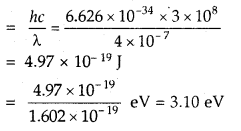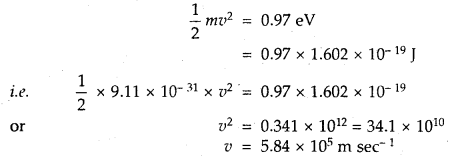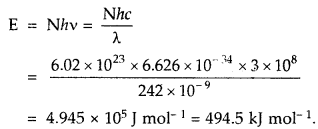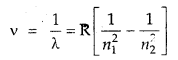We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 6 सदाचारः Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 6 सदाचारः
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 6 सदाचारः Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न: 1.
सर्वान् श्लोकान् सस्वरं गायत। (सभी श्लोकों को लय में गाइए। Recite all the Shlokas.)
उत्तराणि:
छात्र सुस्वर में सभी श्लोकों को गाएँ।
प्रश्न: 2.
उपयुक्तकथनानां समक्षम् ‘आम्’ अनुपयुक्तकथनानां समक्षं ‘न’ इति लिखत- (उचित कथनों के सामने ‘आम्’ और अनुचित कथनों के सामने ‘न’ लिखें- Write ‘आम्’ and ‘न’ in front of right/sentences and ‘न’ opposite the wrong ones.)

उत्तराणि:
क) आम्
(ख) न
(ग) आम्
(घ) न
(ङ) आम्।
प्रश्न: 3.
एकपदेन उत्तरत- (एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखिए- Answer in one word.)
(क) कः न प्रतीक्षते?
उत्तराणि:
मृत्युः
(ख) सत्यता कदा व्यवहारे किं स्यात्?
उत्तराणि:
सर्वदा
(ग) किं ब्रूयात्?
उत्तराणि:
सत्यम्
(घ) केन सह कलहं कृत्वा नरः सुखी न भवेत् ?
उत्तराणि:
मित्रेण
(ङ) कः महरिपुः अस्माक शरीरे तिष्ठिति?
उत्तराणि:
आलस्यम्
प्रश्न: 4.
रेखाङ्कितपदानि आधृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत- (रेखांकित शब्दों के आधार पर प्रश्न निर्माण कीजिए Frame questions based on underlined words.)
(क) मृत्युः न प्रतीक्षते।
उत्तराणि:
कः न प्रतीक्षते?
(ख) कलहं कृत्वा नरः दुःखी भवति।
उत्तराणि:
किम् कृत्वा नरः दुःखी भवति?
(ग) पितरं कर्मणा सेवेत।
उत्तराणि:
कम् कर्मणा सेवेत?
(घ) व्यवहारे मृदुता श्रेयसी।
उत्तराणि:
व्यवहारे का श्रेयसी?
(ङ) सर्वदा व्यवहारे ऋजुता विधेया।
उत्तराणि:
कदा व्यवहारे ऋजुता विधेया?
प्रश्नः 5.
प्रश्नमध्ये त्रीणि क्रियापदानि सन्ति। तानि प्रयुज्य सार्थक-वाक्यानि रचयत- (प्रश्न के बीच में तीन क्रियावाचक शब्द हैं। उनको जोड़कर अर्थपूर्ण वाक्य बनाइए- There are three verbs in the centre of the question. Frame meaningful sentences by joining them.)
(क) ……………………….
(ख) ……………………….
(ग) ……………………….
(घ) ……………………….
(ङ) ……………………….
(च) ……………………….
(छ) ……………………….
(ज) ……………………….
उत्तराणि:
(क) सत्यं प्रियं च ब्रूयात्।
(ख) सत्यं अप्रियं च न ब्रूयात् ।
(ग) अनृतं प्रियं च न ब्रूयात्।
(घ) व्यवहारे कदाचन कौटिल्यं न स्यात् ।
(ङ) व्यवहारे सर्वदा औदार्यं स्यात् ।
(च) वाचा गुरुं सेवेत।
(छ) श्रेष्ठजनं कर्मणा सेवेत।
(ज) मनसा मातरं पितरं च सेवेत।
प्रश्न: 6.
मञ्जूषातः अव्ययपदानि चित्वा रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत- (मञ्जूषा से अव्यय शब्दों को चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए- Fill in the blanks by choosing indeclinables from the box.)
