Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Geography with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Geography Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks : 35
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 5 sections A, B, C, D & E.
- In Section A question number 1 to 3 are Very Short Answer Type Questions. Attempt any 3 Questions.
- In Section B question number 4 is Source Based Question.
- In Section C question number 5 &6 are Short Answer Based Questions.
- In Section D question number 7 to 9 are Long Answer Based Questions.
- In Section E question number 10 is a Map Based Question.
Section – A
(Very Short Answer Type Questions) (2 x 3 = 6)
(Attempt All Questions)
Question 1.
What is soil made up of? [2]
OR
Differentiate between gentle slope and steep slope. [2]
Answer:
Soil is made up of the following things:
(i) Clay: It is the smallest particle of broken rock in soil , less than .0002 mm in diameter, so it is fine dust. When wet, the individual particles stick together to form a solid mass. When they dry , they can bake to a hard crust. Clay holds water that does not drain away.
(ii) Silt: It is slightly larger pieces of rock than clay. It is also soft and smooth, with individual pieces close together. It too holds a lot of water, but the slightly larger particles make it a little better at draining then clay.
(iii) Sand: It is small piece of rock (2mm to ,05mm diameter) such as quartz or sandstone. Sand particles are large enough to allow water to drain easily, but they do not hold water and are easily blown around when dry.
(iv) Stones, rocks and boulders: They are larger pieces of rock which are too big to form part of the soil but are found in many gardens. Under the surface layer of soil, they can help drainage.
Commonly Made Error:
The students try to attempt the question without understanding the physical makeup of the soil:
Answering Tip:
Before attempting the question, student should be aware that the soil is made up of mainly of mineral particles, organic materials, air, water and living organisms.
Or
| Gentle Slope | Steep Slope |
| 1. Slope of 5% of the land is called gentle slope. | 1. Slope of 10% of the land is called steep slope. |
| 2. In gentle slopes the change in elevation is gradual. | 2. The staseep slopes suddenly slopes up and down. |
| 3. On gentle slopes water tends to move slowly. Soils tend to be thicker, more infiltration can occur. | 3. On steep mountain sides, water tends to move downward more rapidly. |
![]()
Question 2.
What cause the occurrence of tides? [2]
Answer:
- The moon’s gravitational pull to a great extent and to a lesser extent the sun’s gravitational pull, are the major causes for the occurrence of tides.
- Another factor is centrifugal force, which is the force that acts to counter the balance the gravity. Together, the gravitational pull and the centrifugal force are responsible for creating the two major tidal bulges on the earth.
Question 3.
Why is ozone an important constituent of atmosphere? [2]
Answer:
Ozone is an important component of the atmosphere because:
- It absorbs the ultra-violet rays radiating from the sun.
- It prevents them from reaching the surface of the earth.
Section – B
Source Based Question (1 x 3 = 3)
Question 4.
Easterly Jet Stream and Tropical Cyclones:
The easterly jet stream steers the tropical depressions into India. These depressions play a significant role in the distribution of monsoon rainfall over the Indian subcontinent. The tracks of these depressions are the areas with the highest rainfall in India. The frequency at which these depressions visit India, their direction and their intensity go a long way in determining the rainfall pattern during the southwest monsoon period.
Attempt All Questions
(i) What role does easterly jet stream play in bringing rainfall? [1]
Answer:
The easterly jet stream steers the tropical depressions into India. These depressions play a significant role in the distribution of monsoon rainfall over the Indian subcontinent.
(ii) What factors determine the rainfall pattern during the southwest monsoon period in India? [1]
Answer:
The easterly jet stream steers the tropical depressions into India. The tracks of these depressions are the areas with highest rainfall in India. The frequency at j which these depressions visit India, their direction, and their intensity, all go a long, way in determining the rainfall pattern during the south – west monsoon period.
![]()
(iii) Which period is referred to as the ‘Southwest Monsoon’ period in India? [1]
Answer:
The period June to September is referred to as the ‘Southwest Monsoon’ period.
Section – C
Short Answer Type Questions (2 x 3 = 6)
Question 5.
What is the economic role of biodiversity. [3]
Answer:
1. Crop diversity: For all humans,biodiversity is an important resource in their day-to-day life. One important part of biodiversity is ‘crop diversity’,which is also called agrobiodiversity.
2. Manufacturing: Biodiversity is seen as a reservoir of resources to be drawn j upon for the manufacture of food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic products. This concept of biological resources is responsible for the deterioration of biodiversity.
3. Economic diversity: At the same time, it is also the origin of new conflicts dealing with rules of division and appropriation of natural resources. Some of the important economic commodities that biodiversity supplies to humankind are: food crops, livestock, forestry, fish, medicinal resources, etc. Spatial distribution of insolation on the earth’s surface:
Question 6.
