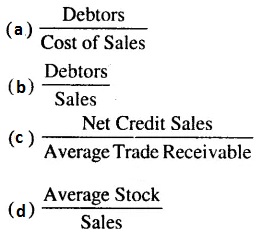
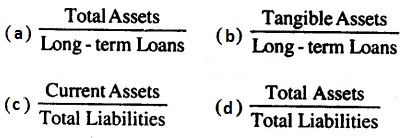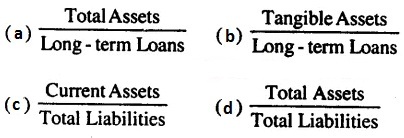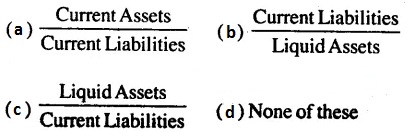Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Directing with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Directing Class 12 Business Studies MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Directing MCQ With Answers
Business Studies Class 12 Chapter 7 MCQs On Directing
Question 1.
Which one of the following is an element of directing?
(a) Delegating authority
(b) Designing organisation structure
(c) Communication
(d) Designing control system
Answer
Answer: (c) Communication
Question 2.
Motivation is not
(a) a complex process.
(b) related to satisfaction
(c) an easy process.
(d) a goal-directed behaviour
Answer
Answer: (c) an easy process.
Question 3.
Need hierarchy theory of motivation has been given by
(a) Maslow.
(b) Fayol.
(c) Taylor.
(d) Koontz.
Answer
Answer: (a) Maslow.
Question 4.
Which one of the following is not a financial incentive?
(a) Bonus
(b) Provident Fund
(c) Co-partnership
(d) Challenging job
Answer
Answer: (d) Challenging job
Question 5.
Which one of the following is a non-financial incentive?
(a) Recognition
(b) Perquisite
(c) Retirement benefit
(d) Stock option
Answer
Answer: (a) Recognition
Question 6.
Leadership is based on a superior’s
(a) authority.
(b) responsibility
(c) accountability.
(d) pesuasive Communication
Answer
Answer: (d) pesuasive Communication
Question 7.
Encoding is related to
(a) converting message into symbols.
(b) converting symbols into machine
(c) transmitting message.
(d) receiving symbols
Answer
Answer: (a) converting message into symbols.
Question 8.
Grapevine is a form of
(a) formal communication.
(b) channel of communication
(c) informal communication.
(d) barrier to communication
Answer
Answer: (c) informal communication.
Question 9.
Which one of the following is a semantic barrier?
(a) Organisational policy
(b) Lack of attention
(c) Technical jargon
(d) Status
Answer
Answer: (c) Technical jargon
Question 10.
___ is the process of stimulating people to engage in goal-directed behaviour.
(a) Communication
(b) Motivation
(c) Directing
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Motivation
Question 11.
The channel of communication which is transmitted through informal channels is called ___
(a) Horizontal communication
(b) Formal communication
(c) Grapevine
(d) Gang plank
Answer
Answer: (c) Grapevine
Question 12.
___ aims at instructing, guiding, motivating people to achieve the desired results.
(a) Communication
(b) Directing
(c) Motivating
(d) Organising
Answer
Answer: (b) Directing
Question 13.
___ is the process of converting a message into symbols.
(a) Encoding
(b) Decoding
(c) Coding
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
Answer: (a) Encoding
Question 14.
Directing flows in ___ direction.
(a) Upward
(b) Downward
(c) Diagonal
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer
Answer: (b) Downward
Question 15.
___ is the process of exchanging information and understanding between two or more persons.
(a) Directing
(b) Leadership
(c) Communication
(d) Motivation
Answer
Answer: (c) Communication
Question 16.
Directing takes place at ___ levels of management.
(a) Top
(b) Middle
(c) Lower
(d) All
Answer
Answer: (d) All
Question 17.
Identify the style of leadership in which the superior uses file forces from within the groups in order to establish control.
(a) Autocratic leadership
(b) Democratic leadership
(c) Laissez-faire leadership
(d) Authoritarian leadership
Answer
Answer: (b) Democratic leadership
Question 18.
Dheeraj Madan works as a Human Resource Manager in Busybee Limited. He gives due care in designing jobs, so that it offers a meaningful work experience by assuming a diversity of work content requiring higher level of knowledge. Identify the type of incentive being adopted by the company.
(a) Employee recognition programme
(b) Organisational climate
(c) Career advancement opportunities
(d) Job enrichment
Answer
Answer: (c) Career advancement opportunities
Question 19.
During the year 2018, Halla Walla Limited made surplus profits due to growing reputation of the business as a result of sincerity of its employees. In order to give due recognition to its employees and motivate them to continue with the good work, the company decided to give a certain percentage of profits to them. Identify the type of financial incentive being adopted by the company.
(a) Perquisites
(b) Productivity linked wage incentives
(c) Co-partnership
(d) Profit sharing
Answer
Answer: (d) Profit sharing
Question 20.
Yamini received a special gold coin from her school management for exceptionally good board result of her students in her subject. Identify the need of Yamini being fulfilled as per Maslow’s Need Heirarchy Theory.
(a) Esteem Needs
(b) Belonging Needs
(c) Self Actualisation Needs
(d) Basic Physiological Needs
Answer
Answer: (a) Esteem Needs

True or False
State with reasons whether the following statements are True or False.
1. Leadership and motivation are the two elements of directing.
Answer
Answer: True; leadership and motivation are the two elements of directing.
2. Directing takes place at the top, middle and bottom level of management.
Answer
Answer: True; directing takes place at all levels of management.
3. Encoding refers to converting symbols received by the receiver into meaning.
Answer
Answer: False; decoding is converting symbols received by the receiver into meaning.
4. Democratic leadership style involves giving orders by a superior to his subordinates and expecting that his orders will be obeyed by them.
Answer
Answer: False; the given leadership style is authoritative leadership style.
5. Formal and Informal communication flow through officially prescribed channels of communication.
Answer
Answer: False; only formal communication flows through officially prescribed channels of communication.
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 7 Directing with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Directing CBSE Class 12 Business Studies MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 12 Business Studies MCQ:
- Nature and Significance of Management Class 12 MCQ
- Principles of Management Class 12 MCQ
- Business Environment Class 12 MCQ
- Planning Class 12 MCQ
- Organising Class 12 MCQ
- Staffing Class 12 MCQ
- Directing Class 12 MCQ
- Controlling Class 12 MCQ
- Financial Management Class 12 MCQ
- Financial Markets Class 12 MCQ
- Marketing Management Class 12 MCQ
- Consumer Protection Class 12 MCQ
- Entrepreneurship Development Class 12 MCQ