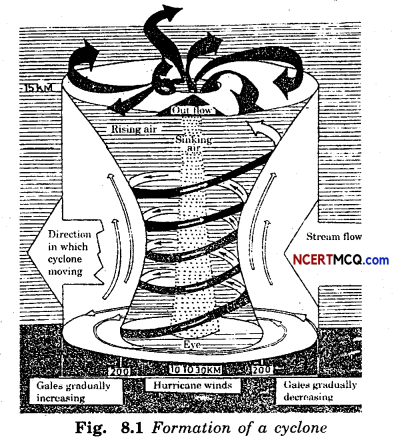
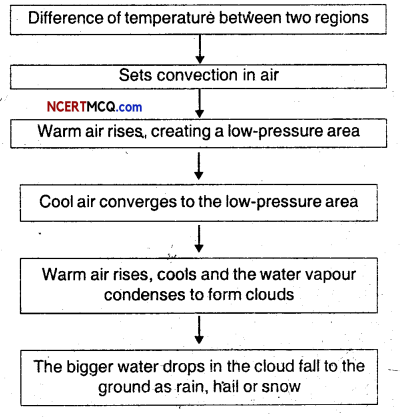
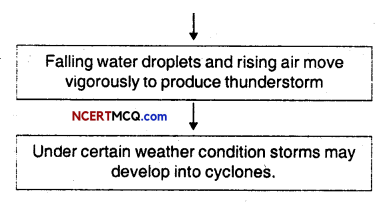
Here we are providing Online Education Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate Class 7 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 7 was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-science/
Online Education for Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions and Answers Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 1.
Who prepares the weather report?
Answer:
The weather reports are prepared by the Meteorological Department of the Govt.
Weather Climate And Adaptation Class 7 Extra Questions Question 2.
What causes the changes in weather?
Answer:
Sun.
Class 7 Science Ch 7 Extra Questions Question 3.
When is the climate of a place called hot?
Answer:
If we find that the temperature at a place is high most of the time, then we say that the climate of that place is hot.
Weather Climate And Adaptation Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 4.
When is the climate of a place called hot and wet?
Answer:
If there is also heavy rainfall along with heat on most of the days at the same place, then we can say that the climate of that place is hot and wet.
![]()
Chapter 7 Science Class 7 Extra Questions Question 5.
Name the location where climate is hot and dry.
Answer:
Rajasthan.
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 6.
Name two countries where there is tropical rainforest.
Answer:
India, Brazil.
Weather, Climate And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Questions And Answer Question 7.
Name one polar animal.
Answer:
Penguin.
Weather Climate And Adaptation Class 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 8.
Which type of paws does a polar bear have?
Answer:
Wide and large.
Questions On Weather And Climate Class 7 Question 9.
What makes penguins good swimmers?
Answer:
Their bodies are streamlined and their feet have Webs, making them good swimmers.
Ncert Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 10.
Name one bird from Siberia that comes to India.
Answer:
Siberian Crane.
![]()
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 11.
Name the various information given on the weather report in newspaper.
Answer:
Maximum and minimum temperatures; time for sunrise, sunset, moonrise and moonset; maximum and minimum humidity, forecast, etc.
Weather And Climate Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 12.
How is rainfall measured?
Answer:
Rainfall is measured by an instrument -called the rain gauge. It is basically a metallic measuring cylinder with a funnel on top to collect rainwater.
Class 7 Chapter 7 Science Extra Questions Question 13.
What is the climate in Rajasthan?
Answer:
In Rajasthan, the temperature is high during most part of the year. But during winter, which lasts only for a few months, the temperature is quite low. This region receives very little rainfall. This is the typical desert climate. It is hot and dry.
Class 7th Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 14.
Name four countries in polar region.
Answer:
Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway.
Class 7 Weather Climate And Adaptation Extra Questions Question 15.
What do birds in polar region do to survive in winter?
Answer:
The birds migrate to warmer regions when winter sets in. They come back after the winter is over.
Weather, Climate And Adaptation Class 7 Extra Questions Question 16.
Name the major types of animals found in rainforests.
Answer:
The major types of animals living in the rainforests are monkeys, apes, gorillas, lions, tigers, elephants, leopards, lizards, snakes, birds and insects.
![]()
Weather, Climate And Adaptation Class 7 Worksheet With Answers Question 17.
How is average temperature of a month calculated?
Answer:
The mean temperature for a given month is found in two steps. First, we find the average of the temperatures recorded during the month. Second, we calculate the average of such average temperatures over many years. That gives the mean temperature.
Question 18.
How do penguins adapt with polar climate?
Answer:
Adaptation of penguins to survive in polar region :
- Penguins are white and merge well with the white background.
- They also have a thick skin and a lot of fat to protect it from cold.
- Penguins huddle together. This they do to keep warm.
- Further, their bodies are streamlined and their feet have webs, making them good swimmers.
Question 19.
Write the adaptations in a polar bear that helps it to survive in extreme cold climate of polar regions.
Answer:
- It has two thick layers of fur. These keep it warm in cold weather.
- The fat insulates its body from cold and keeps it warm. It has a layer of fat under its skin.
- It has long curved and sharp claws. These helps it to walk on ice.
- Its predator and prey are unable to see
- The white fur not easily visible in the snowy white background.
- It has a very strong sense of smell. It helps the bear to locate and catch its prey.
Question 20.
Write the features of lion-tailed macaque.
Answer:
Features of lion-tailed macaque :
- Its most outstanding feature is the silver-white mane, which surrounds the head from the cheeks down to its chin.
- It is a good climber and spends a major part of its life on the tree.
- It feeds mainly on fruits. It also eats seeds, young leaves, stems, flowers and buds.
- Since it is able to get sufficient food on the trees, it rarely comes down on the ground.
- The lion-tailed macaque (also called Beard ape) lives in the rainforests of Western Ghats.
Question 21.
Why do rainforests support a wide variety of plants and animals? Discuss some of the adaptations of animals to the climate of these regions.
Answer:
The tropical rainforests support a wide variety of plants and animals due to continuous warmth and rain. Since the numbers are large, there is intense competition for food and shelter.
This made animals to develop new features which would allow them to survive in such an environment.
For example :
- Many animals are adapted to living on the trees. Red-eye frog has developed sticky pads and monkeys have long tails.
- As there is competition for food, some animals are adapted to get food not easily reachable, e.g., the bird Toucan possesses a long, large beak to reach distant fruits on fragile branches.
- Many tropical animals have sensitive hearing sharp eyesight, thick skin and a skin colour which helps them to camouflage by blending with the surroundings. This is to protect them from predators.
![]()
Question 22.
Explain, with examples why we find animals of certain kind living In particular climatic conditions.
Answer:
The organisms interact with the environment to survive. So. it is necessary for the organisms to have characteristics that suits the environment. Let us take the example of polar bear. Polar bears have white fur so that they are not easily visible in the snowy white background. It protects them from their predators. It also helps them in catching their prey.
To protect them from extreme cold, they have two thick layers of fur. They also have a layer of fat under their skin. Physical activities on warm days necessitate cooling. So, the polar bear goes for swimming. It is a good swimmer. Its paws are wide and large, which help it not only to swim well but also walk with ease in the snow. While swimming underwater, it can close its nostrils and can remain underwater for long durations. It has a strong sense of smell so that it can catch its prey for food.
Question 23.
How do elephants living in the tropical rainforest adapt itself?
Answer:
The elephant has adapted to the conditions of rainforests in. many remarkable ways.
- It uses the trunk as a nose because of which it has a strong sense of smell.
- The trunk is also used by it for picking up food.
- Moreover, its tusks are modified teeth. These can tear the bark of trees that elephant loves to eat.
- Large ears of the elephant help it to hear even very soft sounds. They also help the elephant to keep cool in the hot and humid climate of the rainforest.
img
Question 24.
Collect information about the Indian Meteorological Department. 1f possible visit its website : http//www. imd.gov.in. Write a brief report about the things this department does.
Answer:
In the year 1875, Government of India established the Indian Meteorological Department to bring all meteorological work in the country under a central custody. Presently its headquarter is located in New Delhi.
The work IMD does are:
- To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information.
- To watch against severe weather phenomenon like tropical cyclones, northwestern, dust storms, heavy rains and snow, cold and hot waves.
- To provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resources management. industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities.
- To conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.
- To detect and locate earthquakes and to evaluate seismicity in different parts of the country for development projects.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is the day to day condition of the atmosphere at a place with respect to the temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed etc.?
(i) Climate
(ii) Weather
(iii) Adaptation
(iv) Survival factor.
Answer:
(ii) Weather.
2. Humidity is the measure of :
(i) moisture content in air
(ii) temperature
(iii) atmospheric pressure
(iv) wind speed.
Answer:
(i) moisture content in air.
3. Which of the following department prepares weather reports?
(i) Information Technology
(ii) Meteorological Department
(iii) Space Research Organisation
(iv) Ecological Department.
Answer:
(ii) Meteorological Department.
![]()
4. Which of the following instruments is used for measuring temperature?
(i) Barometer
(ii) Vernier Callipers
(iii) Thermometer
(iv) Osmometer.
Answer:
(iii) Thermometer.
5. Which of the following is correct for polar regions?
(i) 12 hours day and 12 hours night.
(ii) 24 hours day and 24 hours night.
(iii) 6 months day and 6 months night.
(iv) 1 year day and 1 year night.
Answer:
(iii) 6 months day and 6 months night.
6. Which of the following is not an adaptation found in polar bear to prevent cold?
(i) It has two thick layers of fur.
(ii) It has a layer of fat under its skin.
(iii) They huddle together in groups most of the time.
(iv) It has long curved and sharp claws.
Answer:
(iv) It has long curved and sharp claws.
7. Why do penguins huddle together in groups?
(i) For warming themselves.
(ii) For the sake of security.
(iii) They enjoy company of each other.
(iv) They are social beings.
Answer:
(i) For warming themselves.
8. In India, tropical rainforest is found in :
(i) Western Ghats
(ii) Assam
(iii) both Western Ghats and Assam
(iv) Jammu and Kashmir.
Answer:
(iii) both Western Ghats and Assam.
![]()
9. The tropical region has generally a hot climate because of its location around:
(i) Subtropic region
(ii) Equator
(iii) Temperate zone
(iv) Subtemperate zone.
Answer:
(ii) Equator.
10. Which of the following is a tropical animal?
(i) Polar bears
(ii) Penguins
(iii) Seals
(iv) Elephants.
Answer:
(iv) Elephants.
11. Which of the following is a polar animal?
(i) Seal
(ii) Toucan
(iii) Macaque
(iv) Elephant.
Answer:
(i) Seal.
12. Which of the following options best describes the climate of a tropical region?
(i) Hod and humid
(ii) Moderate temperature, heavy rainfall
(iii) Hot and dry
(iv) Cold and humid.
Answer:
(i) Hod and humid.
13. A carnivore with two layers of white fur and heavy deposit of underskin fat, is likely to be found in :
(i) polar region
(ii) deserts
(iii) oceans
(iv) tropical rainforests.
Answer:
(i) polar region.
14. Xerophytes (plants requiring less water for their growth) are likely to be found in :
(i) polar regions
(ii) deserts
(iii) oceans
(iv) tropical rainforests
Answer:
(ii) deserts.
![]()
Keywords:
→ Adaptation: Adjusting to conditions for surviving.
→ climate: The average weather pattern taken over a long time, say 25 years, is called the climate of the place.
→ Elements of weather: The temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed and other factors are called the elements of the weather.
→ Humidity: Amount of water vapour present in air.
→ Maximum temperature: Highest temperature of a day. It occurs generally in the afternoon. ,
→ Migration: Moving from one place to another for surviving. It is a type of adaptation.
→ Minimum temperature: Lowest temperature of a day. It occurs generally in the early morning.
→ Polar region: The regions around the poles of the earth.
→Tropical rainforest: Forests in tropical region. These are dense with high rainfall.
→ Tropical region: The region which lies between the tropic of cancer and the tropic of Capricorn in called tropical region.
→ Weather: The day-to-day condition of the atmosphere at a place with respect to the temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, etc.., is called the weather at that place.