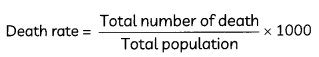Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 11 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Term 2 Set 11 for Practice
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This is a Subjective Question Paper containing 13 questions.
- This paper contains 5 questions of 2 marks each, 5 questions of 3 marks each and 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 30-50 words.
- 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 50-80 words.
- 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
![]()
Question 1.
Ex-post investment means fixed capital with production units during a particular period of time. Defend or refute the statement with valid reason.
OR
Marginal propensity to consume represents the slope of the consumption function. Defend or refute the statement with valid reason. (2)
Question 2.
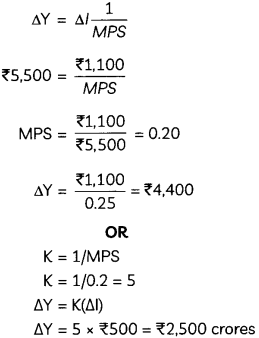
In an economy, 20 percent of increased income is saved. How much will be the increase in income if investment increases by ₹10,000? Calculate.
OR
Estimate the change in final income if Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) is 0.75 and change in initial investment is ₹2,000 crores. (2)
Question 3.
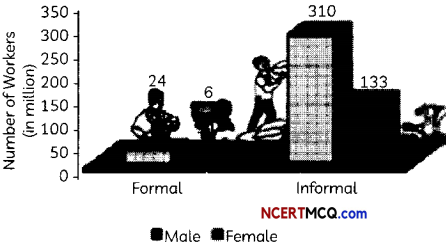
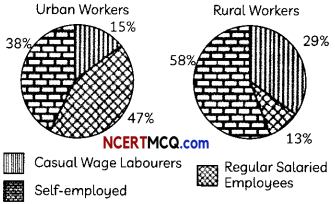
Discuss briefly, the concept of ‘informalisation of workforce’, in the context of Indian economy. (2)
Question 4.
“Sustainable development is the only way that will allow economy to have a proper development.” Justify the statement.
OR
“Infrastructure is the support system on which depends the modern agriculture depends.” Justify the statement. (2)
![]()
Question 5.
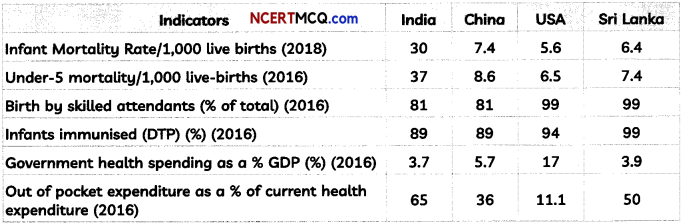
Analyze the following information in reference to India and compare with other countries on the grounds of ‘Government health spending as a % of GDP’.
Question 6.
How will you treat the foLLowing whiLe estimating domestic product of a country?
Give reasons for your answer :
(A) Profits earned by branches of country’s bank in other countries.
(B) Gifts given by an employer to his employees on independence day.
(C) Purchase of goods by foreign tourists.
OR
If the Real Gross Domestic Product is f 400 and Price Index (base=100) is 120, calculate the Nominal Gross Domestic Product. 3
Question 7.
On the basis of below information, compare and contrast India and China’s sectoral contribution towards GVA/GDP. What does it indicate? (3)
| Sector | Contribution to GVS | |
| India | China | |
| Agriculture | 16 | 7 |
| Industry | 30 | 41 |
| Services | 54 | 52 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Read the following case carefully and answer question number 8 and 9 given below:
![]()
India’s ambition of sustaining its relatively high growth depends on one important factor: infrastructure. The country, however, is plagued with a weak infrastructure incapable of meeting the needs of a growing economy and growing population. S&P Global Ratings projects India’s GDP to grow around 8% for the next three fiscal years, among the fastest in large, growing economies. The government also aims to significantly boost the manufacturing sector to contribute an all-time high of about 25% of GDP by 2025, from below 16% currently.
India is striving to improve its manufacturing competitiveness at a time when manufacturing powerhouse China is shifting toward consumption-led growth. China now faces the risk of overcapacity in segments such as port and power. For India, on the other hand, its road to sustainably higher growth and a competitive manufacturing sector goes through robust and reliable national infrastructure, especially in power and transportation.
Question 8.
State and explain the type of infrastructure stated in the above text. (3)
Question 9.
“India is incapable of meeting the needs of a growing economy and growing population.” Explain. (3)
Question 10.
As the examples of India, China and Pakistan show; countries are trying various means to strengthen their own domestic economies. What are the various means by which countries are trying to do so? (3)
![]()
Question 11.
Calculate national income from the following data:
(i) Personal Tax 80
(ii) Private final consumption expenditure 600
(iii) Undistributed profits 30
(iv) Private income 650
(v) Government final consumption expenditure 100
(Vi) Corporate tax 50
(vi) Net domestic fixed capital formation 70
(viii) Net indirect tax 60
Ox) Depreciation 14
(x) Change in stocks (-)10
(xi) Net imports 20
(xii) Net factor income to abroad 10
OR
Suppose the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of Nation X was ₹2,000 crores in 2018 – 19, whereas the Gross Domestic Product of Nation Y in the same year was ₹120,000 crores. If the Gross Domestic Product of Nation X rises to ₹4,000 crores in 2019 – 20 and the Gross Domestic Product of Nation Y rises to ₹200,000 crores in 2019 – 20. Compare the rate of change of GDP of Nations X and Y, taking 2018 – 19 as base year. (5)
Question 12.
(A) Giving reason, state whether following the statement is true or false.
A car covering a distance of 300 km in 5 hours includes both stock as well as flow variable.
(B) ‘Subsidies to the producers, should be treated as transfer payments.’ Defend or refute the given statement with valid reason. (5)
![]()
Question 13.
“India’s GDP contracted 23.9% in the April- June quarter of 2020-21 as compared to same period of 2019-20, suggesting that the lockdown has hit the economy hard”.
State and discuss any two fiscal measures that may be taken by the Government of India to correct the situation indicated in the above news report. (5)