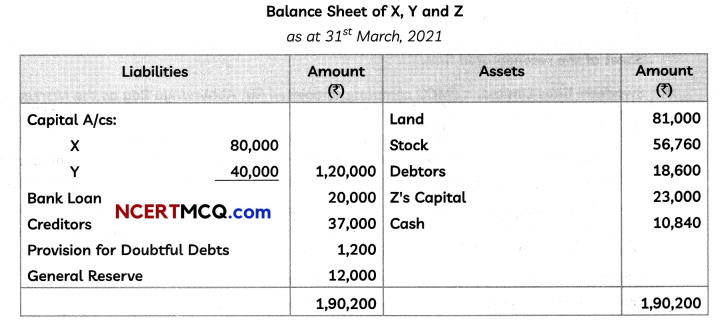
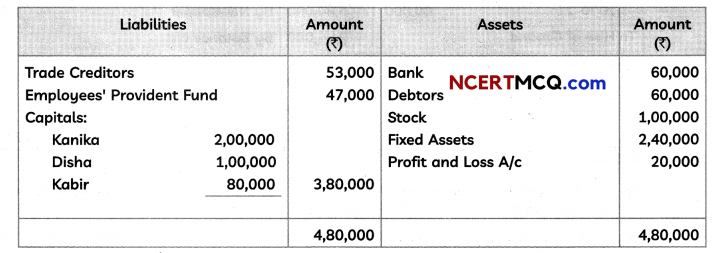
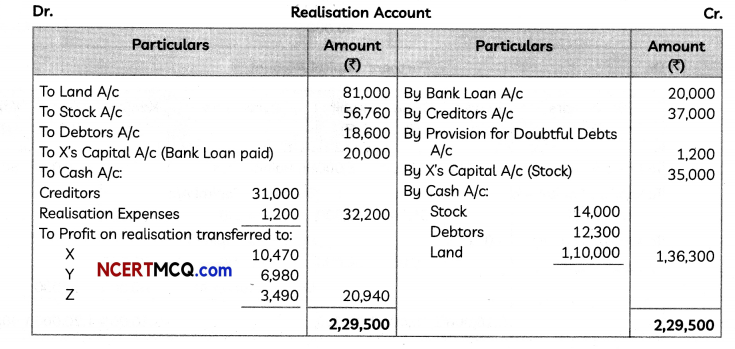
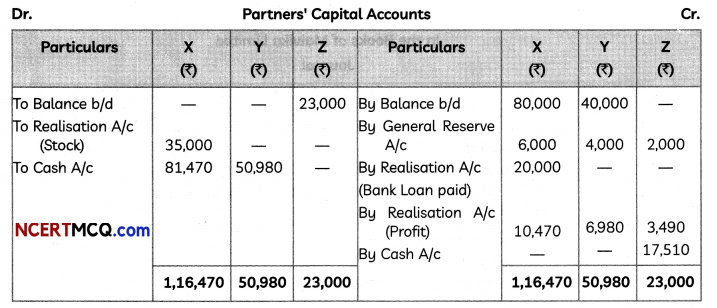
Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 6 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Applied Mathematics Term 2 Set 6 with Solutions
Maximum Marks : 40
Time : 2 Hours
Instructions:
- The question paper is divided into 3 sections-A, B and C
- Section A comprises of 6 questions of 2 marks each. Internal choice has been provided in two questions.
- Section B comprises of 4 questions of 3 marks each. Internal choice has been provided in one question.
- Section C comprises of 4 questions. It contains one case study based question. Internal choice has been provided in one question.
Section – A [12 Marks]
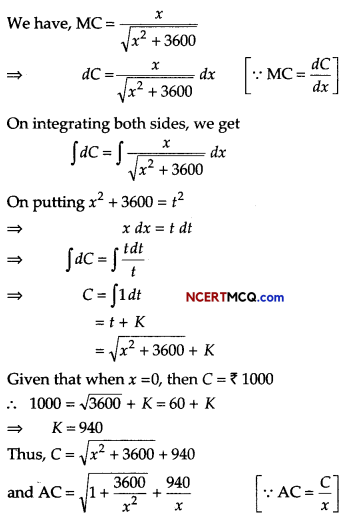
Question 1.
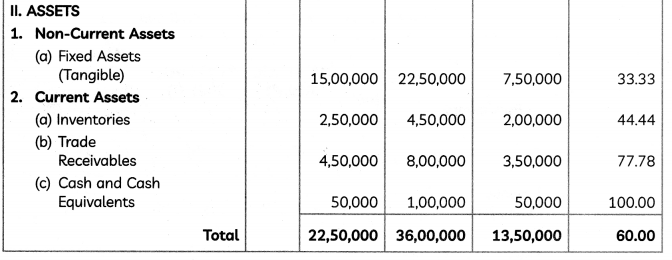
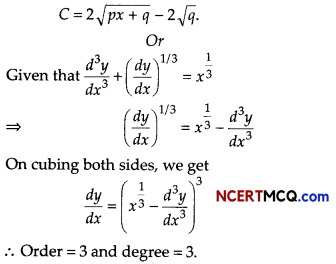
If the marginal cost function at x units of output is given by MC = \(\frac{p}{\sqrt{p x+q}}\), where p, q are constants and the fixed cost of production is zero, find the total cost function.
Or
Find the order and degree of differential equation \(\frac{d^{3} y}{d x^{3}}+\left(\frac{d y}{d x}\right)^{1 / 3}\) = \(x^{\frac{1}{3}}\).
Answer:
We have,
MC = \(\frac{p}{\sqrt{p x+q}}\)
⇒ \(\frac{d C}{d x}=\frac{p}{\sqrt{p x+q}}\) ⇒ dc = \(\frac{p}{\sqrt{p x+q}}\) dx
On integrating both sides, we get
⇒ C = ∫\(\frac{p}{\sqrt{p x+q}}\) dx + K
⇒ C = 2\(\sqrt{p x+q}\) + K …….(i)
where K is the constant of integration.
