Here we are providing Online Education for Class 12 Accountancy Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 5 Dissolution of a Partnership Firm. Accountancy Class 12 Important Questions and Answers are the best resource for students which helps in class 12 board exams.
Online Education for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 5 Important Extra Questions Dissolution of a Partnership Firm
Dissolution of a Partnership Firm Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Differentiate between Dissolution of Partnership and Dissolution of a Partnership Firm on the basis of ‘Court’s Intervention’. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:

Question 2.
State any two situations when a partnership firm can be compulsorily dissolved. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
A firm is compulsorily dissolved in the following cases: (Any two)
- When all the partners or all but one partner become insolvent.
- When the business of the firm becomes illegal.
Question 3.
Distinguish between ‘Reconstitution of Partnership’ and ‘Dissolution of Partnership Firm’ on the basis of ‘Closure of books’.
Answer:

Question 4.
State the basis of calculating the amount of profit payable to the legal representative of a deceased partner in the year of death. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Profit may be estimated
- On the basis of last year’s the profit/Average profits of last given no. of years
- On the basis of Turnover/Sales.
Question 5.
State any two grounds on the basis of which the court may order for the dissolution of the partnership firm. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
At the suit of a partner, the court may order a partnership firm to be dissolved on any of the following grounds:
- when a partner becomes insane;
- when a partner becomes permanently incapable of performing his duties as a partner.
Question 6.
State any two situations when a partnership firm can be compulsorily dissolved. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
A firm is compulsorily dissolved in the following-cases:
- When all the partners or all but one partner become insolvent.
- When the business of the firm becomes illegal.
Question 7.
State any two contingencies that may result into dissolution of a partnership firm.(CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Contingencies that may result into dissolution of a partnership firm: .
- If the firm is constituted for a fixed term, on the expiry of that term
- If constituted to carry out one or more ventures, on the completion of the venture.
Question 8.
State the order of payment of the following, in case of dissolution of the partnership firm.
(i) to each partner proportionately what is due to him/her from the firm for advances as distinguished from capital (i.e. partner’ loan);
(ii) to each partner proportionately what is due to him on account of capital; and
(iii) for the debts of the firm to the third parties; (CBSE Sample Paper 2019-20)
Answer:
(iii) for the debts of the firm to the third parties;
(i) to each partner proportionately what is due to him/her from the firm for advances as distinguished from capital (i.e. partner’ loan);
(ii) to each partner proportionately what is due to him on account of capital
Question 9.
A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 Mrs. B has given a loan of ₹ 40,000 to the firm and A has also given a loan of ₹ 80,000 to the firm. The firm was dissolved and its assets realised ₹ 60,000.
State the order of payment of Mrs. B’s loan and A’s loan assuming that there was no other third party liability – of the firm.
Answer:
Order of payment:
First, the third party loan i.e. Mrs. B’s loan will be paid.
The Partner’s loan i.e. A’s loan will be paid.
Question 10.
A B and C are partners in a firm. On April 1, 2013, A and B were declared insolvent by a court. Will the partnership firm be treated as dissolved?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 11.
Mohan and Kanwar are partners in a firm. Their firm was dissolved on 1.1.2013. Mohan was assigned the work of dissolution. For this work, Mohan was paid ₹ 500. Mohan paid dissolution expenses of₹ 400 from his own pocket. Will any Journal Entry be passed for ₹ 400 paid by Mohan?
Answer:
No.
Question 12.
A firm has investment fluctuation fund of ₹ 10,000. It does not have investments on its Balance Sheet at the time of its dissolution. In which account(s), amount of investments fluctuation fund be transferred?
Answer:
In Partners’ Capital Accounts.
Question 13.
Why is cash balance not transferred to Realisation Account on the dissolution of a partnership firm?
Answer:
Cash is a liquid asset.
Question 14.
A firm was dissolved on April 1, 2013. The assets side of its Balance Sheet has furniture of ₹ 2,500 whereas on the liabilities side, creditors appeared for ₹ 4,000.-Half of the creditors took half of the furniture at 10% discount and the remaining creditors were paid at 10% premium. What journal entries are required?
Answer:
No journal entry will be passed for the first half of the creditors but for the remaining creditors, entry will be:

Question 15.
Should intangible assets be treated in the manner of treatment of tangible assets at the time of dissolution of a partnership firm?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 16.
In case of dissolution of a firm which liabilities are to be paid first?(CBSE 2011 Compartment Delhi)
Answer:
Debts of third parties.
Question 17.
In case of dissolution of a firm, which item on the liabilities side is to be paid last? (CBSE 2011 Compartment Delhi)
Answer:
Partners’ capital.
Question 18.
A firm has furniture of₹ 6,000 which was taken over by a creditor of₹ 5,000 in full settlement of his claim. Mention whether any journal entry will be passed for this. If yes, pass the journal entry.
Answer:
No, journal entry will be passed.
Question 19.
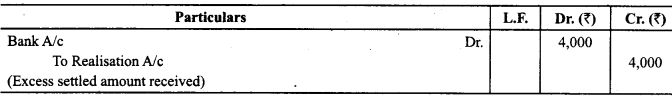
Creditors of ₹ 50,000 took over stock at agreed value of₹ 45,000 and balance Was paid to him. Pass the journal entry for this transaction.
Answer:
The Journal entry will be:

Question 20.
Drawers of bills payable ₹ 25,000 took over furniture at agreed value of₹ 29,000 and paid the excess value. Pass journal entry for this transaction.
Answer:
The Journal entry will be:
Question 21.
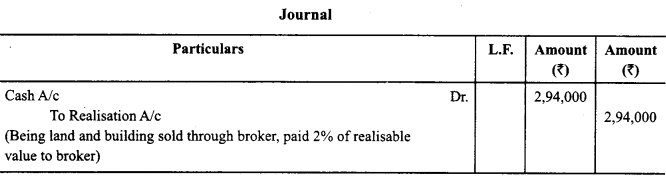
Land and Building (book value) ₹ 1,60,000 sold for ₹ 3,00,000 through a broker who charged 2% commission on the deal. Journalise the transaction, at the time of dissolution of the firm. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018-19)
Answer:
Question 22.
State any one occasion for the dissolution of the firm on court’s orders when a partner becomes. (Compt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Partner becomes permanently incapable of performing his duties as a partner.
Question 23.
Name the asset that is not transferred to the debit side of Realisation account, but brings certain amount of cash against its disposal at the time of dissolution of the firm. (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Unrecorded assets
Question 24.
Ram and Shyam formed partnership at will. Ram gave a notice on January 1, 2013 to dissolve the firm. Can partnership firm be dissolved even without consent of Shyam? Give reason.
Answer:
Yes.