तथा, न, कदाचन, सदा, च, अपि
(क) भक्तः…………….. ईश्वरं स्मरति।
उत्तराणि:
सदा
(ख) असत्यं …………….. वक्तव्यम्।
उत्तराणि:
न
(ग) प्रियं……………….. सत्यं वदेत् ।
उत्तराणि:
तथा
(घ) लता मेधा………………… विद्यालयं गच्छतः।
उत्तराणि:
च
(ङ) ………………… कुशली भवान् ?
उत्तराणि:
अपि
(च) महात्मागान्धी……………….. अहिंसां न अत्यजत्।
उत्तराणि:
कदाचन।
प्रश्न: 7.
चित्रं दृष्ट्वा मञ्जूषातः पदानि च प्रयुज्य वाक्यानि रचयत। (चित्र को देखकर और मञ्जूषा के शब्दों का प्रयोग कर वाक्य बनाइए। See the picture and make sentences with the help of words from the box.)

मञ्जूषा
| लिखति, कक्षायाम्, श्यामपट्टे, लिखन्ति, सः, पुस्तिकायाम्, शिक्षकः, छात्राः, उत्तराणि, प्रश्नम्, ते।
1. ………………………….
2. ………………………….
3. ………………………….
4. ………………………….
5. ………………………….
उत्तराणि:
1. छात्राः कक्षायाम् संस्कृतं पठन्ति।
2. शिक्षक: श्यामपट्टे प्रश्नम् लिखति।
3. ते प्रत्येक प्रश्नम् ध्यानेन पठन्ति।
4. तदा ते उत्तराणि लिखन्ति।
5. एकः छात्रः अन्य-छात्रस्य पुस्तिकायां पश्यति।
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 6 सदाचारः Additional Important Questions and Answers
(1) निम्नलिखित श्लोकं पठित्वा तदाधारितानां प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि लिखत (निम्नलिखित श्लोक को पढ़कर उस पर आधारित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए) –
आलस्यं हि मनुष्याणां शरीरस्थो महान् रिपुः।
नास्त्युद्यमसमो बन्धुः कृत्वा यं नावसीदति॥
I. एकपदेन उत्तरत- (एक पद में उत्तर दीजिए-)
1. किं महरिपुः अस्ति?
उत्तराणि:
आलस्यम्
2. आलस्यं कीदृशः महान् रिपुः अस्ति?
उत्तराणि:
शरीरस्थः
II. पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत-(पूर्ण वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए-)
1. उद्यमसमः कः मनुष्याणां नास्ति?
उत्तराणि:
उद्यमसमः बन्धुः मनुष्याणां नास्ति।
2. कं कृत्वा मनुष्यः नावसीदति?
उत्तराणि:
उद्यम कृत्वा मनुष्यः नावसीदति।
III. निर्देशानुसारमेन उत्तरत (निर्देश के अनुसार उत्तर दीजिए-)
1. ‘महान् रिपुः’ अनयोः विशेषणपदं किम्?
(क) महान्
(ख) रिपुः
(ग) महत्
(घ) रिपु
उत्तराणि:
महान्
2. ‘कृत्वा’ पदे कः प्रत्ययः अस्ति?
(क) त्वा
(ख) कतवा
(ग) क्त्वा
(घ) क्तवा
उत्तराणि:
क्त्वा
(2) पर्यायपदानि लिखत (पर्यायवाची पदों को लिखिए-)
पदानि – पर्यायाः
(i) शत्रुः – बन्धुः
(ii) मानवानाम् – अवसीदति
(iii) परिश्रम – रिपुः
(iv) मित्रम् – उद्यम
(v) दुःखीयति – मनुष्याणाम्
उत्तरम्-
(i) रिपुः
(ii) मनुष्याणाम्
(iii) उद्यम
(iv) बन्धुः
(v) अवसीदति
(3) ‘क’ पदस्य श्लोकांशं ‘ख’ पदस्य श्लोकांशैः सह योजयत (‘क’ पद श्लोकांश को ‘ख’ पद के श्लोकांशों के साथ जोड़िए-)
‘क’ – ‘ख’
(i) आलस्यं हि मनुष्याणाम् – समबन्धुः
(ii) नास्ति उद्यमसमः बन्धुः – मनुष्याणाम्
(iii) शरीरस्थः – कृत्वा यं नावसीदति
(iv) आलस्यं हि – नावसीदति
(v) कृत्वा यम् – महान् रिपुः
(vi) नास्ति उद्यम – शरीरस्थो महान् रिपुः
उत्तरम्-
(i) आलस्यं हि मनुष्याणाम् – शरीरस्थो महान् रिपुः
(ii) नास्ति उद्यमसमः बन्धुः – कृत्वा यं नावसीदति
(iii) शरीरस्थः – महान् रिपुः
(iv) आलस्यं हि – मनुष्याणाम्
(v) कृत्वा यम् – नावसीदति
(v) नास्ति उद्यम – समबन्धुः
(4) परस्परमेलनम् कुरुत- (परस्पर मेल कीजिए-Match the following.)
(क) (i) पर्यायाः
ब्रूयात् – निरन्तरम्
वाचा – व्यवहारः
अनृतम् – वदेत्
सततम् – वचनेन
आचारः – असत्यम्
उत्तराणि:
ब्रूयात् – वदेत्
वाचा – वचनेन
अनृतम् – असत्यम्
सततम् – निरन्तरम्
आचारः – व्यवहारः
(ii) विपर्यायाः
सर्वदा – मरणम्
प्रियम् – अनृतता
सत्यता – अप्रियम्
श्वः – कदाचन/कदापि
जीवनम् – ह्यः
उत्तराणि:
सर्वदा – कदाचन/कदापि
प्रियम् – अप्रियम्
सत्यता – अनृतता
श्वः – ह्यः
जीवनम् – मरणम्
(ख) श्लोकांशाः
(i) श्वः कार्यमद्य कुर्वीत – एषः धर्म सनातनः।
(ii) नहि प्रतीक्षते मृत्युः – न कदापि सुखी जनः।
(iii) प्रियं चानृतं ब्रूयात् – कृतमस्य न वा कृतम्।
(iv) मित्रेण कलहं कृत्वा – पूर्वाह्ने चापराह्निकम्।
उत्तराणि:
(i) श्वः कार्यमद्य कुर्वीत – पूर्वाह्ने चापराह्निकम्।
(ii) नहि प्रतीक्षते मृत्युः – कृतमस्य न वा कृतम्।
(iii) प्रियं चानृतं ब्रूयात् – एषः धर्मः सनातनः।
(iv) मित्रेण कलहं कृत्वा – न कदापि सुखी जनः।
(5) सत्यं ब्रूयात् प्रियं ब्रूयात् न ब्रूयात् सत्यमप्रियम्।
प्रियं च नानृतं ब्रूयात् एषः धर्मः सनातनः॥
सर्वदा व्यवहारे स्यात् औदार्यं सत्यता तथा।
ऋजुता मृदुता चापि कौटिल्यं न कदाचन॥
श्लोकान् पठत प्रश्नान् च उत्तरत- (श्लोकों को पढ़कर प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए- Read the shlokas and answer the questions.)
(क) एकपदेन उत्तरत –
(i) किं न ब्रूया?
(ii) व्यवहारे किं स्यात?
(iii) मृत्युः किं न करोति?
(iv) मित्रेण कलहं कृत्वा जनः कीदृशः भवति?
उत्तराणि:
(i) सत्यमप्रियम् (सत्यम् + अप्रियम्)
(ii) औदार्यम्
(ii) प्रतीक्षाम्
(iv) दु:खी
(ख) पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत-
(i) सनातनः धर्मः कः?
(ii) मनसा वाचा कर्मणा कं कं सेवेत?
(iii) व्यवहारे सदा किं स्यात् किं च न?
उत्तराणि:
उत्तरम्- (i) ‘प्रियं च नानृतं ब्रूयात् एषः धर्मः सनातनः।’
(ii) श्रेष्ठं जनं, गुरुं, मातरं पितरं च अपि मनसा वाचा कर्मणा सेवेत।
(iii) व्यवहारे सदा औदार्यं स्यात् तथा सत्यता, ऋजुता मृदुता चापि स्यात्; कौटिल्यं कदापि न स्यात्।
(6) मञ्जूषातः उचितम् अव्ययपदम् आदाय वाक्यपूर्तिं कुरुत- (मञ्जूषा से उचित पद लेकर वाक्यपूर्ति कीजिए- Pick out the appropriate indeclinable from the box and complete the sentences.)
सततम्, श्वः, सर्वदा, कदापि, एव
(i) अहं ………………… ग्रामं गमिष्यामि।
उत्तराणि:
श्वः
(ii) ‘सत्यम् ………………… जयते।’
उत्तराणि:
एव
(iii) योग्यः छात्रः शोभनान् अङ्कान् लब्धुम् ………………… परिश्रमं करोति।
उत्तराणि:
सततम्
(iv) सत्यवादी हरिशचन्द्रः…………………असत्यं न अवदत्।
उत्तराणि:
कदापि
(v) सः ………………… सत्यम् एव वदति स्म।
उत्तराणि:
सर्वदा।
(7) मञ्जूषायाः सहायतया श्लोकान्वयं पूरयत। (मञ्जूषा की सहायता से श्लोक का अन्वय पूरा कीजिए। Complete the prose order with help from the box.)
अपि, सत्यता, कदाचन, व्यवहारे
…………….. सर्वदा औदार्यं तथा ……………….. स्यात्; ऋजुता मृदुता च ……….. (स्यात्); कौटिल्यम् …………….. न (स्यात्)
उत्तराणि:
व्यवहारे, सत्यता, अपि, कदाचन
(1) उचित-विकल्पं चित्वा प्रश्ननिर्माणम् कुरुत- (उचित विकल्प चुनकर प्रश्न निर्माण कीजिए Pick out the correct option and make questions.)
(i) श्वः कार्यमद्य (कार्यम् + अद्य) कुर्वीत। (कुत्र, कदा, किम्)
उत्तराणि:
श्वः कार्यं कदा कुर्वीत?
(ii) व्यवहारे सर्वदा औदार्यं स्यात्। (के, कुत्र, कस्मिन्)
उत्तराणि:
कस्मिन् सर्वदा औदार्यं स्यात्?
(iii) व्यवहारे कौटिल्यं कदापि न स्यात्। (कः, का, किम्)
उत्तराणि:
व्यवहारे किम् कदापि न स्यात्?
(iv) मित्रेण कलहं न कुर्यात्। (कस्य, कः, केन)
उत्तराणि:
केन कलहं न कुर्यात्?
(v) मातरं पितरं च कर्मणा सेवेत। (कम्, किम्, कथम्)
उत्तराणि:
मातरं पितरं च कथम् सेवेत?
(2) (क) उचितेन विकल्पेन प्रत्येकं रिक्तस्थानं पूरयत- (उचित विकल्प द्वारा प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान भरिए Fill in the blanks with correct option.)
(i) श्वः कार्यम् अद्य कुर्वीत …………….. चापराह्निकम्। (पूवाणे, मध्याह्ने, प्रातः)
उत्तराणि:
पूर्वाह्ने
(ii) प्रियं च नानृतम् ब्रूयात् एषः …………….. सनातनः (आचारः, धर्मः, देशः)
उत्तराणि:
धर्मः
(iii) नहि …………….. मृत्युः कृत्यस्य न वा कृतम्। (परिवर्जयेत्, सेवेत, प्रतीक्षते)
उत्तराणि:
प्रतीक्षते
(iv) मित्रेण …………….. कृत्वा न कदापि सुखी नरः। (कार्यम्, कौटिल्यम्, कलहम्)
उत्तराणि:
कलहम्
(v) सर्वदा …………….. स्यात् औदार्यं सत्यता तथा। ___ (देशे, व्यवहारे, मित्रे)
उत्तराणि:
व्यवहारे।
(ख) (i) मित्रेण कलहम् कृत्वा न…………….. सुखी जनः। (कदा, कदापि, सर्वदा)
उत्तराणि:
कदापि
(ii) नहि प्रतीक्षते मृत्युः कृतम् अस्य न …………….. कृतम्। (च, सततम्, वा)
उत्तराणि:
वा
(iii) ऋतुजा मृदुता चापि कौटिल्यं …………….. कदाचन। (च, वा, न)
उत्तराणि:
न
(iv) ……….. कार्यमद्य कुर्वीत। (ह्यः, अद्य, श्वः)
उत्तराणि:
श्वः
(v) मनसा वाचा कर्मणा सेवेत…………….. सदा। (तथा, चापि, सततम्)
उत्तराणि:
सततम्।