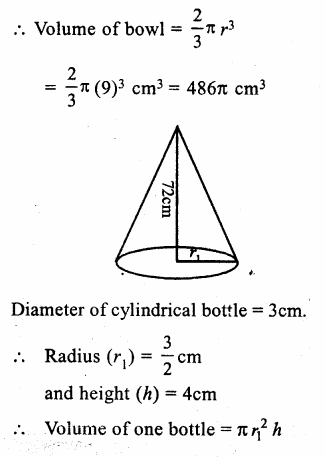
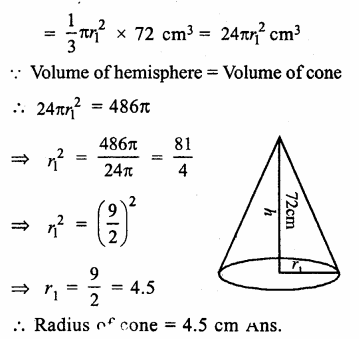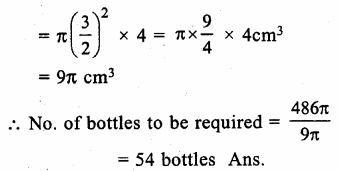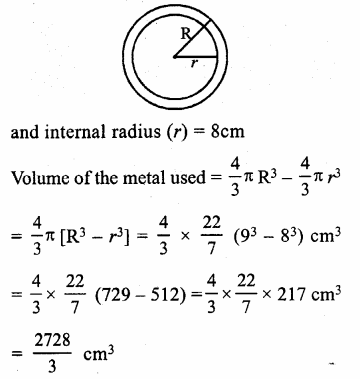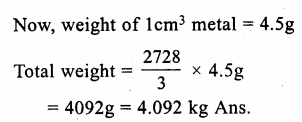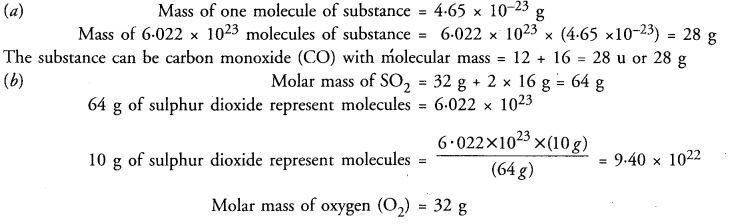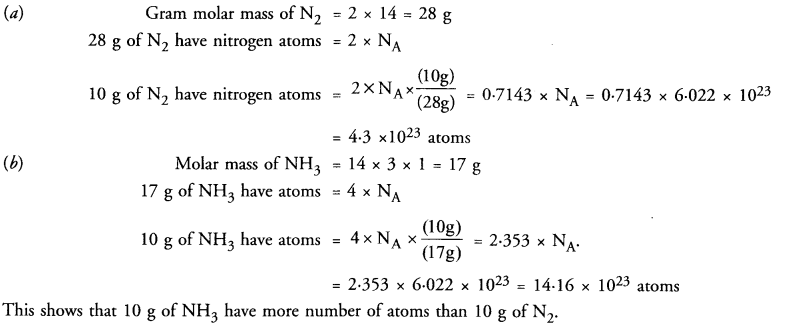Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 7 धर्म की आड़
These Solutions are part of Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 7 धर्म की आड़.
पाठ्य-पुस्तक के प्रश्न-अभ्यास
मौखिक
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-दो पंक्तियों में दीजिए-
प्रश्न 1.
आज धर्म के नाम पर क्या-क्या हो रहा है?
उत्तर:
आज धर्म के नाम पर कुछ स्वार्थी लोगों द्वारा उत्पात किया जा रहा है और भोले-भाले लोगों को आपस में लड़ाया जा रहा है।
प्रश्न 2.
धर्म के व्यापार को रोकने के लिए क्या उद्योग होने चाहिए?
उत्तर:
धर्म के व्यापार को रोकने के लिए साहस और दृढ़ता के साथ उसका विरोध होना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 3.
लेखक के अनुसार स्वाधीनता आंदोलन का कौन-सा दिन सबसे बुरा था?
उत्तर:
स्वाधीनता आंदोलन का वह दिन सबसे बुरा था जब स्वाधीनता के काम में मुल्ला, मौलवी, शंकराचार्य जैसे धर्म के आचार्यों को अधिक महत्त्व दिया गया।
प्रश्न 4.
साधारण से साधारण आदमी तक के दिल में क्या बात अच्छी तरह घर कर बैठी है?
उत्तर:
साधारण से साधारण आदमी तक के दिल में यह बात अच्छी तरह घर करके बैठी है कि धर्म और ईमान के नाम पर अपनी जान दे देना उचित है।
प्रश्न 5.
धर्म के स्पष्ट चिह्न क्या हैं?
उत्तर:
शुद्ध आचरण और सदाचार करना धर्म के स्पष्ट चिह्न हैं।
लिखित
(क) निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर (25-30 शब्दों में) लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
चलते पुरजे लोग धर्म के नाम पर क्या करते हैं?
उत्तर:
चलते पुरज़े लोग धर्म के नाम पर लोगों को बेवकूफ़ बनाकर अपना स्वार्थ सिद्ध करते हैं। वे चाहते हैं कि उनका नेतृत्व कायम रहे। उनका प्रभाव बना रहे।
प्रश्न 2.
चालाक लोग साधारण आदमी की किस अवस्था का लाभ उठाते हैं? [CBSE 2012]
उत्तर:
चालाक लोग साधारण आदमी की धार्मिक भावनाएँ भड़काते हैं। साधारण आदमी धर्माध होकर धर्म के नाम पर मरने-मिटने को तैयार हो जाता है। उसकी इसी स्थिति का लाभ चालाक लोग उठाते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
आनेवाला समय किस प्रकार के धर्म को नहीं टिकने देगा?
उत्तर:
जो लोग धर्म के प्रति दिखावा मात्र करके लोगों को आपस में लड़वाते हैं, आनेवाला समय उन्हें टिकने नहीं देगा। जन साधारण की समझ में आ गया है कि ऐसे धार्मिक नेता उनकी भावनाओं से खेलते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
कौन-सा कार्य देश की स्वाधीनता के विरुद्ध समझा जाएगा?
उत्तर:
प्रत्येक व्यक्ति किसी धर्म को मानने और पूजा-उपासना की कोई भी रीति अपनाने को स्वतंत्र है। उसकी इस स्वाधीनता में हस्तक्षेप करने के कार्य को देश की स्वाधीनता के विरुद्ध समझा जाएगा।
प्रश्न 5.
पाश्चात्य देशों में धनी और निर्धन लोगों में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर:
पाश्चात्य देशों में धनी लोगों के पास पैसा है, ऊँची-ऊँची इमारतें हैं, सुख-सुविधा है। गरीब लोग रोटी के लिए संघर्ष करते हैं और झोंपड़ियों में रहते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
कौन-से लोग धार्मिक लोगों से अधिक अच्छे हैं?
उत्तर:
जिन लोगों का आचरण अच्छा है, जो दूसरों का कल्याण करते हैं, अपने आचरण से दूसरों को दुख नहीं पहुंचाते हैं तथा जो अपनी स्वार्थ सिद्धि के लिए भोले-भाले लोगों का शोषण नहीं करते हैं, वे धार्मिक लोगों से अधिक अच्छे हैं।
(ख) निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर (50-60 शब्दों में) लिखिए
प्रश्न 1.
धर्म और ईमान के नाम पर किए जाने वाले भीषण व्यापार को कैसे रोका जा सकता है? [CBSE 2012]
उत्तर:
धर्म और ईमान के नाम परं दंगे-फसाद हो रहे हैं। कुछ स्वार्थी आदमी धर्म के नाम पर लोगों को आपस में लड़वाते हैं। अपने निजी स्वार्थों के लिए आम आदमी के प्राण ले लिए जाते हैं। इसको रोकने का उपाय है कि लोगों को उन आदमियों और धर्म की सही शिक्षा के लिए जानकारी दी जाए। लोगों को समझाया जाए कि दंगा करके खून बहाने वालों का कोई धर्म नहीं होता।
प्रश्न 2.
‘बुद्धि को मार’ के संबंध में लेख़क के क्या विचार हैं?” [CBSE 2012]
उत्तर:
बुधि की मार के संबंध में लेखक का विचार है-कुछ चलते-पुरज़े लोगों द्वारा साधारण लोगों के मस्तिष्क में ऐसे विचार भर देना कि वे अपनी बुधि से कुछ भी सोचने-समझने योग्य न रह जाएँ। ऐसे लोगों की धार्मिक भावनाएँ भड़काकर अपने हित साधने योग्य बना लेना ताकि स्वार्थी लोग अपना स्वार्थ आसानी से पूरा कर सकें।
प्रश्न 3.
लेखक की दृष्टि में धर्म की भावना कैसी होनी चाहिए?
उत्तर:
लेखक के अनुसार, धर्म के विषय में मानव स्वतंत्र होना चाहिए। हर व्यक्ति आजाद हो। वह जो धर्म अपनाना चाहे, अपनाए। कोई किसी की स्वतंत्रता में बाधा न खड़ी करे। धर्म का संबंध हमारे मन से, ईमान से, ईश्वर और आत्मा से होना चाहिए। वह मन को शुद्ध करने का मार्ग होना चाहिए, अपने जीवन को ऊँचा उठाने का साधन होना चाहिए, दूसरे को कुचलने का नहीं।
प्रश्न 4.
महात्मा गाँधी के धर्म संबंधी विचारों पर प्रकाश डालिए। [CBSE 2012]
उत्तर:
गांधी जी धर्म को मानने वाले थे। इसके बिना वे एक कदम भी नहीं चलते थे। वे पूजा-पाठ, नमाज पढ़ने जैसी दिखावापूर्ण धार्मिक क्रियाओं को सच्चा धर्म नहीं मानते थे। उनका धर्म पवित्र भावनाओं से भरपूर था। वे धर्म को लोगों के कल्याण का साधन समझते थे। उनका मानना था कि धर्म ऊँचे और उदार तत्वों का हुआ करता है, जिसे अपनाने में किसी को आपत्ति नहीं हो सकती।
प्रश्न 5.
सबके कल्याण हेतु अपने आचरणा को सुधारना क्यों आवश्यक है?
उत्तर:
जब तक हम स्वयं का आचरण ठीक नहीं रखेंगे, दूसरे लोगों को उसकी प्रेरणा नहीं दे सकते। समाज में उदाहरण बनने के लिए हमें स्वयं का आचरण सुधारना होगा। मानव मात्र की भलाई तभी हो सकती है, जब हम निजी स्वार्थ को छोड़कर पूरे समाज की भलाई के बारे में सोचें।
(ग) निम्नलिखित का आशय स्पष्ट कीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
उबल पड़ने वाले साधारण आदमी को इसमें केवल इतना ही दोष है कि वह कुछ भी नहीं समझता-बूझता, और दूसरे लोग उसे जिधर जोत देते हैं, उधर जुत जाता है।
उत्तर:
कुछ चालू-पुरज़े लोग तथा धर्म के तथाकथिक ठेकेदार साधारण लोगों के दिमाग में यह बात अच्छी तरह बिठा देते हैं कि धर्म और ईमान ही तुम्हारे लिए सब कुछ हैं। इसी से तुम्हारा कल्याण होने वाला है। इसकी रक्षा करते हुए तुम्हें अपनी ज्ञान की परवाह नहीं करनी चाहिए। ये अनपढ़ साधारण भोले लोग धर्म क्या है, यह जाने-समझे बिना तनिक-सा उकसाए जाते ही मरने-कटने के लिए तैयार हो जाते हैं। वे दूसरों के बहकावे में जल्दी आ जाते हैं। इससे उनकी शक्ति और साहस का दुरुपयोग स्वार्थी लोग अपने हित के लिए करते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
यहाँ है बुद्धि पर परदा डालकर पहले ईश्वर और आत्मा का स्थान अपने लिए लेना, और फिर धर्म, ईमान, ईश्वर और आत्मा के नाम पर अपनी स्वार्थ सिद्धि के लिए लोगों को लड़ाना-भिड़ाना।
उत्तर:
भारत में धार्मिक नेता लोगों की बुद्धि का शोषण करते हैं। पहले वे अपने प्रति अंध श्रद्धा उत्पन्न करते हैं। लोग उन्हें ईश्वर, आत्मा और धर्म का पूज्य प्रतीक मान बैठते हैं। जब लोगों की श्रद्धा उन पर जम जाती है तो वे ईमान, धर्म, ईश्वर या आत्मा का नाम लेकर उन्हें दूसरे धर्म वालों से लड़ाते-भिड़ाते हैं तथा अपने स्वार्थ सिद्ध करते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
अब तो, आपका पूजा-पाठ न देखा जाएगा, आपकी भलमनसाहत की कसौटी केवल आपका आचरण होगी।
उत्तर:
धर्म और ढोंग में अंतर है। धर्म ईश्वर तक पहुँचाने की कड़ी है। कुछ लोग धर्म का आडंबर करते हुए दो-दो घंटे तक पूजा-पाठ करते हैं, शंख बजाते हैं, नमाज़ पढ़ते हैं। ऐसा करके वे समझते हैं कि वे कुछ भी करने के लिए स्वतंत्र हैं। ऐसे लोग यदि अपना आचरण नहीं सुधारते हैं, तो यह पूर्जा-पाठ सब व्यर्थ हो जाएगा। उनके आचरण-व्यवहार में सज्जनता और दूसरों के कल्याण की भावना निहित होनी चाहिए।
प्रश्न 4.
तुम्हारे मानने ही से मेरा ईश्वरत्व कायम नहीं रहेगा, दया करके, मनुष्यत्व को मानो, पशु बनना छोड़ो और आदमी बनो! [CBSE 2012]
उत्तर:
स्वयं ईश्वर भटके हुए लोगों को कहता है-लोगों को धर्म के नाम पर लड़वाना छोड़ो। अपवित्र काम छोड़ो, खुद की पूजा करवाना छोड़ दो। मानवता को समझो। आदमी बनो और पशु वाला आचरण त्याग दो। आशय यह है कि धर्म के नाम पर कट्टरता त्याग दो और मनुष्य के साथ उदारतापूर्वक सहयोग और स्नेह से व्यवहार करो।
भाषा-अध्ययन
प्रश्न 1.
उदाहरण के अनुसार शब्दों के विपरीतार्थक लिखिए
सुगम – दुर्गम
- धर्म – …………………..
- ईमान – …………………..
- साधारण – …………………..
- स्वार्थ – …………………..
- दुरुपयोग – …………………..
- नियंत्रित – …………………..
- स्वाधीनता – …………………..
उत्तर:
- धर्म – अधर्म
- ईमान – बेईमान
- साधारण – असाधारण
- स्वार्थ – निस्वार्थ
- दुरुपयोग – सदुपयोग
- नियंत्रित – अनियंत्रित
- स्वाधीनता – पराधीनता
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित उपसर्गों का प्रयोग करके दो-दो शब्द बनाइए-
- ला,
- बिला,
- बे,
- बद,
- ना,
- खुश,
- हर,
- गैर
उत्तर:
- ला – लापता, लाजवाब, लापरवाही।
- बिला – बिलावजह, बिलानागा।
- बे – अदब, बेवज़ह, बेवफ़ा, बेशक ।
- बद – बदनाम, बदसूरत, बदतमीज़ ।
- ना – नासमझ, नादानी, नामर्द ।
- खुश – खुशफहमी, खुशगवार।
- हर – हररोज़, हरदम।
- गैर – गैरकानूनी, गैरहाज़िर।
प्रश्न 3.
उदाहरण के अनुसार ‘त्व’ प्रत्यय लगाकर पाँच शब्द बनाइए-
उदाहरण : देव + त्व = देवत्व
उत्तर:
- लघु + त्व = लघुत्व
- प्रभु + त्व = प्रभुत्व
- महत् + त्व = महत्त्व
- नारी + त्व = नारीत्व
- मनुष्य + त्व = मनुष्यत्व।
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित उदाहरण को पढ़कर पाठ में आए संयुक्त शब्दों को छाँटकर लिखिए-
उदाहरण : चलते पुरजे
उत्तर:
- समझता – बूझता,
- पढ़े – लिखे,
- इने – गिने,
- मन – माना,
- स्वार्थ – सिद्धि,
- लड़ाना – भिड़ाना,
- दीन – दीन,
- नित्य – प्रति,
- भली – भाँति,
- दिन – भर,
- पूजा – पाठ,
- देश – भर,
- सुख – दुःख।
प्रश्न 5.
‘भी’ का प्रयोग करते हुए पाँच वाक्य बनाइए-
उदाहरण : आज मुझे बाज़ार होते हुए अस्पताल भी जाना है।
उत्तर:
- यह भोजन मेरे साथ तुम्हें भी करना है।
- गाँधीजी के साथ नेहरू भी आए हैं।
- आज सब्जीमंडी से आम भी लाना।
- नौकरी के लिए मेहनत ही नहीं, सिफ़ारिश भी करनी पड़ती है।
- हम मसूरी-नैनीताल ही नहीं, कौसानी भी गए थे।
योग्यता-विस्तार
प्रश्न 1.
‘धर्म एकता का माध्यम है-इस विषय पर कक्षा में परिचर्चा कीजिए।
उत्तर:
- एक छात्र – धर्म से एकता बढ़ती है। धार्मिक आयोजनों में लोग ऊँच-नीच भूलकर मित्र भाव से भाग लेते हैं।
- दूसरा छात्र – परंतु कुछ लोग धर्म के नाम पर ही स्वयं को अलग मानते हैं। कोई खुद को सिख कहता है, कोई बौद्ध कहता है, कोई हिंदू तो कोई मुसलमान।।
- तीसरा छात्र – परंतु वे सब हैं तो आदमी ही। चौथा छात्र-परंतु धर्म का नाम लेते ही वे स्वयं को इनसान नहीं हिंदू, ईसाई या मुसलमान कहने लगते हैं।
Hope given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Sparsh Chapter 7 are helpful to complete your homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online tutoring for you.