What do you know about the spatial distribution of insolation on the earth’s surface? [3]
OR
How many types of the front are there? Explain each of them. [3]
Answer:
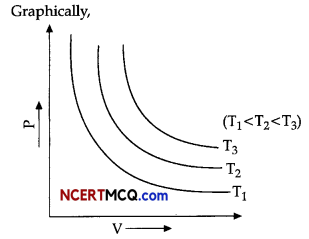
1. The insolation received at the surface varies from about 320 Watt/m² in the tropics to about 70 Watt/ m² in the poles.
2. Maximum insolation is received over the subtropical deserts, where the j cloudiness is the least. The Equator receives comparatively less insolation than the tropics.
3. Generally, at the same latitude the insolation is more over the continent than over the oceans. In winter the middle and higher latitudes receive less radiation than in summer.
Or
There are four different types of front:
1. Stationary Front: When the front remains stationary, it is called a stationary front.

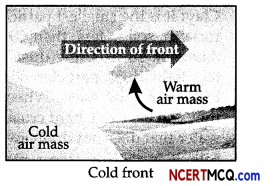
2. Cold Front: When the cold air moves towards the warm air mass, its contact zone is called the cold front.
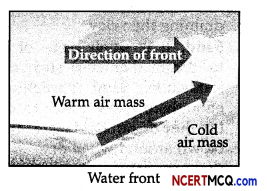
3. Warm Front: When the warm air mass moves towards the cold air mass, the contact zone is called the warm front.
4. Occluded Front: It is formed when a warm air mass gets caught between two cold air masses. The warm air mass rises as the cool air masses push and meet in the middle. The temperature drops as the warm air mass is occluded, or “cut off,” from the ground and pushed upward.

Section – D
Long Answer Type Questions (3 x 5 = 15)
Question 7.
What are the characteristics of monsoonal rainfall? [5]
Answer:
Characteristics of monsoon rainfall:
(i) Rainfall received from the southwest monsoons is seasonal, which occurs between June and September.
(ii) Monsoonal rainfall is largely governed by relief or topography. For instance, the windward side of the Western Ghats register a rainfall of over 250 cm. Again, the heavy rainfall in the north eastern states can be attributed to their hill ranges and the Eastern Himalayas.
(iii) The monsoon rainfall has a declining trend with increasing distance from the sea. Kolkata receives 119 cm during the southwest monsoon period, Patna 105 cm, Allahabad 76 cm and Delhi 56 cm.
(iv) The monsoon rains occur in wet spells of few days duration at a time. The wet spells are interspersed with rainless interval known as ‘breaks’. These breaks in rainfall are related to the cyclonic depressions mainly formed at the head of the Bay of Bengal, and their crossing into the mainland. Besides the frequency and intensity of these depressions, the passage followed by them determines the spatial distribution of rainfall.
(v) The summer rainfall comes in a heavy downpour leading to considerable run off and soil erosion. Monsoons play a pivotal role in the agrarian economy of India because over three-fourths of the total rain in the country is received during the southwest monsoon season.
(vi) Its spatial distribution is also uneven which ranges from 12 cm to more than 250 cm. The beginning of the rains sometimes is considerably delayed over the whole or a part of the country.
(vii) The rains sometimes end considerably earlier than usual, causing great damage to standing crops and making the sowing of winter crops difficult.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the factors that control the temperature distribution of any place. [5]
OR
Explain the tropical cyclone with the help of a diagram. [5]
Answer:
The factors that control the temperature distribution of any place:
(i) The latitude:
The latitude can be explained as an angular distance of a place North or South of the earth’s
sequator or of the equator of celestial object usually expressed in degrees and minutes. The temperature of a place depends on the insolation received. The insolation varies according to the latitude hence the temperature also varies accordingly.
(ii) The altitude:
The atmosphere is indirectly heated by terrestrial radiation from below. Therefore, the places near the sea-level record higher temperature than the places situated at higher elevations. In other words, the temperature generally decreases with increasing height. The rate of decrease of temperature with height is termed as the normal lapse rate. It is 6.5°C per 1,000 m.
(iii) Distance from the sea:
Another factor that influences the temperature is the location of a place concerning to the sea. Compared to land, the sea gets heated slowly and loses heat slowly. Land heats up and cools down quickly. Therefore, the variation in temperature over the sea is less compared to land. The places situated near the sea come under the moderating influence of the sea and land breezes which moderate the temperature.
(iv) Air mass:
An air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapour content. Air masses may cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. Like the land and sea breezes, the passage of air masses also affects the temperature. The places, which come under the influence of warm air masses experience higher temperature and the places that come under the influence of cold air masses experience low temperature.
