Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Relations and Functions with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Relations and Functions Class 12 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 MCQ With Answers
Maths Class 12 Chapter 1 MCQs On Relations and Functions
Relation And Function Class 12 MCQ Question 1.
If f(x1) = f (x2) ⇒ x1 = x2 ∀ x1 x2 ∈ A then the function f: A → B is
(a) one-one
(b) one-one onto
(c) onto
(d) many one
Answer
Answer: (a) one-one
Relations And Functions Class 12 MCQ Question 2.
What type of a relation is R = {(1, 3), (4, 2), (2, 4), (2, 3), (3, 1)} on the set A – {1, 2, 3, 4}
(a) Reflexive
(b) Transitive
(c) Symmetric
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
MCQ On Relation And Function Class 12 Question 3.
If F : R → R such that f(x) = 5x + 4 then which of the following is equal to f-1(x).
(a) \(\frac{x-5}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{x-y}{5}\)
(c) \(\frac{x-4}{5}\)
(d) \(\frac{x}{4}\) -5
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{x-4}{5}\)
MCQ Of Relation And Function Class 12 Question 4.
If an operation is defined by a* b = a² + b², then (1 * 2) * 6 is
(a) 12
(b) 28
(c) 61
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 61
Relation And Function MCQ Question 5.
Consider the binary operation * on a defined by x * y = 1 + 12x + xy, ∀ x, y ∈ Q, then 2 * 3 equals
(a) 31
(b) 40
(c) 43
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 31
Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 MCQ Questions Question 6.
The range of the function f(x) = \(\sqrt{(x-1)(3-x)}\) is
(a) [1, 3]
(b) [0, 1]
(c) [-2, 2]
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) [1, 3]
Relation And Function Class 12 MCQ Questions Question 7.
If f: R → R defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 then f-1(x) =
(a) 2x – 3
(b) \(\frac{x-3}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{x+3}{2}\)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{x-3}{2}\)
Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 MCQ Question 8.
The function f(x) = log (x² + \(\sqrt{x^2+1}\) ) is
(a) even function
(b) odd function
(c) Both
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) even function
Relation And Function MCQ Class 12 Question 9.
Let E = {1, 2, 3, 4} and F = {1, 2} Then, the number of onto functions from E to F is
(a) 14
(b) 16
(c) 12
(d) 8
Answer
Answer: (a) 14
MCQ Of Maths Class 12 Chapter 1 Question 10.
If A, B and C are three sets such that A ∩ B = A ∩ C and A ∪ B = A ∪ C. then
(a) A = B
(b) A = C
(c) B = C
(d) A ∩ B = d
Answer
Answer: (c) B = C
Relations And Functions MCQ Question 11.
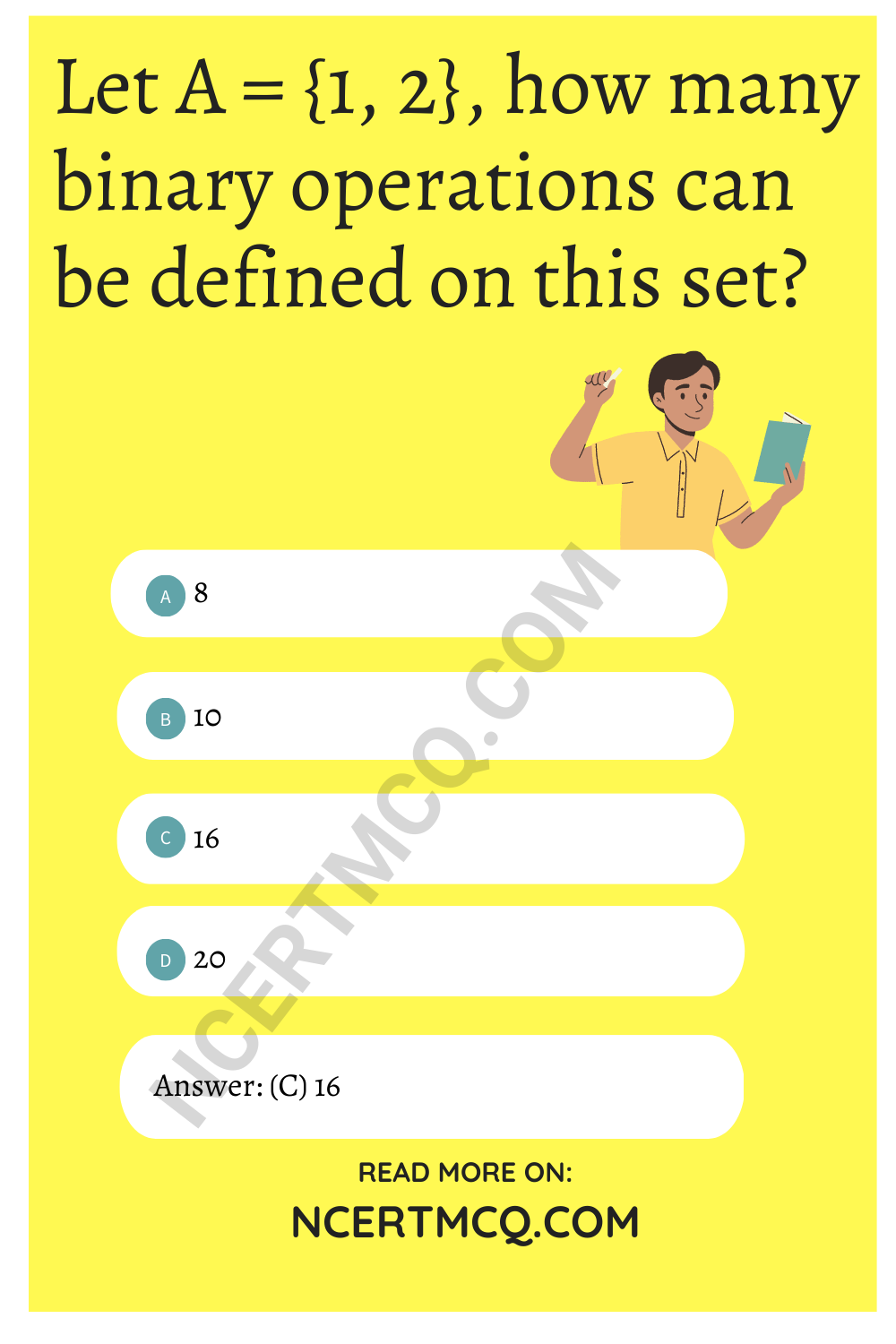
Let A = {1, 2}, how many binary operations can be defined on this set?
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 16
(d) 20
Answer
Answer: (c) 16
MCQ Relation And Function Class 12 Question 12.
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4,…. n} How many bijective function f : A → B can be defined?
(a) \(\frac{1}{2}\)n
![]()
(d) n
Answer
Answer: (c) [n
Class 12 Maths Ch 1 MCQ Questions Question 13.
If A = (1, 2, 3}, B = {6, 7, 8} is a function such that f(x) = x + 5 then what type of a function is f?
(a) Many-one onto
(b) Constant function
(c) one-one onto
(d) into
Answer
Answer: (c) one-one onto
Relation Function Class 12 MCQ Question 14.
Let function R → R is defined as f(x) = 2x³ – 1, then ‘f’ is
(a) 2x³ + 1
(b) (2x)³ + 1
(c) (1 – 2x)³
(d) (\(\frac{1+x}{2}\))1/3
Answer
Answer: (d) (\(\frac{1+x}{2}\))1/3
Relation And Function Class 12 MCQ Term 1 Question 15.
Let the functioin ‘f’ be defined by f (x) = 5x² + 2 ∀ x ∈ R, then ‘f’ is
(a) onto function
(b) one-one, onto function
(c) one-one, into function
(d) many-one into function
Answer
Answer: (d) many-one into function
MCQs On Relations And Functions Class 12 Question 16.
A relation R in human being defined as, R = {{a, b) : a, b ∈ human beings : a loves A} is-
(a) reflexive
(b) symmetric and transitive
(c) equivalence
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) equivalence
Class 12 Relation And Function MCQ Question 17.
If f(x) + 2f (1 – x) = x² + 2 ∀ x ∈ R, then f(x) =
(a) x² – 2
(b) 1
(c) \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x – 2)²
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x – 2)²
MCQ Questions On Relations And Functions Class 12 Question 18.
The period of sin² θ is
(a) π²
(b) π
(c) 2π
(d) \(\frac{π}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) π
Class 12 Maths MCQ Chapter 1 Question 19.
The domain of sin-1 (log (x/3)] is. .
(a) [1, 9]
(b) [-1, 9]
(c) [-9, 1]
(d) [-9, -1]
Answer
Answer: (a) [1, 9]
Ch 1 Maths Class 12 MCQ Question 20.
f(x) = \(\frac{log_2(x+3)}{x^2+3x+2}\) is the domain of
(a) R – {-1, -2}
(b) (- 2, ∞) .
(c) R- {- 1,-2, -3}
(d) (-3, + ∞) – {-1, -2}
Answer
Answer: (d) (-3, + ∞) – {-1, -2}
Class 12 Relations And Functions MCQ Question 21.
If the function f(x) = x³ + ex/2 and g (x) = fn(x), then the value of g'(1) is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer
Answer: (b) 2
Chapter 1 Maths Class 12 MCQ Question 22.
What type of relation is ‘less than’ in the set of real numbers?
(a) only symmetric
(b) only transitive
(c) only reflexive
(d) equivalence
Answer
Answer: (b) only transitive
Relations And Functions Class 12 MCQs Question 23.
If A = [1, 2, 3}, B = {5, 6, 7} and f: A → B is a function such that f(x) = x + 4 then what type of function is f?
(a) into
(b) one-one onto
(c) many-onto
(d) constant function
Answer
Answer: (b) one-one onto
Relation And Function Class 12th MCQ Question 24.
f: A → B will be an into function if
(a) range (f) ⊂ B
(b) f(a) = B
(c) B ⊂ f(a)
(d) f(b) ⊂ A
Answer
Answer: (a) range (f) ⊂ B
Question 25.
If f : R → R such that f(x) = 3x then what type of a function is f?
(a) one-one onto
(b) many one onto
(c) one-one into
(d) many-one into
Answer
Answer: (c) one-one into
Question 26.
If f: R → R such that f(x) = 3x – 4 then which of the following is f-1(x)?
(a) \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x + 4)
(b) \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x – 4)
(c) 3x – 4
(d) undefined
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{1}{3}\) (x + 4)
Question 27.
A = {1, 2, 3} which of the following function f: A → A does not have an inverse function
(a) {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3)}
(b) {(1, 2), (2, 1), (3, 1)}
(c) {(1, 3), (3, 2), (2, 1)}
(d) {(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 1)
Answer
Answer: (b) {(1, 2), (2, 1), (3, 1)}
Question 28.
Let T be the set of all triangles in the Euclidean plane, and let a relation R on T be defined as aRb if a congruent to b ∀ a, b ∈ T. Then R is
(a) reflexive but-not transitive
(b) transitive but not symmetric
(c) equivalence
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) equivalence
Question 29.
Consider the non-empty set consisting of children is a family and a relation R defined as aRb If a is brother of b. Then R is
(a) symmetric but not transitive
(b) transitive but not symmetric
(c) neither symmetric nor transitive
(d) both symmetric and transitive
Answer
Answer: (b) transitive but not symmetric
Question 30.
The maximum number of equivalence relations on the set A = {1, 2, 3} are
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer
Answer: (d) 5
Question 31.
If a relation R on the set {1, 2, 3} be defined by R = {(1, 2)}, then R is
(a) reflexive
(b) transitive
(c) symmetric
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) transitive
Question 32.
Let us define a relation R in R as aRb if a ≥ b. Then R is
(a) an equivalence relation
(b) reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
(c) neither transitive nor reflexive but symmetric
(d) symmetric, transitive but not reflexive
Answer
Answer: (b) reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
Question 33.
Let A = {1, 2, 3} and consider the relation R = {(1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3), (1, 3)}. Then R is
(a) reflexive but not symmetric
(b) reflexive-but not transitive.
(c) symmetric and transitive
(d) neither symmetric, nor transitive
Answer
Answer: (a) reflexive but not symmetric
Question 34.
The identity element for the binary operation * defined on Q ~ {0} as
a * b = \(\frac{ab}{2}\) ∀ a, b ∈ Q ~ {0} is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 2
Question 35.
If the set A contains 5 elements and the set B contains 6 elements, then the number of one-one and onto mappings from A to B is
(a) 720
(b) 120
(c) 0
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 0
Question 36.
Let A = {1, 2,3,…. n} and B = { a, b}. Then the number of surjections from A into B is
(a) nP2
(b) 2n – 2
(c) 2n – 1
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 2n – 2
Question 37.
Let f : R → R be defined by f (x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\) ∀ x ∈ R. Then f is
(a) one-one
(b) onto
(c) bijective
(d) f is not defined
Answer
Answer: (d) f is not defined
Question 38.
Let f: R → R. be defined by f (x) = 3x² – 5 and g : R → R by g (x) = \(\frac{x}{x^2+1}\). Then g o f is
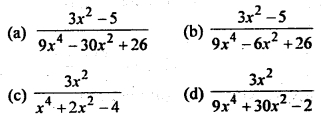
Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 39.
Which of the following functions from Z into Z are bijective?
(a) f(x) = x³
(b) f(x) = x + 2
(c) f(x) = 2x + 1
(d) f{x) = x² + 1
Answer
Answer: (b) f(x) = x + 2
Question 40.
Let f: R → R be the function defined by f(x) = x³ + 5. Then f-1 (x) is
(a) (x + 5)1/3
(b) (x -5)1/3
(c) (5 – x)1/3
(d) 5 – x
Answer
Answer: (b) (x -5)1/3
Question 41.
Let f: A → B and g : B → C be the bijective functions. Then (g o f)-1 is,
(a) f-1 o g-1
(b) f o g
(c ) g-1 o f-1
(d) g o f
Answer
Answer: (a) f-1 o g-1
Question 42.
Let f: R – {\(\frac{3}{5}\)} → R be defined by f(x) = \(\frac{3x+2}{5x-3}\) then
(a) f-1(x) = f(x)
(b) f-1(x) = -f(x)
(c ) (f o f)x = -x
(d ) f-1(x) = \(\frac{1}{19}\) f(x)
Answer
Answer: (a) f-1(x) = f(x)
Question 43.
Let f: [0, 1| → [0, 1| be defined by
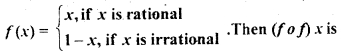
(a) Constant
(b) 1 + x
(c) x
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) x
Question 44.
Let f: |2, ∞) → R be the function defined by f(x) – x² – 4x + 5, then the range of f is
(a) R
(b) [1, ∞)
(c) [4, ∞)
(d) [5, ∞)
Answer
Answer: (b) [1, ∞)
Question 45.
Let f: N → R be the function defined by f(x) = \(\frac{2x-1}{2}\) and g: Q → R be another function defined by g (x) = x + 2. Then (g 0 f) \(\frac{3}{2}\) is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) \(\frac{7}{2}\)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 46.
Let f: R → R be defined by
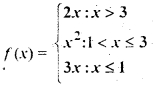
then f(- 1) + f (2) + f (4) is
(a) 9
(b) 14
(c) 5
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 9
Question 47.
Let f : R → R be given by f (,v) = tan x. Then f-1(1) is
(a) \(\frac{π}{4}\)
(b) {nπ + \(\frac{π}{4}\) : n ∈ Z}
(c) does not exist
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) {nπ + \(\frac{π}{4}\) : n ∈ Z}
Question 48.
The relation R is defined on the set of natural numbers as {(a, b): a = 2b}. Then, R-1 is given by
(a) {(2, 1), (4, 2), (6, 3),….}
(b) {(1, 2), (2, 4), (3, 6),….}
(c) R-1 is not defined
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) {(1, 2), (2, 4), (3, 6),….}
Question 49.
The relation R = {(1,1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (1, 2), (2, 3), (1, 3)} on set A = {1, 2, 3} is
(a) Reflexive but not symmetric
(b) Reflexive but not transitive
(c) Symmetric and transitive
(d) Neither symmetric nor transitive
Answer
Answer: (a) Reflexive but not symmetric
Question 50.
Let P = {(x, y) | x² + y² = 1, x, y ∈ R]. Then, P is
(a) Reflexive
(b) Symmetric
(c) Transitive
(d) Anti-symmetric
Answer
Answer: (b) Symmetric
Question 51.
Let R be an equivalence relation on a finite set A having n elements. Then, the number of ordered pairs in R is
(a) Less than n
(b) Greater than or equal to n
(c) Less than or equal to n
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Greater than or equal to n
Question 52.
For real numbers x and y, we write xRy ⇔ x – y + √2 is an irrational number. Then, the relational R is
(a) Reflexive
(b) Symmetric
(c) Transitive
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Reflexive
Question 53.
Let R be a relation on the set N be defined by {(x, y) | x, y ∈ N, 2x + y = 41}. Then R is
(a) Reflexive
(b) Symmetric
(c) Transitive
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these

Question 54.
Which one of the following relations on R is an equivalence relation?
(a) aR1b ⇔ |a| = |b|
(b) aR2b ⇔ a ≥ b
(c) aR3b ⇔ a divides b
(d) aR4b ⇔ a < b
Answer
Answer: (a) aR1b ⇔ |a| = |b|
Question 55.
Let R be a relation on the set N of natural numbers denoted by nRm ⇔ n is a factor of m (i.e. n | m). Then, R is
(a) Reflexive and symmetric
(b) Transitive and symmetric
(c) Equivalence
(d) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
Answer
Answer: (d) Reflexive, transitive but not symmetric
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 1 Relations and Functions with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Relations and Functions CBSE Class 12 Maths MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 12 Maths MCQ:
- Relations and Functions Class 12 MCQ
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 MCQ
- Matrices Class 12 MCQ
- Determinants Class 12 MCQ
- Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 MCQ
- Application of Derivatives Class 12 MCQ
- Integrals Class 12 MCQ
- Application of Integrals Class 12 MCQ
- Differential Equations Class 12 MCQ
- Vector Algebra Class 12 MCQ
- Three Dimensional Geometry Class 12 MCQ
- Linear Programming Class 12 MCQ
- Probability Class 12 MCQ