Students can also read Online Education MCQ Questions for Class 10 Civics Chapter 6 Political Parties Questions with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-10-social-science-with-answers/
Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers
Civics Class 10 Chapter 6 MCQs On Political Parties
Political Parties Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Fill in the blank by choosing the most appropriate option:
The rise of political parties is directly linked to
(a) Emergence of representative democracies
(b) rise of large scale economies
(c) rise of mechanism of restrain and support the government
(d) rise of internet
Answer:
(a) Emergence of representative democracies
MCQ On Political Parties Class 10 Question 2.
Which one of the following is a National Political Party”?
(a) Samajwadi Party
(b) Rashtriya Janata Dal
(c) Rashtriya Lok Dal
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer:
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
MCQ Of Political Parties Class 10 Question 3.
Which one of the following facilities is offered by the “Election Commission” to a recognised political party?
(a) Party Name
(b) Election Funds
(c) Election Symbol
(d) Manifesto
Answer:
(c) Election Symbol
Class 10 Political Parties MCQ Question 4.
Who among the following recognises “Political parties” in India? [CBSE 2014]
(a) Election Commission
(b) President of India
(c) Speaker of Lok Sabha
(d) Supreme Court
Answer:
(a) Election Commission
Related Theory
More than 750 parties are registered with the Election Commission of India.
![]()
Political Parties Class 10 MCQ With Answers Question 5.
……………… in which one of the following states does “Shiv Sena” exist as a regional political party?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Karnataka
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Answer:
Political Parties MCQ Class 10th Question 6.
Who among the following organised the dalits into the Depressed Classes Association in 1930? [CBSE 2012]
(a) Kanshi Ram
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) Gandhiji
(d) Alluri Sitaram Raju
Answer:
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Explanation: Dr. Ambedkar was known as the father of Indian Constitution and worked extensively for the Depressed classes. He arranged them into an association in 1932. It gave the Depressed Classes (Later to be known as the Schedule Castes) reserved seats in provincial and central legislative councils, but they were to be voted in by the general electorate.
Class 10 Civics Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers Question 7.
Which one of the following political parties seeks to represent and secure power for Dalits, OBCs and Adivasis?
(a) Bahujan Samaj Party
(b) Bharatiya Janata Party
(c) Forward Bloc
(d) Janata Dal (s)
Answer:
MCQ Political Parties Class 10 Question 8.
The political party which believes in Marxism-Leninism is:
(a) Nationalist Congress Party
(b) Communist Party of India
(c) Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK)
(d) Bahujan Samaj Party
Answer:
(b) Communist Party of India
Explanation: It was formed in 1925. The party espouses secularism and democracy.
It is opposed to the forces of secessionism and communalism. It accepts parliamentary democracy as a means of promoting the interests of the working class, farmers and the poor.
![]()
Political Parties Class 10 MCQs Question 9.
Which one of the following countries has one party system?
(a) China
(b) Indo-China
(c) Japan
(d) Germany
Answer:
(a) China
Explanation: In some countries, only one party is allowed to control and run the government. These are called one-party systems.
MCQ Of Chapter Political Parties Class 10 Question 10.
Which of the following countries have bi-party system?
(a) United Kingdom and Belgium
(b) United States of America and Canada
(c) United Kingdom and United States of America
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) United Kingdom and United States of America
Political Party Class 10 MCQ Question 11.
Which of the following political party was founded in 1998?
(a) All India Trinamool Congress
(b) Nationalist Congress Party
(c) Aam Admi Party
(d) Bharatiya Janata Party
Answer:
(a) Alt India Trinamool Congress
Explanation: All India Trinamool Congress was founded under the leadership of Mamta Banerjee and is currently ruling in West Bengal since 2011.
Related Theory
This party became a national political party in 2016.
Political Parties MCQ Class 10 Question 12.
In this party system, generally power changes between two main parties:
(a) Bi-party system
(b) Single party system
(c) Multi-party system
(d) None of these
Answer:
MCQs Of Political Parties Class 10 Question 13.
What does UPA stands for?
(a) United Party Alliance
(b) United Progressive Alliance
(c) Unified Political Alliance
(d) None of the above
Answer:
MCQ Of Political Parties Question 14.
Which of the following statements are not associated with a regional political party in India?
(a) It gets 6 per cent of the total votes in the Lok Sabha election
(b) It gets 2 seats in the elections for state legislatures
(c) It gets 6 percent of the total votes in an election to the legislative assembly of a state
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) It gets 6 per cent of the total votes in the Lok Sabha election

![]()
MCQs On Political Parties Question 15.
Which of the following institutions in India has passed an order for every candidate who contests elections to file an giving details of property and criminal cases?
(a) Supreme court of India
(b) Election Commission of India
(c) Constitution of India
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Supreme court of India
Question 16.
The rise of political parties can be linked directly to the emergence of:
(a) Direct democracy
(b) Dictatorship
(c) Monarchy
(d) Representative democracy
Answer:
(d) Representative Democracy
Explanation: Political Parties are a symbol of Representative Democracy. Political parties are groups of politically aware citizens who’re interested in running the government/country as representatives of common people.
Related Theory
Large societies/countries need Representative Democracies. In a representative democracy, repre-sentatives are chosen through public support in elections to form a responsible government because direct democracy is not possible or feasible in these countries. Representatives take care of the needs and requirements of the people who’ve voted for him.
In direct democracies, people do not chose any representatives, rather decide everything through methods like referendum where everyone votes in negative or affirmative at the time of decision making.
Dictatorship is the rule of a single person. No Political parties are allowed to rise in Dictatorship because all powers lie in the hands of an individual and the will of the people is not considered important.
In Monarchy, power is vested in the hands of a non- elected ruler. This position is hereditary. The ruler runs the country and there’s no significance attached to the needs of the people.
Question 17.
What does NDA stands for?
(a) Natural Democratic Alliance
(b) Nominative Democratic Alliance
(c) Nautical Democratic Alliance
(d) National Democratic Alliance
Answer:
(d) National Democratic Alliance
Explanation: NDA is led by BJP and is ruling in the centre currently.
Question 18.
Which of the following political party draws inspiration from the ideas and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Ramaswamy Naicker and Dr. Ambedkar?
(a) BJP
(b) BSP
(c) NCP
(d) CPI
Answer:
(b) BSP
Explanation: BSP was formed in 1984 under the leadership of late Kanshi Ram.
Related Theory
This party enjoys its main base in the state of Uttar Pradesh and formed governments in this state several times by taking support of different parties at different times.
Question 19.
Arrange political parties according to their year of formation in increasing order:
(i) BSP
(ii) BJP
(iii) INC
(iv) CPI
Options:
(a) (i)-(iv)-(iii)-(ii)
(b) (iii)-(iv)-(i)-(ii)
(c) (iv)-(i)-(ii)-(iii)
(d) (iii)-(iv)-(ii)-(i)
Answer:
(d) (iii)-(iv)-(ii)-(i)
Explanation: INC — 1885 CPI— 1925 BJP— 1980 BSP — 1984
![]()
Question 20.
Uniform civil code for all people living in the country irrespective of religion is the agenda of:
(a) Indian National Congress
(b) Bharatiya Janata Party
(c) Nationalist Party of India
(d) Nationalist Congress Party
Answer:
(b) Bharatiya Janata Party
Question 21.
Which one of the following party systems is against the basic principle of democracy?
(a) Multi-party system
(b) Bi-party system
(c) Single party system
(d) None of the above
Answer:
Question 22.
This party was founded in 1964 and believes in Marxism-Leninism. Identify the party:
(a) Communist Party of India
(b) Community Party of India
(c) Communist Party of India-Marxist
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Communist Party of India-Marxist
Explanation: This party is known as CPI-M and was formed after a spilt in the CPI in 1964.
Question 23.
In India, which of the following alliance is NOT active?
(a) National Democratic Alliance
(b) United Progressive Alliance
(c) Left Front
(d) Right Front
Answer:
(d) Right Front
Explanation: In India, there are three major alliances since the 2004 parliamentary elections-NDA (led by BJP), UPA (led by the Congress Party) and the Left Front.
Identify the following on basis of the hints given in each question.
Question 24.
Identify the party:
(1) Several parties compete for power
(2) More than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power.
(3) The government is formed by various parties coming together.
Answer:
Multi-party system.
Question 25.
Identify the party:
(1) Launched on 1 January, 1998 under the leadership of Mamata Banerjee.
(2) The party’s symbol is flowers and grass.
(3) Committed to secularism and federalism.
Answer:
All India Trinamool Congress (AITC)
Explanation: It has been in power in West Bengal since 2011. It also has a presence in Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur and Tripura. In the General Elections held in 2019, it got 4.07 per cent votes and won 22 seats, making it the fourth largest party in the Lok Sabha.
Question 26.
Identify the party:
(1) It is critical of the new economic policies that allow free flow of foreign capital and goods into the country.
(2) It was in power in West Bengal without a break for 34 years.
(3) It was founded in 1964.
(4) The party believes in Marxism-Leninism
Answer:
Correct and Rewrite /True-False
State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct the statement.
Question 27.
India has evolved a multiparty system because the social and geographical diversity in such a large country is not easily absorbed by two or even three parties.
Answer:
True
Question 28.
‘National parties’ have one unit in one state only.
Answer:
False
‘National parties’ have units in various states all across the country.
![]()
Question 29.
Political parties are not crucial for the working of democracy.
Answer:
Question 30.
Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) was formed under the leadership of Mayawati.
Answer:
False
Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP) was formed under the leadership of Kanshi Ram.
Explanation: Formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram, BSP seeks to represent bahujan samaj and secure power for them, which includes the dalits, adivasis, OBCs and religious minorities. Mayawati is one of the leaders affiliated to the party.
Question 31.
The election commission is the most visible institution of any Democracy.
Answer:
False
A Political Party is the most visible institution of any Democracy.
Explanation: Political Parties link the lower most unit of the society- Humans to the entire administration and political system. They become a medium through which Democracy is executed at times of elections. They are the most visible institution because they play the most important role in helping people choose their true and correct representatives. They compete to bring up different issues and problems and compete for public support.
Question 32.
The Supreme Court passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organizational elections and file their income tax returns.
Answer:
The Election Commission of India passed an order making it necessary for political parties to hold their organizational elections and file their income tax returns.
![]()
Question 33.
Indian National Congress wants that high in government be confined to natural-born citizens of the country.
Answer:
Nationalist Congress Party wants that high offices in government be confined to natural-born citizens of the country.
Fill in the blanks/tables with suitable information:
Question 34.
Complete the following table with regards to information about political parties:
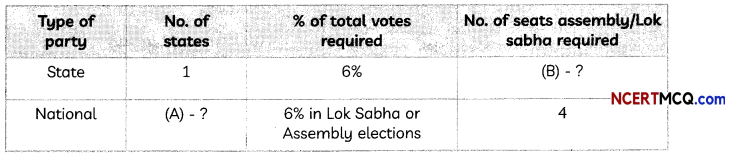
Answer:
(A) 4
(B) 2
Question 35.
The ……….. was leading the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) government from 2004 to 2014.
Answer:
Indian National Congress
Question 36.
Any democratic system must allow at least parties to contest elections to provide fair chances.
Answer:
Question 37.
The body which recognizes and registers Political Parties in India is called
Answer:
Election Commission
Explanation: It is a specific body created to conduct elections in India and to check, recognise and moniror political parties. Central Election Commission recognises National Parties. State Election Commissions are subunits of central election commission at the state level.
![]()
Question 38.
The Bharatiya Janta Party came into power in 1998 as the leader of the ………….. coalition.
Answer:
NDA
Explanation: Bharatiya Janata Party headed the National Democratic Alliance led Coalition Government in 1998.
Related Theory
Coalition government means when any party is incapable of proving majority, single handedly, multiple parties come together and form a government.
Question 39.
………… was the last party to become a national level party in India.
Answer:
All India Trinamool Congress
Explanation: All India Trinamool Congress was formed in 1998 under the leadership of Mamta Banerjee, recognised as a national party in 2016 and in power in West Bengal since 2011.
Question 40.
………….. is the oldest party of India.
Answer:
![]()
Question 41.
…………. is a National Political Party in India formed in 1984 by late Kanshi Ram.
Answer:
Bahujan Samaj party
Match the Columns Choose the correct pairs:
Question 42.
Match the following political parties from column A with their ideologies given in column B:
| Column A (Political Parties) | Column B (Ideologies) |
| (a) Bharatiya Janata Party | (i) Believes in Marxism- Leninism |
| (b) Bahujan Samaj Party | (ii) Supports new economic reforms with a human face |
| (c) Indian National Congress | (iii) Seeks to represent and secure power for the Bahujan Samaj |
| (d) Communist Party of India | (iv) Uniform civil code |
Answer:
| Column A (Political Parties) | Column B (Ideologies) |
| (a) Bharatiya Janata Party | (iv) Uniform civil code |
| (b) Bahujan Samaj Party | (iii) Seeks to represent and secure power for the Bahujan Samaj |
| (c) Indian National Congress | (ii) Supports new economic reforms with a human face |
| (d) Communist Party of India | (i) Believes in Marxism- Leninism |
Question 43.
Match the following political parties from column A with their years of foundation given in column B:
| Column A (Political Parties) | Column B (Year of Foundation) |
| (a) Communist Party of India | (i) 1885 |
| (b) Bharatiya Janata Party | (ii) 1984 |
| (c) Bahujan Samaj Party | (iii) 1980 |
| (d) Indian National Congress | (iv) 1925 |
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Civics Chapter 6
In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding statement of Reason (R). Select the correct answers to codes (a), (b), (c) or (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Question 44.
Assertion (A): The quality of democracy depends on the degree of public participation.
Reason (R): Public participation brings transparency.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: The problem of bad politics can be solved by more and better politics which can be achieved only when people participate more.
Question 45.
Assertion (A): It is mandatory for every candidate who contests elections to file an affidavit giving details of his property and criminal cases pending against him.
Reason (R): It makes the voters more informed.
Answer:
![]()
Question 46.
Assertion (A): The fourth challenge is that very often parties do not seem to offer a meaningful choice to the voters.
Reason (R): The politicians are the same everywhere.
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Explanation: Parties and politicians agree on more fundamental aspects but differ only in details on how policies are to be framed and implemented. In India, the differences among all the major parties on the economic policies have reduced. Those who want really different policies have no option available to them.
Question 47.
Assertion (A): Party system is something any country can choose.
Reason (R): It evolves over time.
Answer:
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Explanation: The party system is not something any country can choose. It evolves over a long time, depending on the nature of society, its social and regional divisions, its history of politics and its system of elections.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
Read the given source and answer the question that follows:
Thus, parties reflect fundamental political divisions in a society. Parties are about a part of the society and thus involve PARTISANSHIP. Thus a party is known by which part it stands for, which policies it supports and whose interest it upholds.
Which out of the following is not a feature of ‘Partisanship’?
(a) inability to take a balanced view.
(b) Partiality towards one group.
(c) Representation of only certain interests.
(d) Equal significance to all issues in the country.
Answer:
(d) Equal significance to all issues in the country. Explanation: Partisanship means inability to hold a balanced view. When one is a partisan, he is biased towards a group.
Question 2.
Observe the table given below and answer the question that follows:

Which area of the world shows maximum political participation through parties?
(a) America
(b) South Asia
(c) Africa
(d) Europe
Answer:
(b) South Asia
Explanation: The proportion of those who said they were members of some political party is higher in India than many advanced countries like Canada, Japan, Spain and South Korea,
Question 3.
Read the given source and answer the question that follows:
A political party is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. They agree on some policies and programmes for the society with a view to promote the collective good.
Which one of these is NOT a function of a political party?
(a) To reflect fundamental political divisions in a society.
(b) To contest elections.
(c) To play a decisive role in making laws.
(d) To form and run governments.
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the question that follows:
Only a handful of parties are effectively in the race to win elections and form the government. So the question, then is: how many major or effective parties are good for a democracy? In some countries, only one party is allowed to control and run the government. These are called one-party systems. China is one such country.
Based on your reading, complete the following statement:
The is the only political party that is allowed to function in China.
Answer:
The Chinese communist party
Explanation: China follows the One party system where only one party is allowed to contest elections. It is a flawed form of Democracy.
Question 5.
Read the source given below and answer the question that follows:
Formed in 1999 following a split in the Congress party. Espouses democracy, Gandhian secularism, equity, social justice and federalism. Wants that high in government be confined to natural born citizens of the country. Identify this political party.
Answer:
Nationalist Congress party
Question 6.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Most of the major parties of the country are classified by the Election Commission as ‘State parties’. These are commonly referred to as regional parties. Yet these parties need not be regional in their ideology or outlook. Over the last three decades, the number and strength has expanded. This made the Parliament of India politically more and more diverse. As a result, the national parties are compelled to form alliances with State parties. Since 1996, nearly every one of the state parties has got an opportunity to be a part of one or the other national level coalition government. This has contributed to the strengthening of federalism
and democracy in our country.
(A) What is a State party?
Answer:
(B) Which one of the following parties is active in Punjab?
(a) Samajwadi Party
(b) Akali Dali
(c) Trinamool Congress Party
(d) Communist Party of India
Answer:
(b) Akali Dal
Explanation: Samajwadi Party is active in UP, Trinamool congress and Communist Party of India are national parties.
(C) Which of the following has contributed to the strengthening of federalism and democracy in our country?
(a) that every regional political party has been a part of national governments through coalitions.
(b) that every national political party has been a part of state governments through coalitions.
(c) that every national and regional political party has been a part of state and national level coalition governments.
(d) that the national parties have allowed state parties to thrive.
Answer:
(a) that every regional political party has been a part of national governments through coalitions.
Explanation: Since 1996, there has been a trend of coalition governments in India in the centre particularly.
(D) Assertion (A): Over the last three decades, the number and strength of regional political parties has expanded.
Reason(R): More people are aware and enthusiastic to participate in the political process and articulate their interests through gaining power.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Seeks to represent and secure power for the bahujan samaj which includes the dalits, adivasis, OBCs and religious minorities. Draws inspiration from the ideas and teachings of Sahu Maharaj, Mahatma Phule, Periyar
Ramaswami Naicker and Babasaheb Ambedkar. Stands for the cause of securing the interests and welfare of the dalits and oppressed people. It has its main base in the state of Uttar Pradesh and substantial presence in neighbouring states like Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Delhi and Punjab. Formed government in Uttar Pradesh several times by taking the support of different parties at different times. In the Lok Sabha elections held in 2019, it polled about 3.63 per cent votes and secured 10 seats in the Lok Sabha.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Identify the party mentioned in the source.
(a) BJP
(b) AITC
(c) Janata Dal
(d) BSP
Answer:
(d) BSP

Explanation: It was formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram. It seeks to represent and secure power for the Bahujan Samaj which includes the Dalits, Adivasis, OBCs and religious minorities.
(B) Fill in the blank by choosing an appropriate option:
AITC – Bengal; NCP- ………………
(a) Kerala
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Kashmir
Answer:
(b) Maharashtra
(C) Categorise the given party as a regional or national party based on the necessary criteria laid by Election Commission.
(a) Regional Party
(b) National Party
(c) Not recognised Party
(d) Recognised party but elects candidates for local self government bodies.
Answer:
(D) Identify the symbol of the party.
(a) Lion
(b) Lotus
(c) Elephant
(d) Grass and Flowers.
Answer:
(c) Elephant
Question 8.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Political parties are easily one of the most visible institutions in a democracy. For most ordinary citizens, democracy is equal to political parties. If you travel to remote parts of our country and speak to the less educated citizens, you could come across people who may not know anything about our Constitution or about the nature of our government. But chances are that they would know something about our political parties. At the same time this visibility does not mean popularity. Most people tend to be very critical of political parties. They tend to blame parties for all that is wrong with our democracy and our political life.
Parties have become identified with social and political divisions.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Consider the following statements and mark which of them are true:
(I) Political parties do not enjoy much trust among the people in South Asia.
(II) Political parties are one of the least trusted institutions all over the world.
(III) The proportion of those who said they were members of some political party was higher in India than many advanced countries like Canada, Japan, Spain and South Korea.
(IV) Over the last three decades the proportion of those who report to be members of political parties in India has gone up steadily.
(V) Political parties are easily one of the most invisible institutions in a democracy.
(a) (l)&(V)
(b) (I) & (III)
(c) (I), (II), (III) & (IV)
(d) (I), (II), (III), (IV) & (V)
Answer:
(c) (I), (II), (III) & (IV)
(B) Which of the following can be the right definition of Political parties?
(a) A political party is a group of people who contest elections.
(b) A political party is a group of people who come together for power.
(c) A political party is a group of people who are of different ideologies and contest elections for authority and power.
(d) A political party is a group of people who influence decision making.
Answer:
(c) A political party is a group of people who are of different ideologies and contest elections for authority and power.
(C) Why do people blame parties?
(a) Because there are no other way to blame anyone.
(b) Because they are undemocratic.
(c) Because they represent democracy the best.
(d) Because they are the most visible democratic institutions.
Answer:
(d) Because they are the most visible democratic institutions.
Explanation: They are the true representatives of democracy across the country. They are blamed due to that connection.
(D) What is the main purpose of a political party?
(a) To look for issues.
(b) To increase political participation.
(c) To change the country territorially.
(d) To bring reformation in political system of the country.
Answer:
(b) To increase political participation Explanation: Political parties incorporate more people through adding them as members, activists etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
We have seen how crucial political parties are for the working of democracy. Since parties are the most visible face of democracy, it is natural that people blame parties for whatever is wrong with the working of democracy. All over the world, people express strong dissatisfaction with the failure of political parties to perform their functions well. This is the case in our country too. Popular dissatisfaction and criticism has focussed on four problem areas in the working of political parties. Political parties need to face and overcome these challenges in order to remain effective instruments of democracy.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(A) Which of the following challenges affects the internal working of a political party?
(a) The challenge of growing role of money and muscle power in parties.
(b) The challenge of lack of internal democracy within parties.
(c) The challenge of dynastic succession.
(d) The challenge of not giving adequate choices to people.
Answer:
(b) The challenge of lack of internal democracy within parties.
Explanation: Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings, and do not conduct internal elections regularly. Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information on what happens inside the party. This affects internal working of a party.
(B) Mishra ji, a political party head is not ready to leave his position as the head of a party for any other leader except his son. Which challenge does this situation represent?
(a) The challenge of growing role of money and muscle power in parties.
(b) The challenge of lack of internal democracy within parties.
(c) The challenge of dynastic succession.
(d) The challenge of not giving adequate choices to people.
Answer:
(C) Following are some suggestions to reform parties. Which of them is helpful to curb the misuse of money and muscle power in politics?
(I) There should be state funding of elections.
(II) Parties should give one-third of its tickets to women candidates.
(III) Parties should look for leaders from rural areas.
(IV) A body should be set up for regulation of economic affairs of the party.
(a) (I) & (IV)
(b) (II) & (III)
(c) (I), (II), (III)
(d) (IV) only
Answer:
(D) Berlusconi was the Prime Minister of Italy. He is also one of the top businessmen in Italy. He is the leader of the Forza Italia founded in 1993. His company owns TV channels, the most important publishing company, a football club (AC Milan) and a bank. Identify the challenge posed.
(a) The challenge of growing role of money and muscle power in parties.
(b) The challenge of lack of internal democracy within parties.
(c) The challenge of dynastic succession.
(d) The challenge of not giving adequate choices to people.
Answer:
(a) The challenge of growing role of money and muscle power in parties
Explanation: He controlled the economic market and could make decisions which forfeited him keeping aside all the interests of the people in his country.
![]()
Question 10.
Read the source and answer the questions that follow:
The first challenge is lack of internal democracy within parties. Allover the world there is a tendency in political parties towards the concentration of power in one or few leaders at the top. Parties do not keep membership registers, do not hold organisational meetings, and do not conduct internal elections regularly. Ordinary members of the party do not get sufficient information on what happens inside the party. They do not have the means or the connections needed to influence the decisions. As a result the leaders assume greater power to make decisions in the name of the party.
The second challenge of dynastic succession is related to the first one. Since most political parties do not practice open and transparent procedures for their functioning, there are very few ways for an ordinary worker to rise to the top in a party. Questions:
(A) Name one state and one national political party in India?
Answer:
National Party: Indian National Congress State Party: Janata Dal(U) of Jharkhand
(B) What is the challenge of dynastic succession faced by a party?
Answer:
The challenge of Dynastic Succession in parties is a result of favouritism and nepotism practiced openly. It becomes difficult for an outsider/common man to rise to influential positions in a party regardless of his talent. Most powerful positions are reserved for relatives or friends.
(C) Suggest reforms which can help political parties to face the lack of internal democracy.
Answer:
To face lack of internal democracy, a party should make its functioning more transparent. Regular meetings should be held, communication should be made stronger, favouritism should be removed and everybody should be given an equal chance to contribute to party affairs. Apart from this, selection process or utilisation of funds should be made transparent by setting up a committee-properly represented by all areas of members present in the country
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Examine the reason to accept a multi-party system in India.
Answer:
India is a diverse country and needs to accommodate its diversity to help in better administration. This is possible only through a Multi-party system.
Question 2.
Correct the following statements and rewrite it.
Bahujan Samaj Party was formed under the leadership of the Mayawati.
Answer:
Bahujan Samaj Party was formed under the leadership of the Mayawati.
Question 3.
Name any one political party that has National level political organization but not recognized as the National Political Party.
Answer:
Rashtriya Janata Dal or Samajwadi Party
![]()
Question 4.
Name an Alliance formed by the Congress Party?
Answer:
Question 5.
What is the guiding philosophy of Bharatiya Janata Party?
Answer:
India’s ancient culture, values and cultural nationalism (or ‘Hindutvaj is the guiding philosophy of BJP.
Question 6.
Name any two Regional parties of West Bengal.
Answer:
Forward Bloc and Trinamool Congress
Question 7.
If all the decisions of a political party are made by a single family and all other members are neglected then what challenge is being faced by that party?
Answer:
The challenge of dynastic succession
Question 8.
Suggest any one way to make political parties more responsive to people’s needs and demands.
Answer:
Political parties can be- made more responsive through organised petitions, agitations and publicity by various groups.
Explanation: This shall make political parties pay more attention to people’s needs to secure their support.
![]()
Question 9.
Name any one regional party of Uttar Pradesh.
Answer:
The Samajwadi Party is one of the regional parties of Uttar Pradesh.
Related Theory
Regional political party (or state party) is a party that has its presence only in one or some states. Regional parties may not always be regional in their ideology or outlook.
Question 10.
Why is one party political system not considered a good democratic system?
Answer:
One party political system is not considered a good democratic system because it doesn’t offer a meaningful choice to the citizens of the country as they have no options to choose from.
Related Theory
Because of this, the right to vote given to the citizens of a democracy having one party political system is useless as there is only one party which wins the elections every time.
Question 11.
Suggest any one way to promote public participation in political parties for enhancing the quality of democracy.
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
Name any two Indian national political parties.
Answer:
Indian national political parties are:
- Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
- Indian National Congress (INC)
- Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP)
- All India Trinamool Congress (AITC)
Related Theory
A national political party is a party that secures at least 6% of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four States and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha.
Question 13.
Which organization recognize ‘political parties in India?
Answer:
The Election Commission of India is responsible for recognizing and registering ‘political parties in India.
Related Theory
The Election Commission of India is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for organizing and administering election processes in India at national, state and district levels.
Question 14.
What is defection?
Answer:
![]()
Question 15.
Name any one political party that is a national-level political organization but is not recognized as a national political party.
Answer:
Samajwadi Party is a political party that has a national-level political organization but is not recognized as a national political party.
Related Theory
Other examples of such political parties are Rashtriya Janata Dal and Samata Party. Such parties have their units in several states.
Question 16.
In which year did the Communist Party of India split into two parties?
Answer:
1964
Question 16.
Explain the meaning of political party.
Answer:
Question 17.
Why do political parties involve partisanship?
Answer:
Political parties involve partisanship because The parties are a part of the society and thus they involve partisanship.
Question 18.
Which type of government is formed when two or more political parties come together to form a government?
Answer:
Coalition Government
Explanation: At times, when no single party is able to gather majority votes, two or more parties come together to form a government. This is called Coalition Government.
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science with Answers
Class 10 Social Science Civics MCQ: