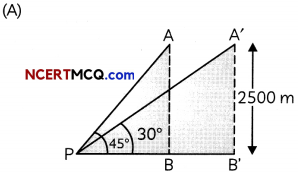
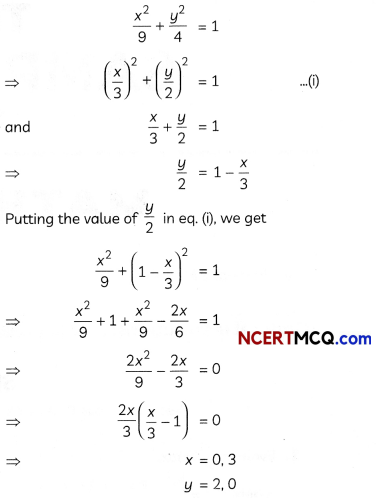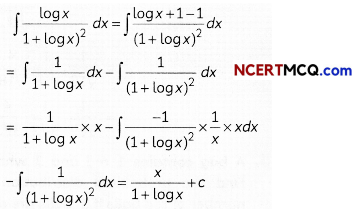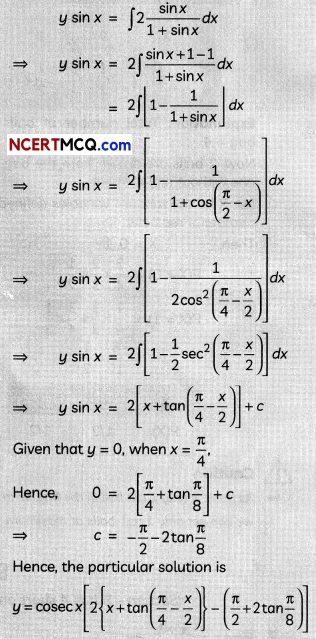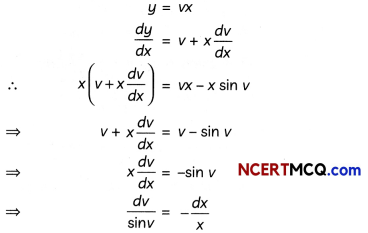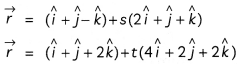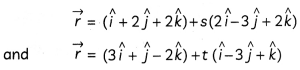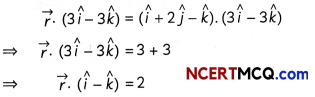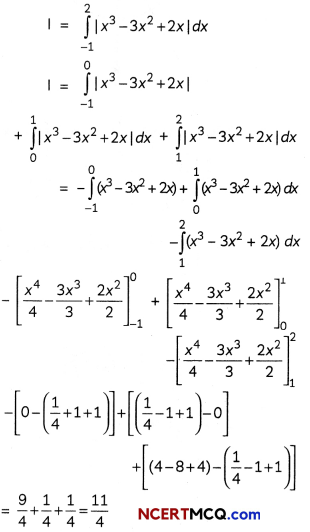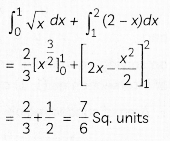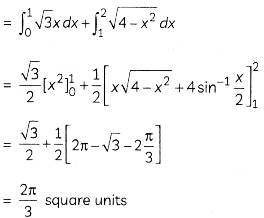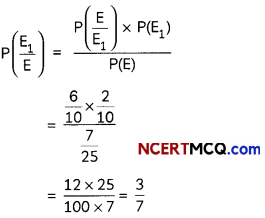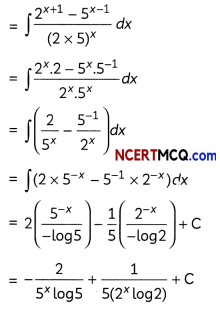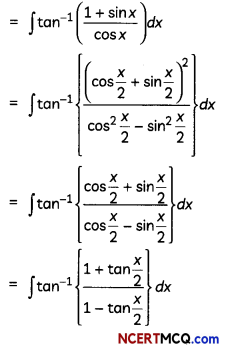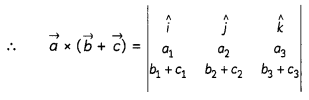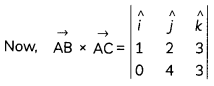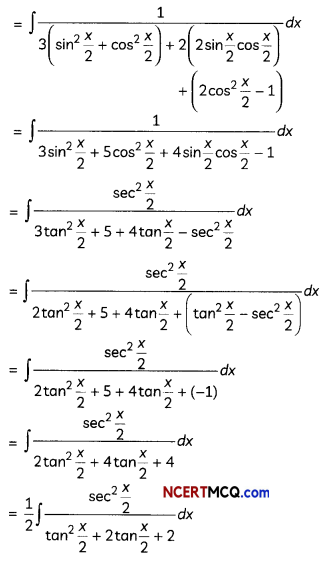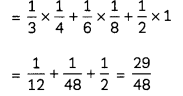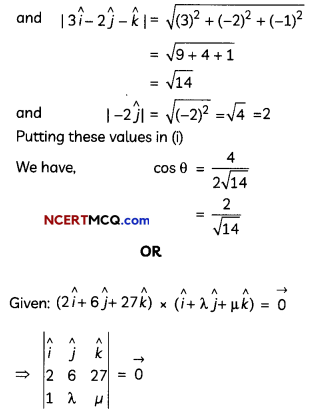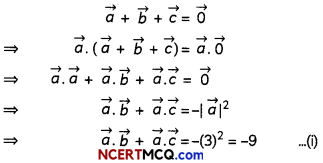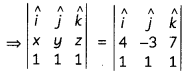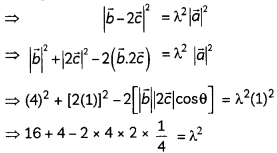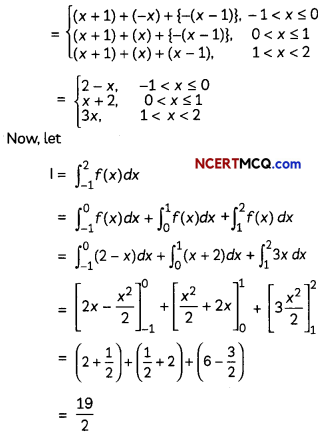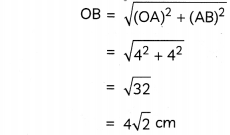Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Maths with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 12 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Maths Term 2 Set 12 for Practice
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains three sections-A. B and C. Each part is compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 short answer type (SA1) questions of 2 marks each.
- Section-B has 4 short answer type (SA2) questions of 3 marks each.
- Section-C has 4 long answer type questions (LA) of 4 marks each.
- There is an Internal choice in some of the questions.
- Q14 is a case-based problem having 2 sub parts of 2 marks each.
Section – A
(Section – A has 6 short answer type (SA-1) questions of 2 marks each.)
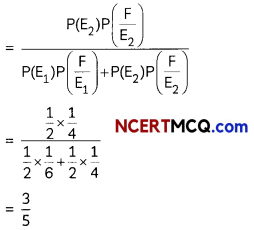
Question 1.
Let E and F be two events such that P(E) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) P(F) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) and P(E ∪ F) = \(\frac{1}{2}\). Show that E and F are independent events. (2)
Question 2.
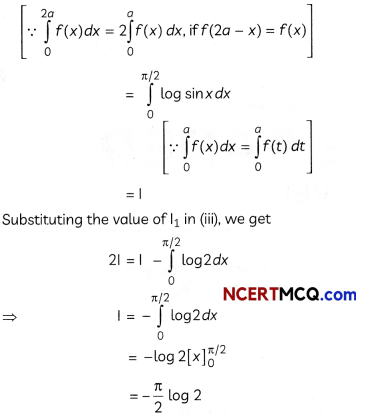
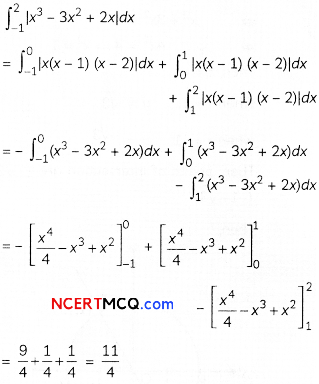
Evaluate ∫x.2x2 dx. 2
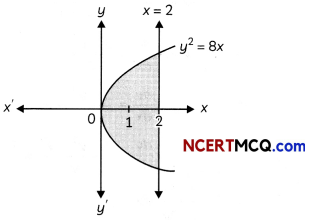
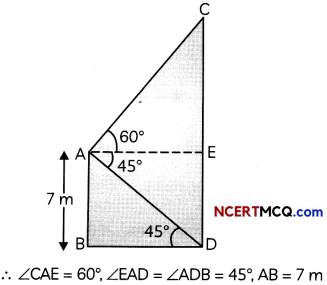
Question 3.
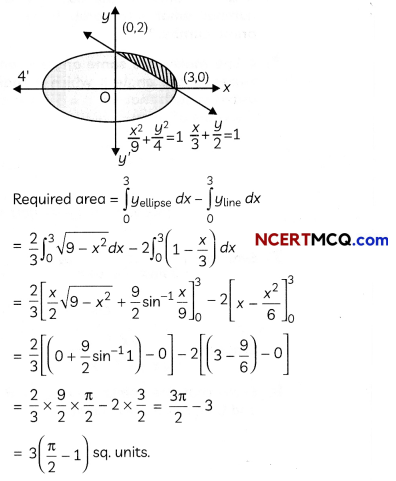
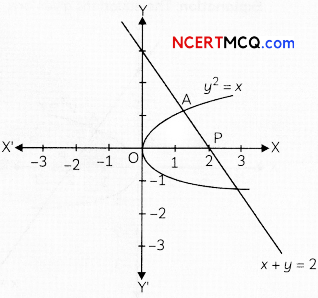
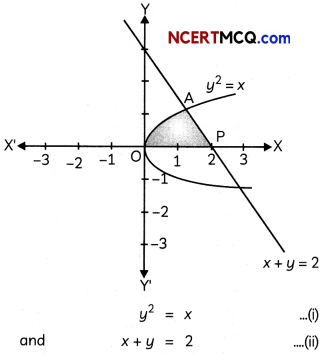
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve x2 = 16y, the lines y = 1 and y = 4 and the y-axis in the first quadrant. (2)
![]()
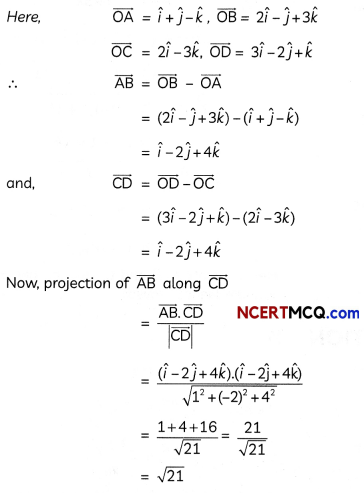
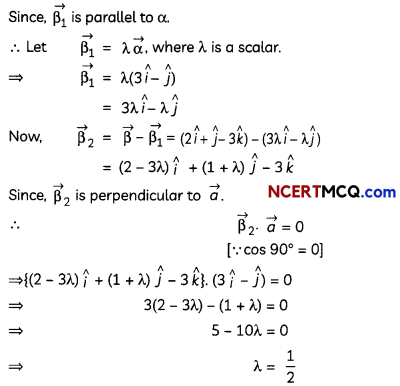
Question 4.
If \(\vec{a}\) is any vector, then prove that \(\vec{a}\) = \((\vec{a} \cdot \hat{i}) \hat{i}+(\vec{a} \cdot \hat{j}) \hat{j}+(\vec{a} \cdot \hat{k}) \hat{k}\)
OR
Prove that (\(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}\)) – (\((\vec{a} \cdot \vec{b})\)) tan θ, where θ is the angle between the vector \(\vec{a}\) and \(\vec{b}\). (2)
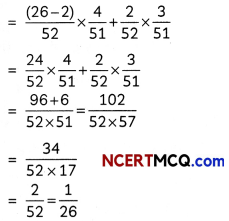
Question 5.
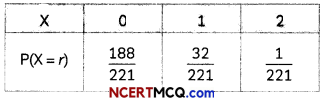
Two cards are drawn successively without replacement from a well-shuffled pack of 52 playing cards. Find the probability distribution of the number of kings. (2)
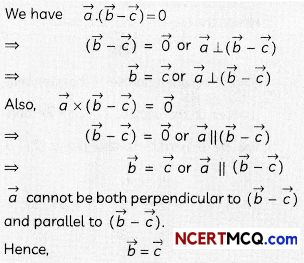
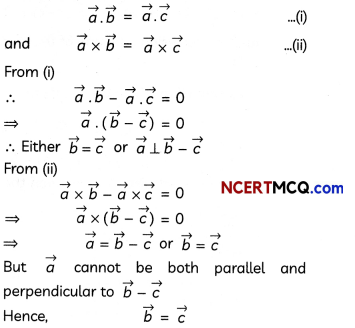
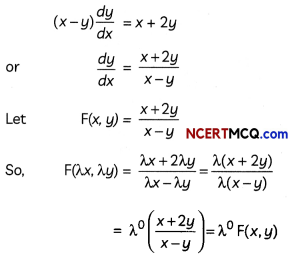
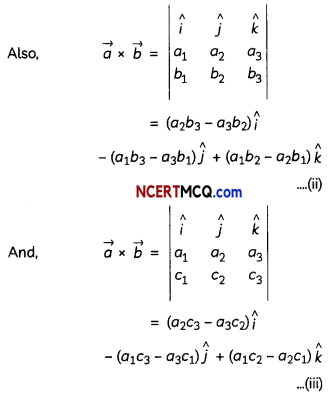
Question 6.
Does \(\vec{a} \times \vec{b}\) = \(\vec{a} \times \vec{c}\) always imply \(\vec{b}\) = \(\vec{c}\)? Give reasons with your answer. (2)
Section – B
(Section – B has 4 short answer type (SA-2) questions of 3 marks each.)
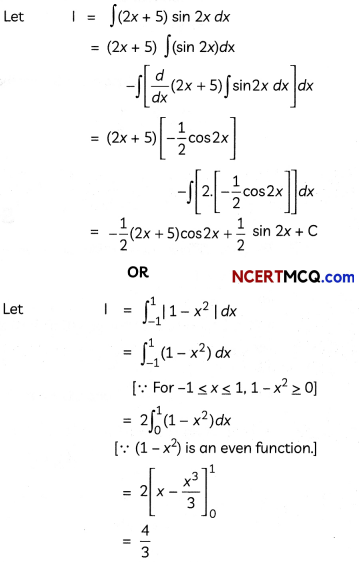
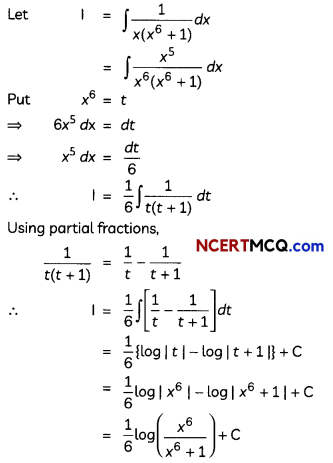
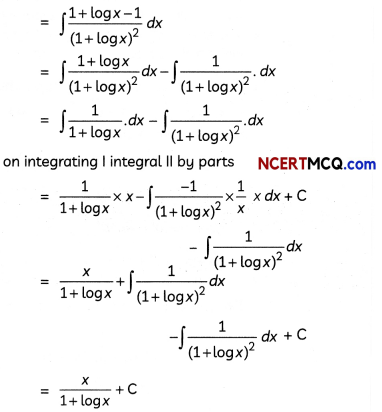
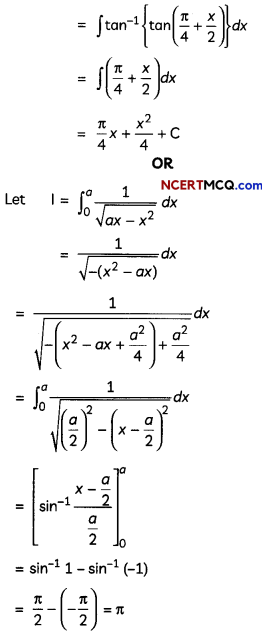
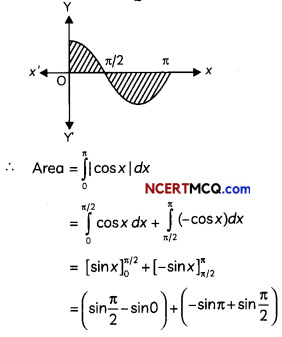
Question 7.
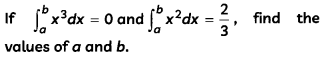
OR
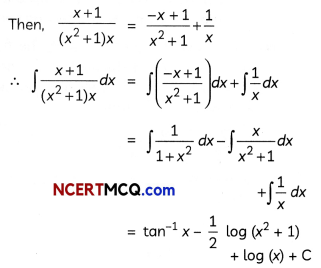
Evaluate \(\int \frac{1}{3 \sin x+4 \cos x}\) dx. (3)
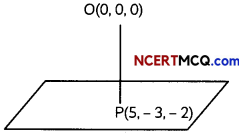
Question 8.
A variable plane which is at a constant distance p from the origin, meets the axes in A, B and C. Through A, B and C, planes are drawn parallel to the coordinate planes. Show that the locus of their point of intersection is:
x-2 + y-2 + z-2 = p-2
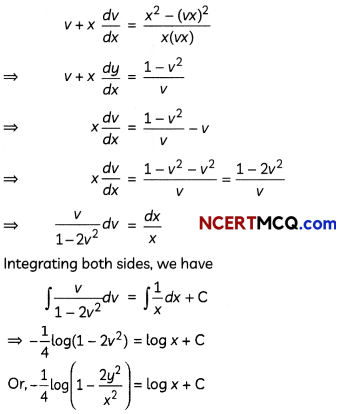
Question 9.
Solve the differential equation:
(y – x\(\frac{d y}{d x}\))x = y
OR
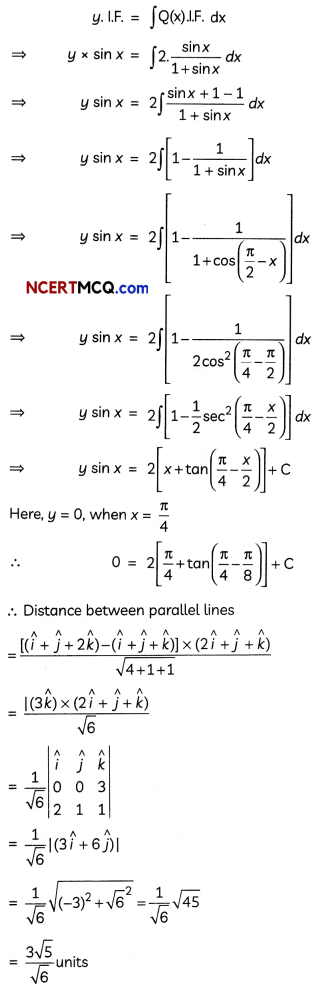
Find the particular solution of the differential equation \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + 2y tan x = sin x, given that y = 0 when x =\(\frac{\pi}{3}\). (3)
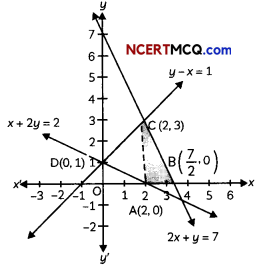
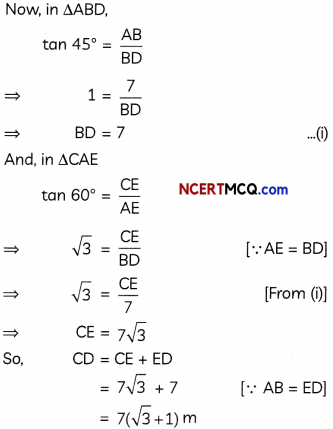
Question 10.
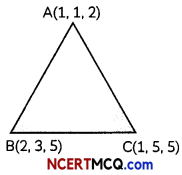
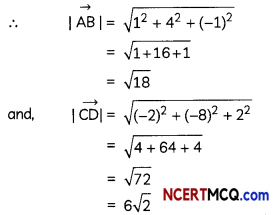
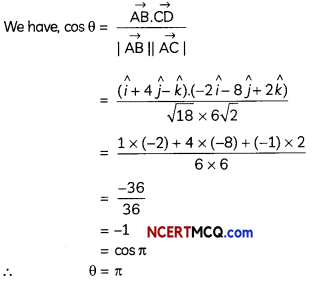
Using vectors, prove Pythagoras Theorem. (3)
![]()
Section – C
(Section – C has 4 long answer type questions (LA) of 4 marks each.)
Question 11.
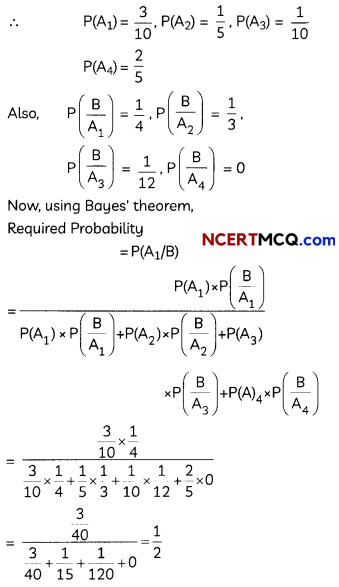
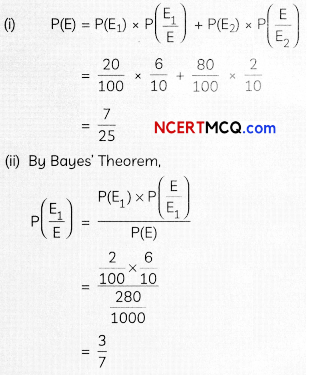
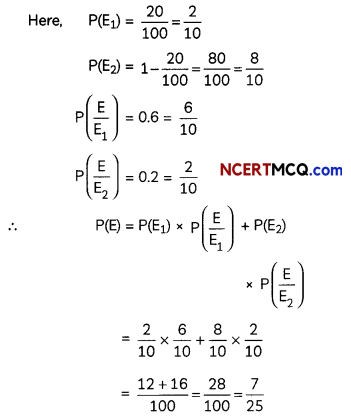
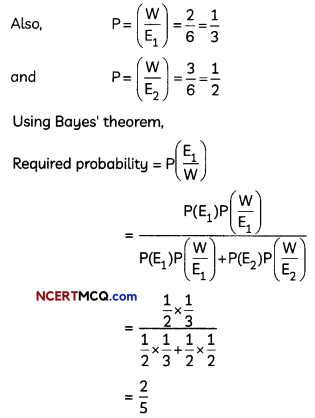
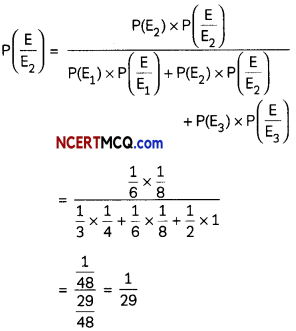
A bag contains (2n + 1) coins. It is known the n of these coins have a head on both sides whereas the rest of the coins are fair. A coin is picked up at random from the bag and is tossed. If the probability that the toss results in a head is \(\frac{31}{42}\) , determine the value of n. (4)
Question 12.
