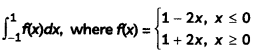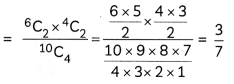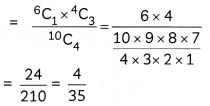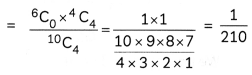Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
Roll No. ___________
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 5 sections A, B, C, D & E
- In section A, question number 1 to 3 are Very Short Answer type questions. Attempt any 3 questions.
- In section B, question number 4 is Source based question.
- In section C, question number 5 & 6 are Short Answer type questions.
- In section D, question number 7 to 9 are Long Answer type questions.
- In section E, question number 10 is a Map based question.
Section – A
Very Short Answer type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between tertiary activities and quaternary activities. (2)
Or
Differentiate between trade and trading centres.
Answer:
Tertiary activities are related to the service sector. Tertiary activities include both production and exchange. The production involves the provision of services that are ‘consumed’. On the other hand, the service sector which is knowledge oriented comes under quaternary activities. These activities centre around research, development and may be seen as an advance form of services involving specialised knowledge and technical skills.
Or
Trade is essentially buying and selling of items produced elsewhere. All the services in retail and wholesale trading or commerce are specifically intended for profit. On the other hand, the towns and cities where all these works take place are known as trading centres.
Question 2.
Among the non-metallic minerals produced in India, mica is one of the most important minerals. Name the states where mica is produced. (2)
Answer:
Mica is one of the most important non-metallic minerals produced in India. In India, it is produced in Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Rajasthan followed by Tamil Nadu, West Bengal and Madhya Pradesh.
![]()
Question 3.
Outline the distribution of sources of manganese in two major states in India. (3)
Answer:
The distribution of sources of manganese in two major states in India are
- Major mines in Odisha are located in the central part of the iron ore belt of India, particularly in Bonai, Kendujhar, Sundergarh, Gangpur, Koraput, Kalahandi and Bolangir.
- Karnataka is another major producer and here the mines are located in Dharwar, Ballari, Belagavi, North Canara, Chikkmagaluru, Shivamogga, Chitradurg and Tumakuru.
SECTION – B
Source Based Question
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions by choosing the correct option.
Land Transport
Most of the movement of goods and services takes place over land. In early days, humans themselves were carriers. Have you ever seen a bride being carried on a palanquin (palki/doli) by four persons (Kahars in North India). Later animals were used as beasts of burden. Have you seen mules, horses and camels, carrying loads of cargo in rural areas? With the invention of the wheel, the use of carts and wagons became important. The revolution in transport came about only after the invention of the steam engine in the eighteenth century.
Perhaps the first public railway line was opened in 1825 between Stockton and thern England and then onwards, railways became the most popular and fastest form of transport in the nineteenth century. It opened up continental interiors for commercial grain farming mining and manufacturing in U.S.A. The invention of the internal combustion engine revolutionised road transport in terms of road quality and vehicles (motor cars and trucks) plying over them.
Among the newer developments in land transportation are pipelines, ropeways and cableways. Liquids like mineral oil, water, sludge and sewers are transported by pipelines. The great freight carriers are the railways, ocean vessels, barges, boats and motor trucks and pipelines. In general, the old and elementary forms like the human porter, pack animal, cart or wagon are the most expensive means of transportation and large freighters are the cheapest. They are important in supplementing modern channels and carriers which penetrate the interiors in large countries. In the densely populated districts of India and China, overland transport still takes place by human porters or carts drawn or pushed by humans.
i. Which were the earliest mode of land transportation? (1)
Answer:
Humans and animals were the earliest mode of land transportation.
ii. Which event can be considered as a revolution in transport? (1)
Answer:
Invention of steam engine can be considered as a revolution in transport.
iii. Which place in Europe witnessed the first public railway line? (1)
Answer:
England witnessed the first public railway line in Europe.
![]()
Section – C
Short Answer Questions
Question 5.
How does access to labour supply and transportation and communication facilities influence industrial locations? (3)
Or
Explain the difference between household industries and small scale manufacturing.
Answer:
Access to labour supply and transportation and communication facilities influence industrial location in the following ways
- Labour supply is an important factor in the location of industries. Some types of manufacturing require skilled labour.
