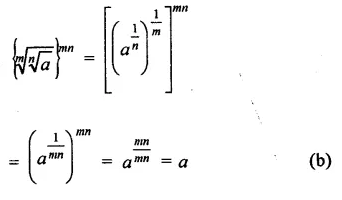
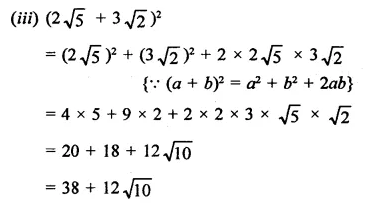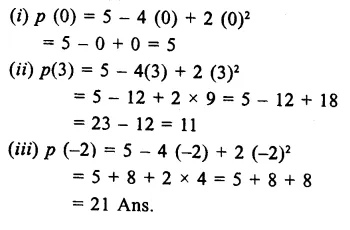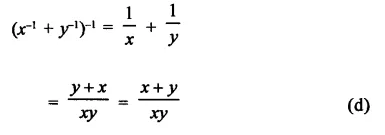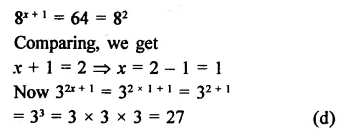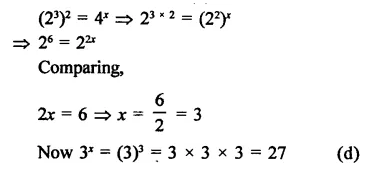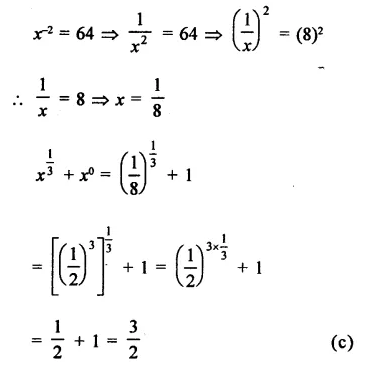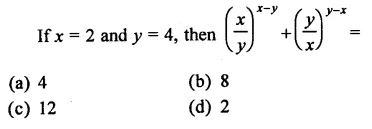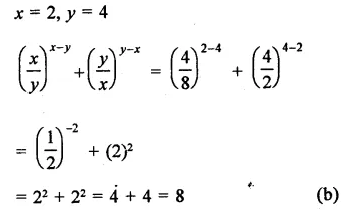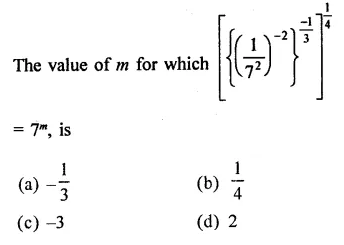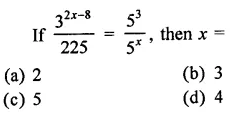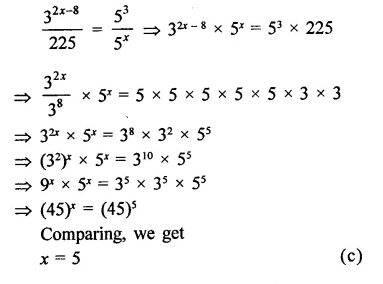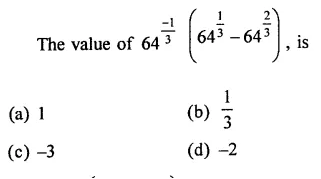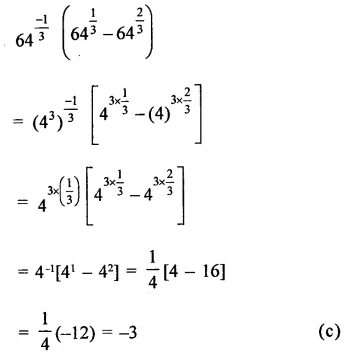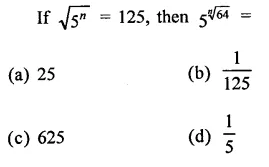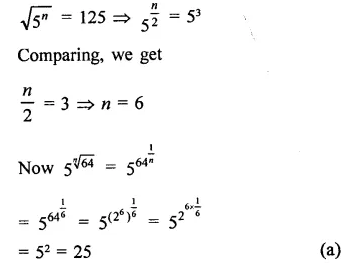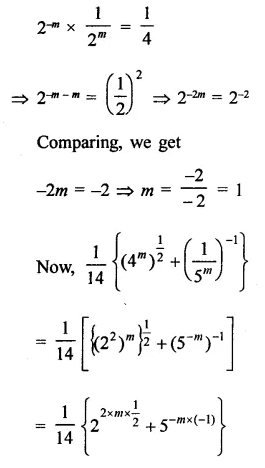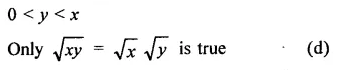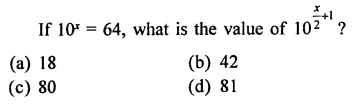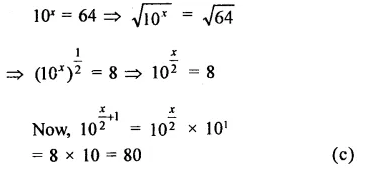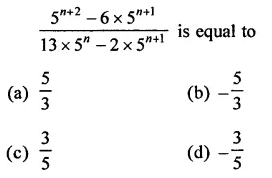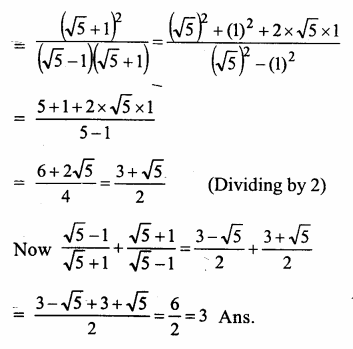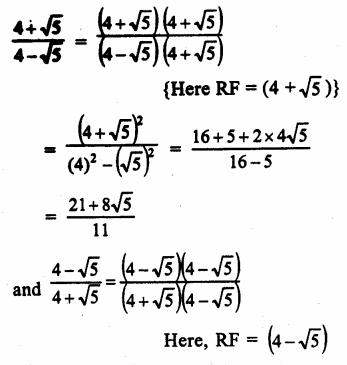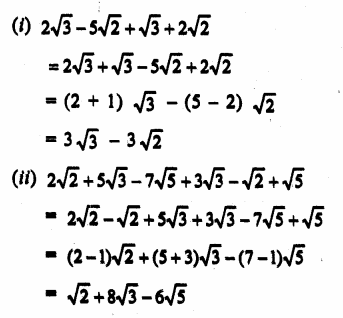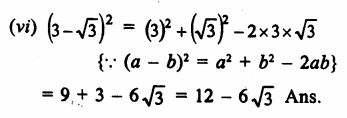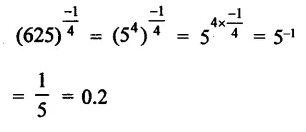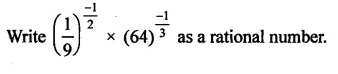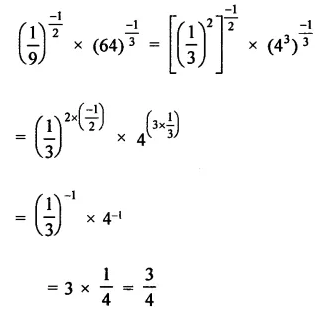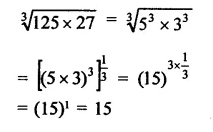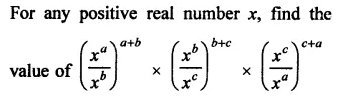HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
These Solutions are part of HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Question 1.
The diagram shows an experiment in which gases hydrogen and carbon dioxide are placed in two jars as shown in the figure. If the lid separating the two jars be removed, what will the constituents in the gas jar A after a few minutes ?
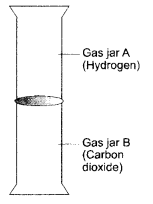
(a) carbon dioxide only
(b) hydrogen only
(c) mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
Answer:
(c) The gas jar A will contain both the gases carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Actually, the molecules of the gas present in one jar will move into the empty spaces present in the other jar and vice versa.
More Resources
- HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 9
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
Question 2.
The given graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The temperature rises with time as the substance is heated :
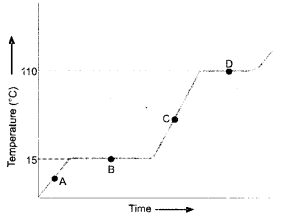
- What is the physical state of the substance at the points A, B, C and D ?
- What is the melting point of the substance ?
- What is its boiling point ?
- What happens to the temperature while the substance is changing state ?
- The substance is not water. How can you judge from the graph ?
Answer:
- At point A : The substance is in the solid state.
At point B : The substance has started melting. It exists both in the solid and liquid states.
At point C : The substance is in the liquid state.
At point D : The substance has started boiling. It exists both in the liquid and gaseous states. - The melting point of the substance is 15°C.
- The boiling point of the substance is 110°C.
- The temperature remains the same during the change of state.
- Had substance been water, its melting point should have been 0°C and boiling point 100°C. It is therefore, not water.
Question 3.
In severe cold weather, a family burnt wood in the room during the night by keeping the windows close. After sometime, they felt suffocated. They immediately opened the windows and got relief. What did actually happen ?
Answer:
When wood burns, the carbon present is oxidised to carbon dioxide (CO2) which is non-poisonous. When the windows are close, the air or oxygen cannot enter the room. In the incomplete supply of oxygen, carbon is oxidised to carbon monoxide (CO) which is a highly poisonous gas. It caused suffocation in a close room. On opening the windows, the poisonous gas slowly diffused out the room and fresh air came inside. That is how the poisonous effect of carbon monoxide gas was neutralised and the family got relief.
Question 4.
Small quantities of water and ether are placed on the palms of both the hands. Which will experience more cooling ?
Answer:
The palm containing ether will experience extra cooling. Actually ether is more volatile than water. Therefore, it will evaporate at a faster rate than water. Since cooling is always caused during evaporation, the palm containing ether will become cooler.
Hope given HOTS Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.