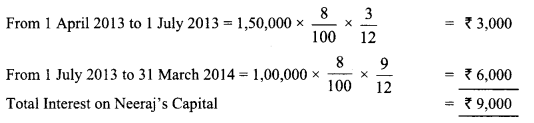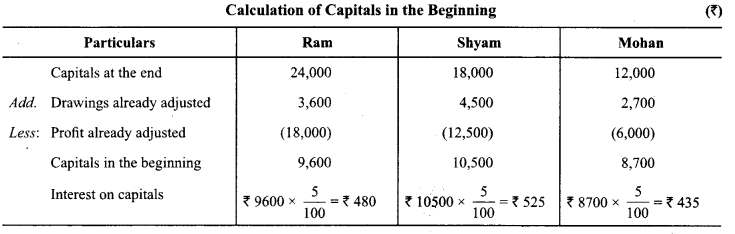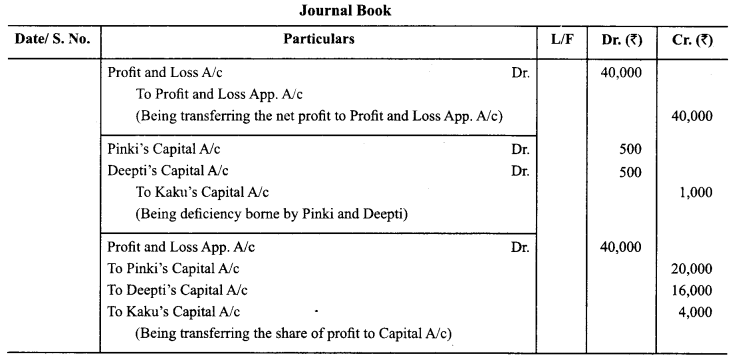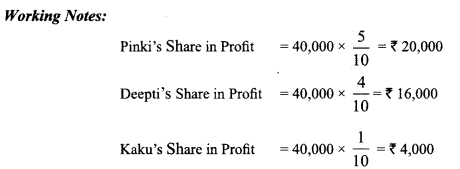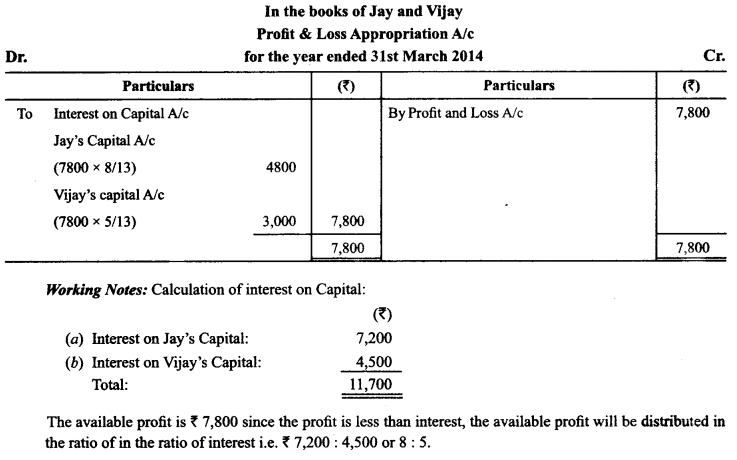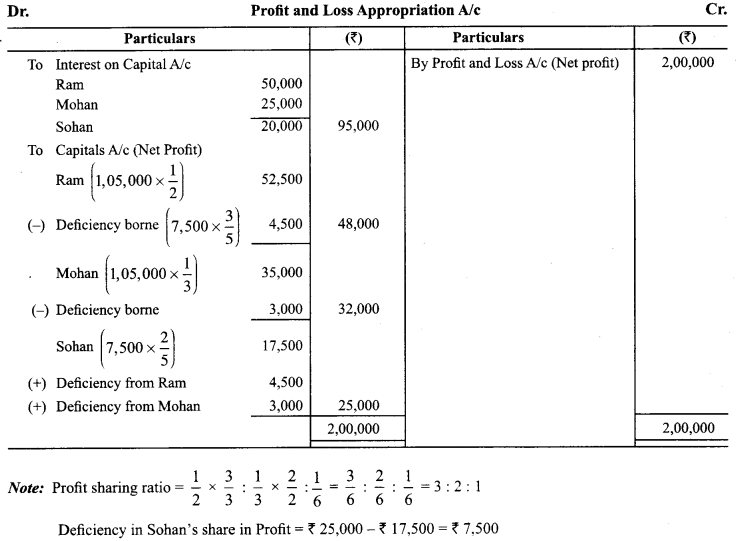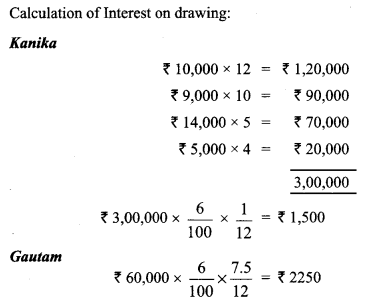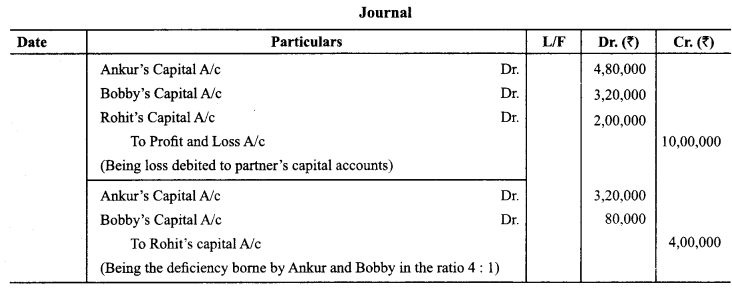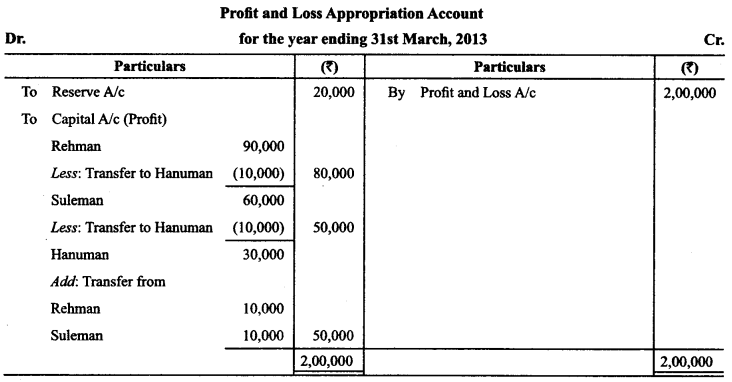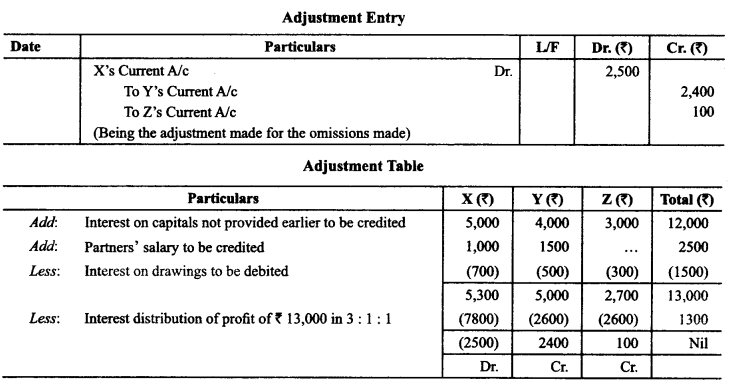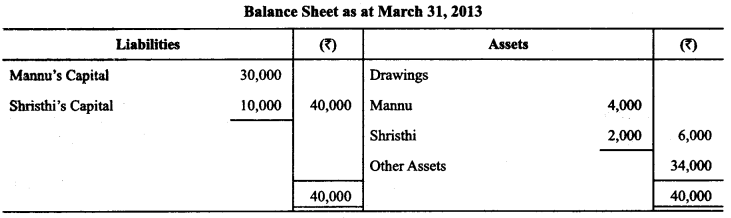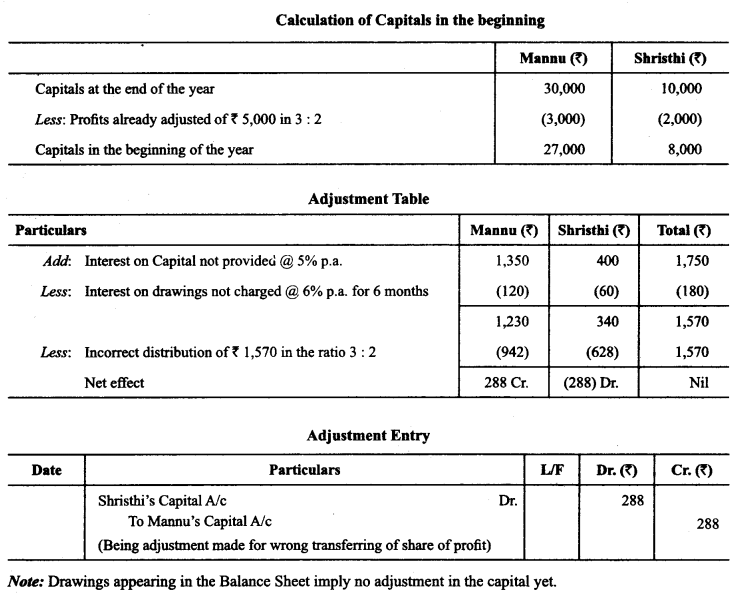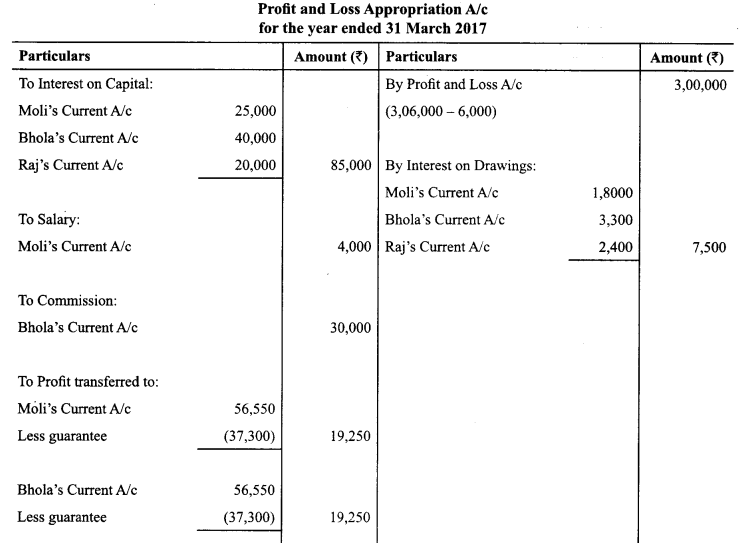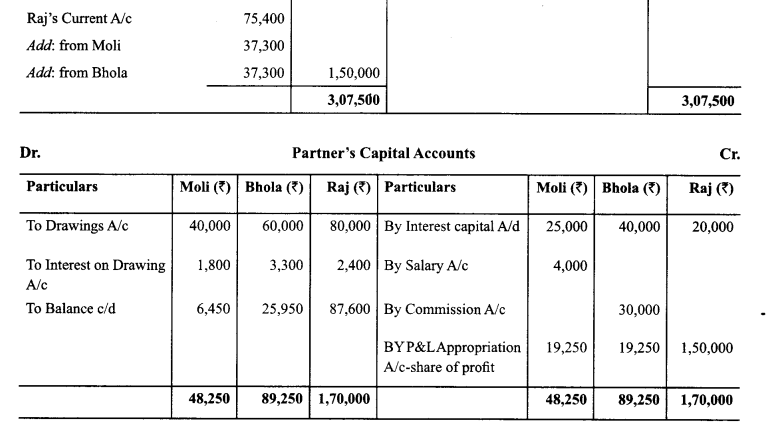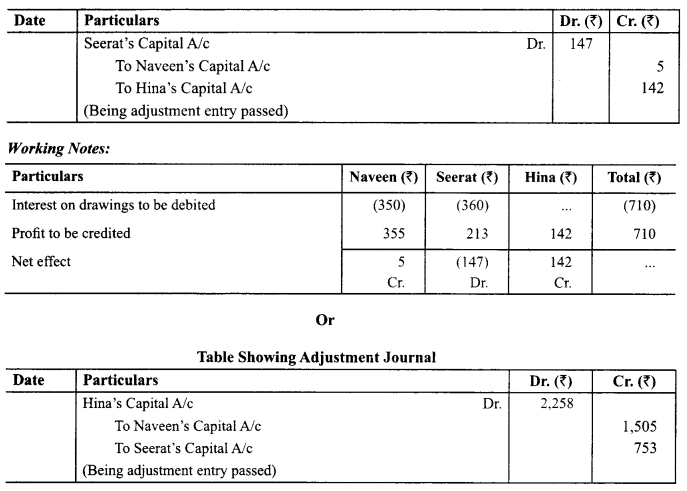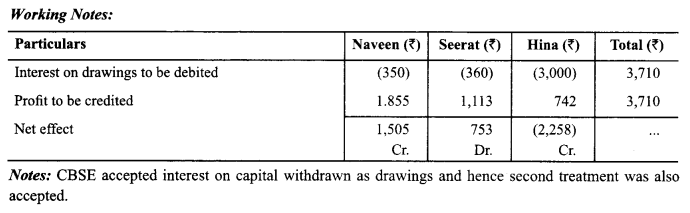
In Online Education Letter writing is an essential skill. Despite the prevalence of emails and text messages, everyone has to write letters at some point. Letters of complaint, job applications, thank you letters, letters requesting changes or – making suggestions – the list goes on and on. Encouraging children to write letters from an early age will improve their communication, social and handwriting skills, and teach them what they need to know about writing and structuring letters.
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 7 English. Every question of the textbook has been answered here. https://ncertmcq.com/formal-letter-writing-topics-for-class-7/
Children are expected to learn how to write letters, notes and messages. They have to be aware of different styles of writing, the use of formal and informal letters, and to select style and vocabulary appropriate to the intended reader.
There are two types of letter:
- Formal letters
- Informal letters
Online Education for Formal Letter Writing Topics for Class 7 Format, Samples Formal letters
- Written only for official purposes
- Written to The Editor, The Principal, The Municipal Commissioner, The Secretory of a Society, The Mayor etc.
- Should be brief and precise.
- Formal tone and polite expression.
- Preferably left side of the page.
These are sometimes known as business letters. They are written in a strictly formal style. Such letters are always written on an A4 (8″ x 11″ sheet of paper. They can be folded three times so that the address to which the letter is being sent can appear in the window of a business envelope. The layout is always the same.
Formal Letter For Class 7
Structure:
- The senders address is put at the top right hand side
- Include telephone number and email if available
- The address of the person receiving the letter goes on the left hand side below the sender’s address
- The date
- Greeting – Dear Sir or Madam. You can use the titles Miss, Mrs. or Mr. if you know the name of the person to whom you are writing
- The message
- Complimentary close – Yours faithfully or Yours sincerely
- Signature
- Write name in block letters (this is to ensure that the person receiving the letter knows exactly who has sent it.
- Signatures may not be very clear).
Formal Letter Topics For Class 7
Layout for a formal letter
| Writer’s Address | A-225, Mayur Vihar Phase 1, Delhi-94 |
| Date | March 25, 2010 |
| Address of the receiver | YZX Technology, C-12, Azad Nagar East, Delhi-18/ The Principal, ABC School, Dhaula Kuan, Delhi-75 |
| Subject | This part contains the objective of writing the letter. It must be concise. |
| Salutation | Respected Madam/Dear Sir |
| Main Body | This part should be divided into three paragraphs. The first paragraph must contain a short mention of the reason for writing the letter; the middle paragraph must contain all the details, while the last paragraph must express what one would want the other person to do in the event of receiving the letter. |
| Subscription | Yours truly/obediently/sincerely |
| Name or Signature | Rajesh/Pavan/Atul, Roll No. 123, Class 10-A |
Formal Letter Writing Topics Solved Examples for Class 7 CBSE
Formal Letter Class 7
Formal Letters (Official)
Write a letter to the Editor of The Times of India complaining about the nuisance created by the use of loudspeakers. You are Peeyush Sharma, a resident of Sector 15, Vasundhara Enclave, New Delhi.
| Sector 15, Vasundhara Enclave, New Delhi – 110096 18th October, 2016 The Editor, The Times of India, New Delhi Subject: Regarding the indiscriminate use of loudspeakersDear Sir, I would like to draw the kind attention of the concerned authorities towards the indiscriminate use of loudspeakers through the columns of your esteemed newspaper.Now – a – days, the use of loudspeakers at religious places, political gatherings, marriages, etc. has become a very common sight. The organisers of these events do not bother to turn off the loudspeakers after the stipulated time when their use is over. In a lot of cases, the use of loudspeakers continues till late in the night. This creates a lot of nuisance and disturbance for many people.I would want the authorities to look into this matter and put stricter rules in place. They must ensure that the use of loudspeakers does not continue after the stipulated time is over. Their efforts in this regard would be much appreciated by one and all.Yours truly, Peeyush Sharma |
Letter To Editor Class 7 Question 2.
Write an application to the Principal of your school to request him to open a Computer Club in your school.
Answer:
The Principal
Rose wood Public School
Naraina, Delhi
17 June 20XX
Subject: Request for computer club
Sir,
We the students of your school would like to inform you that our school is one of the best school in the district but it is a matter of great regret that there is no computer club in our school. Because of not having this facility, our school is lagging behind. We are badly in need of this facility in order to keep pace with the present world. Undoubtedly, the present age is very competitive, communicative and progressive. Time has come for us to prove our talent and so, we need the facility. We are hoping that you would be really kind enough to consider our problem and solve it as soon as possible.
Faithfully yours
Rahul (Head boy)
Student union
Letter Writing For Class 7 Question 3.
Write an application to Principal of your college for a seat accommodation in the hostel.
Answer:
The Principal
Springales school
Pusa Road
12 November, 20XX
Subject : Request for a seat accommodation in the school hostel.
Sir,
With due respect, I would like to state that I am a student of class VII and I read in Science Group. My father is a government employee who has recently been transferred From Udaypur to Delhi and I have no relative here. My family is about to leave for Udaypur. Now I am badly in need of a seat in the hostel. I, therefore, request and hope that you would be kind enough to arrange a seat for me soon and oblige thereby.
Yours truly
Md Nasir Hossain
Class VII
Topics For Formal Letter Writing For Class 7 Question 4.
Write an application to the Mayor of the municipality of your town asking him to provide street lights in your locality.
Answer:
The Mayor South Delhi M. Corporation
Saket
2 November, 20XX
Subject: Request for street lights.
Sir,
We, the inhabitants of Mahipalpur inform you that most of the streets of our locality are without street lights. As the streets remain dark, many crimes take place here. People are afraid of going anywhere at night. So, we want to get rid of this problem. We, therefore, request and hope that you would be kind enough to provide street lights and oblige thereby.
Yours faithfully
Secretary Mahipalpur
Formal Letter Questions For Class 7 Question 5.
Write an application to the principal of your school for fee concession.
Answer:
The Principal,
Abhigyan School
Vasant Kunj Delhi
2 March, 20XX
Sir,
Most respectfully I would like to inform you that I am a student of class VII in your college. The financial condition of my family is very bad. My father’s monthly income is Rs 9000/–. He has to support a family of six members. He is not in a position to pay my fees. But I have a keen desire to get my education as I am brilliant student. Kindly grant me full fee concession and oblige.
Yours faithfully,
Aditya
Roll. No. 31
Formal Letter Writing For Class 7 Question 6.
Write an application to the principal for arranging extra classes in and maths.
Answer:
The Principal,
Arya Balika school
16 August, 20XX
Subject: Arrangement of extra classes
Sir,
I am a student of your school and the reason why I am writing this application is that our courses of Maths and are not covered and the exams are in the next 2 weeks. As there were other activities going on in school secondly the subject teachers were also not regular in their periods. I request you to arrange extra classes for the respective courses so that we can complete the course before exams.
Thanking you,
Yours faithfully,
XYZ
Formal Letter Writing Topics For Class 7 Question 7.
Write an application to your headmaster for permission to arrange a friendly cricket match.
Answer:
The Headmaster
X high school, Dhaka.
2 May, 20XX
Subject: Prayer for permission for a friendly cricket match.
Sir,
I, on behalf of the students of your school, would like to draw your kind attention to the fact that our JDC test examination is over and so we are willing to play a friendly cricket match with the students of Class 7 of our neighboring K.D high school. We have already finished many activities for the cricket match. Our game teacher has consented to guide us and extend his help. But all will be vain without your permission. We therefore are requesting you to give us your permission for the match and obliged thereby.
Yours faithfully
The students of class 7
Formal Letter Format Class 7 Question 8.
The students of your school suffer much from excessive heat. Now write an application to the headmaster for hanging some electric fans in the classroom.
Answer:
The Headmaster,
Ahlcon Public School Barakhamba Road
Delhi
20 July, 20XX
Subject: Request for hanging some electric fans in the classroom.
Sir,
We, the students of your school, would like to draw your kind attention to the fact that our school is housed in the tin shedded building. The classrooms are not spacious. But there are many students in every class. During the summer the rooms become very hot and suffocating. There is no electric fan in any of the rooms. So, it is almost impossible to attend classes during the summer season. Only hanging a few electric fans in the classroom can relieve the students from this inconvenience. So, we are requesting you arrangement to hang a few electric fans for each classroom.
Your most obedient student
Fatima Class VII
Roll No–01
Formal Letter Writing Class 7 Question 9.
Write an application to the principal of your college requesting him/her not to allow any student or teacher to use the ‘cell phone in the classroom or in the examination hall.
Answer:
The principal
Holy Angel’s Sr. Sec. school Ajmeri Gate,
Delhi
11 April, 20XX
Subject: Application for the prohibition of the cell phone in the classroom and in the examination hall.
Dear sir
With due respect, I would like to inform you that the students, as well as the teachers, very often use their cell phone in the classroom and even in the examination hall. It literally disturbs the smooth learning environment to a great extent. The use of cell phone in the classroom and in the examination hall must be stopped.
Yours sincerely,
Anisha
Roll no 3, Class 7th
Letter For Class 7 Question 10.
Write an application to the Manager, requesting him to open a new saving account for scholarship.
Answer:
B– 168 Vivek Vihar
Delhi–110094
16th December 20XX
The Account Manager
State Bank of India
Vivek–Vihar Branch
Delhi–110094,
Sub: Request for Opening a New Saving Account for scholarship
Dear Sir,
This is to inform you that I Sunil Kumar is interested in opening a new saving account in your bank. I am a student Ramagya Model School, Vivek Vihar. I am enclosing the required documents and photographs as per your verification. I would appreciate if you do the needful to initiate the process as soon as possible.
Thanking You.
Yours Sincerely,
Sunil Kumar
Enclosure:
- Voter ID card
- A completed application form
- Photographs
- A copy of address proof
Formal Letter Writing Topics Practice Examples for Class 7 CBSE
Letter Writing Topics For Class 7
Formal Letters (Official)
- Application to the principal for sick leave
- Write an application to the principal to arrange a school picnic.
- Write an application to the principal of your school for arranging extra classes in Science and Maths
- Application to the principal for leave to attend sister’s wedding.
You are Deepshikha Arora. You have passed out of DAV Public School. Write an application to your Principal, requesting him to issue you a character certificate as you need one for university admissions. - You are Srishti Gupta, a student of Bright star public school. You have been promoted to class 9th with Hindi as an optional subject. But you would like to opt for Sanskrit. Write an application to the principal requesting her to change your section having Sanskrit as the optional subjects.


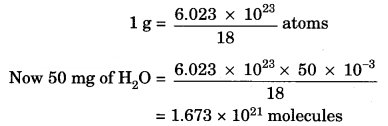

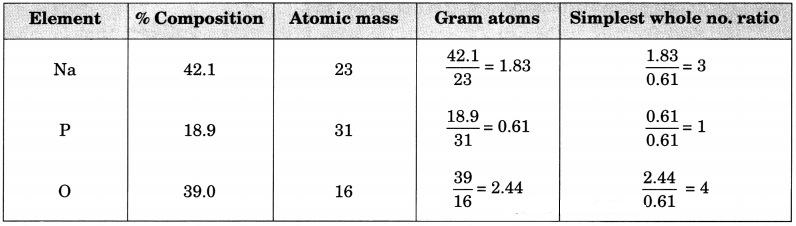
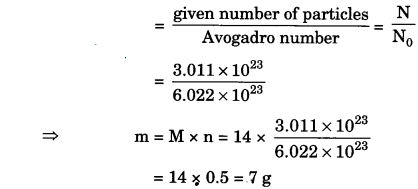
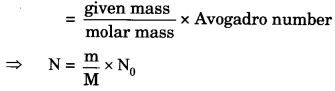
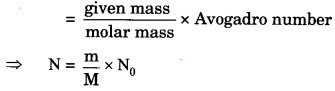

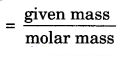







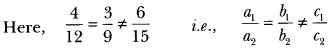
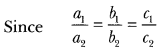
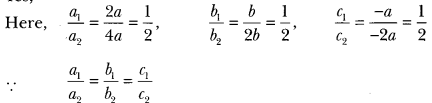
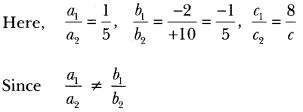


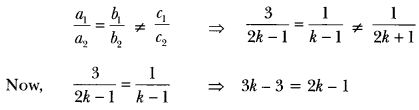
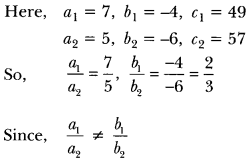
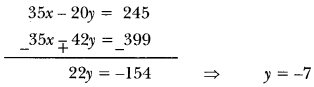
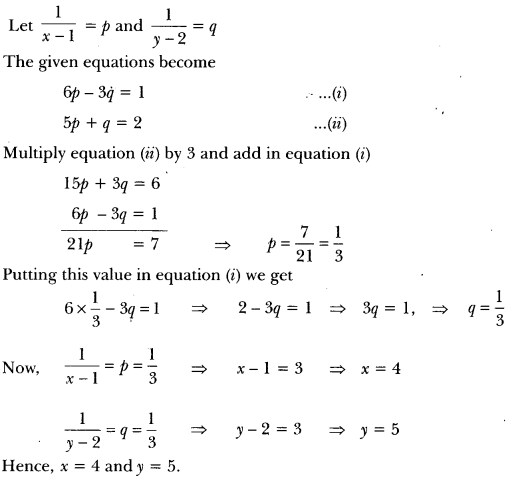







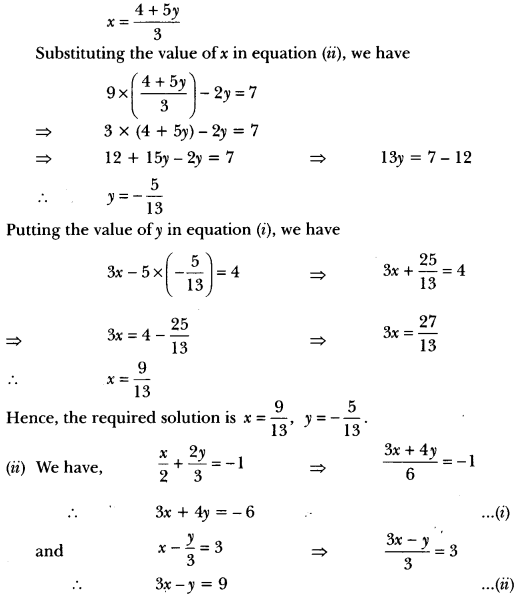
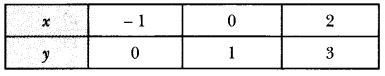
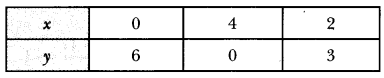
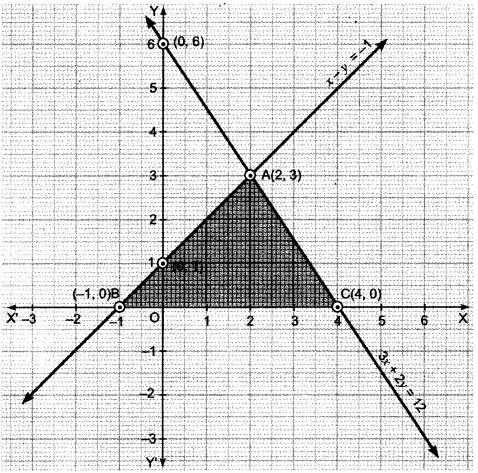

 ”
”

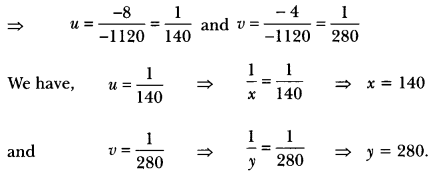

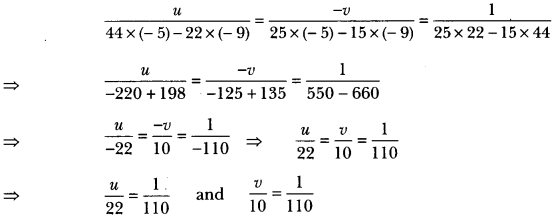
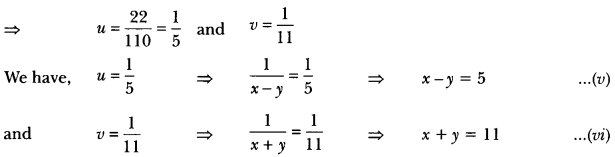
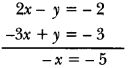
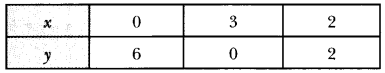
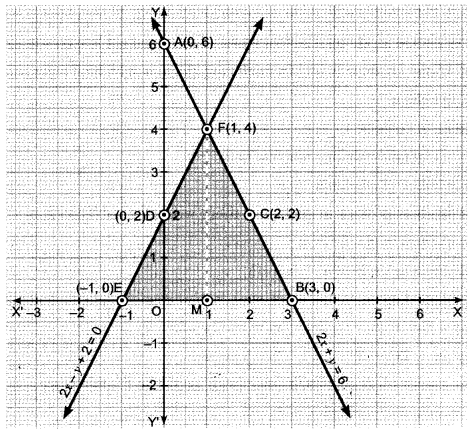
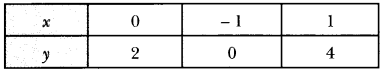
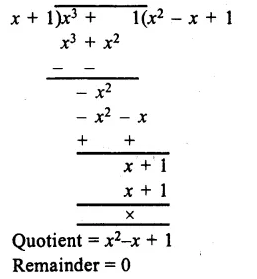
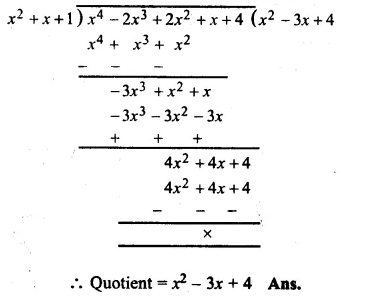
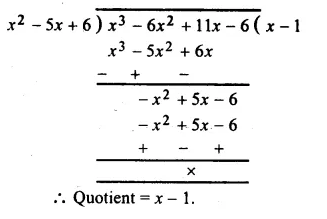
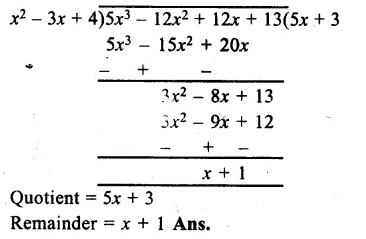
 In Online Education Letter writing is an essential skill. Despite the prevalence of emails and text messages, everyone has to write letters at some point. Letters of complaint, job applications, thank you letters, letters requesting changes or – making suggestions – the list goes on and on. Encouraging children to write letters from an early age will improve their communication, social and handwriting skills, and teach them what they need to know about writing and structuring letters.
In Online Education Letter writing is an essential skill. Despite the prevalence of emails and text messages, everyone has to write letters at some point. Letters of complaint, job applications, thank you letters, letters requesting changes or – making suggestions – the list goes on and on. Encouraging children to write letters from an early age will improve their communication, social and handwriting skills, and teach them what they need to know about writing and structuring letters. On this page, you will find Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 4 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT
On this page, you will find Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 4 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT