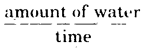Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 11 with Answers Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-8-science/
Online Education for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions and Answers Force and Pressure
Force And Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Question 1.
Force per unit area is called as
Answer:
Pressure.
Force And Pressure Class 8 Questions Answers Question 2.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate word: While sieving grains, small pieces fell down from sieve due to.
Answer:
gravity
Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions And Answers Question 3.
Write the answer in one sentence. Where do we apply force while walking?
Answer:
On the ground in backward direction.
Force And Pressure Extra Questions Question 4.
Write the name of the force which has changed the shape of the dough and rolled it into flat chapati.
Answer:
Muscular force.
![]()
Class 8 Force And Pressure Extra Questions Question 5.
What happens when a force acts on an object?
Answer:
The force acting on an object changes its state, form or direction.
Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Extra Questions Question 6.
What is magnitude of the state of rest?
Answer:
It is zero.
Class 8 Science Ch 11 Extra Questions Question 7.
What is required to keep the bob. moving along a circular path with a constant speed?
Answer:
Force.
Force And Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions And Answers Question 8.
Give an example of change of shape by applying a force. ,
Answer:
When an inflated balloon is pressed between two palms, it is deshaped.
Class 8 Force And Pressure Question Answer Question 9.
Which of the following is a contact force
(i) muscular force or
(ii) gravitational force?
Answer:
(i) Muscular force.
Force And Pressure Class 8 Notes Questions And Answers Question 10.
Why does a ball rolling along the ground gradually slows down and finally comes to rest?
Answer:
Frictional force acts on it which opposes the motion of a body.
Force And Pressure Class 8 Questions Answers Pdf Question 11.
Which frictional force is smaller, the force due to friction between two solid surfaces or between liquids, or friction due to air?
Answer:
The force of friction due to air is very small, nearly negligible.
![]()
Force And Pressure Class 8 Important Questions Answers Question 12.
Is it essential for the agent applying a force on an object to be always in contact with it?
Answer:
No, magnetic force and electrostatic force are examples where there is no contact.
Extra Questions Of Force And Pressure Class 8 Question 13.
Why do objects fall from the height?
Answer:
It happens due to the gravitational force of the earth acting on the objects.
Extra Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question 14.
How are winds and cyclones caused?
Answer:
They are caused by the differences in air pressure.
Extra Questions On Force And Pressure Class 8 Question 15.
What is the formula of pressure?
Answer:
Force exerted Area on which force is exerted.
Question 16.
Is attraction between the piece of iron and a magnet a pull? What about repulsion between two similar poles of two magnets?
Answer:
Yes, attraction between the opposite poles of two magnets is a pull and the repulsion between two similar poles is a push.
Question 17.
What causes motion in objects?
Answer:
The motion imparted to objects is due to the action of force.
Question 18.
What has to happen for a force to come into play?
Answer:
At least two objects must interact for a force to come into play.
![]()
Question 19.
An airplane is flying in the sky. Identify any two forces acting on it.
Answer:
Weight in downward direction Lift in upward direction.
Question 20.
What happens if the force is applied in the direction of motion of the body?
Answer:
If the applied force is in the direction of motion of the body, the speed of the body increases.
Question 21.
What happens if the force is applied in the direction opposite to the motion of the body?
Answer:
If the force is applied in the direction opposite to the motion of a body, then it results in a decrease in the speed of the object. The body may also come in a static state.
Question 22.
What infers the change in state of motion of an object?
Answer:
A change in either the speed of an object, or its direction of motion, or both, is described as a change in its state of motion.
Question 23.
What does the state of rest mean?
Answer:
The state of rest is considered to be the state of zero speed.
Question 24.
What happens to a body in motion along a circle?
Answer:
When a force makes a body to move in a circle, then its velocity changes at every point in the circular path due to change in direction.
![]()
Question 25.
What do you mean by muscular force?
Answer:
The force resulting due to the action of muscles is known as the muscular force.
Question 26.
What does muscular force enable us to do?
Answer:
Muscular force enables us to carry out our physical activities and other tasks. It helps us in movement, locomotion, bending of different parts of our body, lifting, kicking, pushing or pulling objects, etc.
Question 27.
Is muscular force a contact force? Why?
Answer:
Yes, muscular force is a contact force, since muscular force can be applied only when it is in contact with an object.
Question 28.
Where does friction act and what is its direction?
Answer:
Friction acts on all the moving objects and its direction is always opposite to the direction of motion of the object.
Question 29.
Is friction a contact force? Why?
Answer:
Yes, friction is a contact force. Since the force of friction arises due to contact between surfaces.
Question 30.
What do two magnets do on each other when they are brought close?
Answer:
Two magnets with like poles exert a force of repulsion on each other and two unlike poles attract each other. A magnet can exert forces on another magnet without being in contact with each other.
![]()
Question 31.
Can force of gravity act on all distant objects?
Answer:
Yes, force of gravity is not restricted to the near or distant objects. It acts on all the objects.
Question 32.
Do gases exert pressure? Where?
Answer:
The gases also exert pressure. They exert pressure on the walls of the container in-which they are filled.
Question 33.
What are contact and noncontact forces? Give two examples each.
Answer:
Contact forces: A contact force is a force which acts on an object when comes in physical contact with it. The most familiar examples of a contact force are muscular force and frictional force.
Non-contact forces: A non-contact force is a force which acts on an object without coming physically in contact with it. The most familiar examples of a non-contact force are gravitational force and magnetic force.
Question 34.
What is meant by the state of motion and the state of rest?
Answer:
The state of motion of an object is described by its speed and the direction of motion. The state of rest is considered to be the state of zero speed.
![]()
Question 35.
Give some examples to support that application of a force on an object may change its shape.
Answer:
Examples are :
- When a force is applied on an inflated balloon by pressing it between two palms, the shape of the balloon undergoes a change.
- The shape of a ball of dough changes when it is rolled to make a chapati. The roller applies the force in this case.
Question 36.
Define friction. How does friction act?
Answer:
Friction is a kind of force which arises between two surfaces in contact. The two surfaces in contact may be solid, liquid or gaseous.
The force of friction always acts on all the moving objects and its direction is always opposite to the direction of motion.
Question 37.
What is force of gravity? Give some examples to show that it is an attractive force.
Answer:
Objects or things fall towards the earth because it pulls them. This force is called the force of gravity or just gravity. It is an attractive force.
Examples which show that gravity is an attractive force :
- Water begins to flow towards the ground as soon as we open a tap.
- Water in rivers flows downward due to the force of gravity.
Question 38.
Discuss the characteristics of force of gravity;
Answer:
Characteristics of force of gravity:
- The force of gravity is an attractive but non-contact force.
- This force acts on all objects on or near ‘ the surface of the earth.
- The force of gravity acts On all things v including us all the time without their being aware of it.
Question 39.
Why does a car or a scooter come to rest once its engine is switched off?
Answer:
Only frictional force acts immediately after the vehicle is switched off. Vehicles only moves, when their mechanical force exceeds the frictional force.
But when engine is switch off, the mechanical force becomes zero but frictional force persist. This brings vehicle (car or scooter) to rest.
![]()
Question 40.
Write the answer of following questions:
(a) Why is it comfortable to lift a school bag with broad straps than thin straps?
(b) Give an example to show that force can change the shape of an object.
Answer:
(a) Broad straps have larger area and decrease the pressure of the weight of the bag on the shoulders. But if the straps are thin the shoulders will be under large pressure and will be painful. That’s why we feel comfortable with a bag with broad straps.
(b) When we apply a force on an inflated balloon by pressing it between our palms the shape of a balloon changes. When a force is applied on the dough, it is rolled to make a Chapati.
Question 41.
(a) How does the medicine or water enter a dropper? Explain the mechanism.
(b) Name the type of force in the j following cases :
(i) Raindrops falling on the earth.
(ii) Running a comb through dry hair.
(iii) A bar magneto suspended freely.
Answer:
(a) When we press the bulb of a dropper with its nozzle kept in water, air in the dropper is seen to escape in the form of bubbles. On releasing the pressure on the bulb, water gets filled in the dropper. The rise of water in the dropper is due to atmospheric pressure which is acting on the water or the medicine and make it rise in the dropper.
(b)
- Gravitational force or gravity
- Electrostatic or electric force
- Magnetic force.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is the net force acting on the body?

(a) 10 N
(b) 25 N
(c) 0 N
(d) 5 N
Answer:
(d) 5 N.