Dissolution of a Partnership Firm Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
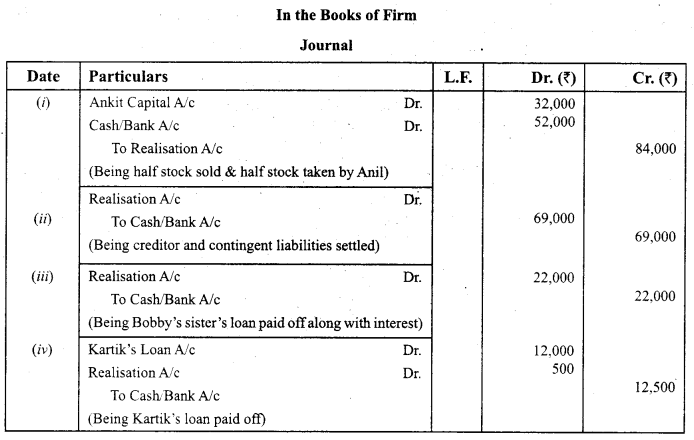
Ankit, Bobby and Kartik were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio 4:3:3. The firm was dissolved on 31-3-2018. Pass the necessary Journal entries for the following transactions after various assets (other than cash and bank) and third party liabilities had been transferred to Realisation Account:
(i) The firm had stock of ₹ 80,000. Ankit took over 50% of the stock at a discount of 20% while the remaining stock was sold off at a profit of 30% on cost.
(ii) A liability under a suit for damages included in creditors was settled at ₹ 32,000 as against only ₹ 13,000 provided in the books. Total creditors of the firm were ₹ 50,000.
(iii) Bobby’s sister’s loan of ₹ 20,000 was paid off along with interest of ₹ 2,000.
(iv) Kartik’s Loan of₹ 12,000 was settled at ₹ 12,500. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Question 2.
State any two contingencies that may result into dissolution of a partnership firm. (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Contingencies that may result into dissolution of a partnership firm: (Any two)
- If the firm is constituted for a fixed term, on the expiry of that term.
- If constituted to carry out one or more ventures, on the completion of the venture.
Question 3.
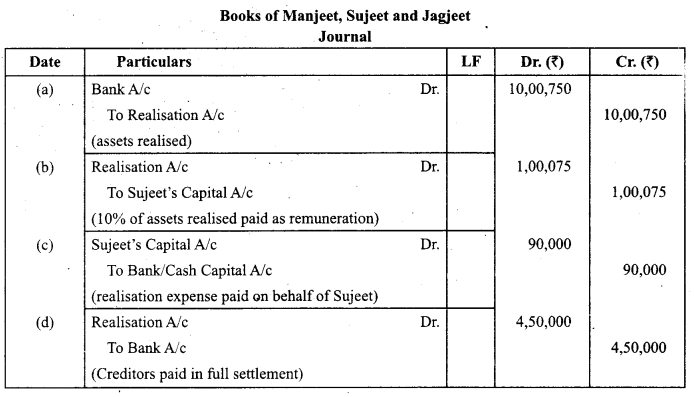
The firm of Manjeet, Sujeet and Jagjeet was dissolved on 31st March, 2018. It was agreed that Sujeet will take care of the dissolution related activities and will get 10% of the value of assets realised. Sujeet agreed to bear the realisation expenses. Assets realised ₹ 10,00,750 and realisation expenses were ₹90,000, which were paid from the firm’s cash. ₹4,50,000 were paid to the creditors in full settlement of their claim.
Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of the firm.
(CBSE Outside Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Question 4.
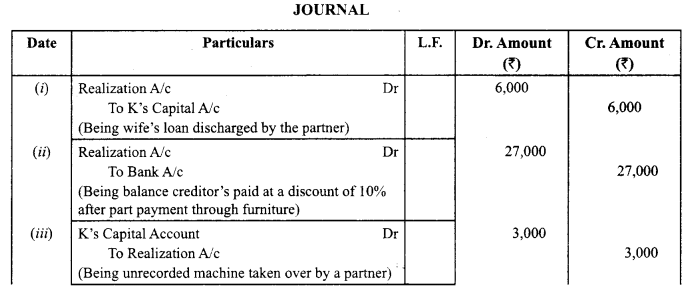
The firm of R, K and S was dissolved on 31.3.2019. Pass necessary journal entries for the following after various assets (other than cash and Bank) and the third party liabilities had been transferred to realisation account.
(i) K agreed to pay off his wife’s loan of ₹ 6,000.
(if) Total Creditors of the firm were ₹ 40,000. Creditors worth ₹ 10,000 were given a piece of furniture costing ₹8,000 in full and final settlement. Remaining creditors allowed a discount of 10%.
(iii) A machine that was not recorded in the books was taken over by K at ₹ 3,000 whereas its expected value was ₹ 5,000.
(iv) The firm had a debit balance of ₹ 15,000 in the profit and loss A/c on the date of dissolution.
(‘CBSE Sample Paper 2019-20)
Answer:

Question 5.
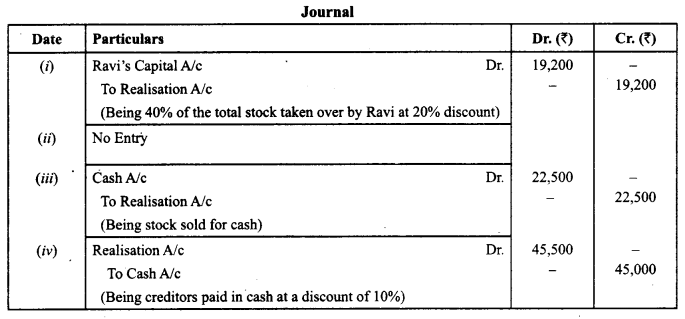
Ravi and Mukesh were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. On 31st March, 2019 their firm was dissolved. On the date of dissolution their Balance Sheet showed stock of ₹ 60,000 and creditors of ₹ 70,000. After transferring stock and creditors to realisation account the following transaction took place:
(i) Ravi took over 40% of total stock at 20% discount.
(ii) 30% of total stock was taken over by creditors of₹ 20,000 in full settlement.
(iii) Remaining stock was sold for cash at a profit of 25%.
(iv) Remaining creditors were paid in cash at a discount of 10%.
Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the book of the firm. (CBSE Compt. 2019)
Answer:
Question 6.
Singh and Jain were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 7. On 31st March, 2019 their firm was dissolved. On the date of dissolution the Balance Sheet showed stock of ₹ 90,000 and creditors of₹ 1,00,000. After transferring the assets (other than cash in hand and cash at bank) and third party liabilities to realisation account the following transactions took place:
(i) Singh took over 50% of the total stock at 10% discount.
(if) 20% of the total stock was taken over by creditors of₹ 20,000 in full settlement.
(iii) Remaining stock was sold for cash at 10% loss.
(iv) Remaining creditors were paid by cheque at a discount of 5%.
Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of the firm. (CBSE Compt. 2019)
Answer:
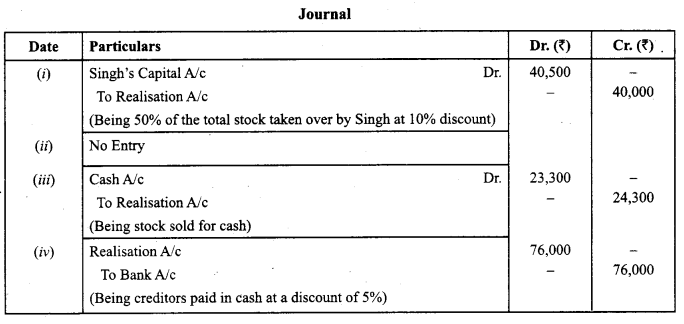
Question 7.
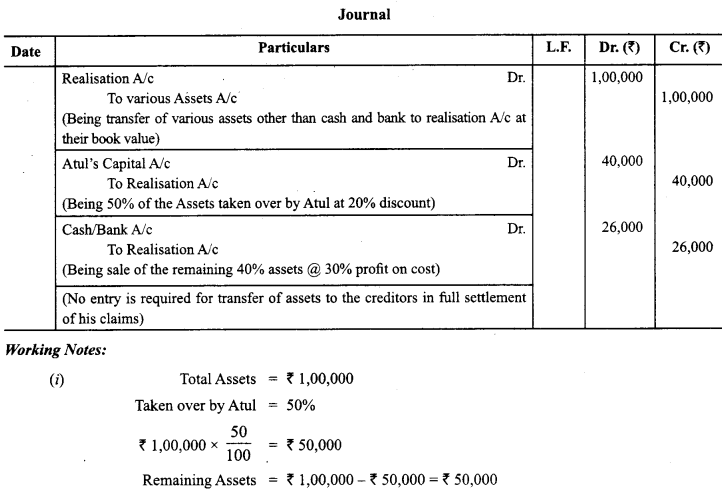
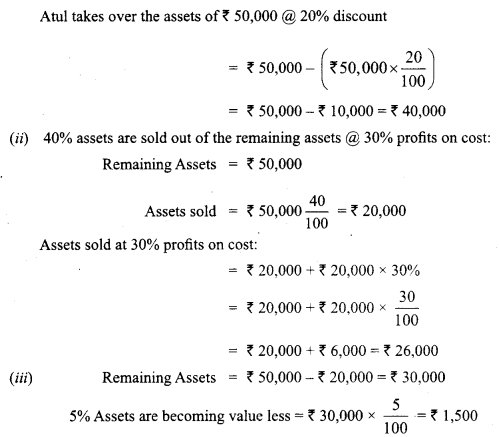
The book value of assets (other than cash and bank) transferred to Realisation Account is ₹ 1,00,000. 50% of the assets are taken over by a partner Atul, at a discount of 20%. 40% of the remaining assets are sold at a profit of 30% on cost; 5% of the balance being obsolete, realised nothing and remaining assets are handed over to a creditor, in full settlement of his claim. You are required to record the journal entries for realisation of assets.
Answer:
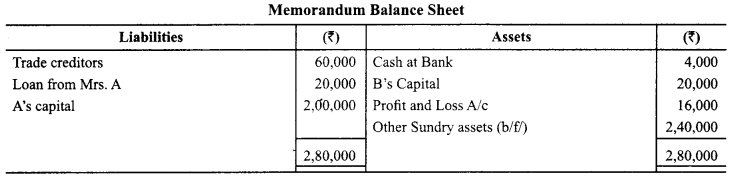
Question 8.
A and B who were sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:1 respectively decide to dissolved the firm on March 31, 2014 at which date some of the balances were as follows:
A’s capital ₹ 2,00,000, B’s capital ₹ 20,000 (debit balance). Profit and Loss A/c ₹ 16,000 (debit balance! Trade Creditors ₹ 60,000, Loan from Mrs. A ₹ 20,000, Cash at Bank ₹ 4,000.
Assets (other than cash at bank) realised ₹ 1,10,000 and all creditors were paid off less 5% discount. Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 1,000. Prepare Memorandum Balance sheet.
Answer:
Question 9.
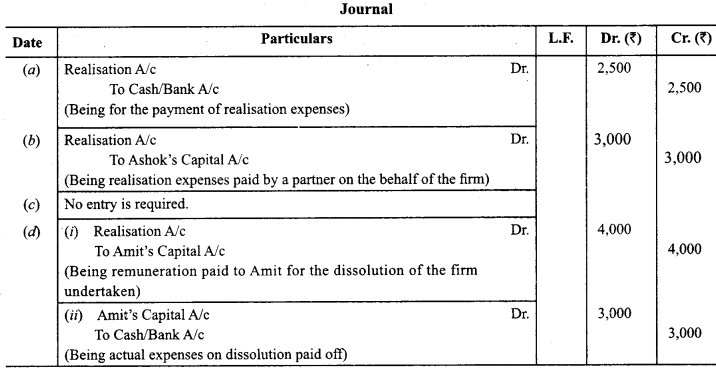
Journalise the following transactions regarding realisation expenses:
(a) Realisation expenses amounted to ₹ 2,500.
(b) Realisation expenses amounting to ₹ 3,000 were paid by Ashok, one of the partners.
(c) Realisation expenses ₹ 2,300 borne by Tarun, personally.
(d) Amit, a partner was appointed to realise the assets, at a cost of ₹ 4,000. The actual amount of realisation amounted to ₹ 3,000.
Answer:
Question 10.
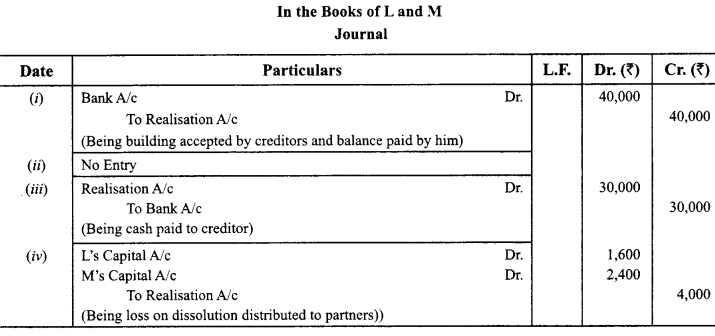
L and M were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 3. On 28.2.2016 the firm was dissolved. After transferring assets (other than cash) and outsider’s liabilities to realisation account you are given the following information:
(i) A creditor of ₹ 1,40,000 accepted building valued at ₹ 1,80,000 and paid to the firm ₹ 40,000.
(ii) A second creditor for ₹ 30,000 accepted machinery valued at ₹ 28,000 in full settlement of his claim.
(iii) A third creditor amounting to ₹ 70,000 accepted ₹ 30,000 in cash and investments of the book value of ₹ 45,000 in full settlement of his claim.
(iv) Loss on dissolution was ₹ 4,000.
Pass necessary journal entries for the above transactions in the books of firm assuming that all payments were made by cheque. (CBSE Outside Delhi 2016)
Answer:
Dissolution of a Partnership Firm Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
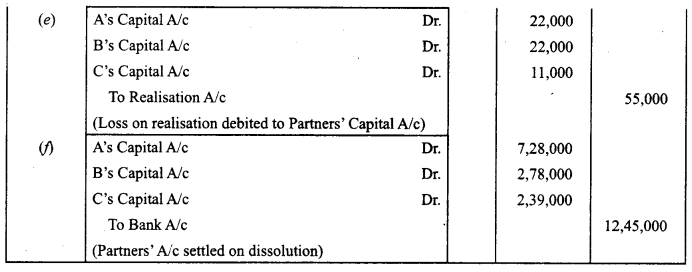
A, B and C were partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. Their Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2018 was as follows :
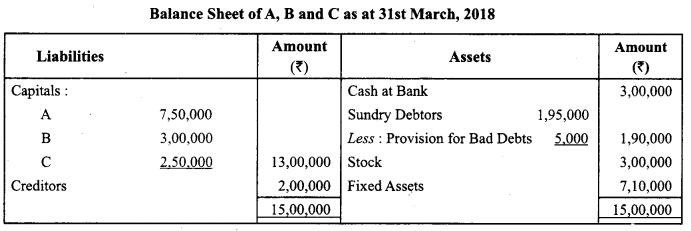
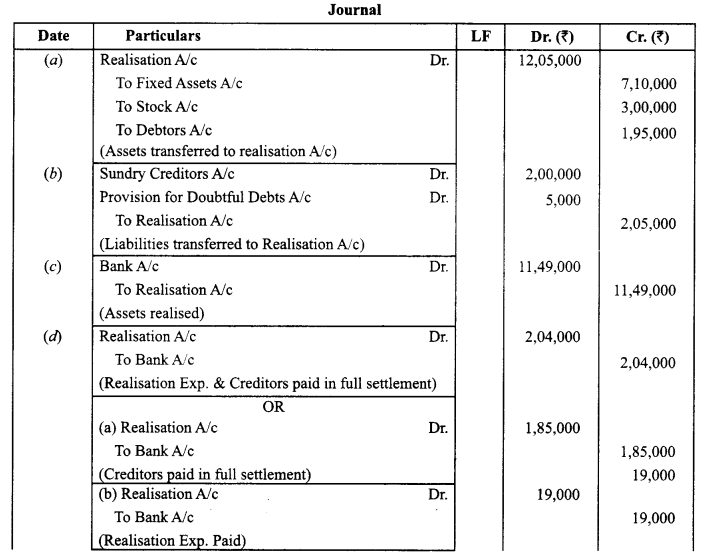
On the above date they dissolved the firm and following amounts were realised :
Fixed Assets ₹ 6,75,000; Stock ₹ 3,39,000; Debtors ₹ 1,35,000; Creditors were paid ₹ 1,85,000 in full settlement of their claim. Expenses on Realisation amounted to ₹ 19,000.
Pass the necessary journal entries on the dissolution of the firm.
Answer:
Question 2.
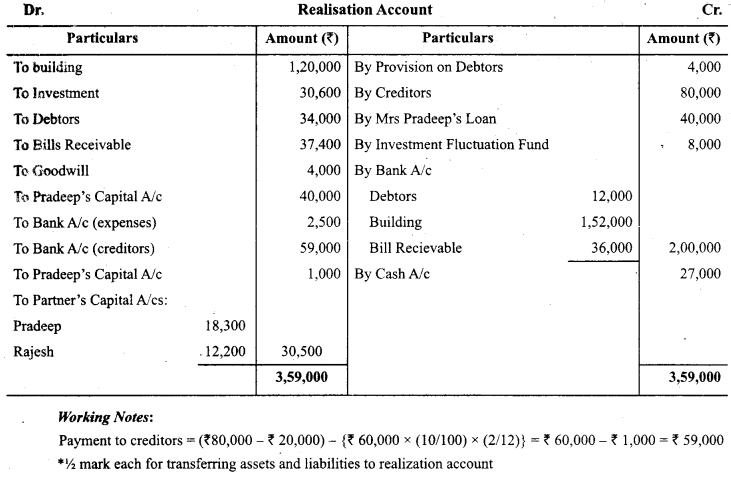
Pradeep and Rajesh were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:2. They decided to dissolve their partnership firm on 31st March, 2018. Pradeep was deputed to realize the assets and to pay off the liabilities. He was paid ₹ 1,000 as commission for his services. The financial position of the firm on 31st March, 2018 was as follows:
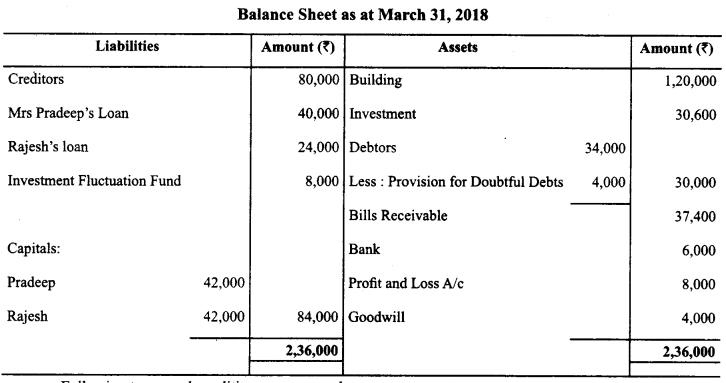
Following terms and conditions were agreed upon:
(i) Pradeep agreed to pay off his wife’s loan.
(ii) Half of the debtor’s realized ₹ 12,000 and remaining debtors were used to pay off 25% of the creditors.
(iii) Investment sold to Rajesh for ₹ 27,000
(iv) Building realized ₹ 1,52,000
(v) Remaining creditors were to be paid after two months, they were paid immediately at 10% p.a. discount
(vi) Bill receivables were settled at a loss of ₹ 1,400
(vii) Realization expenses amounted to ₹ 2,500
Prepare Realization Account. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018-19)
Answer:
Question 3.
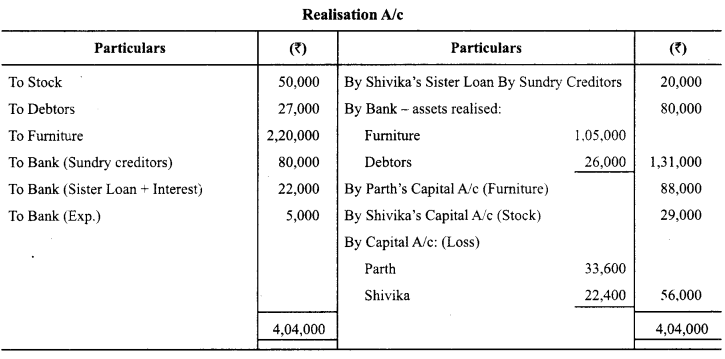
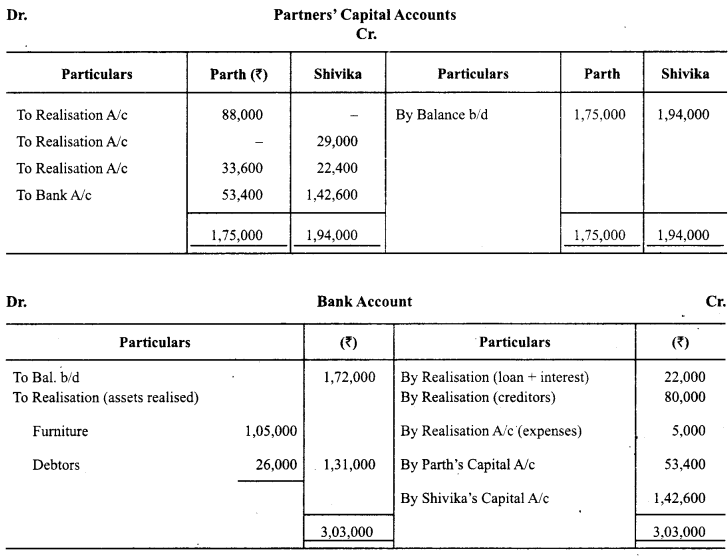
Parth and Shivika were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. The Balance Sheet of the firm on 31st March, 2014 was as follows:
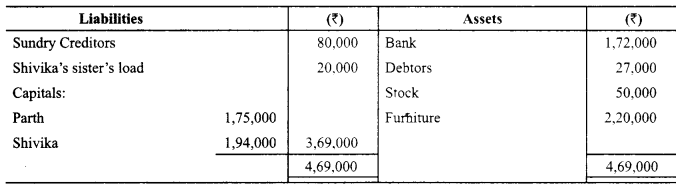
On the above date the firm was dissolved. The assets were realized and the liabilities were paid off as follows:
(a) 50 % of the furniture was taken over by Parth at 20% less than book value. The remaining furniture was sold for ₹ 1,05,000.
(b) Debtors realised ₹ 26,000.
(c) Stock was taken over by Shivika for 29,000.
(d) Shivika’s sister’s loan was paid off along with an interest of ₹ 2,000.
(e) Expenses on realisation amounted to ₹ 5,000.
Prepare Realisation Acount, Partners’ Capital Accounts and Bank Account. (Compartment Delhi 2015)
Answer:
Question 4.
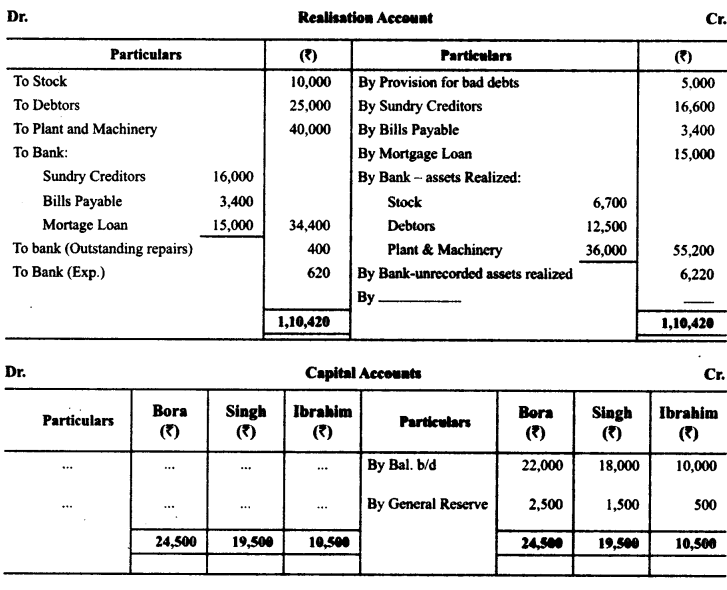
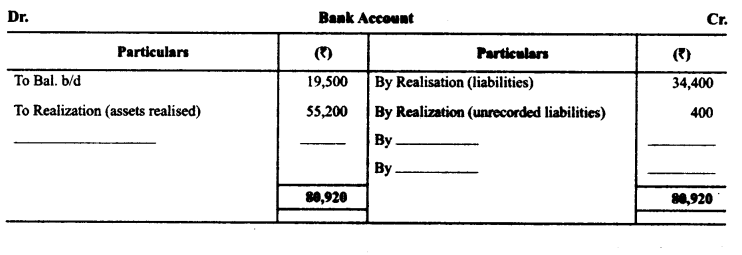
Bora, Singh and Ibrahim were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 5 :3 :1. On 2-3-2015 their firm was dissolved. The assets were realized and the liabilities were paid off. Given below are the Realisation Account, Partners’ Capital Accounts and Bank Account of the firm. The accountant of the firm left a few amounts unposted in these accounts. You are required to complete these accounts by posting the correct amounts.
Answer:
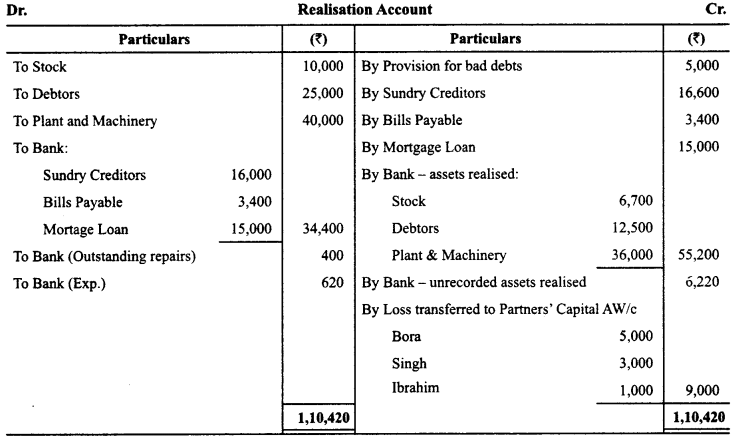
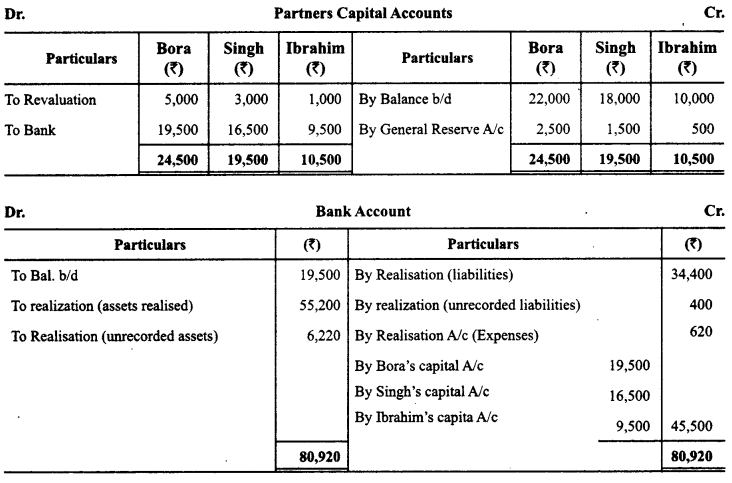
Question 5.
Ashish and Neha were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio 4:3. They decided to dissolve the firm on 1st May 2014. From the information given below, complete Realisation A/c, Partner’s Capital Accounts and Bank A/c:
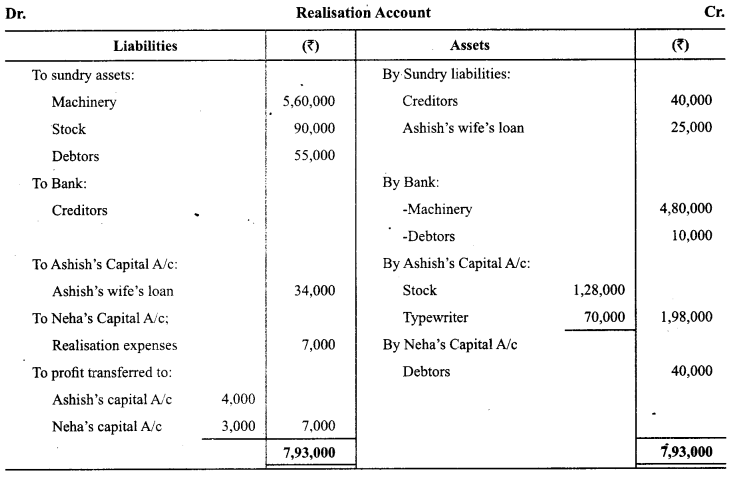
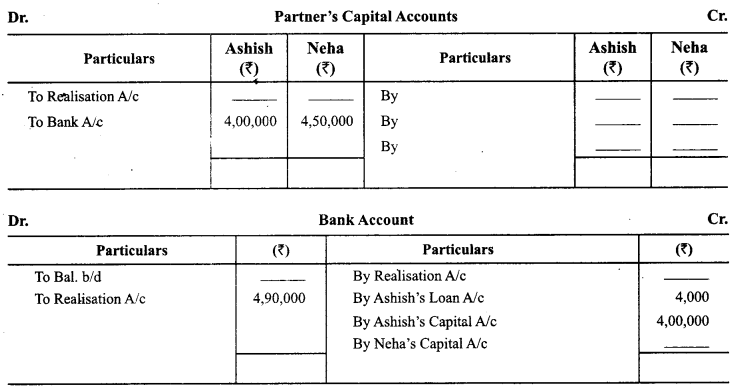
Answer:
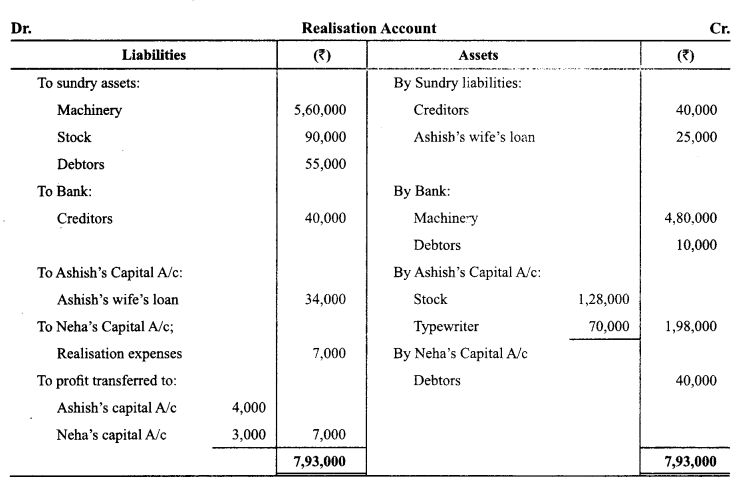
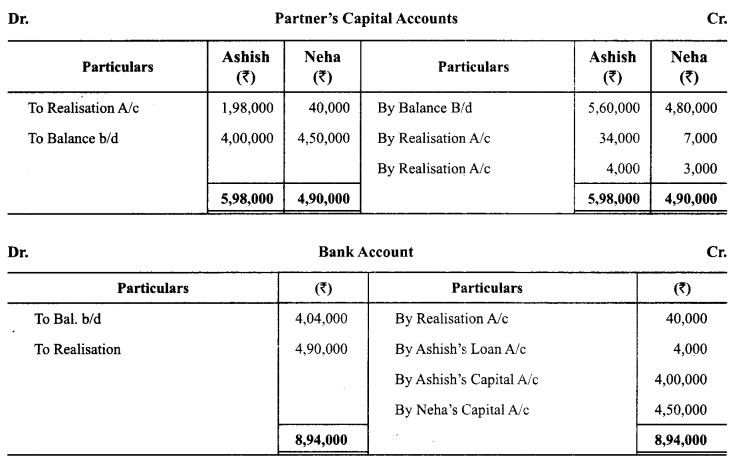
Question 6.
Give journal entries for the following transactions:
1. To record the realisation of various assets and liabilities.
2. A firm has a stock of₹ 1,60,000. Aziz, a partner took over 50% of the stock at a discount of 20%.
3. Remaining stock was sold at a profit of 30% on cost.
4. Land and Building (book value ₹ 1,60,000) sold for ₹ 3,00,000 through a broker who charged 2%, commission on the deal.
5. Plant and Machinery (book value ₹ 60,000) was handed over to a creditor at an agreed valuation of 10% less than the book value.
6. Investment whose face value was ₹ 4,000 was realised at 50%.
Answer:
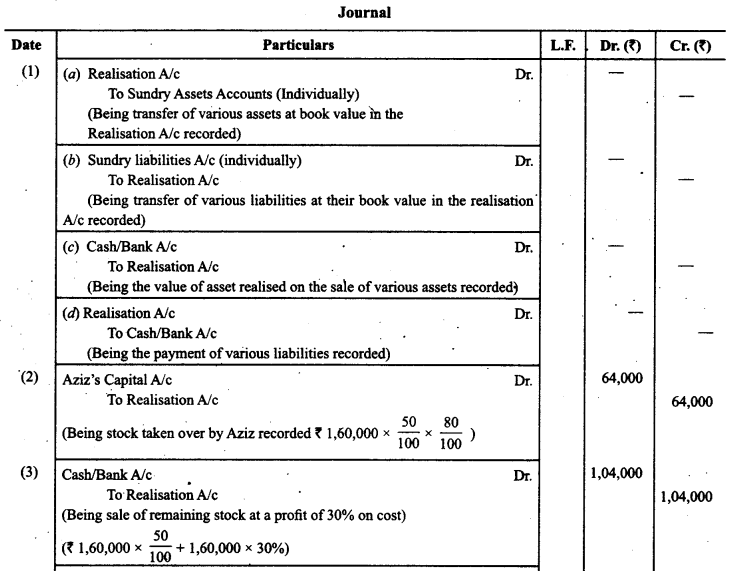

Question 7.
Record necessary journal entries to record the following unrecorded assets and liabilities in the books of Paras and Priya:
1. There was an old furniture in the firm which had been written-off completely in the books. This was sold for ₹ 3,000.
2. Ashish, an old customer whose account for ₹ 1,000 was written-off as bad in the previous year, paid 60% of die amount
3. Paras agreed to takeover the firm’s goodwill (not recorded in the books of the firm), at a valuation of ₹ 30,000.
4. There was an old typewriter which had been written off completely from the books. It was estimated to realize ₹ 400. It was taken away by Priya at an estimated price less 25%.
5. There were 100 shares of ₹ 10 each in Star Limited acquired at a cost of ₹ 2,000 which had been written-off completely from die books. These shares are valued @ ₹ 6 each and divided among the partners in their profit sharing ratio.
Answer:
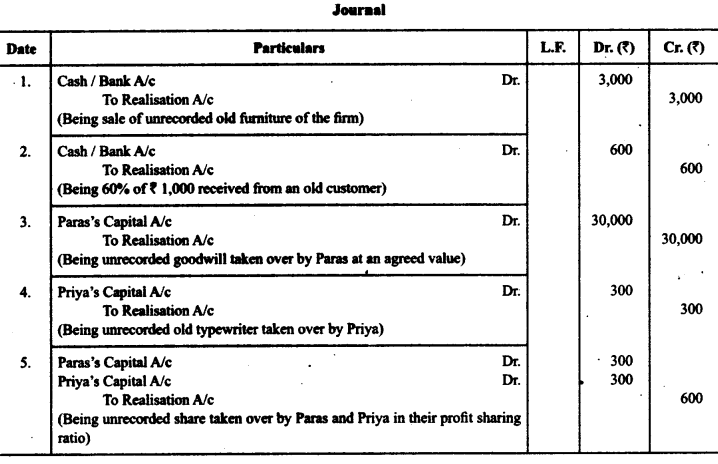
Question 8.
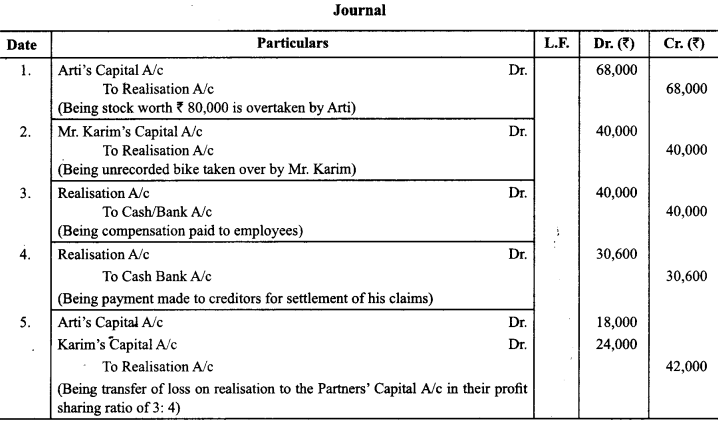
What journal entries would be recorded for the following transactions on die dissolution of a firm after various assets (other than cash) and the third party liabilities have been transferred to Realisation account₹
1. Arti took over die stock worth ₹ 80,000 at ₹ 68,000.
2. There was unrecorded bike of₹ 40,000 which was taken over By Mr. Karim.
3. The firm paid ₹ 40,000 as compensation to employees.
4. Sundry creditors amounting to ₹ 36,000 were settled at a discount of 15%.
5. Loss on realisation ₹ 42,000 was to be distributed between Arti and Karim in the ratio of 3:4.
Answer:
Question 9.
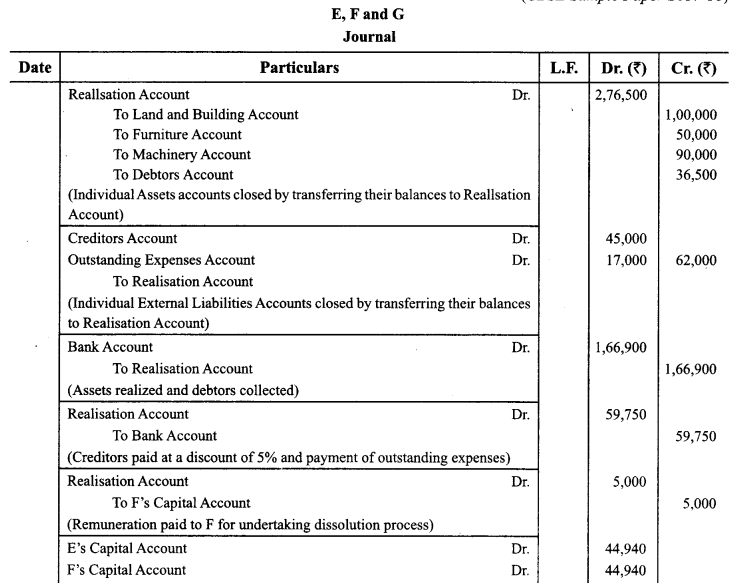
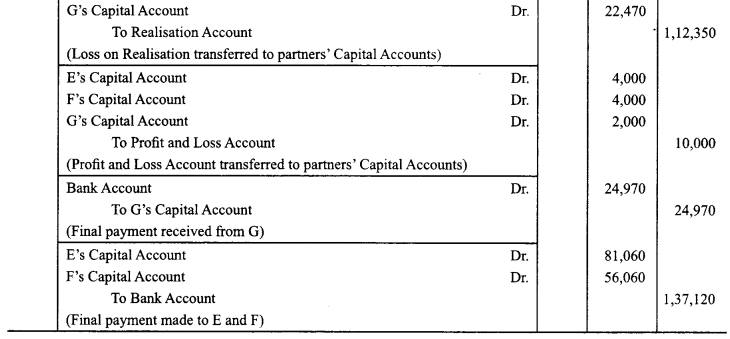
E, F and G were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1. On March 31,2017, their firm was dissolved. On the date of dissolution, the Balance Sheet of the firm was as follows:
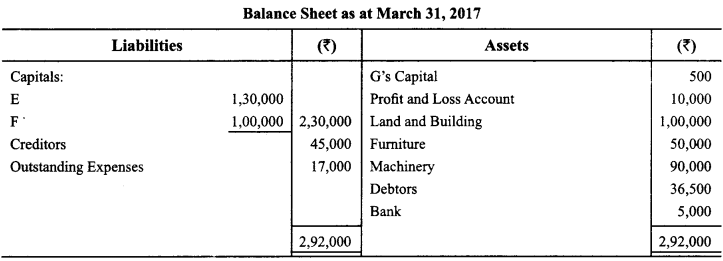
F was appointed to undertake the process of dissolution for which he was allowed a remuneration of ₹ 5,000. F agreed to bear the dissolution expenses. Assets realized as follows:
(i) The Land & Building was sold for ₹ 1,08,900.
(ii) Furniture was sold at 25% of book value.
(iii) Machinery was sold as scrap for ₹ 9,000.
(iv) All the Debtors were realized at full value.
Creditors were payable on an average of 3 months from the date of dissolution. On discharging the Creditors on the date of dissolution, they allowed a discount of 5%.
Pass necessary Journal entries for dissolution in the books of the firm. (CBSE Sample Paper 2017-18)
Answer:
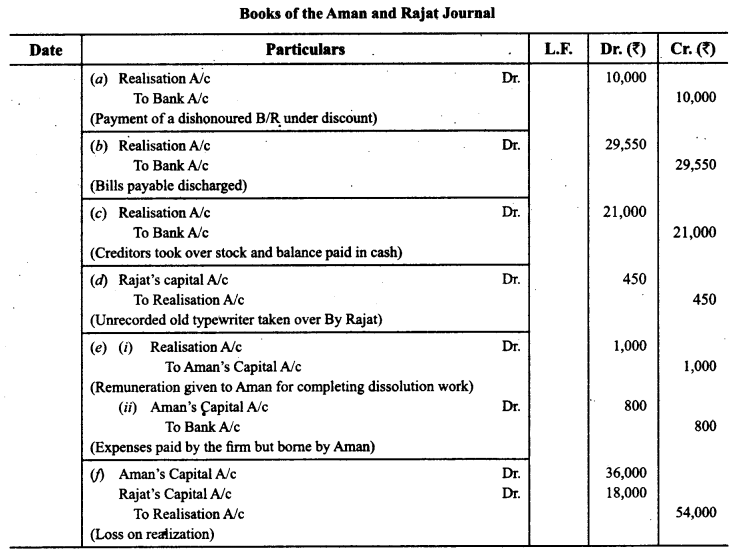
Question 10.
Give the necessary journal entries for the following transactions on dissolution of the firm of Aman and Rajat on 31 st March, 2016, after the transfer of various assets (other than cash) and the third party liabilities to Realisation Account. They shared profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 1.
(а) There was a bill of exchange of ₹ 10,000 under discount. The bill was received from Derek who became insolvent.
(b) Bills payable of ₹ 30,000 falling due on 30th April, 2016 were discharged at ₹ 29,550.
(c) Creditors of ₹ 30,000 took over stock of ₹ 10,000 at 10% discount and the balance was paid to them in cash.
(d) There was an old typewriter which had been written off completely. It was estimated to realize ₹ 600. It was taken away by Rajat at 25% less than the estimated price.
(e) Aman agreed to take over the responsibility of completing dissolution at an agreed remuneration of ₹ 1,000 and to bear all realization expenses. Actual realisation expenses ₹ 800 were paid by the firm.
(f) Loss on realization was ₹ 54,000.
Answer:










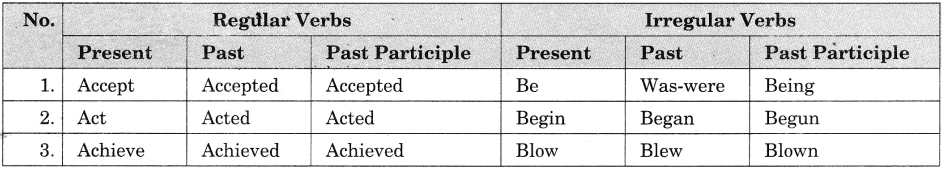
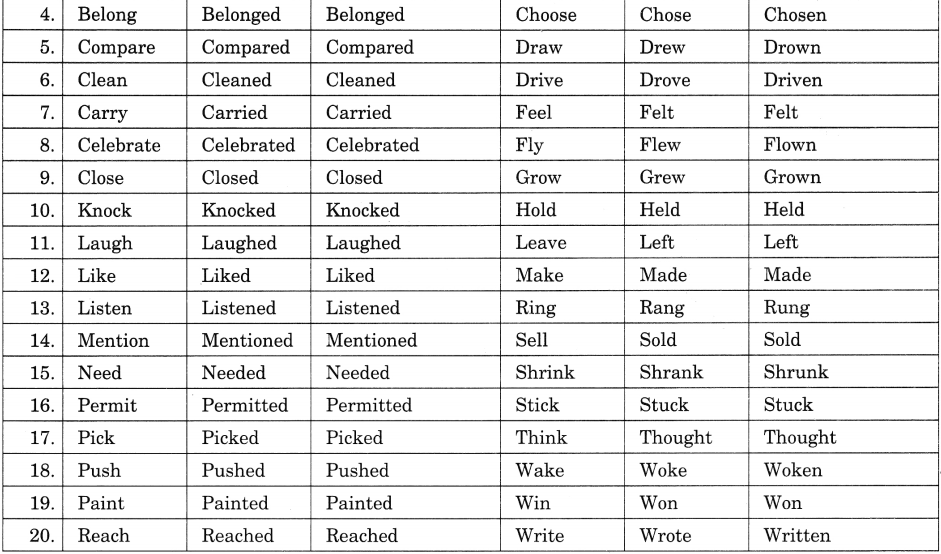
 In Online Education conjunction is a part of speech that is used to connect words, phrases, clauses, or sentences. Conjunctions are considered to be invariable grammar particles, and they may or may not stand between items they conjoin. Conjunctions are words which join together words, sentences, and part of sentences.
In Online Education conjunction is a part of speech that is used to connect words, phrases, clauses, or sentences. Conjunctions are considered to be invariable grammar particles, and they may or may not stand between items they conjoin. Conjunctions are words which join together words, sentences, and part of sentences.