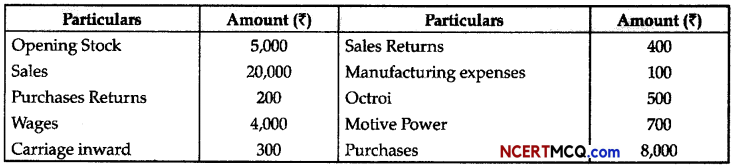
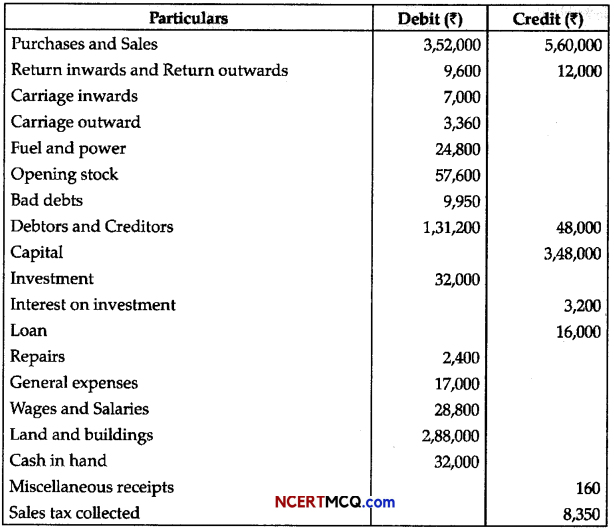
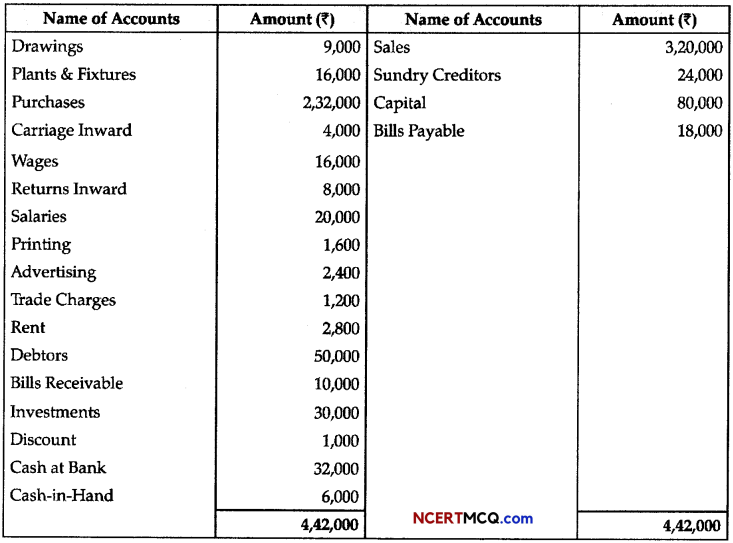
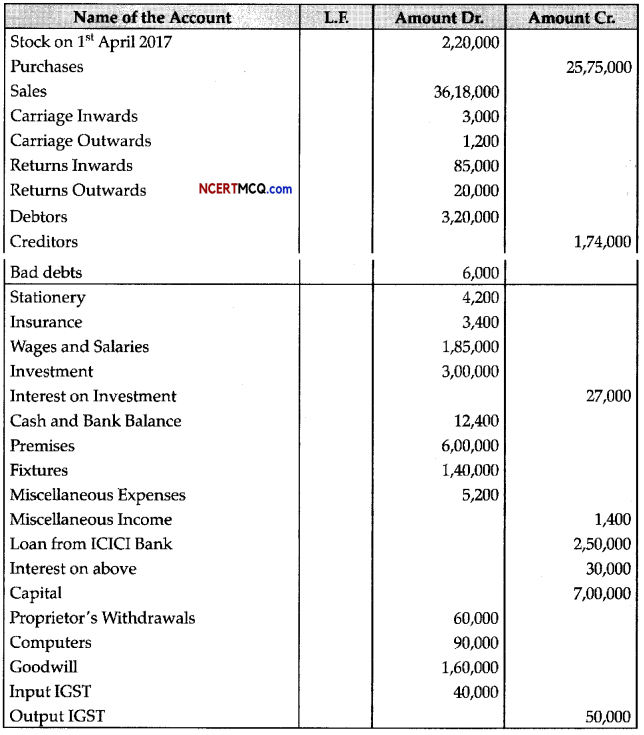
Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 3 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Term 2 Set 3 for Practice
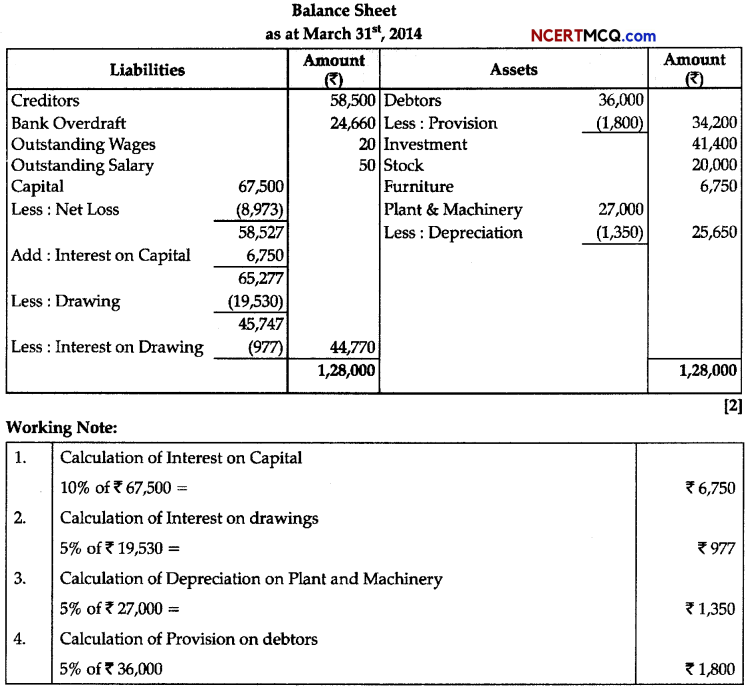
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks : 35
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections of 23 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Sedion-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
![]()
Section – A
(2 Marks)
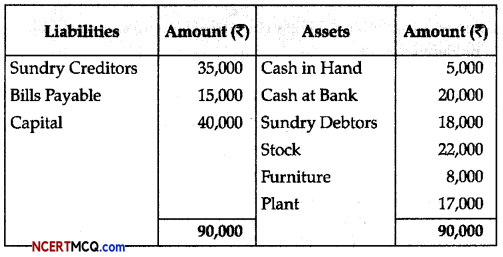
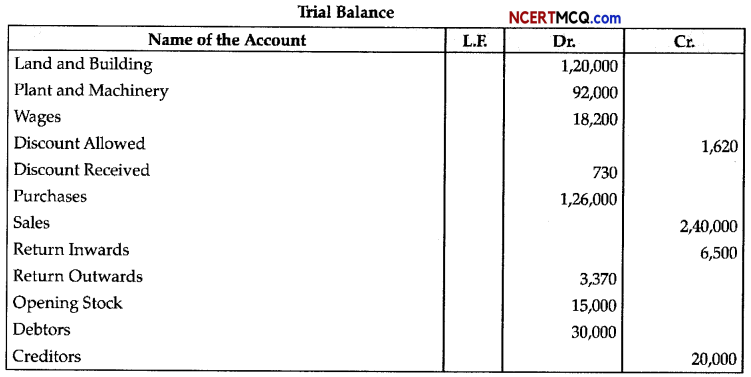
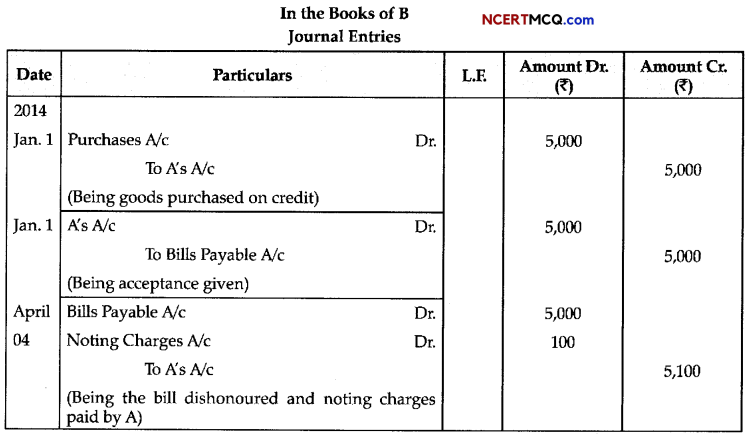
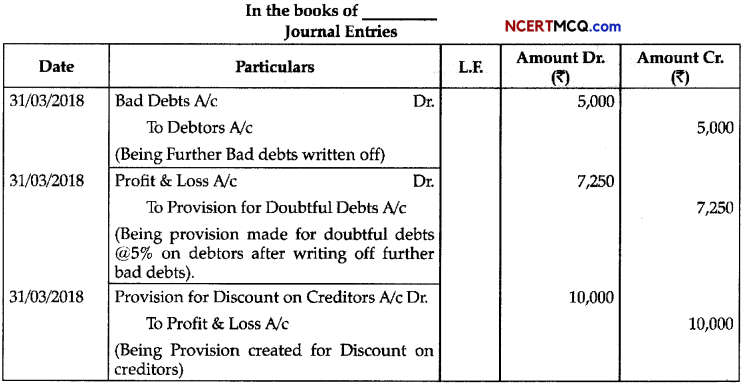
Question 1.
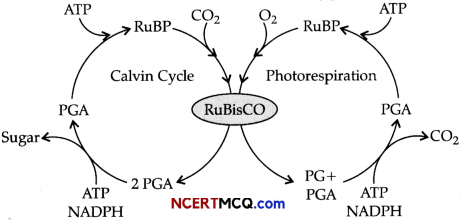
Study the given diagram.
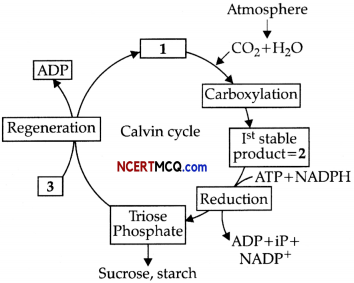
(a) Identify the name of the cycle.
(b) Name the labels: 1,2 and 3.
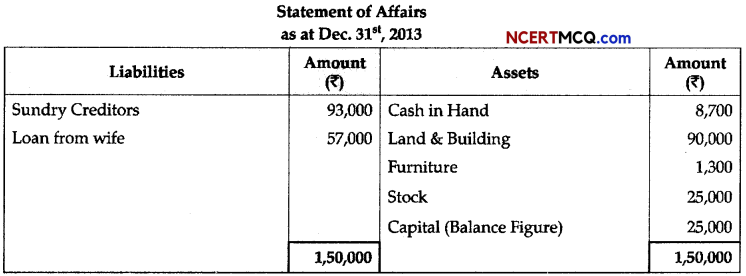
Question 2.
There are two types of cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic. One occurs in the presence of oxygen (aerobic), and one occurs in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic). Both begin with glycolysis – the splitting of glucose.
The energy yield in terms of ATP is higher in aerobic respiration than that of during anaerobic respiration. Explain.
OR
Even though a very few cells in a C4 plant carry out the biosynthetic – Calvin pathway, yet they are highly productive. Can you discuss why?
![]()
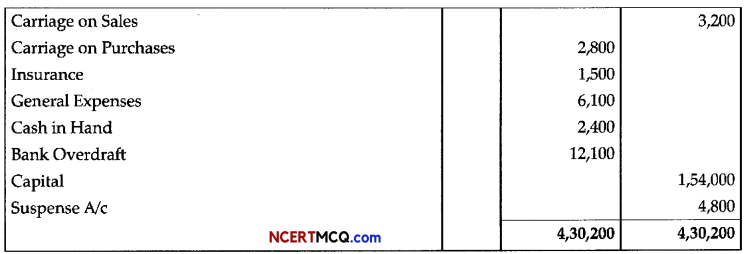
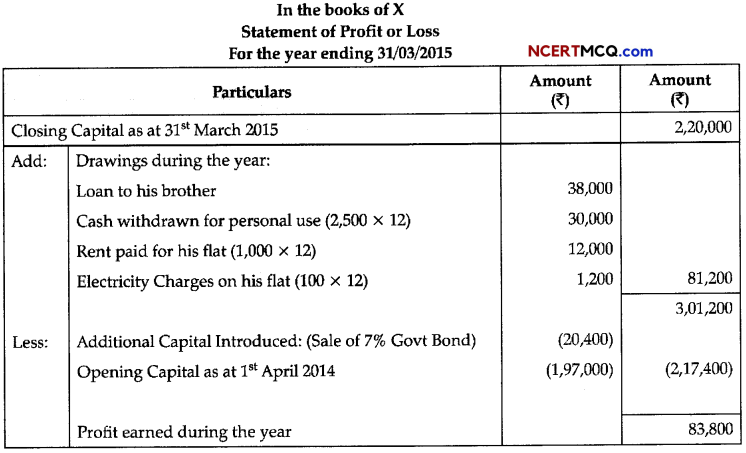
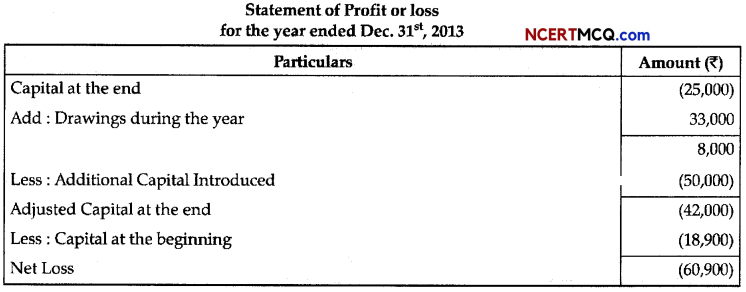
Question 3.
Plant growth regulators (PGRs) have innumerable practical applications. Name the PGRs you should use to: ED
(a) Increase yield of sugar cane.
(b) Promote lateral shoot growth.
(c) Cause sprouting of potato tuber.
(d) Inhibit seed germination.
Question 4.
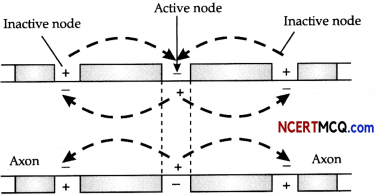
Radha was running on a treadmill at a great speed for 15 minutes continuously. She stopped the treadmill and abruptly came out. For the next few minutes, she was breathing heavily/fast. By reading this statement, answer the following questions:
(a) What happened to her muscles when she did strenuous exercise?
(b) What is the effect of this exercise on her breathing rate?
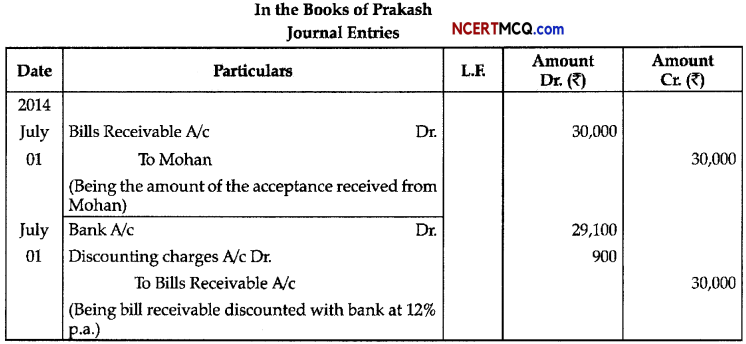
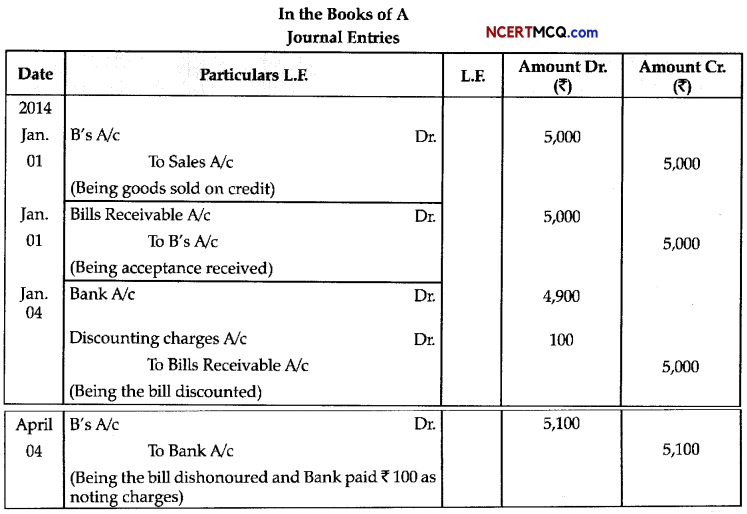
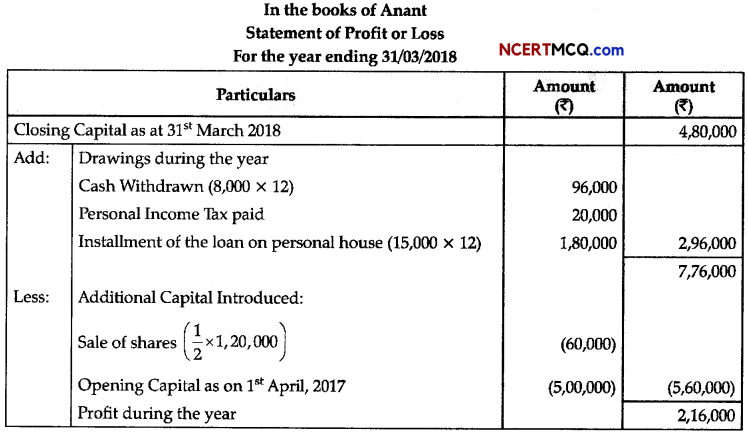
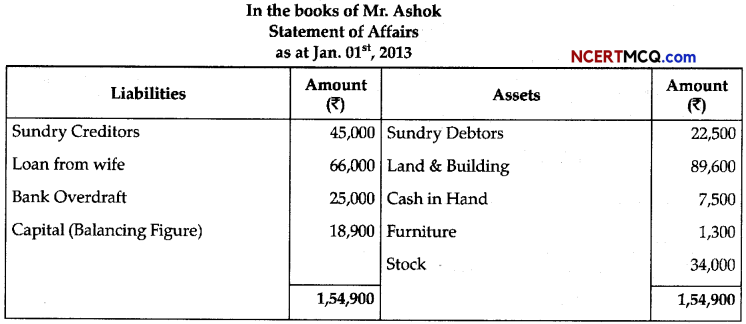
Question 5.
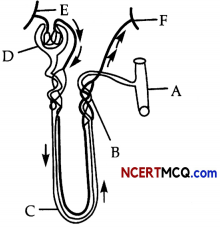
The diagram given below is of Actin filament.
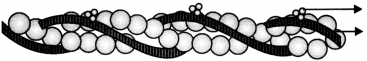
(a) Label the different components of actin filament. (1)
(b) What is the source of energy for the contraction of muscles? (1)
![]()
Question 6.
Diabetes is known as one of the major causes of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, etc. It is a key fact mentioned in WHO global report, that this disease could be treated and its consequences can be avoided or delayed with diet, physical activity, medication, regular screening and treatment for complications.
Explain the differences between Diabetes mellitus and Diabetes insipidus.
OR
Glucocorticoids hormones are secreted by the middle region of the adrenal cortex. State the importance of glucocorticoids in humans.
Section – B
(3 Marks each)
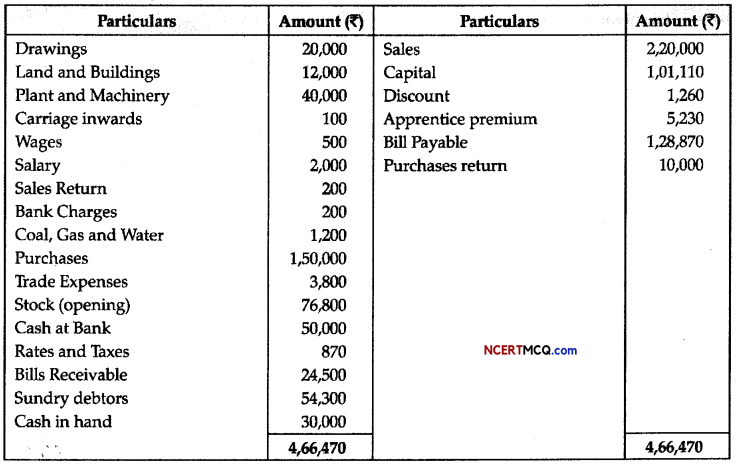
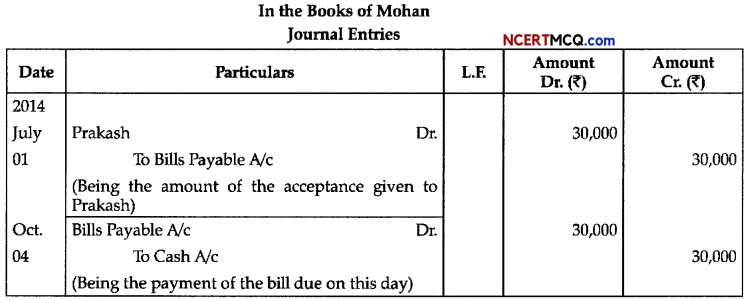
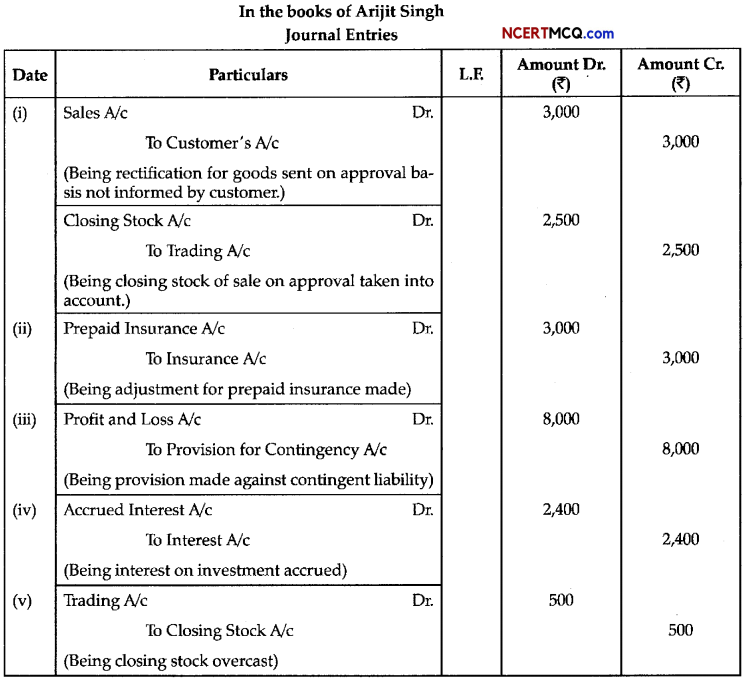
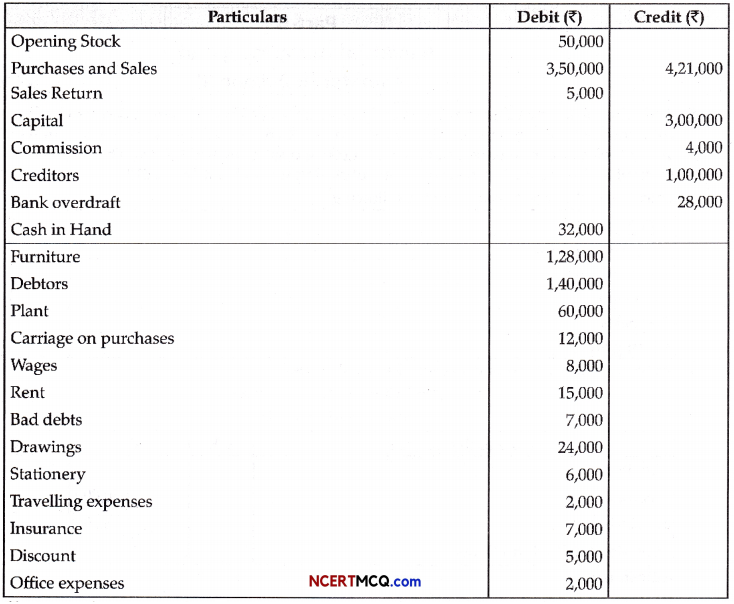
Question 7.
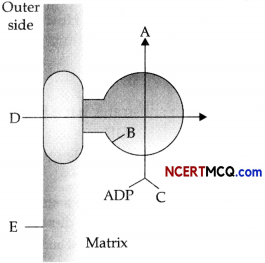
In the following flow chart, replace the symbols a, b, c and d with appropriate terms. Name the process.
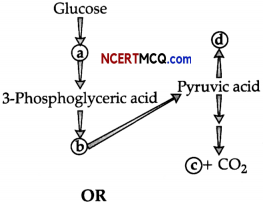
The diagram below represents the substrate-level phosphorylation reaction. In substrate-level phosphorylation reactions, the phosphate group of an intermediate reactant is transferred to an ADP molecule to synthesize ATP.
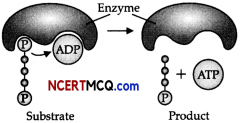
How is ATP produced during glycolysis is a result of substrate-level phosphorylation? Explain.
![]()
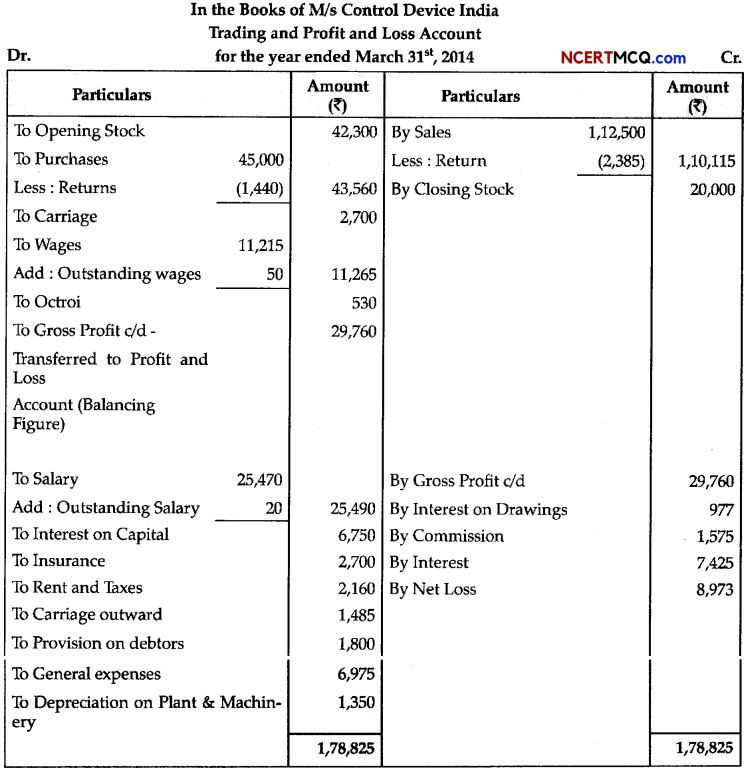
Question 8.
Photorespiration is a process which involves loss of fixed carbons as CO2 in plants in the presence of light. Chloroplast, peroxisome and mitochondria are three cellular organelles involved in photorespiration. Mention the various steps of photo respiratory pathway.
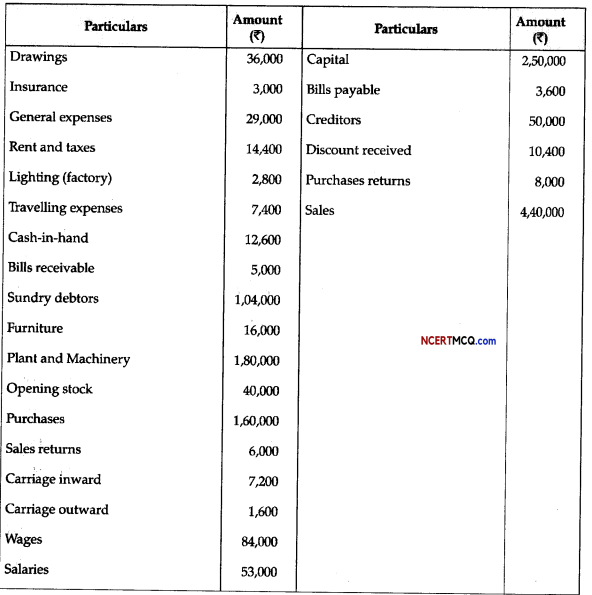
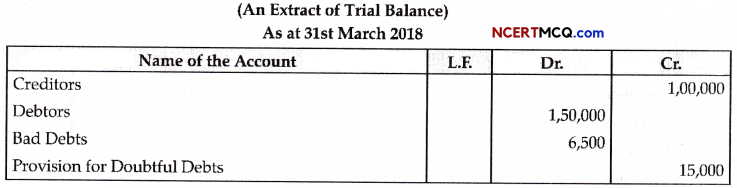
Question 9.
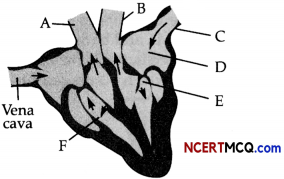
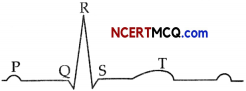
(a) Given below is the diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG.
(i) Label the different peaks of an ECG.
(b) What does the T wave in a normal electrocardiogram indicates ? (1)
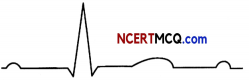
![]()
Question 10.
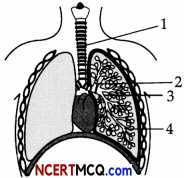
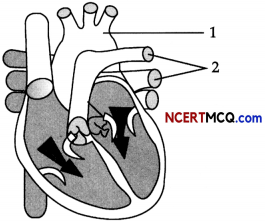
The given diagram shows the lungs of a normal human being. In mammals, the lungs replace the skin very effectively as a respiratory organ.
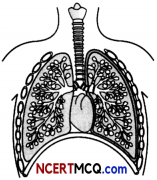
Explain by giving three reasons.
Question 11.
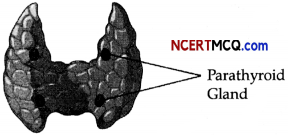
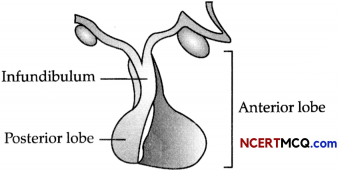
On an educational trip to Uttaranchal, Ketki and her friends observe that many local people were having swollen necks. Please help Ketki and her friends to find out the solutions to the following questions.
(a) Which probable disease are these people suffering from?
(b) How is it caused?
(c) Do this condition have any effect on pregnancy? If yes, then explain those effects.
![]()
Question 12.
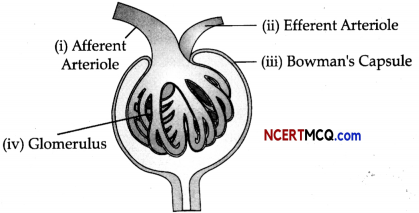
The diagram given below is that of a structure present in a human kidney.
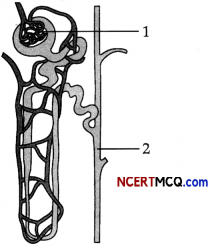
(a) Name the part labelled as 1. What is the liquid entering in it called? (1)
(b) Name the two substances present in this liquid that are re-absorbed in the tubule. (1)
(c) Mention the three main steps involved in the formation of the fluid mentioned in (b) above. (1)
Section – C
(5 Marks)
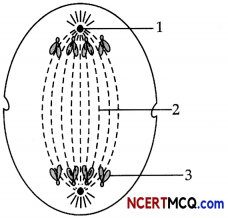
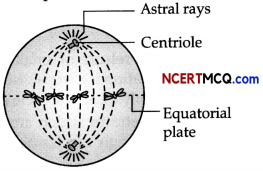
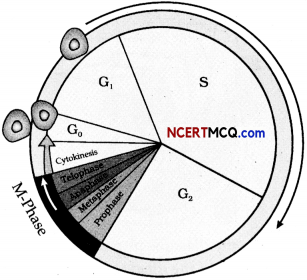
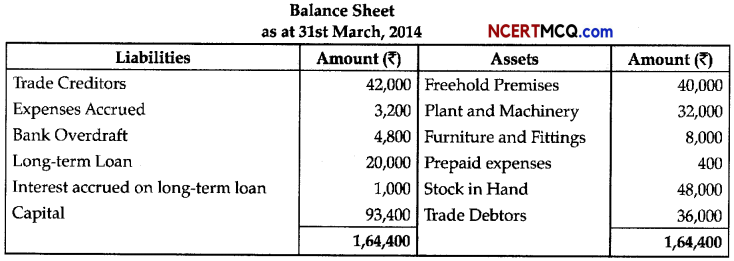
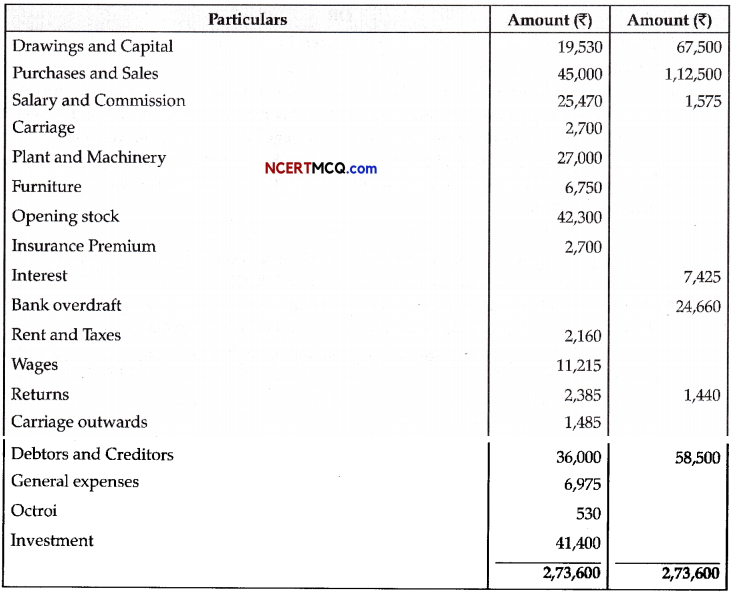
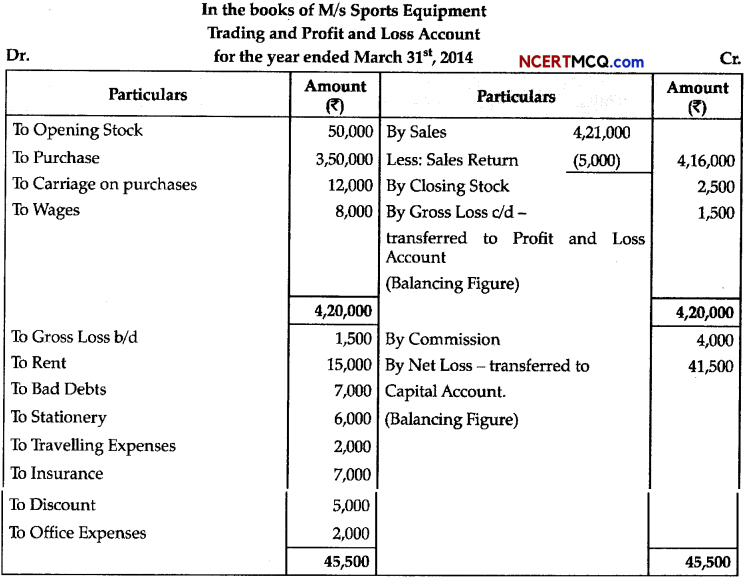
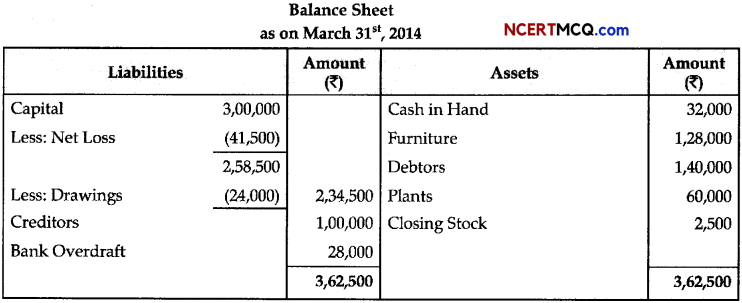
Question 13.
During a class fest, biology teacher shown a diagram representing the stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell and asked students to examine it carefully and answer the questions which follow.
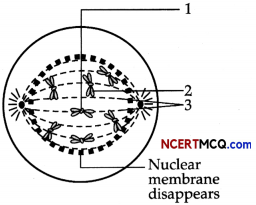
(a) Identify the stage. Give one reason in support of your answer. (1)
(b) Name the cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’. (1)
(c) Name the parts labeled 1,2 and 3. (1)
(d) Name the stage that comes after the one shown here. How is that stage identified? (2)
OR
The fusion of two gametes during sexual reproduction, each with a complete haploid set of chromosomes results in the production of offspring. Gametes are formed from specialised diploid cells. This type of division is called meiosis. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half which results in the production of haploid daughter cells. This cell division ensures the production of haploid phase in the life cycle of sexually reproducing organisms whereas fertilization restores the diploid phase. Meiosis occurs during gametogenesis in plants and animals. This leads to the formation of haploid gametes.
![]()
(a) Mention two points of difference between mitosis and meiosis with regard to:
(i) The number of daughter cells produced.
(ii) The chromosome number in the daughter cells. (2)
(b) Distinguish between metaphase of mitosis and metaphase-I of meiosis. (2)
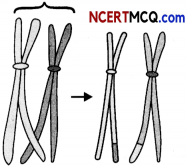
(c) Name the stage of cell cycle at which one of the following events occur:
(i) Centromere splits and chromatids separate.
(ii) Pairing between homologous chromosomes takes place. (1)