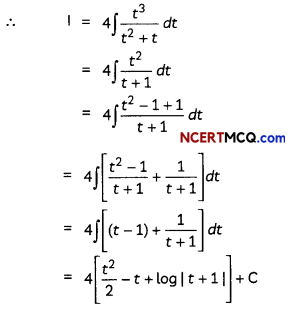
Evaluate \(\int \frac{5 x-2}{3 x^{2}+2 x+1}\) dx. (4)
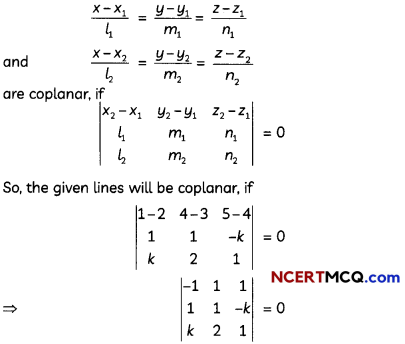
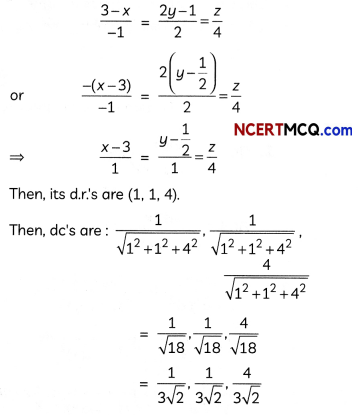
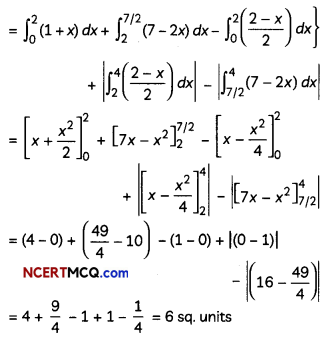
Question 13.
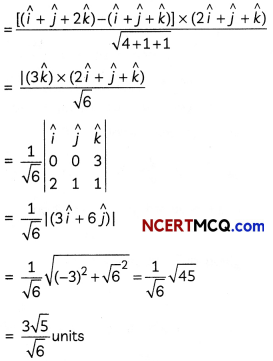
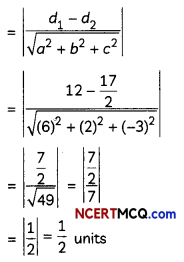
Find the shortest distance between the following pairs of lines:
\(\frac{x-3}{3}=\frac{y-8}{-1}=\frac{z-3}{1}\)
and \(\frac{x+3}{-3}=\frac{y+7}{2}=\frac{z-6}{4}\)
OR
Find the foot of perpendicular from the point (2, 3, -8) to the line \(\frac{4-x}{2}=\frac{y}{6}=\frac{1-z}{3}\). Also find the perpendicular distance from the given point to the line. (4)
![]()
CASE-BASED/DATA-BASED
Question 14.
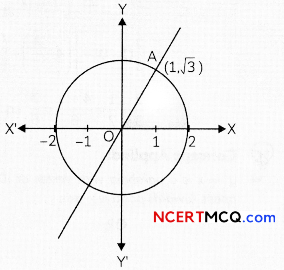
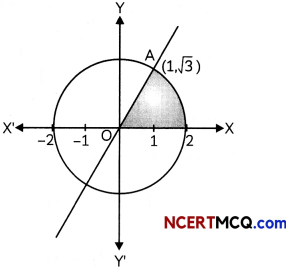
Ramesh went to a pizza shop and he ordered a pizza. After sometime, the pizza boy serves a pizza to the Ramesh and he cut off it with a knife. Pizza is circular in shape which is represented by the equation x2 + y2 = 4 and sharp edge of the knife represents a line given by x = √3y.
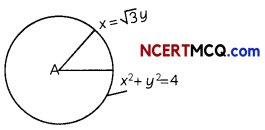
Based on the above information, answer the following two questions:
(A) Determine the points of intersection of the circle and the line. (2)
(B) Find the smaller area of the region bounded by the circular pizza and the edge of the knife in the first quadrant. (2)