(v) Ocean currents:
An ocean current is a seasonal directed movement of sea water generated by forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, the Coriolis effect, temperature and salinity differences, while tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the sun and moon, the places located on the coast where the warm ocean currents flow record higher temperature than the places located on the coast where the cold currents flow.
Or
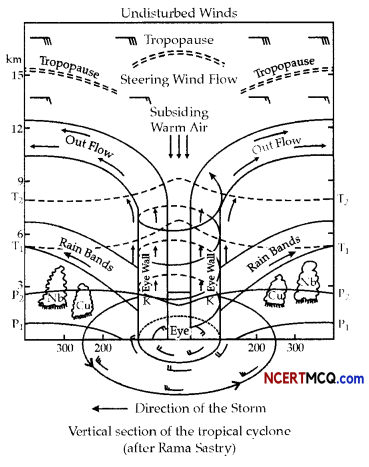
Tropical cyclones are violent storms that originate over oceans in tropical areas and move over to the coastal areas bringing about large scale destruction caused by violent winds, very heavy rainfall and storm surges. This is one of the most devastating natural calamities. They are known as Cyclones in the Indian Ocean, Hurricanes in the Atlantic, Typhoons in the Western Pacific and South China Sea, and Willy-willies in the Western Australia. Tropical cyclones originate and intensify over warm tropical oceans. The conditions favourable for the formation and intensification of tropical storms are:
- Large sea surface with temperature higher than 27° C.
- Presence of the Coriolis Force.
- Small variations in the vertical wind speed.
- A pre-existing weak low-pressure area or low-level-cyclonic circulation.
- Upper divergence above the sea level system.
The energy that intensifies the storm, comes from the condensation process in the towering cumulonimbus clouds, surrounding the centre of the storm. With continuous supply of moisture from the sea, the storm is further strengthened. On reaching the land the moisture supply is cut off and the storm dissipates. The place where a tropical cyclone crosses the coast is called the landfall of the cyclone. The cyclones, which cross 20°N latitude generally, recurve and they are more destructive. A mature tropical cyclone is characterized by the strong spirally circulating wind around the centre, called the eye. The diameter of the circulating system can vary between 150 and 250 km. The cyclone creates storm surges and they inundate the coastal low lands. The storm peters out on the land.
![]()
Question 9.
What are clouds? Explain the various types of clouds. [5]
Answer:
Cloud is a mass of minute water droplets or tiny crystals of ice formed by the condensation of the water vapour in free air at considerable elevations. As the clouds are formed at some height over the surface of the earth, they take various shapes.
According to their height, expanse, density and transparency or opaqueness clouds are grouped under four types:
1. Cirrus: Cirrus clouds are formed at high altitudes (8,000 – 12,000m). They are thin and detached clouds having a feathery appearance. They are always white in colour.
2. Cumulus: Cumulus clouds look like cotton wool. They are generally formed at a height of 4,000-7,000 m. They exist in patches and can be seen scattered here and there. They have a flat base.
3. Stratus: As their name implies, these are layered clouds covering large portions of the sky. These clouds are generally formed either due to loss of heat or the mixing of air masses with different temperatures.
4. Nimbus: Nimbus clouds are black or dark grey. They form at middle levels or very near to the surface of the Earth. These are extremely dense and opaque to the rays of the sun. Sometimes, the clouds are so low that they seem to touch the ground. Nimbus clouds are shapeless masses of thick vapours.
Section – E
Map Based Questions (1 x 5 = 5)
Question 10.
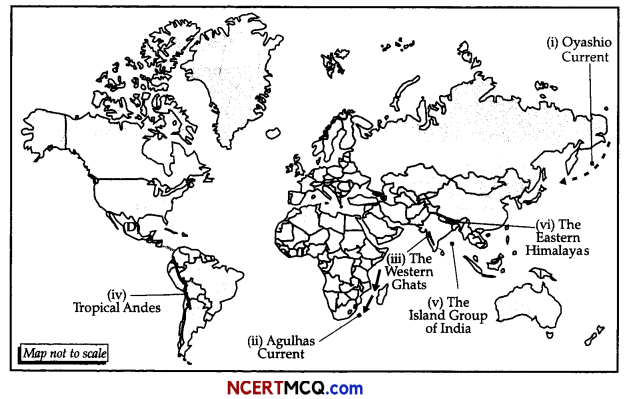
On the outline map of the world indicate and mark the following features. (Attempt any 5)
(i) The cold current that meet the warm Kuroshio current near the coast of Japan.
(ii) The surface oceanic current that forms the western boundary current of the southern Indian Ocean.
(iii) Anamalai hills, Nilgiri hills and Cardamom hills are all a part of these Ghats.
(iv) The ecological hotspot running along the entire western part of south America.
(v) The Island Group of India.
(vi) The ecological hotspot that extend from Nepal across North-east India, Bhutan to China and northern Myanmar.
Answer: