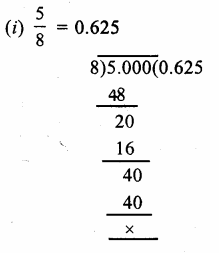
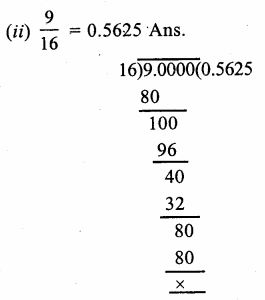
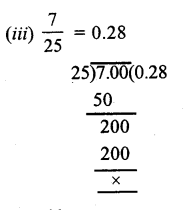
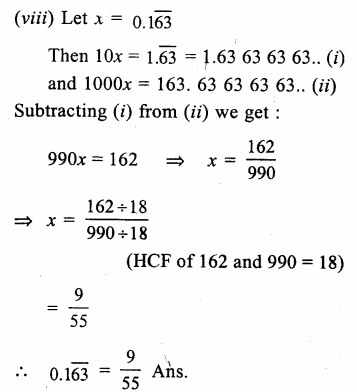
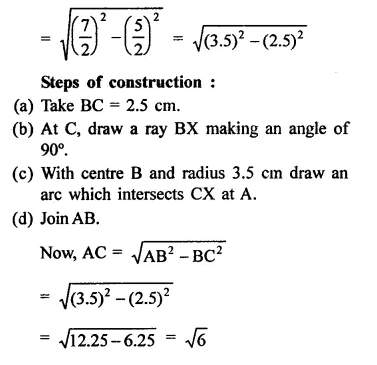
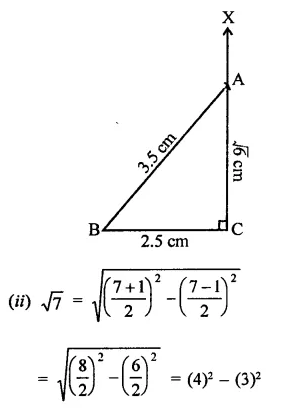
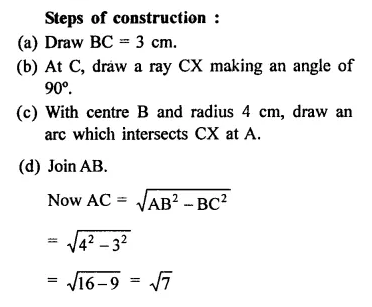
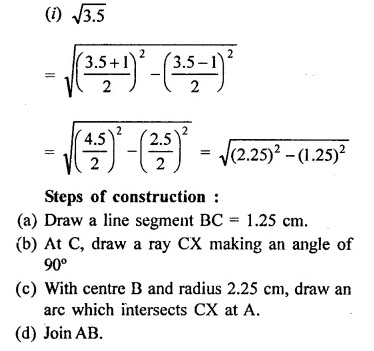
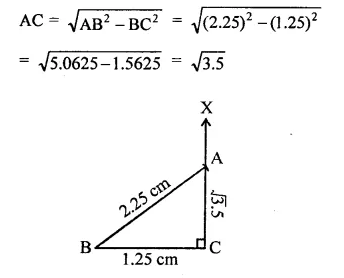
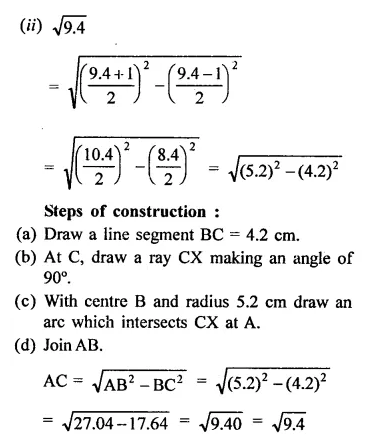
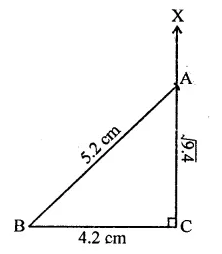
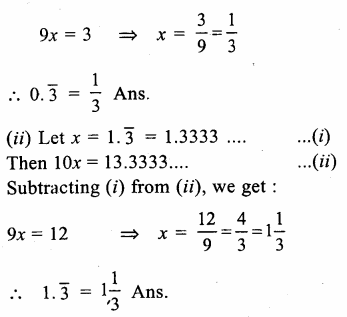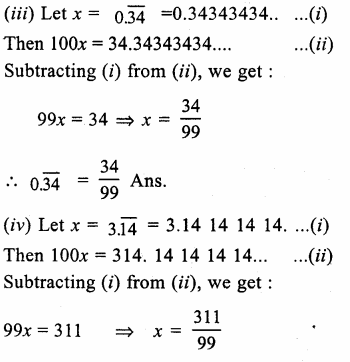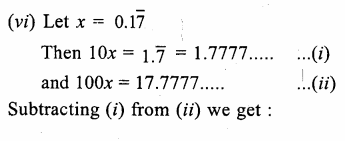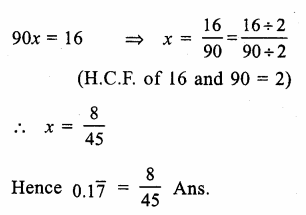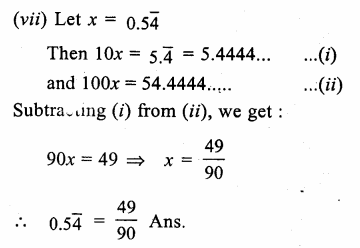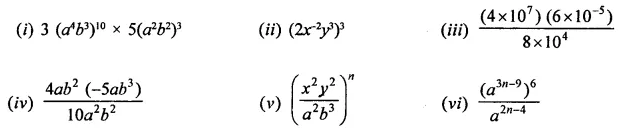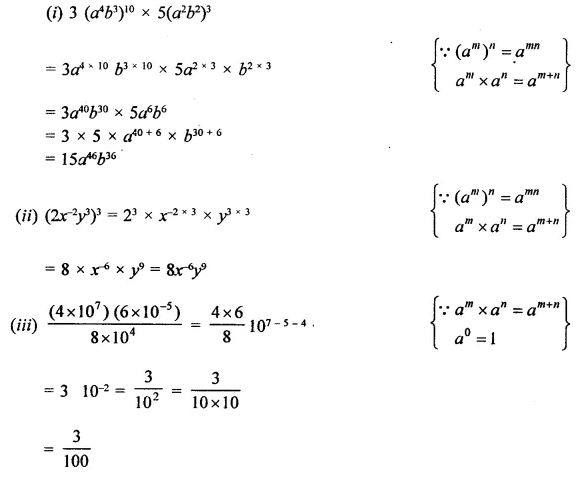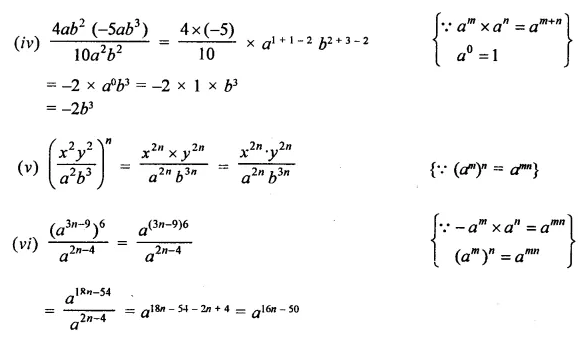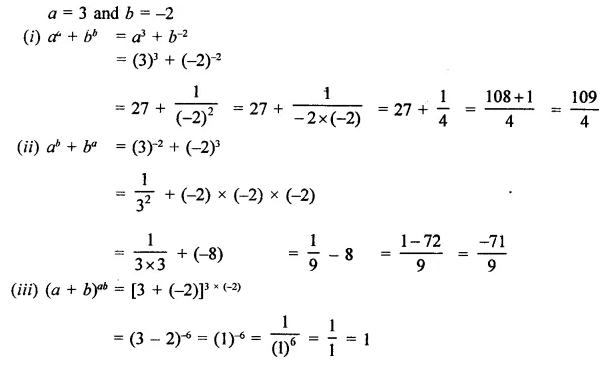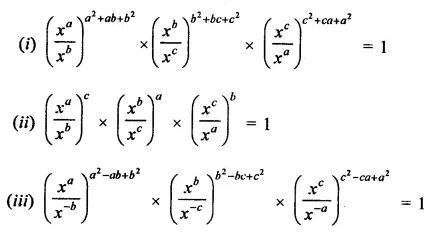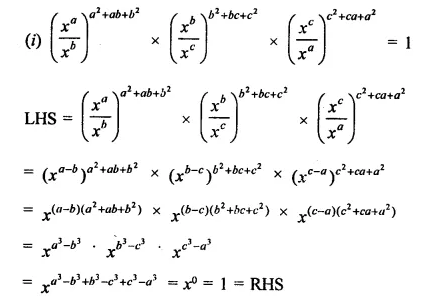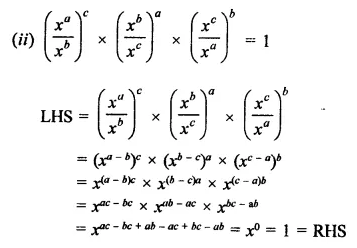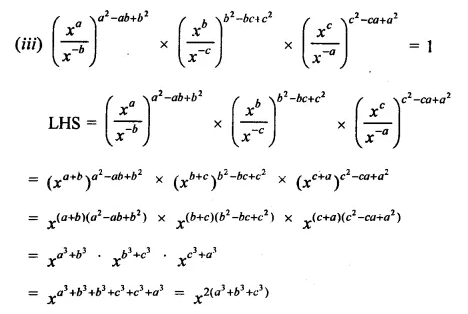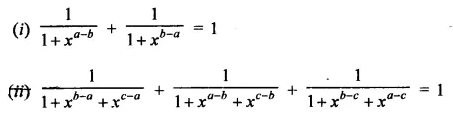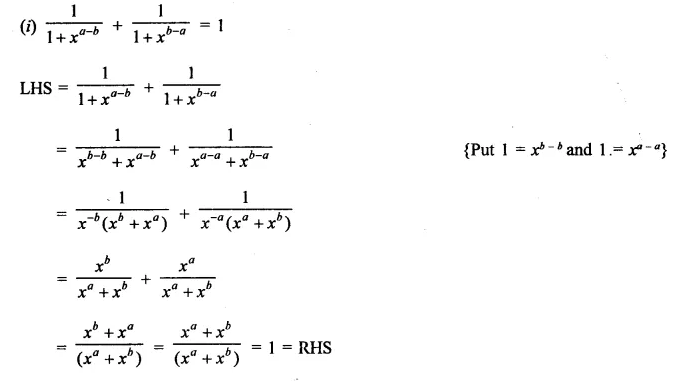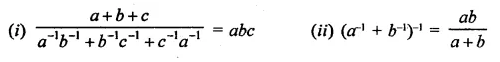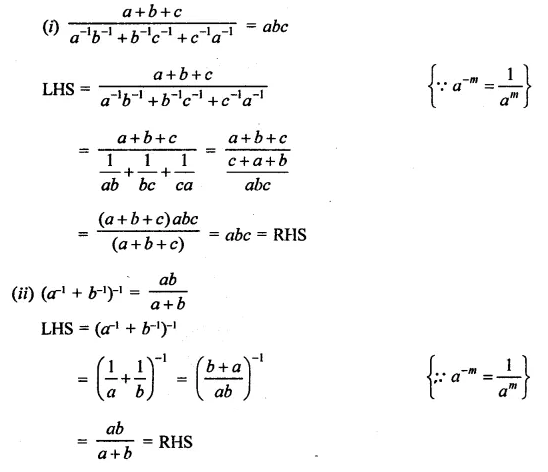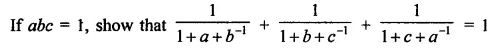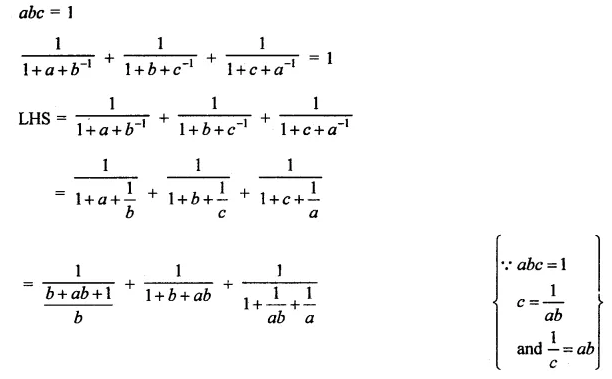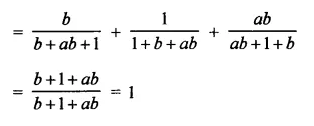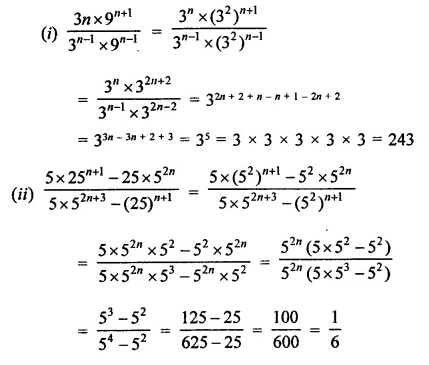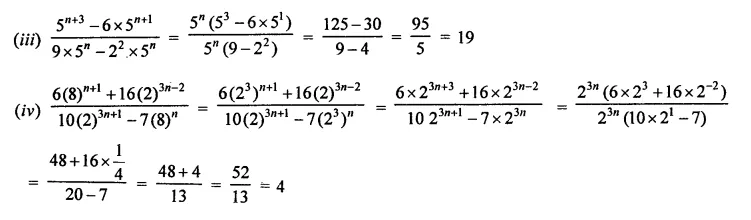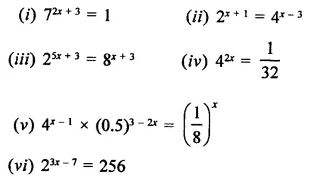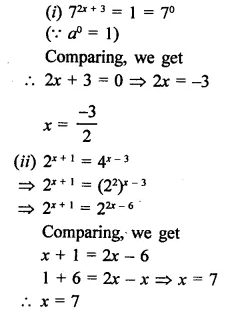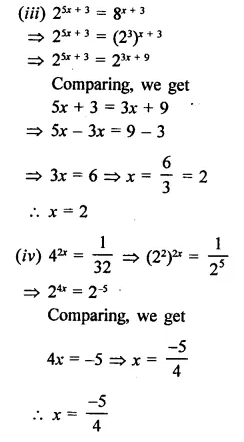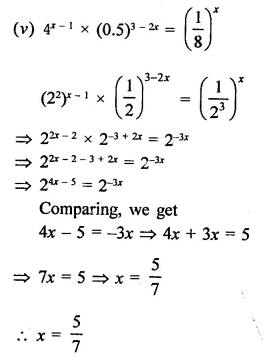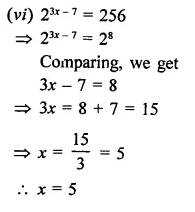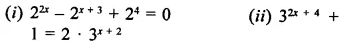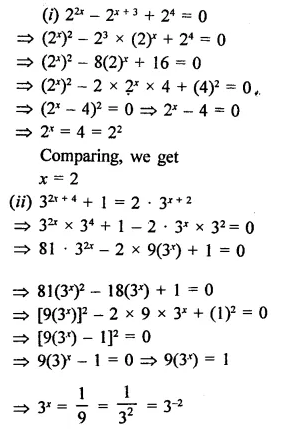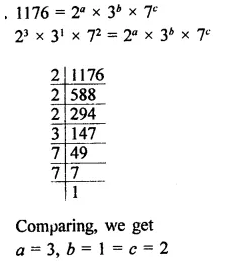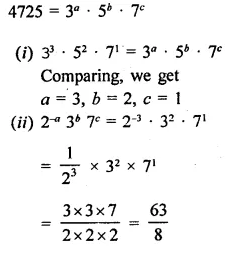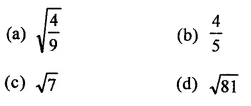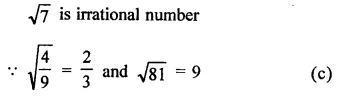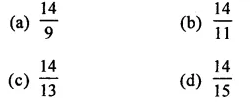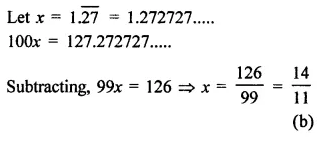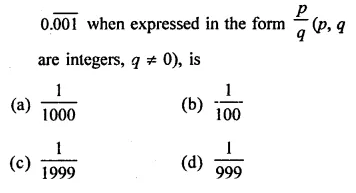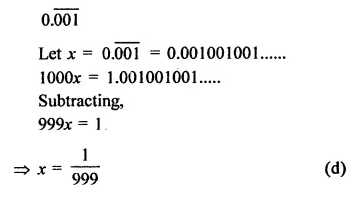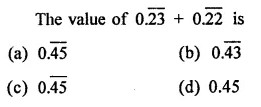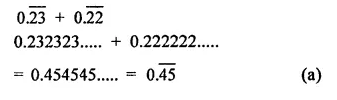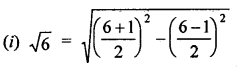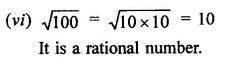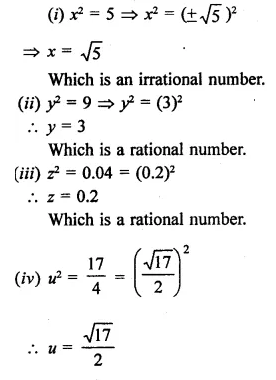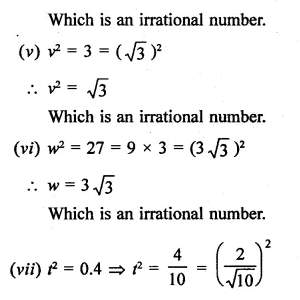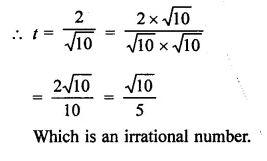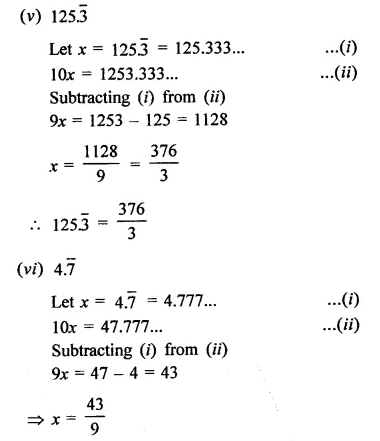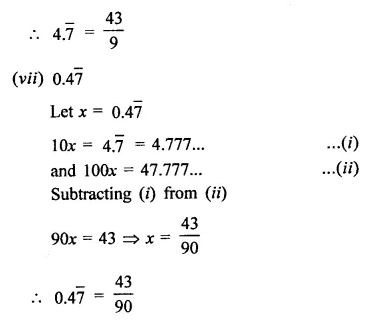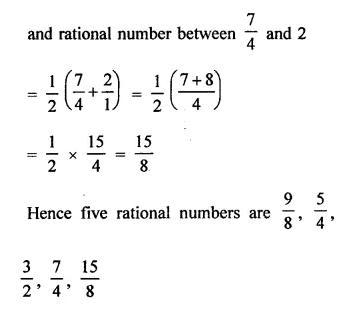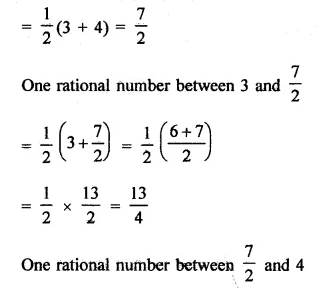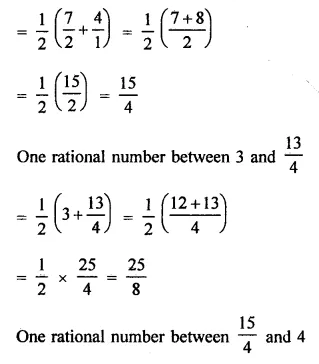RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 2 Exponents of Real Numbers Ex 2.2
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 2 Exponents of Real Numbers Ex 2.2
Question 1.
