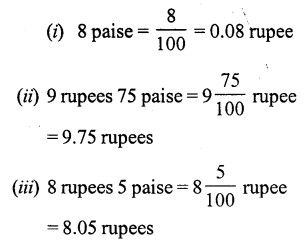
Question 4.
Solution:

Question 5.
Solution:
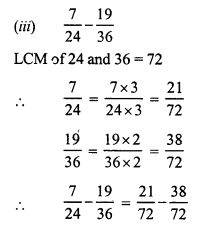
(b) 70g = \(\frac { 70 }{ 1000 }\) = 0.07 kg
Question 6.
Solution:
(c) 5 kg 6 g = 5\(\frac { 6 }{ 1000 }\) kg = 5.006 kg
Question 7.
Solution:
(c) 2 km 5 m = 2\(\frac { 5 }{ 1000 }\) km = 2.005 km
Question 8.
Solution:
(c)
1.007 – 0.7 = 1.007 – 0.700 = 0.307
Question 9.
Solution:
(b)
0.1 – 0.03 = 0.10 – 0.03 = 0.07
Question 10.
Solution:
(c)
3.5 – 3.07 = 3.50 – 3.07 = 0.43
Question 11.
Solution:
(c)
0.23 x 0.3 = 0.069
Question 12.
Solution:
(b)
0.02 x 30 = .60 = .6
Question 13.
Solution:
(b)
0.25 x 0.8 = 0.200 = 0.2
Question 14.
Solution:
(c)
0.4 x 0.4 x 0.4 = 0.064
Question 15.
Solution:
(b)
1.1 x .1 x .01 = .0011
Question 16.
Solution:
(a)
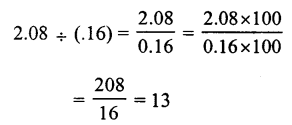
Question 17.
Solution:
(b)
1.02 ÷ 6 = \(\frac { 1.02 }{ 6 }\) = 0.17
Question 18.
Solution:
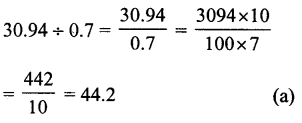
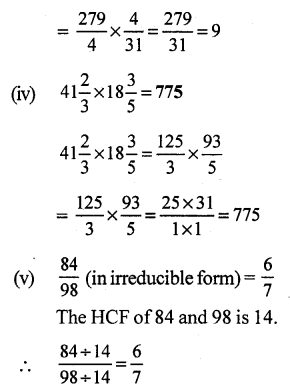
Question 19.
Solution:
(b)
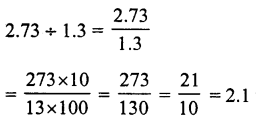
Question 20.
Solution:
(a)
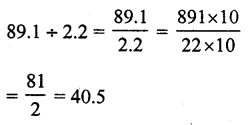
Question 21.
Solution:
(c)
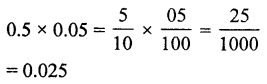
Hope given RS Aggarwal Solutions Class 7 Chapter 3 Decimals Ex 3E are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.