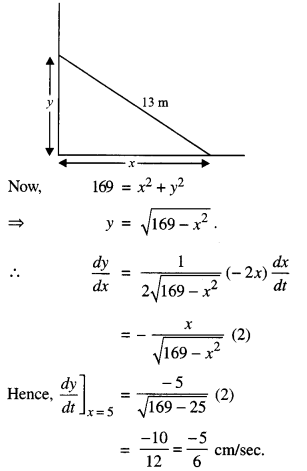
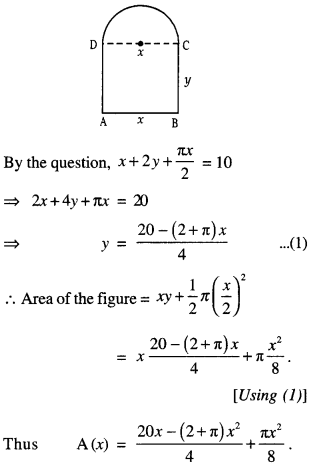
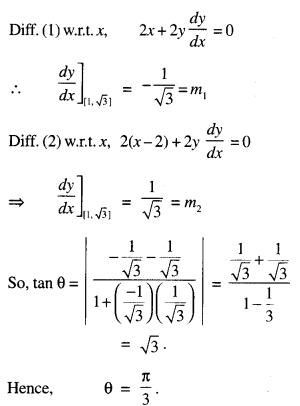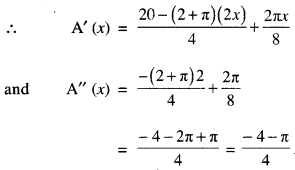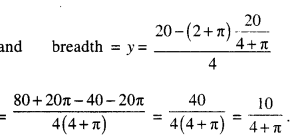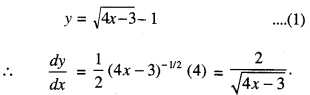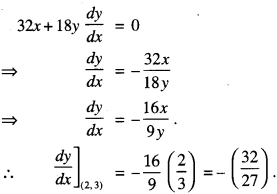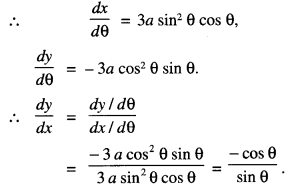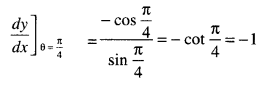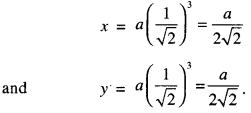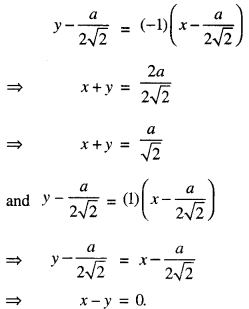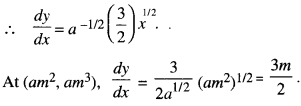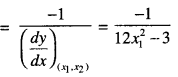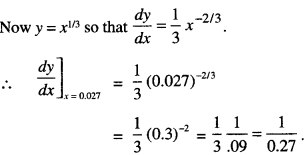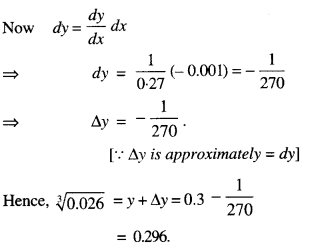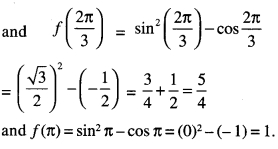We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 5 पण्डिता रमाबाई Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 5 पण्डिता रमाबाई
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 5 पण्डिता रमाबाई Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न: 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरत- (एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए- Answer in one word.)
(क) ‘पण्डिता’ ‘सरस्वती’ इति उपाधिभ्यां का विभूषिता?
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई
(ख) रमा कुतः संस्कृतशिक्षा प्राप्तवती? ।
उत्तराणि:
स्वमातुः
(ग) रमाबाई केन सह विवाहम् अकरोत् ?
उत्तराणि:
विपिनबिहारीदासेन
(घ) कासां शिक्षायै रमाबाई स्वकीयं जीवनम् अर्पितवती?
उत्तराणि:
नारीणाम्
(ङ) रमाबाई उच्चशिक्षार्थं कुत्र अगच्छत् ?
उत्तराणि:
इंग्लैण्डदेशम्।
प्रश्न: 2.
रेखाङ्कितपदानि आधृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत- (रेखांकित पदों के आधार पर प्रश्न निर्माण कीजिए – Frame questions based on the underlined words.)
(क) रमायाः पिता समाजस्य प्रतारणाम् असहत।
उत्तराणि:
कस्याः पिता समाजस्य प्रतारणाम् असहत?
(ख) पत्युः मरणानन्तरं रमाबाई महाराष्ट्र प्रत्यागच्छत्।
उत्तराणि:
कस्य मरणानन्तरं रमाबाई महाराष्ट्र प्रत्यागच्छत् ?
(ग) रमाबाई मुम्बईनगरे ‘शारदा-सदनम्’ अस्थापयत्।
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई कुत्र ‘शारदा-सदनम्’ अस्थापयत् ?
(घ) 1922 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे रमाबाई-महोदयायाः निधनम् अभवत्।
उत्तराणि:
1922 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे कस्याः निधनम् अभवत् ?
(ङ) स्त्रियः शिक्षां लभन्ते स्म।
उत्तराणि:
काः शिक्षां लभन्ते स्म?
प्रश्न: 3.
प्रश्नानामुत्तराणि लिखत- (प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए- Write answers to the questions.)
(क) रमाबाई किमर्थम् आन्दोलनं प्रारब्धवती?
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई बालिकानां स्त्रीणां च कृते संस्कृतस्य वेदशास्त्रादिकस्य च शिक्षायै आन्दोलनं प्रारब्धवती।
(ख) निस्सहायाः स्त्रियः आश्रमे किं लभन्ते स्म?
उत्तराणि:
निस्सहायाः स्त्रियः आश्रमे मुद्रण-टङ्कण-काष्ठकलादीनां च प्रशिक्षणम् लभन्ते स्म।।
(ग) कस्मिन् विषये रमाबाई-महोदयायाः योगदानम् अस्ति? ।
उत्तराणि:
लेखनक्षेत्र-विषये रमाबाई-महोदयायाः योगदानम् अस्ति।
(घ) केन रचनाद्वयेन रमाबाई प्रशंसिता वर्तते?
उत्तराणि:
‘स्त्रीधर्म नीति’ ‘हाई कास्ट हिन्दू विमेन’ इति रचनाद्वयेन रमाबाई प्रशंसिता वर्तते ।
प्रश्न: 4.
अधोलिखितानां पदानां निर्देशानुसारं पदपरिचयं लिखत- (निम्नलिखित शब्दों के निर्देश के अनुसार पद-परिचय लिखिए- Write the gender, inflexion and number of words given below.)
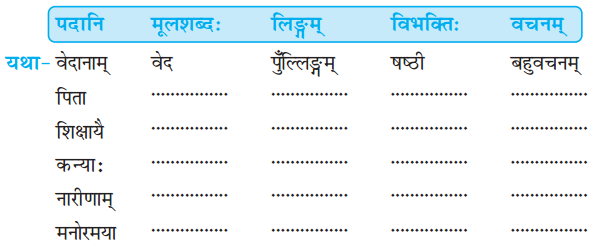
उत्तराणि:
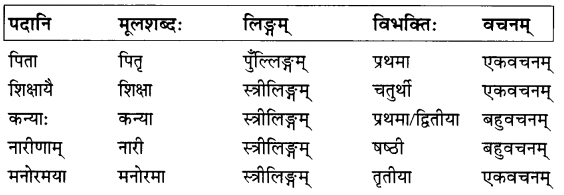
प्रश्नः 5.
अधोलिखितानां धातूनां लकारं पुरुषं वचनञ्च लिखत- (निम्नलिखित शब्दों के धातु, लकार, पुरुष और वचन लिखिए- Write the complete form of roots of words given below.)
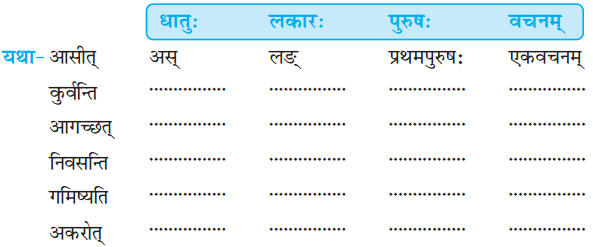
उत्तराणि:
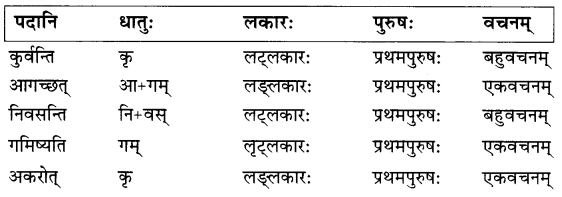
प्रश्न: 6.
अधोलिखितानि वाक्यानि घटनाक्रमानुसारं लिखत। (निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को घटना के क्रम के अनुसार लिखिए।) (Rewrite the sentences in the order of events as they took place.)
(क) रमाबाई-महोदयायाः विपिनबिहारीदासेन सह विवाहः अभवत्।
उत्तराणि:
1858 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे रमाबाई जन्म अलभत।
(ख) 1858 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे रमाबाई जन्म अलभत।
उत्तराणि:
सा स्वमातुः संस्कृतशिक्षा प्राप्तवती।
(ग) सा उच्चशिक्षार्थम् इंग्लैण्डदेशं गतवती।
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई-महोदयायाः विपिनबिहारीदासेन सह विवाहः अभवत् ।
(घ) 1922 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे रमाबाई-महोदयायाः निधनम् अभवत्।
उत्तराणि:
सा उच्चशिक्षार्थम् इंग्लैण्डदेशं गतवती।
(ङ) सा मुम्बईनगरे शारदा-सदनम् अस्थापयत्।
उत्तराणि:
सा मुम्बईनगरे शारदा-सदनम् अस्थापयत्।
(च) सा स्वमातुः संस्कृतशिक्षा प्राप्तवती।
उत्तराणि:
1922 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे रमाबाई-महोदयायाः निधनम् अभवत्।
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 4 हास्यबालकविसम्मेलनम् Additional Important Questions and Answers
(1) एकपदेन उत्तरत- (एक पद में उत्तर दीजिए- Answer in one word.)
(i) पण्डिता रमाबाई किमर्थम् इंग्लैण्ड-देशम् अगच्छत्?
उत्तराणि:
उच्चशिक्षार्थम्
(ii) मुम्बई-नगरे सा किम् अस्थापयत्?
उत्तराणि:
शारदा-सदनम्
(iii) रमा स्वमातुः किं प्राप्तवती?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृत-शिक्षणम्
(iv) ब्रह्मसमाजेन प्रभाविता सा किम् अकरोत्?
उत्तराणि:
वेदाध्ययनम्
(v) समाजसेवायाः अतिरिक्तं कस्मिन् क्षेत्रे रमाबाई-महोदयायाः योगदानम् अस्ति?
उत्तराणि:
लेखन-क्षेत्रे
(2) एकवाक्येन उत्तरत- (एक वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए Answer in a sentence.)
(i) रमाबाई किमर्थं जीवनम् अर्पितवती?
उत्तराणि:
नारीणां सम्मानाय शिक्षायै च रमाबाई स्व-जीवनम् अर्पितवती।
(ii) सा कासु निपुणा आसीत्?
उत्तराणि:
सा देश-विदेशानाम् अनेकासु भाषासु निपुणा आसीत्।
(iii) रमायाः पिता डोंगरे किमर्थं समाजस्य प्रतारणाम् सहते स्म?
उत्तराणि:
रमायाः पिता डोगरे रूढिबद्धां धारणां परित्यज्य स्वपत्नी संस्कृतम् अशिक्षयत्; एतदर्थं सः समाजस्य प्रतारणां सहते स्म।
(iv) तस्याः किं रचनाद्वयं प्रसिद्धम्?
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई-महोदयायाः ‘स्त्रीधर्म-नीति’ ‘हाई कास्ट हिन्दू विमेन’ इति रचनाद्धयम प्रसिद्धम् अस्ति ।
(3) अधोदत्तानि वाक्यानि घटनाक्रमानुसारेण संयोजयत- (निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को घटना क्रम के अनुसार लगाइए- Arrange the following sentences according to the order of events as they take place)
(i) सा पादाभ्याम् सकलं भारतम् अभ्रमत्।
उत्तराणि:
पण्डिता रमाबाई 1858 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे जन्म अलभत।
(ii) ब्रह्मसमाजेन प्रभाविता सा वेदाध्ययनम् अकरोत्।
उत्तराणि:
तस्याः माता पुत्रीं संस्कृतम् अशिक्षयत्।
(iii) पण्डिता रमाबाई 1858 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे जन्म अलमत।
उत्तराणि:
सा पादाभ्याम् सकलं भारतम् अभ्रमत्।
(iv) सा मुम्बईनगरे ‘शारदा-सदनम्’ अस्थापयत्।
उत्तराणि:
ब्रह्मसमाजेन प्रभाविता सा वेदाध्ययनम् अकरोत्।
(v) नारीणां सम्मानाय शिक्षायै च सा स्वजीवनम् अर्पितवती।
उत्तराणि:
नारीणां सम्मानाय शिक्षायै च सा स्वजीवनम् अर्पितवती।
(vi) 1922 तमे खिष्टाब्दे तस्याः निधनम् अभवत्।
उत्तराणि:
सा मुम्बईनगरे ‘शारदा-सदनम्’ अस्थापयत्।
(vii) अस्मिन् आश्रमे निःसहायाः स्त्रियः वसन्ति स्म।
उत्तराणि:
अस्मिन् आश्रमे नि:सहायाः स्त्रियः वसन्ति स्म।
(viii) तस्याः माता पुत्रीं संस्कृतम् अशिक्षयत्।
उत्तराणि:
1922 तमे खिष्टाब्दे तस्याः निधनम् अभवत्।
(4) मञ्जूषातः समानार्थकम् पदं चित्वा रिक्तस्थाने लिखत- (मञ्जूषा से समानार्थक शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थान में लिखिए- Pick out the synonym from the box and write in the blanks)
शोचनीया, अशिक्षयत्, धन-संग्रहः, पश्चात्, निःसहायाः
(i) निराश्रयाः – ……………
(ii) चिन्तनीया – ……………
(iii) अर्थसञ्चयः – ……………
(iv) अध्यापयत् – ……………
(v) अनन्तरम् – ……………
उत्तराणि:
(i) निराश्रयाः – नि:सहायाः
(ii) चिन्तनीया – शोचनीया
(iii) अर्थसञ्चयः – धनसंग्रहः
(iv) अध्यापयत् – अशिक्षयत्
(v) अनन्तरम् – पश्चात्
(5) अधोदत्तं वाक्यं पठत प्रत्येकं पदपरिचयं च यच्छत- (निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पढ़िए और प्रत्येक पद का परिचय दीजिए- Read the sentence given below and give grammatical details of each word.)
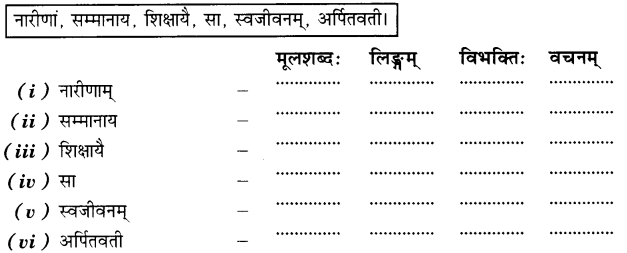
उत्तराणि:

(1) रेखांकितपदम् आधृत्य प्रश्न-निर्माणं कुरुत- (रेखांकित पद के आधार पर प्रश्न निर्माण कीजिए- Frame questions on the basis of words underlined)
(i) अत्र निराश्रिताः स्त्रियः ससम्मानं जीवनं यापयन्ति। (कः, के, काः)
उत्तराणि:
अत्र निराश्रिताः काः ससम्मानं जीवनं यापयन्ति।
(ii) रमाबाई उच्चशिक्षार्थ इंग्लैण्डदेशं गतवती। (कस्मै, कुत्र, किमर्थम्)
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई किमर्थम् इंग्लैण्डदेशं गतवती।
(iii) रमाबाई 1858 तमे ख्रिष्टाब्दे जन्म अलभत। (कस्मिन्, कुत्र, कदा)
उत्तराणि:
रमाबाई कदा जन्म अलभत।
(iv) डोंगरे स्वपत्नीम् संस्कृतम् अध्यापयत्। (कम्, किम्, काम्)
उत्तराणि:
डोंगरे काम् संस्कृतम् अध्यापयत्।
(v) कालक्रमेण रमायाः पिता विपन्नः सञ्जातः। (कस्य, कया, कस्याः )
उत्तराणि:
कालक्रमेण कस्याः पिता विपन्नः सञ्जातः।
(2) अधोदत्तं वाक्यं पठित्वा प्रश्नानुसारेण शुद्धम् उत्तरम् कोष्ठाकात् चिनुत-(निम्नलिखित वाक्य पढ़कर प्रश्नानुसार कोष्ठक से शुद्ध उत्तर चुनिए- Read the sentences given below and pick out the correct answer from the bracket.)
तदनन्तरं रमा स्व-ज्येष्ठ भ्रात्रा सह पद्भ्याम् समग्रं भारतम् अभ्रमत्।
(i) ‘अभ्रमत्’-क्रियापदस्य कः कर्ता? (रमा, भारतम्, तदनन्तरम्)
उत्तराणि:
रमा
(ii) ‘स्वज्येष्ठ-भ्रात्रा सह’ अत्र सह योगे का विभक्तिः ? (प्रथमा, तृतीया, षष्ठी)
उत्तराणि:
तृतीया
(iii) ‘समग्रम् भारतम्’-अत्र विशेषणपदम् किम्? (समग्रम्, भारतम्)
उत्तराणि:
समग्रम्
(iv) ‘पद्भ्याम्’ – एतस्य पदस्य अर्थः कः? (पादैः, पादेन, पादाभ्याम्)
उत्तराणि:
पादाभ्याम्
(v) ‘तदनन्तरम्’ अस्य विच्छेदः कः? (तदनन्तरम्, तदनम्+तरम्, तत्+अनन्तरम्)
उत्तराणि:
तत्+अनन्तरम्।