When x = 0, then fixed cost of production is zero,
i.e. C = 0
Putting x = 0 and C = 0 in Eq. (i), we get
0 = 2√q + K
⇒ K = – 2√q
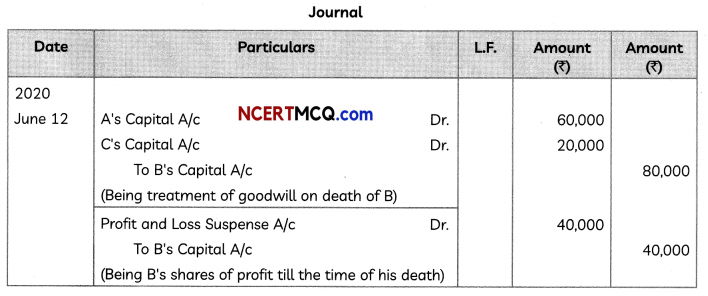
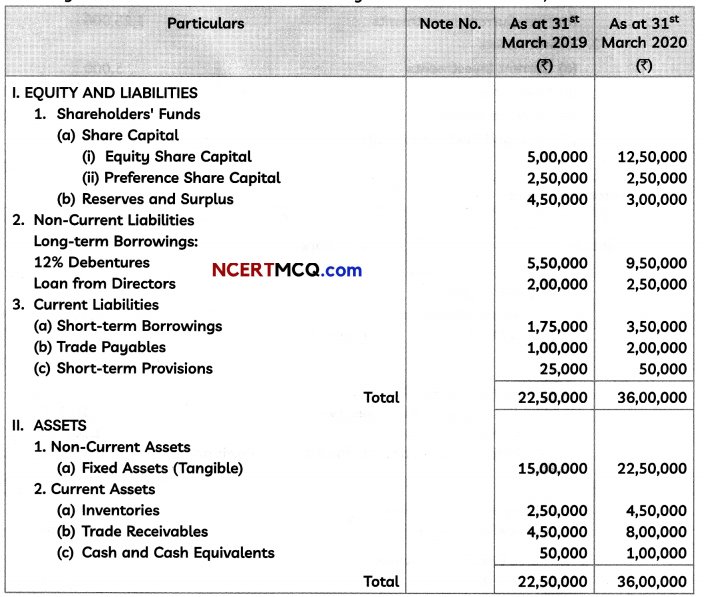
Putting K = – 2√q in Eq. (i), we find that the total cost function is given by
![]()
Question 2.
Samples of two different types of bulbs were tested for length of life and the following data were obtained
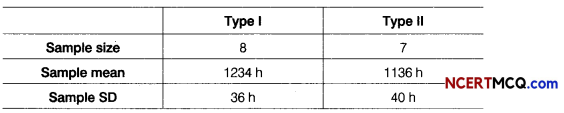
Is the difference in mean life of two types of bulbs significant?
Answer:
Given, n1 = 8, n2 = 7, s1 = 36, s2 = 40, x̄1 = 1234 and x̄2 = 1136
Let us take the null hypothesis that there is no significant difference in the mean life of the two types of bulbs.
Test statistics,
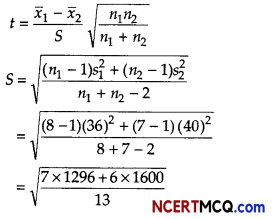
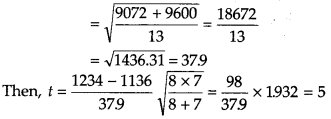
From table with v = 8 + 7 – 2 =13, test statistics to.05 = 2.16. Since, the calculated value of t is greater than the tabulated value. Therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Hence, there is a significant difference in the mean life of two types of bulbs.
Question 3.
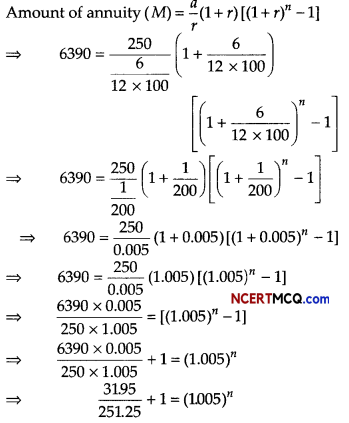
A man borrowed some money and paid back in 3 equal installments of ₹ 2160 each. What sum did he borrow, if the rate of interest charged was 20% per annum compounded annually? Find also the total interest charged, [given, (1.20)-3 = 0.5786]
Or
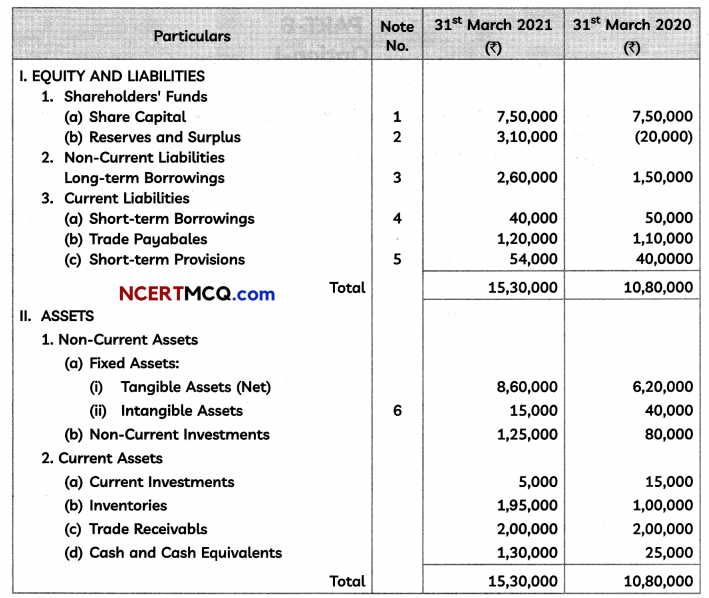
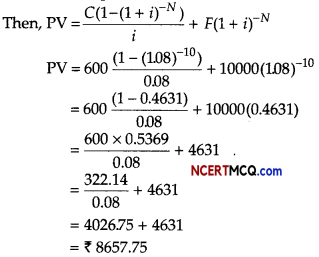
Find the present value of a sequence of payments of ₹ 2000 made at the end of every 6 months and continuing forever, if money is worth 10% per annum compounded semi-annually.
Answer:

Hence, the man borrowed ₹ 4551.12
In 3 yr the amount paid = ₹ (3 × 2160) = ₹ 6480
∴ Total interest charged = ₹ (6480 – 455L12)
= ₹ 1928.88
Or
Given, R = ₹ 2000, r = \(\frac{10}{2}\)% = 5% (per half)
So, i = 5 /100 = 0.05
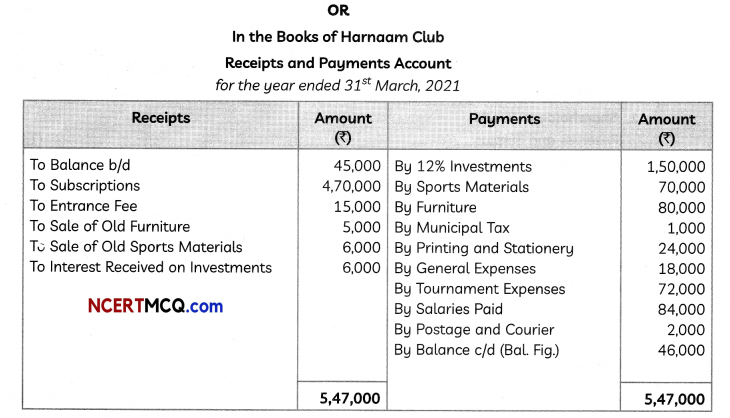
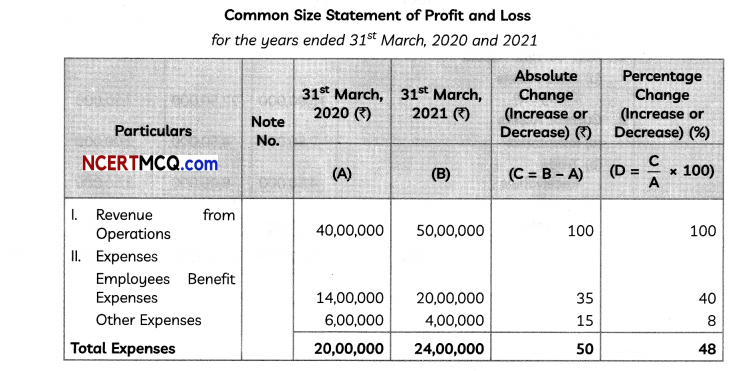
∴ Present value,
P = \(\frac{R}{i}=\frac{2000}{0.05}\) = ₹ 40000
![]()
Question 4.
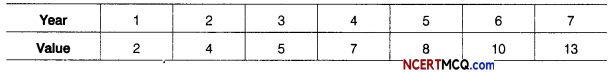
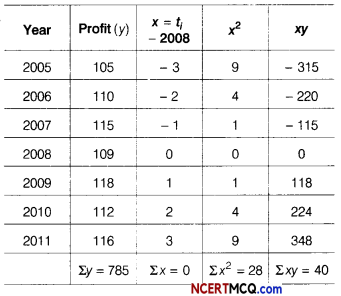
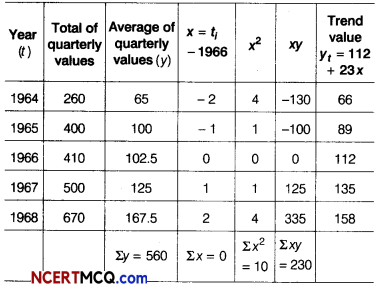
If Σ y = 91, n = 7, Σ x2 – 28 and Σ xy = 33, then find the equation of the trend line.
Answer:
We know, a = \(\frac{\Sigma y}{n}\)
∴ a = \(\frac{91}{7}\) = 13 and b = \(\frac{\Sigma x y}{\Sigma x^{2}}=\frac{33}{28}\) = 1.179
∴ Equation of trend line,
yt = a + bx = 13 + 1.179x.
Question 5.
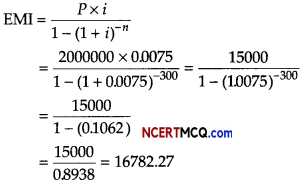
Neera borrows a sum of ₹ 150000 at an interest rate of 10% (flat) for a tenure of 3 yr. Find her EMI.
Answer:
Given, principal = ₹ 150000
Interest (yearly) = 10% of ₹ 150000 = ₹ 15000
∴ Interest of 3 yr = ₹ 45000
∴ EMI = \(\frac{\text { Principal + Interest }}{\text { Period of months }}\)
= \(\frac{150000+45000}{3 \times 12}\) = \(\frac{195000}{36}\)
= ₹ 5416.67
Question 6.
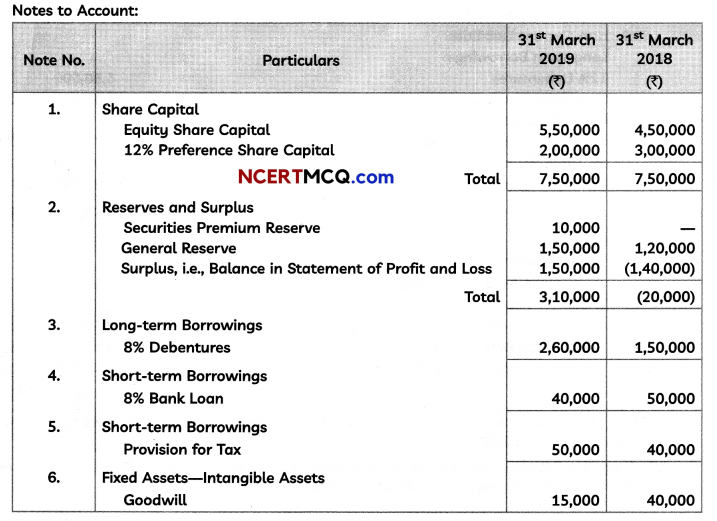
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is atmost 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is ₹ 100 and that on a bracelet is ₹ 300. Formulate on LPP, for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximise the profit? It is being given that atleast one of each must be produced.
Answer:
Let number of necklaces and bracelets produced by firm per day be x and y, respectively.
Clearly, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
∵ Total number of necklaces and bracelets that the firm can handle per day is atmost 24.
∴ x + y ≤ 24
Since, it takes one hour to make bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace and maximum number of hour available per day is 16.
∴ \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + y ≤ 16 ⇒ x + 2y ≤ 32
Let Z be the profit function.
Then, Z = 100x + 300y
∴ The given LPP reduces to
Maximise Z = 100x + 300y
Subject to constraints,
x + y ≤ 24
x + 2y ≤ 32
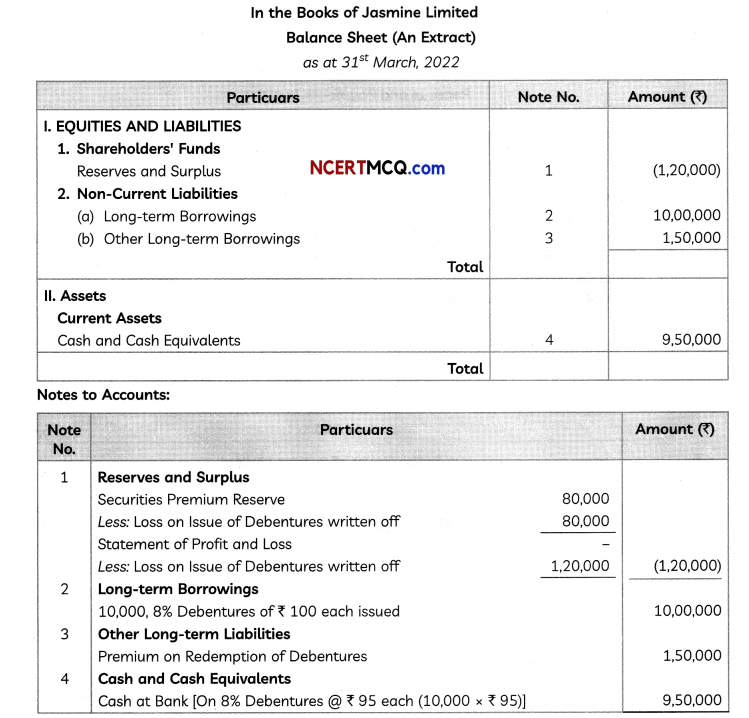
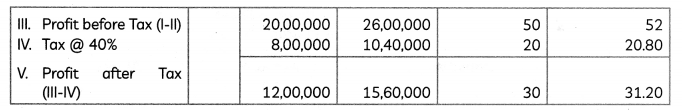
and x, y ≥ 0
![]()
Section – B [12 Marks]
Question 7.
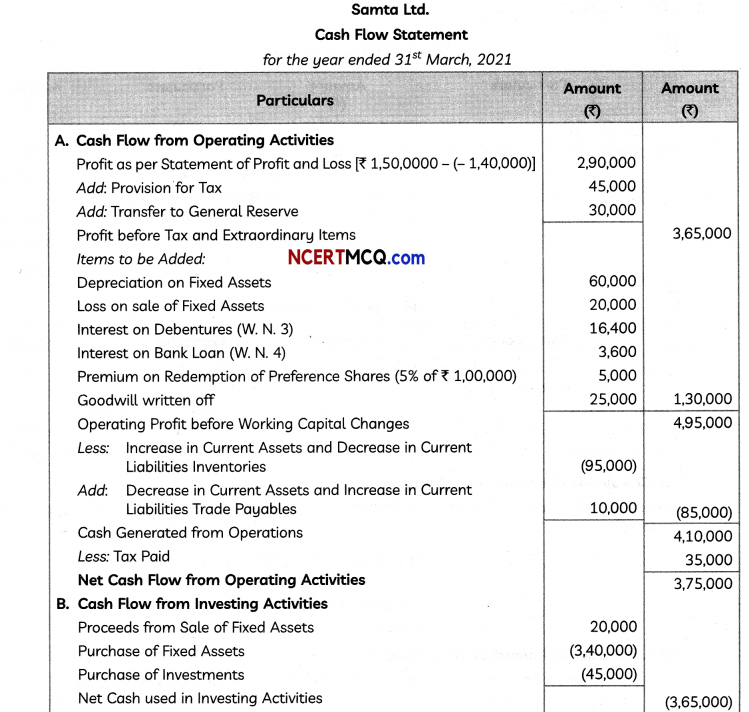
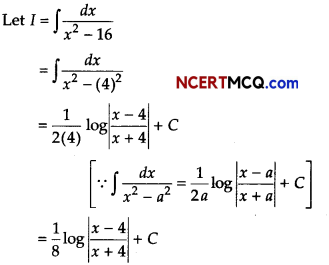
Evaluate \(\frac{x^{2}-3 x+1}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\).
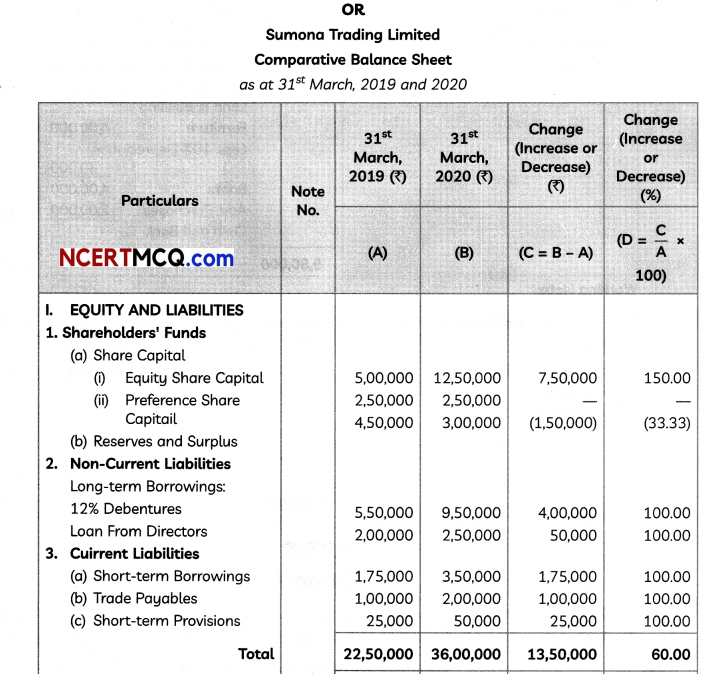
Or
![]()
Answer:
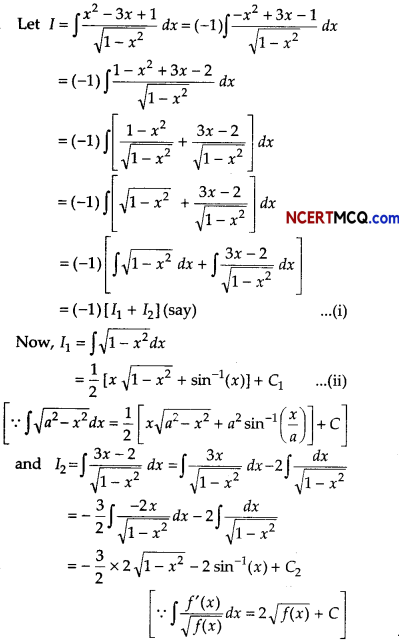
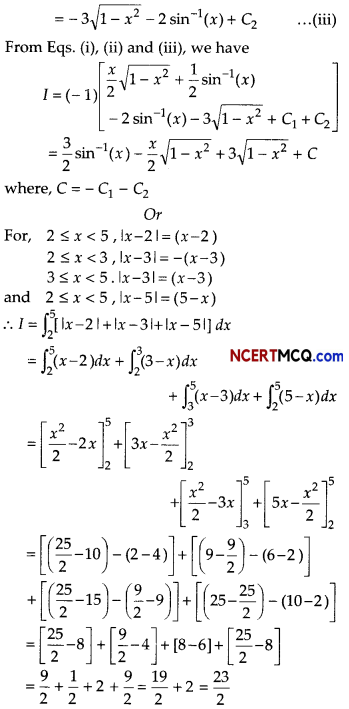
![]()
Question 8.
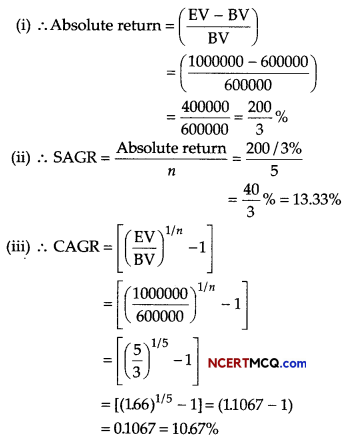
Pramod invested ₹ 21000 in a mutual fund and the value of investment at the time of redemption was ₹ 35000. If CAGR for this investment is 7.55%. Calculate the time period for which the amount was invested?
[given log(1.667) = 0.2219 and log(1.0755) = 0.0316]
Answer:
Given, BV = ₹ 21000
EV = ₹ 35000 and CAGR = 7.55%
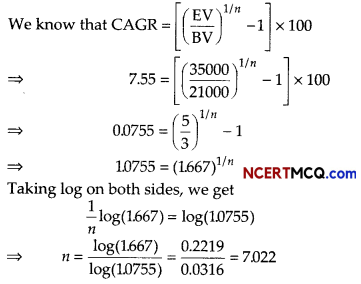
⇒ n = 7.022 = 7
Hence, the time period is 7 yr.
Question 9.
A random sample of size 16 has 53 as mean. The sum of squares of deviations from mean is 150. Can this sample be regard as taken from the population having 56 as mean? Level of significance is 5% (given t15 (0.05) = 1.753)
Answer:
Consider: H0: µ = 56
Ha: µ > 56
Here, n = 16, x̄ = 53 and Σ(xi – x̄)2 = 150
∴ S2 = \(\frac{1}{n-1}\) Σ(xi – x̄)2 = \(\frac{150}{15}\) = 10 ⇒ S = √10 = 3.1622
Test statistics, t = \(\frac{\bar{x}-\mu}{(S / \sqrt{n})}=\frac{53-56}{3.1622 / \sqrt{16}}=\frac{(-3) \times 4}{3.1622}\) = – 3.795
Since, calculated value of |t| = 3.795 is greater than tabulated value, so H0 can be rejected.
![]()
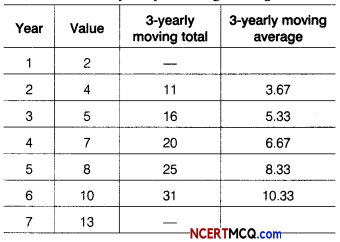
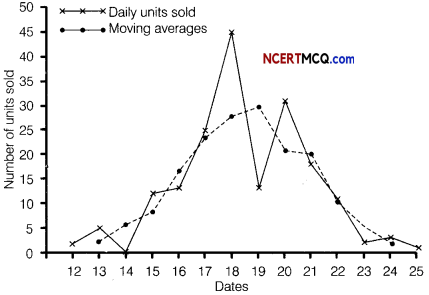
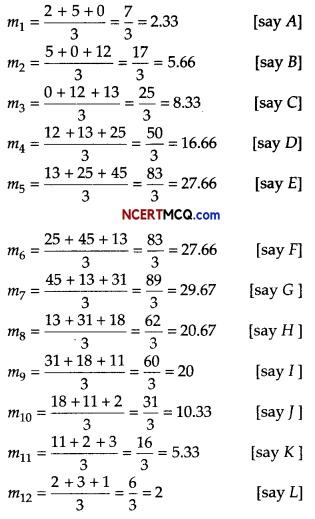
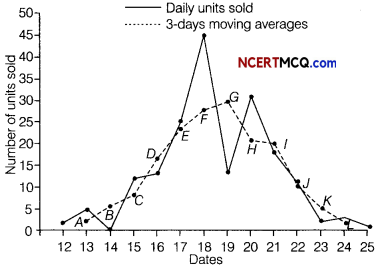
Question 10.
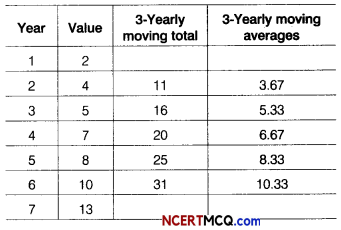
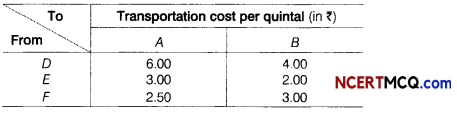
The number of letters (in hundred) received in a town on each day of a fortnight is given below
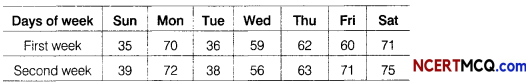
Calculate the 7-days moving average and display it on a graph.
Answer:
Given, table is shown below:
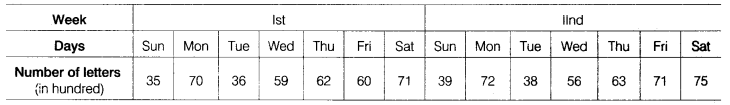
Let the moving average for 7 days is m, then

On the basis of above data we can draw the following graph for moving average
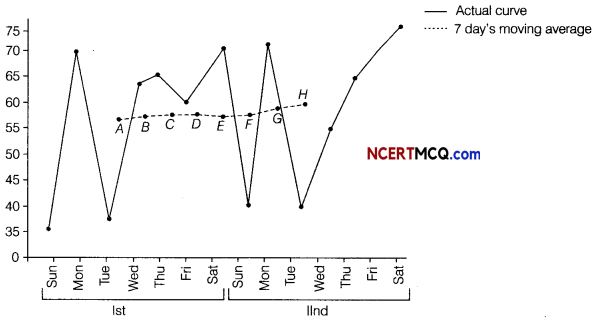
![]()
Section – C [16 Marks]
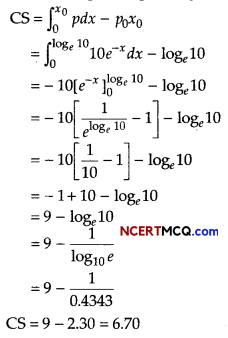
Question 11.
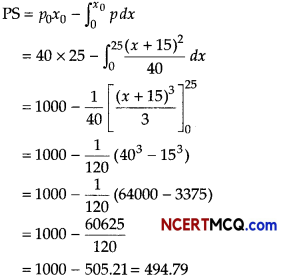
The demand and supply function are p = 25 – x2 and p = 2x + 1, respectively. Find the
(i) the equilibrium point
(ii) the consumer’s surplus at the equilibrium points.
Answer:
Given, the demand function and supply are
p = D(x) = 25 – x2 and p = S(x) = 2x +1
(i) At equilibrium point D(x) = S(x)
⇒ 25 – x20 = 2x0 + 1
⇒ x20 +2x0 – 24 = 0
⇒ (x0 – 4) (x0 + 6) = 0
⇒ x0 = 4 [∵ x0 = -6]
Now, putting x0 = 4 in S(x), we get p0 = 9
Hence, the equilibrium point (x0, p0) is (4,9)
(ii) The consumer’s surplus at the equilibrium point (4, 9) is given by

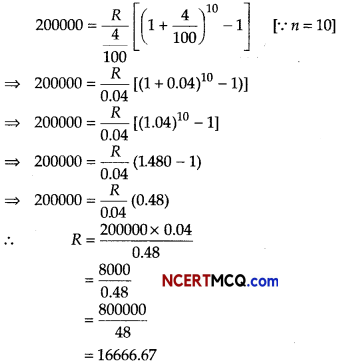
Question 12.
A firm anticipates on expenditure of ₹ 300000 for plant modernization at the end of 15 yr from now. How much should the company deposite at the end of each year into a sinking fund earning interest 6% per annum? [given, (1.06)15 = 23966 ]
Answer:
Given, A = ₹ 300000
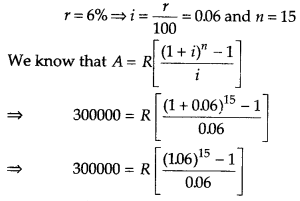
⇒ R [(1.06)15 – 1] = 300000 × 0.06
⇒ R (2.3966 – 1) = 18000
⇒ R(1.3966) = 18000
⇒ R = \(\frac{18000}{1.3966}\)
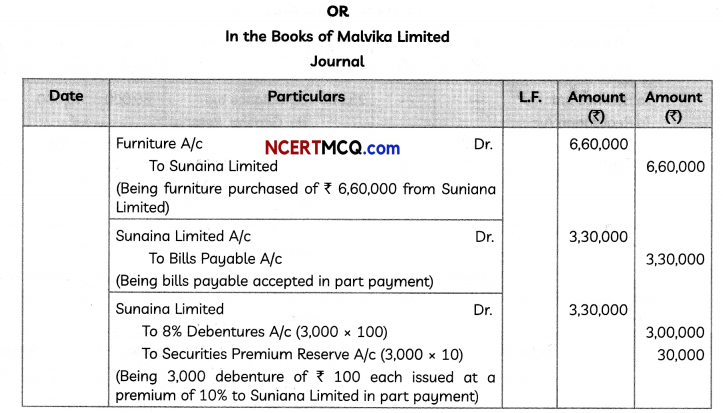
= 12888.44
Hence, the company deposite at the end of each year into a sinking fund ₹ 12888.44.
![]()
Question 13.
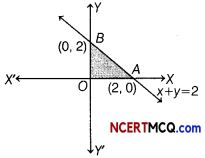
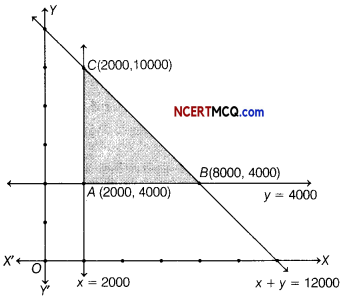
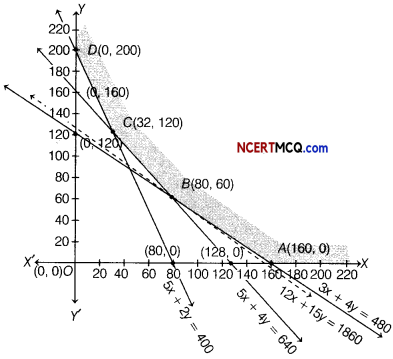
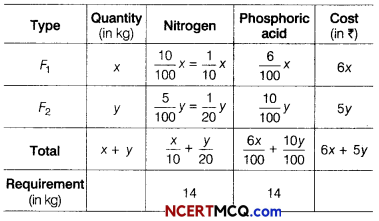
A dietician wishes to mix two types of foods in such a way that the vitamin contents of mixture contains atleast 8 units of vitamin A and 10 units of vitamin C. Food I contains 2 units per kg of vitamin A and 1 unit per kg of vitamin C, while food II contains 1 unit per kg of vitamin A and 2 units per kg of vitamin C. It costs ₹ 5 per kg to purchase food I and ₹ 7 per kg to purchase food II. Find the minimum cost of such a mixture. Formulate above as an LPP and solve it graphically.
Or
Solve the following LPP graphically.
Maximise Z = 3x + 2y, subject to constraints are x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + y ≤ 15 and x, y ≥ 0.
Also, determine the area of the feasible region.
Answer:
The given data can be put in the tabular form as follows
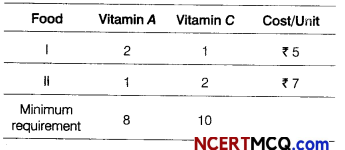
Suppose the diet contains x kg of food I and y kg of food II.
Then, the required LPP is minimise
Z = 5x + 7y
Subject to constraints 2x + y ≥ 8, x + 2y ≥ 10 and x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
On considering the inequalities as equations,
we get
2x + y = 8 …… (i)
and x + 2y = 10 …… (ii)
Table for line 2x + y = 8 is
| X | 0 | 4 |
| y | 8 | 0 |
So, it passes through the points (0, 8) and (4, 0).
On putting (0,0) in the inequality 2x + y ≥ 8,
we get
0 ≥ 8 [which is false]
So, the half plane is away from the origin.
Table for line x + 2y = 10 is
| X | 10 | 0 |
| y | 0 | 5 |
So, it passes through the points (10,0) and (0, 5).
On putting (0,0) in the inequality x + 2y ≥ 10,
we get
0 ≥ 10 [which is false]
So, the half plane is away from the origin.
Also, x, y ≥ 0, so the feasible region lies in the first quadrant.
On solving Eq. (i) and Eq. (ii), we get
x = 2 and y = 4
So, these lines intersect at P(2, 4).
The graphical representation of the system of inequations given below
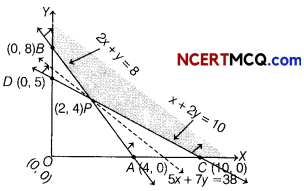
From the graph, the feasible region is BPC which is unbounded.
The values of Z at comer points are as follows
| Corner points | Value of Z = 5x + 7y |
| C(10, 0) | Z = 5(10)+ 7(0) = 50 |
| P{2, 4) | Z = 5(2)+7(4) = 10 + 28 =38 (minimum) |
| 6(0. 8) | Z = 5(0)+ 7(8) = 0+ 56 = 56 |
From table, the minimum value of Z is 38 at P(2,4).
As the feasible region is unbounded, therefore 38 may or may not be the minimum value of Z. For this, we draw a dotted graph of the inequality 5 x + 7y < 38 and check whether the resulting half plane has point in common with the feasible region or not.
It can be seen that the feasible region has no common point with 5x + 7y < 38.
Hence, the minimum cost is ₹ 38, when x = 2 and y = 4.
Or
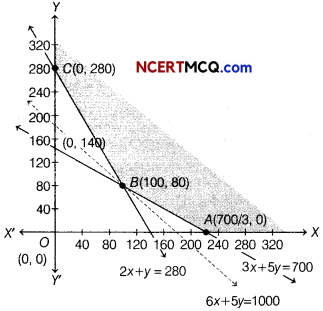
Our problem is to maximise Z = 3x + 2 y …(i) Subject to constraints,
x + 2y ≤ 10 …(ii)
3x + y ≤ 15 …(iii)
and x, y ≥ 0 …(iv)
Table for line x + 2y = 10 is
| X | 0 | 4 |
| y | 5 | 3 |
So, the line passes through the points (0, 5) and (4, 3).
On putting (0,0) in the inequality x + 2y ≤ 10, we get
0 + 2 × 0 ≤ 10
⇒ 0 ≤ 10, which is true.
So, the half plane is towards the origin.
Table for line 3x + y = 15 is
| X | 4 | 5 |
| y | 3 | 0 |
So, the line passes through the points (4, 3) and (5,0).
On putting (0,0) in the inequality 3x + y ≤ 15, we get
3 × 0 + 0 ≤ 15
⇒ 0 ≤ 15, which is true.
So, the half plane is towards the origin.
Also, x, y ≥ 0, so the region lies in the first quadrant.
On solving equations x + 2y = 10 and 3x + y = 15, we get x = 4 and y = 3
So, the intersection point is 6(4,3).
∴ Feasible region is OABCO
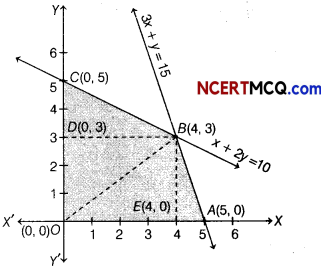
The corner points of the feasible region are 0(0,0), A(5,0), 6(4,3) and C(0,5).
The values of Z at the corner points are given below
| Corner points | Value of Z = 3x + 2y |
| 0(0, 0) | Z = 3 × 0 + 2 × 0 = 0 |
| 4(5, 0) | Z = 3 × 5 + 2 × 0 = 15 |
| 6(4, 3) | Z = 3 × 4 + 2 × 3 = 18 (Maximum) |
| C(0, 5) | Z = 3 × 0 +2 × 5 = 10 |
Therefore, the maximum value of Z is 18 at the point B(4, 3).
∴ Area of feasible region
= Area of ∆BOC + Area of ∆OAB
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × OC × BD + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × OA × BE
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 × 4 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 5 × 3
= 10 + \(\frac{15}{2}\) = 10 + 7.5
= 17.5 sq units
![]()
Case Based/Data Based
Question 14.
An entertainment company has gained much popularity all over the countary. They buy a car to travel to their destination. The purchase price is ₹ 1000000. The car will be depreciated linearly over 10 yr and will have a scrap value of ₹ 500000.

On the basis of above information, answer the following questions.
(i) Find the rate of depreciation.
Answer:
∴ Rate of depreciation
= \(\frac{500000-1000000}{10-0}\)
= – \(\frac{500000}{10}\)
= – 50000
∴ Rate of depreciation is ₹ 50000
(ii) When will the car be worth ₹ 800000?
Answer:
According to the question,
800000 = – 500001 +1000000
⇒ – 200000 = -50000 t
⇒ t = 4 yr


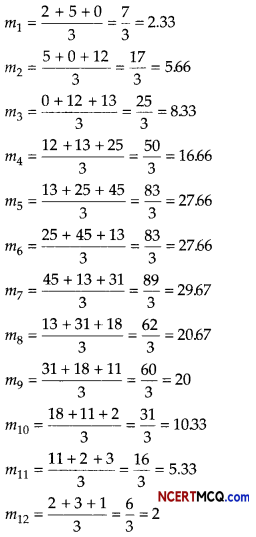








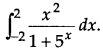
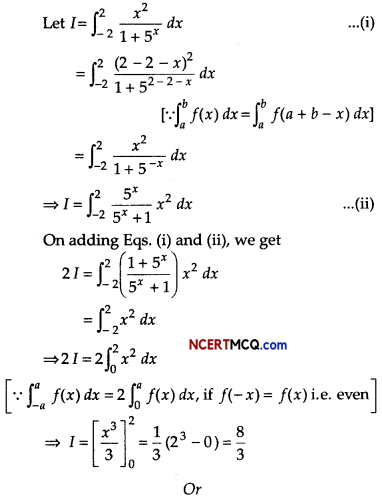

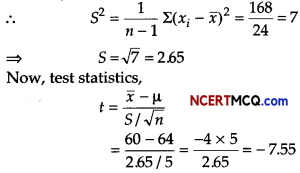
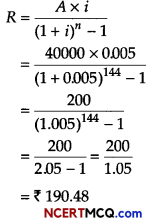
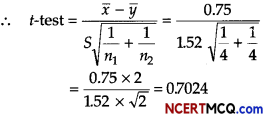

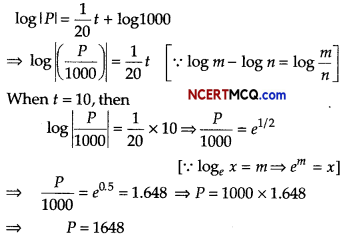





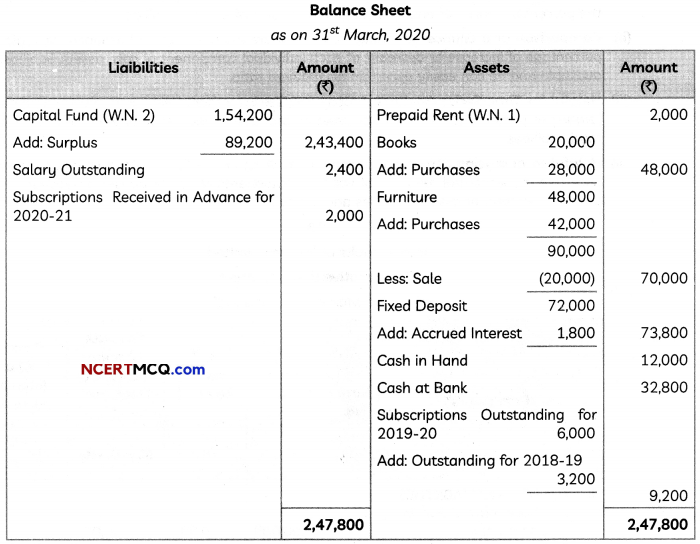
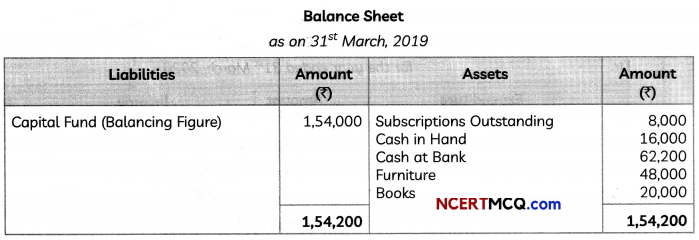
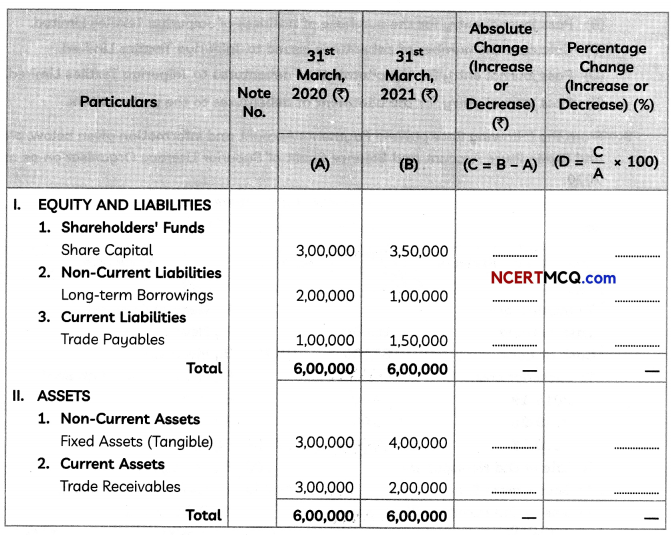
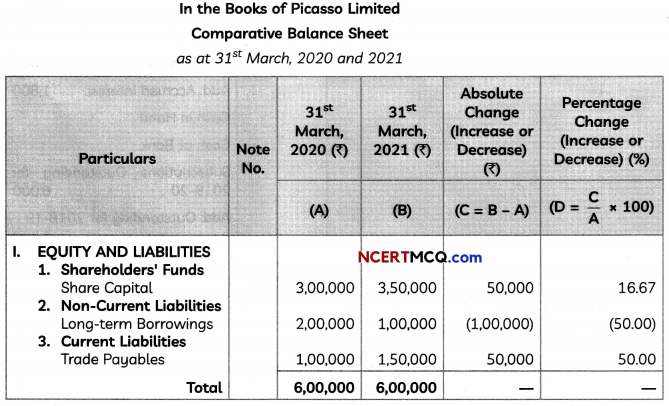
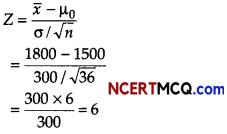

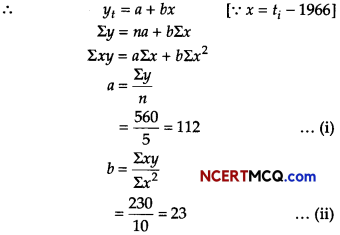
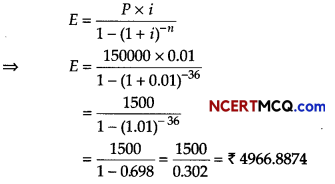
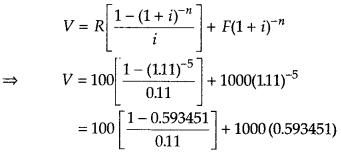
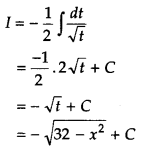
 (2)
(2)