Assuming that x, y, z are positive real numbers, simplify each of the following:
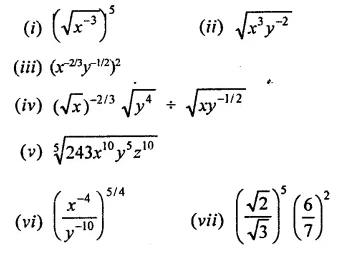
Solution:
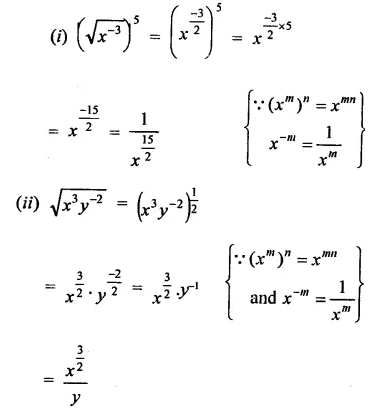
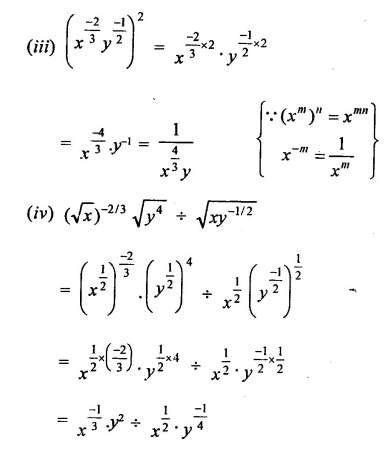
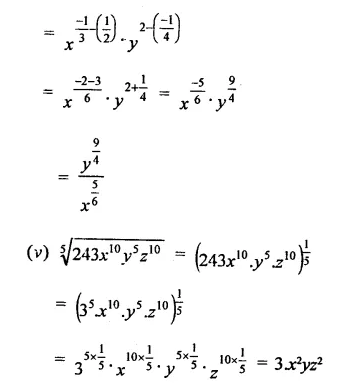
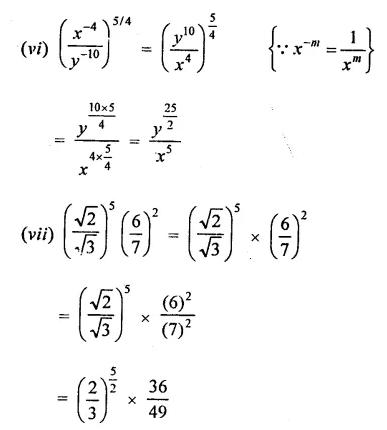
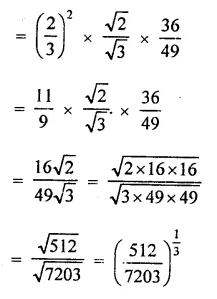
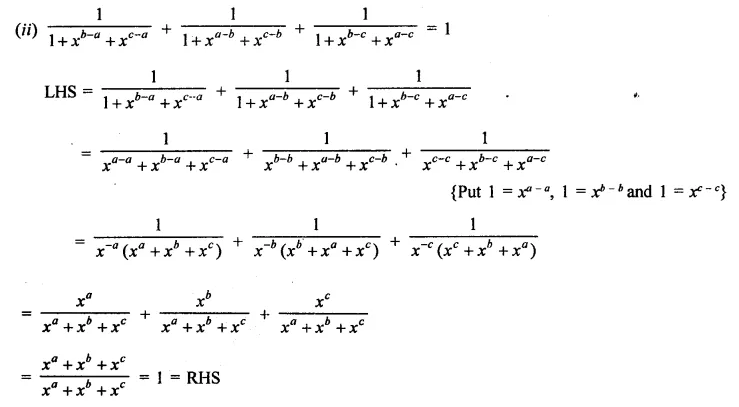
Question 2.
Simplify:
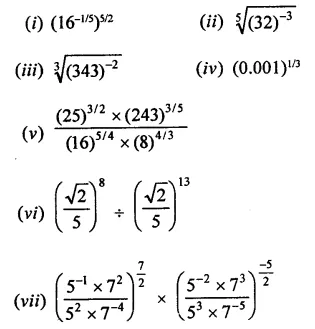
Solution:
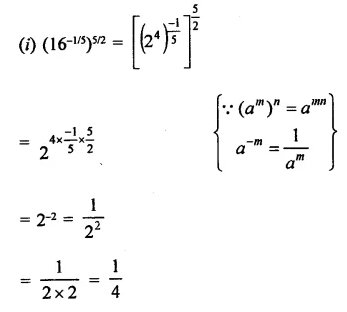
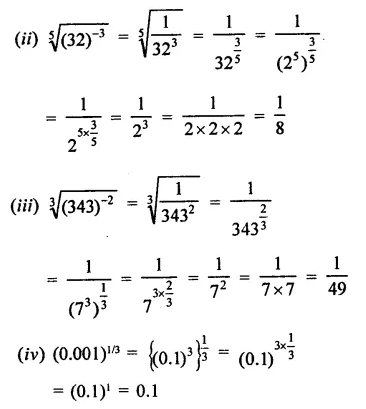
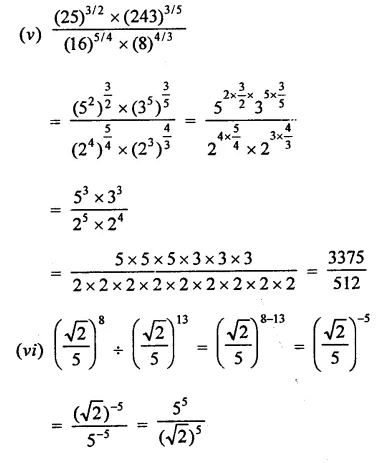
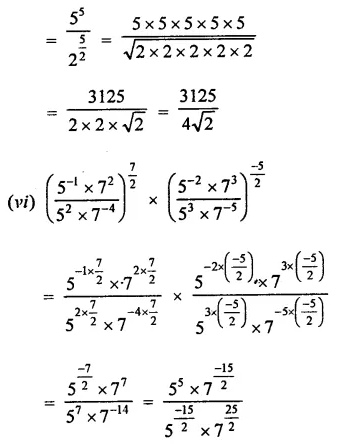
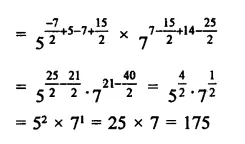
Question 3.
Prove that:
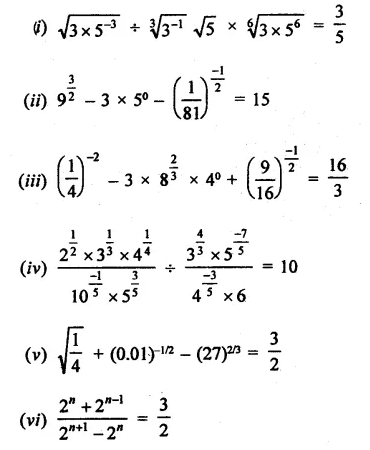
Solution:
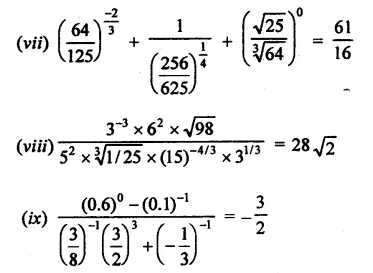
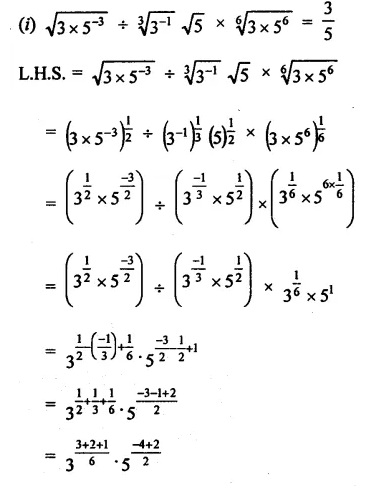
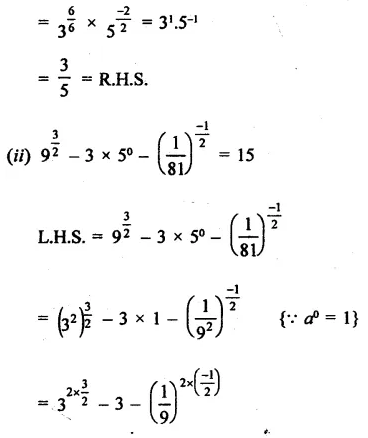
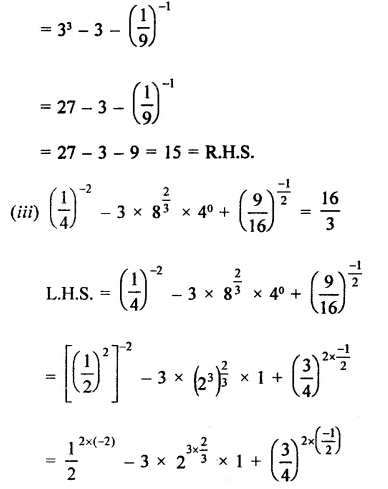
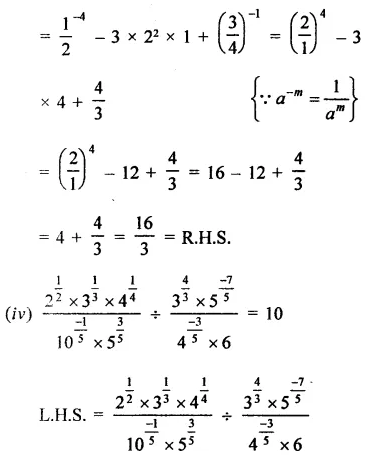
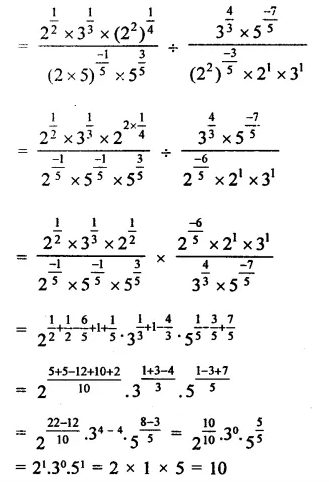
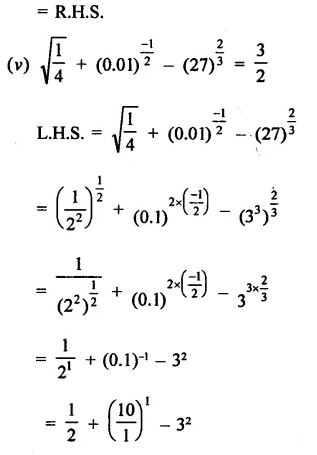
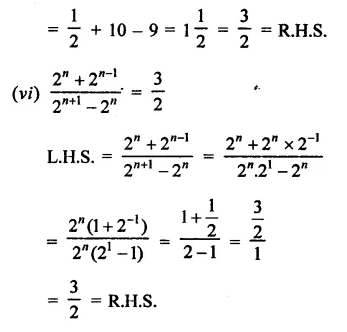
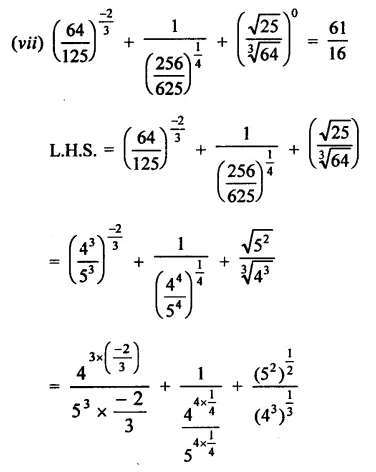
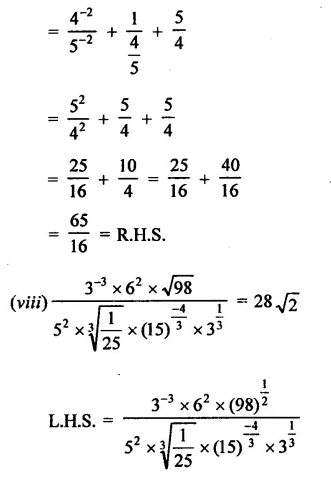
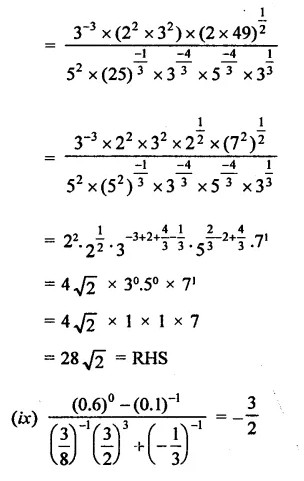
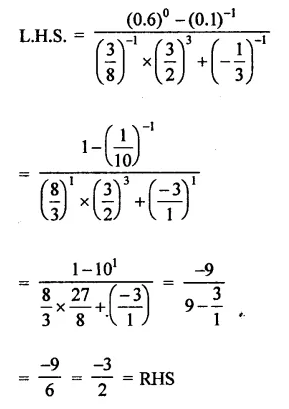
Question 4.
Show that:
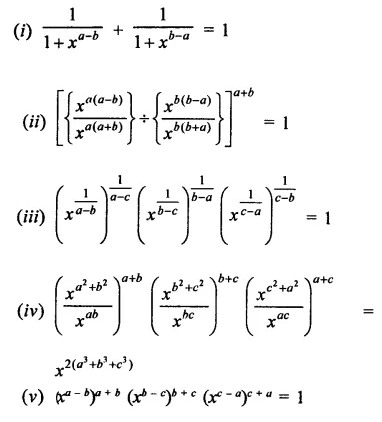
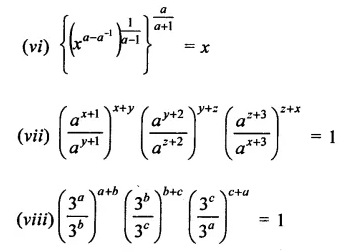
Solution:
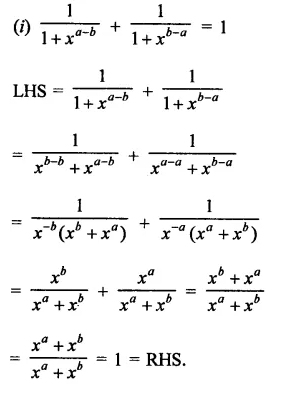
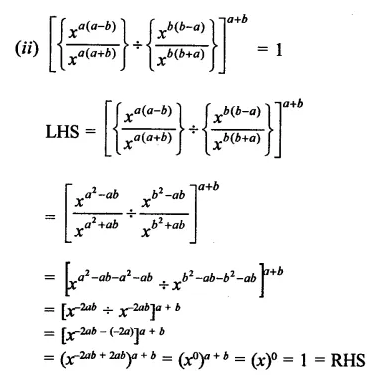
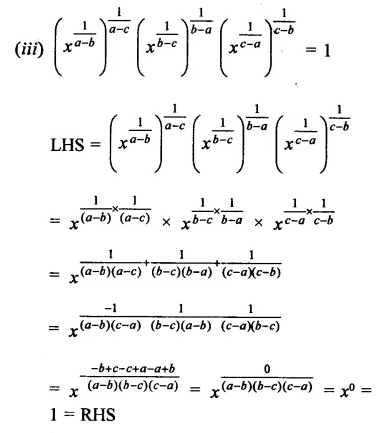
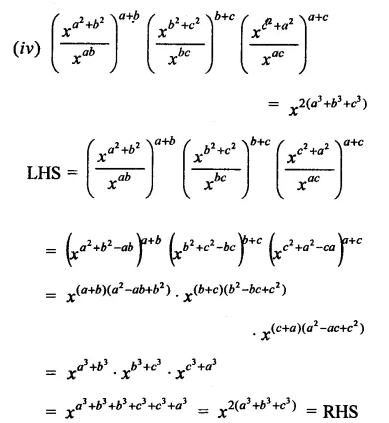
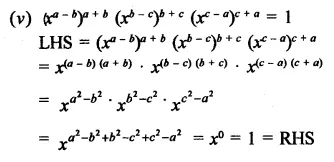
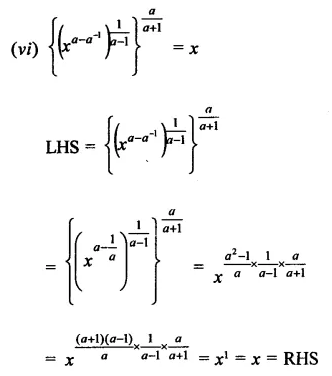
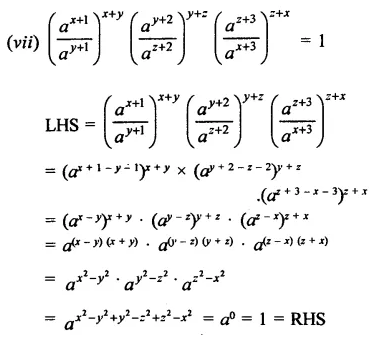
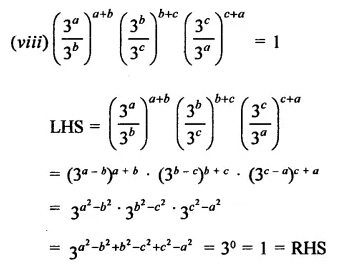
Question 5.

Solution:
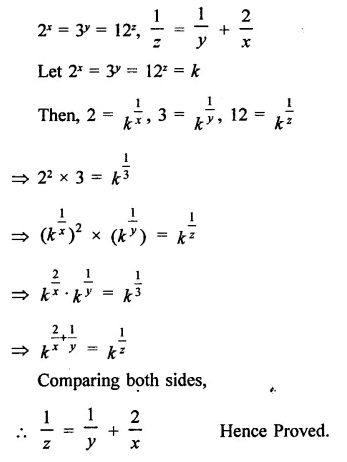
Question 6.
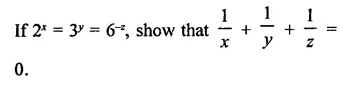
Solution:
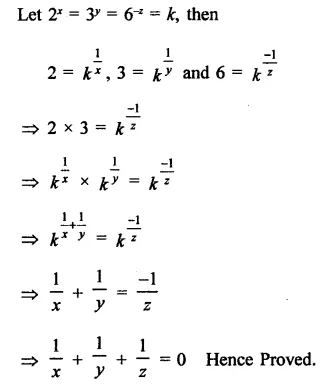
Question 7.
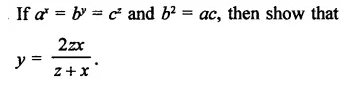
Solution:
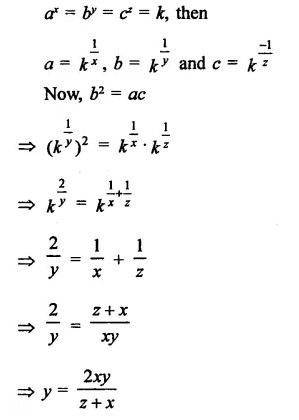
Question 8.

Solution:
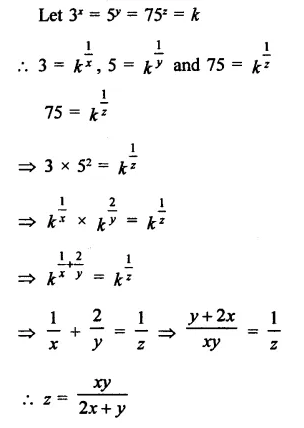
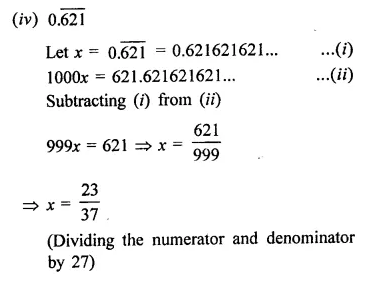
Question 9.
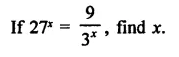
Solution:
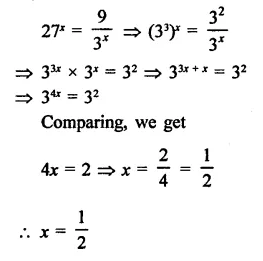
Question 10.
Find the values of x in each of the following:
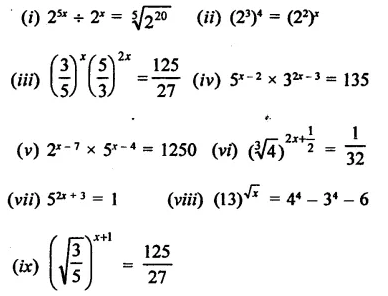
Solution:
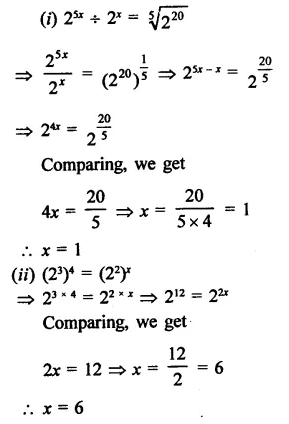
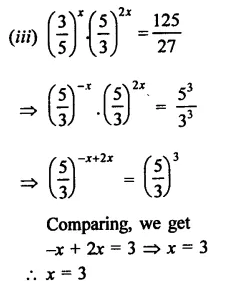
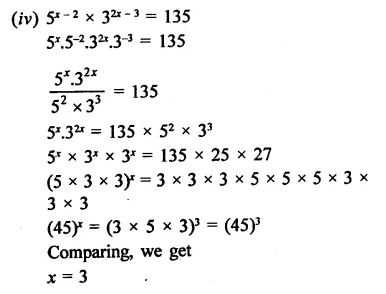
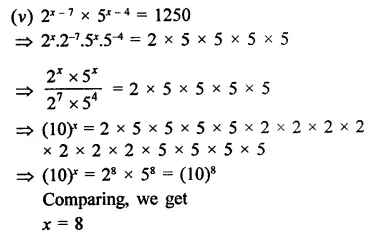
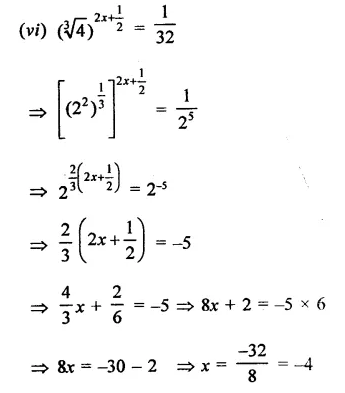
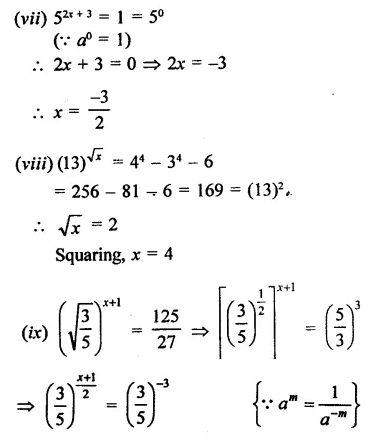
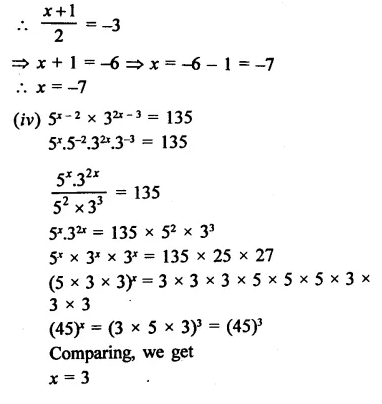
Question 11.
If x = 21/3 + 22/3, show that x3 – 6x = 6.
Solution:
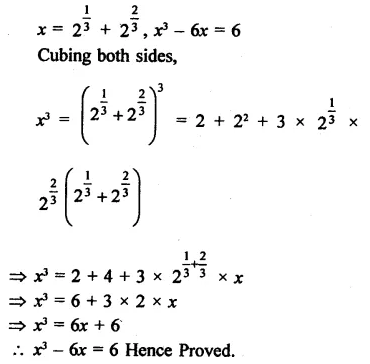
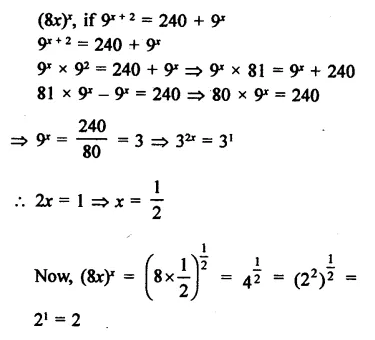
Question 12.
Determine (8x)x, if 9x+ 2 = 240 + 9x.
Solution:
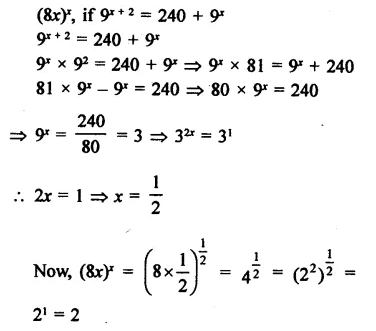
Question 13.
If 3x+1 = 9x-2, find the value of 21 +x.
Solution:
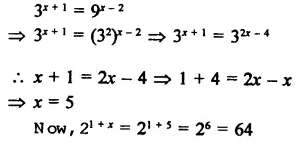
Question 14.
If 34x = (81)-1 and 101/y = 0.0001, find the value of 2-x+4y
Solution:
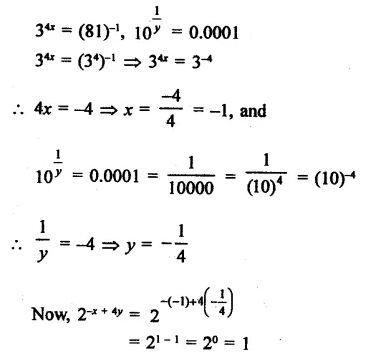
Question 15.
If 53x = 125 and 10y = 0.001 find x and y.
Solution:
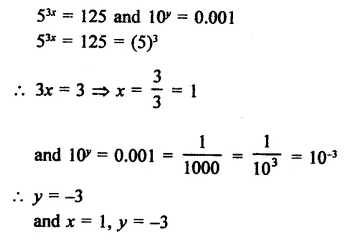
Question 16.
Solve the following equations:
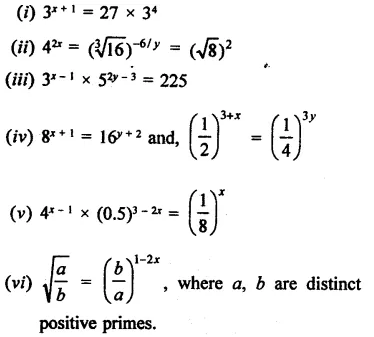
Solution:
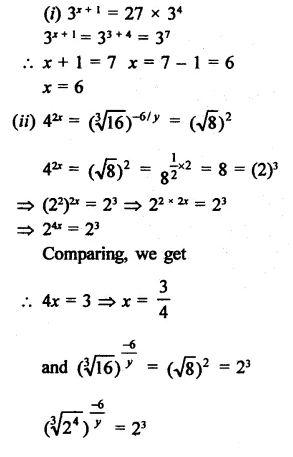
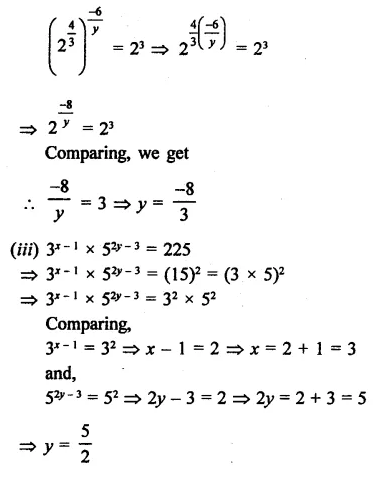
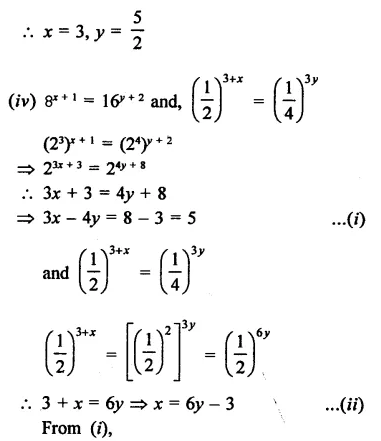
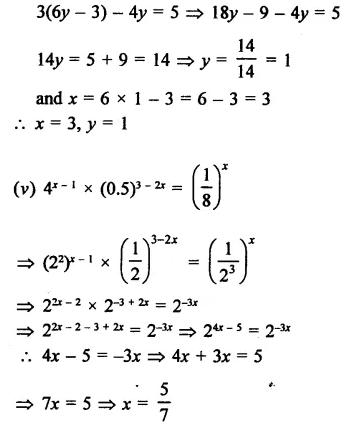
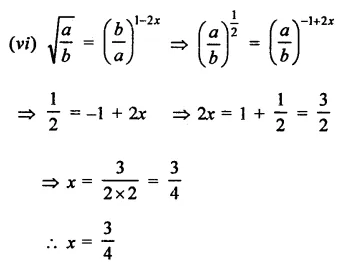
Question 17.

Solution:
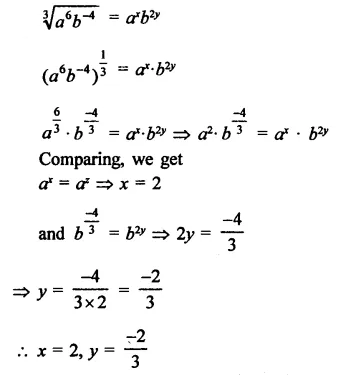
Question 18.
If a and b are different positive primes such that
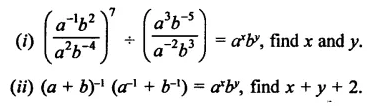
Solution:
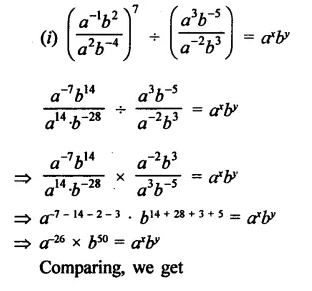
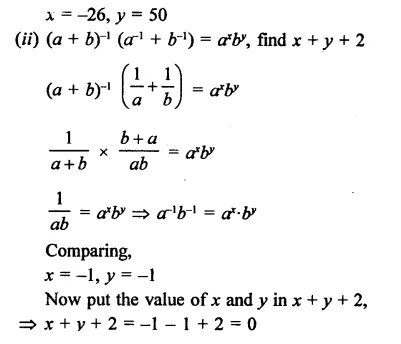
Question 19.
If 2x x 3y x 5z = 2160, find x, y and z. Hence, compute the value of 3x x 2-y x 5-z.
Solution:
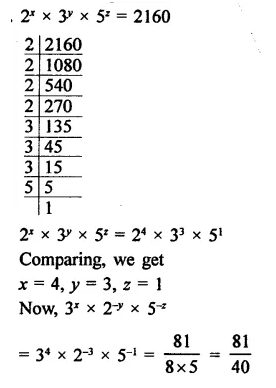
Question 20.
If 1176 = 2a x 3b x 7c, find the values of a, b and c. Hence, compute the value of 2a x 3b x 7-c as a fraction.
Solution:
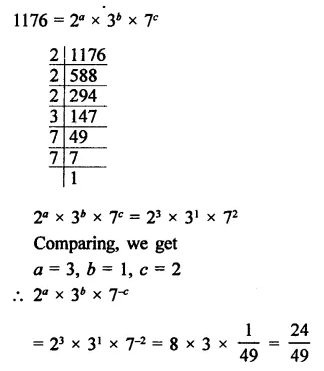
Question 21.
Simplify:
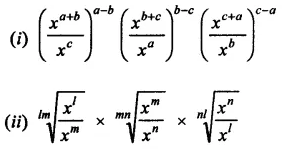
Solution:
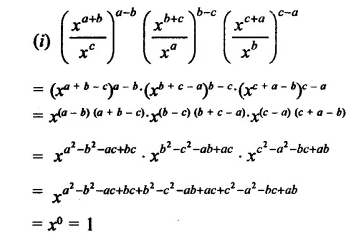
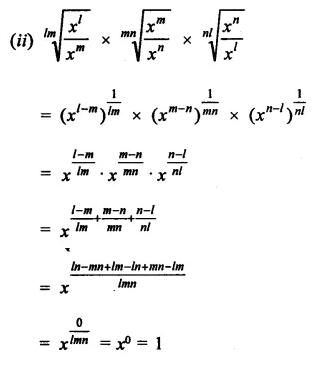
Question 22.
Show that:
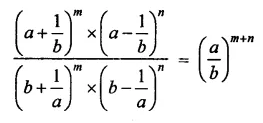
Solution:
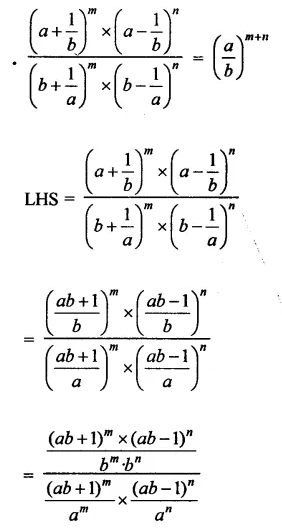
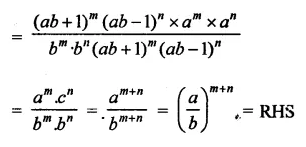
Question 23.
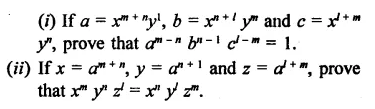
Solution:
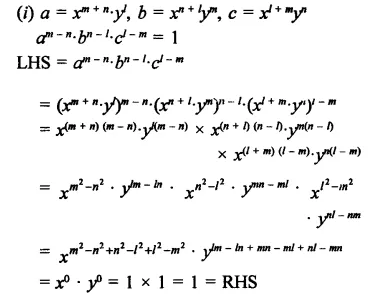

Hope given RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 2 Exponents of Real Numbers Ex 2.2 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.