- Speedy and efficient transport facilities to carry raw materials to the factory and to move finished goods to the market are essential for the development of industries.
- The cost of transport plays an important role in the location of industrial units. For example, Western Europe and Eastern North America have a highly-developed transport system which has always induced the concentration of industries in these areas.
- Modern industry is inseparably tied to transportation systems. Improvements in transportation led to integrated economic development and regional specialisation of manufacturing.
Or
Household industries is the smallest manufacturing unit. The artisans use local raw materials and simple tools to produce everyday goods in their homes with the help of their family members or part time labour. Finished products may be for consumption in the same household or, for sale in local (village) markets, or, for barter.
Capital and transportation do not wield much influence as this type of manufacturing has low commercial significance and most of the tools are devised locally. Manufacturing of jewellery, artefacts and crafts made of wood or bamboo, fabrics, mats tools etc are examples of household industries.
Small scale manufacturing is distinguished from household industries by its production techniques and place of manufacture. This type of manufacturing uses local raw material, simple power-driven machines and semi-skilled labour. It provides employment and raises local purchasing power. Examples of small scale industry can include the manufacturing of spices, biscuits, soaps and oils etc.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the role of the National Highways Authority of India? Highlight some major projects undertaken by the National Highways Authority of India. (3)
Answer:
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) was operationalised in 1995. It is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Surface Transport. It is entrusted with the responsibility of development, maintenance and operation of National Highways. This is also the apex body to improve the quality of the roads designated as National Highways.
NHAI has taken up some major projects in the country under different phases which are
i. Golden Quadrilateral It comprises construction of 5,846-km long 4/6 lane, high density traffic corridor, to connect India’s four big metro cities of Delhi-Mumbai- Chennai-Kolkata. With the construction of Golden Quadrilateral, the time, distance and cost of movement among the mega cities of India will be considerably minimised.
ii. North-South and East-West Corridors North-South Corridor aims at connecting Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir with Kanniyakumari in Tamil Nadu (including Kochchi-Salem Spur) with 4,076-km long road. The East-West Corridor has been planned to connect Silchar in Assam with the port town of Porbandar in Gujarat with 3,640-km of road length.
Section – D
Long Answer Questions
Question 7.
What are secondary economic activities and the role of manufacturing in secondary activity? (5)
Or
The locations of industries are dependent on several factors including access to raw material, transport and energy. Discuss these dependent factors for industry locations.
Answer:
Secondary economic activities are the activities which add value to natural resources by transforming raw materials into valuable products. It refers to those activities which produce a finished and usable product. For instance, cotton in the boll has limited use but after it is transformed into yarn, becomes more valuable and can be used for making clothes. Iron ore, cannot be used; directly from the mines, but after being converted into steel it gets its value and can be used for making many valuable machines, tools, etc. The same is true of most of the materials from the farm, forest, mine and the sea.
Secondary activities, therefore, are concerned with manufacturing processing and construction (infrastructure) industries. Manufacturing which is an essential first step in a secondary activity can involve a full array of production from handicrafts to moulding iron and steel and stamping out plastic toys to assembling delicate computer components or space vehicles. The role of manufacturing in secondary activities may entail the following common characteristics (i) The application of power. (ii) The mass production of identical products. (iii) Specialised labour in factory settings for the production of standardised commodities.
Or
The location of industries are dependent on the following factors
→ Access to Market The existence of a market for manufactured goods is the most important factor in the location of industries.
→ Access to Raw Material Raw material used by industries should be cheap and easy to transport. Industries based on cheap, bulky and weight-losing material (ores) are located close to the sources of raw material such as steel, sugar, and cement industries.
→ Access to Labour Supply Labour supply is an important factor in the location of industries. Increasing mechanisation, automation and flexibility of industrial processes have reduced the dependence of industry upon the labours.
→ Access to Sources of Energy Industries which use more power are located close to the source of the energy supply such as the aluminium industry.
→ Access to Transportation and Communication Facilities Speedy and efficient transport facilities to carry raw materials to the factory and to move finished goods to the market are essential for the development of industries. Access to Agglomeration Economies Links between Industries Many industries benefit from nearness to a leader industry and other industries. These benefits are termed as agglomeration economies. Savings are derived from the linkages which exist between different industries.
Question 8.
What is a mineral? State its characteristics and types with relevant example. (5)
Answer:
A mineral is a natural substance of organic or inorganic origin with definite chemical and physical properties, e.g. gold, silver, iron ore, bauxite, etc. Minerals have certain characteristics such as
→ They are unevenly distributed over space. In India, bulk of the valuable minerals are associated with metamorphic and igneous rocks of the peninsular India. The vast alluvial plain tract of North India is devoid of minerals of economic use.
→ There is an inverse relationship in quality and quantity of minerals i.e. good quality minerals are less in quantity as compared to low quality minerals.
→ All minerals are exhaustible over time. These take long to develop geologically and they cannot be replenished immediately at the time of need. Thus, they have to be conserved and not misused as they do not have the second crop. Minerals may be grouped under two main categories of metallic and non-metallics based on chemical and physical properties
(i) Metallic minerals are the sources of metals. Iron ore, copper, gold produce metal and are included in this category. Metallic minerals are further divided into ferrous and non-ferrous metallic minerals. Ferrous refers to iron. All those minerals which have iron content are ferrous such as iron ore itself and those which do not have iron content are non-ferrous such as copper, bauxite, etc.
(ii) Non-metallic minerals are either organic in origin such as fossil fuels also known as mineral fuels which are derived from the buried animal and plant life such as coal and petroleum. Other type of non-metallic minerals are inorganic in origin such as mica, limestone and graphite, etc..
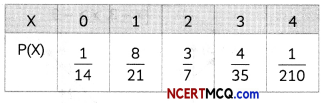
![]()
Question 9.
Non-conventional sources of energy are considered to be an environmental friendly and sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels. Discuss non-conventional sources of energy available in India along with their current status and examples. (5)
Answer:
Non-conventional sources of energy such as solar and wind energy, are renewable sources. They are equitably distributed and environment friendly as there are no carbon or pollution emissions upon their use. They are not exhaustible as they do not have fixed deposits or reserves.
These sources can provide sustained, cheap and environment friendly energy and hence they are considered as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Some of the commonly used nonconventional sources of energy in India are
→ Solar Energy Sun rays tapped in photovoltaic cells can be converted into energy, known as solar energy. The two effective processes considered to be very effective to tap solar energy are photovoltaics and solar thermal technology, The Western part of India has greater potential for the development of solar energy in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
→ Wind Energy This form of energy is absolutely pollution free, inexhaustible source of energy. The kinetic energy of wind, through turbines is converted into electrical energy. The permanent wind systems such the trade winds, westerlies and seasonal wind like monsoon have been used as source of energy. Besides these, local winds, land and sea breezes can also be used to produce electricity. In Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Karnataka, favourable conditions for wind energy exist.
→ Tidal and Wave Energy Ocean currents are the store house of infinite energy. Large tidal waves are known to occur along the West Coast of India. Hence, India has great potential for the development of tidal energy along the coasts but so far these have not yet been utilised.
→ Geothermal Energy When the magma from the interior of earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells is also used in the generation of thermal energy. It is popularly known as geothermal energy. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
Section – E
Map Based Question
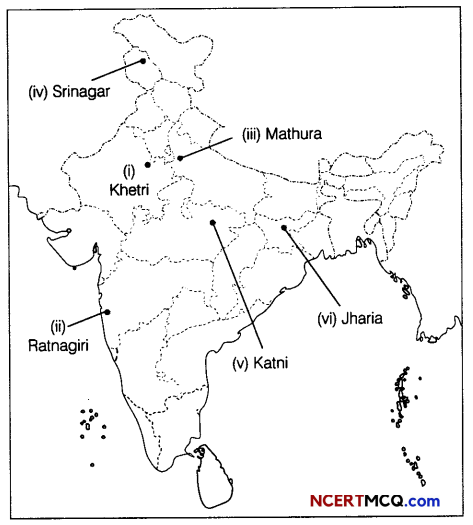
Question 10.
On a political map of India, mark and indicate the following features. (Attempt any 5) (1 × 5 = 5)
(i) Khetri copper mine
(ii) Ratnagiri iron ore mine
(iii) Mathura oil refinery
(iv) Important node of North connidor
(v) Katni bauxite mine
(vi) Jharia coal mine
Answer: