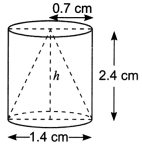
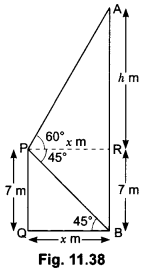
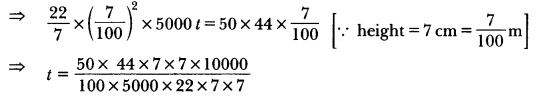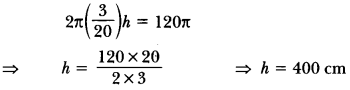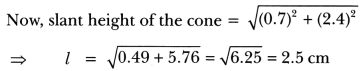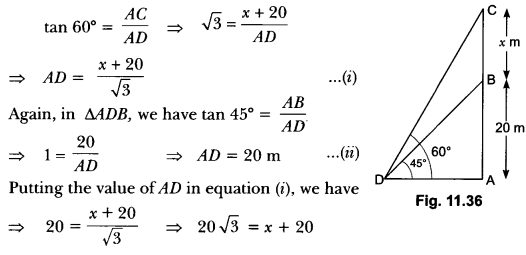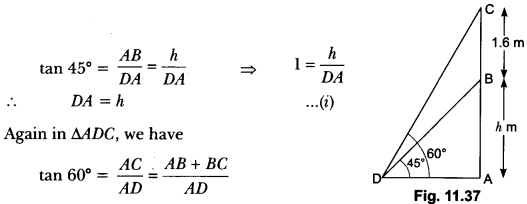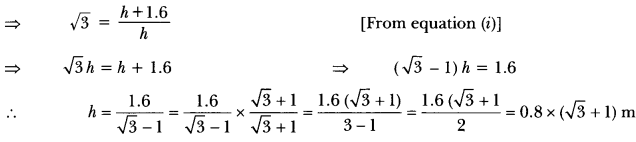Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Extra Questions and Answers Globalisation and the Indian Economy Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-social-science/
Online Education Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Extra Questions Economics Chapter 4
Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10 Extra Questions Question 1.
In which year had the Indian Government adopted the policy of liberalisation, privatisation and globalisation?
Answer:
Since 1991.
Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Extra Questions Question 2.
Why the private sector was subjected to many controls and regulations?
Answer:
The private sector was subjected to many controls and regulations so: that wealth could not get concentrated in a few hands.
Extra Questions For Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Question 3.
Point out the main features of economic reforms.
Answer:
The main features of economic reforms are
- Liberalisation
- Privatisation
- Globalisation.
Globalisation And The Indian Economy Extra Questions Question 4.
What is meant by the term LQP and LPG in economic reforms?
Answer:
LQP: The term LQP means Licence, Quota and Permit. This was the Indian Economic pattern before 1991
LPG: It is meant by Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation. LPG replaced LQP in 1991.
Extra Questions Of Globalisation And The Indian Economy Question 5.
What is meant by Tariff?
Answer:
Tariff is meant by the tax or levy imposed on each unit of a commodity imported into the country.
![]()
Globalisation Class 10 Extra Questions Question 6.
Name a country which provides the advantage of being a cheap manufacturing location.
Answer:
China.
Class 10 Economics Chapter 4 Extra Questions And Answers Question 7.
Name two countries which are useful for their location to the markets in the USA and Europe.
Answer:
Mexico is close to the USA, and the Eastern European countries are close to Europe.
Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10 Extra Questions Answers Question 8.
What is meant by investment?
Answer:
The money that is spent to buy assets such as land, building, machines and other equipment is called investment.
Globalisation Extra Questions Question 9.
Why is foreign investment called foreign?
Answer:
Investment made by MNCs is called foreign investment.
Globalisation Class 10 Important Questions Question 10.
What is the basic utility of foreign trade?
Answer:
Foreign trade leads to connecting the markets or integration of markets in different countries.
Globalization Class 10 Extra Questions Question 11.
Define the form ‘Globalisation’.
Answer:
Globalisation is the process through which rapid integration is made possible. It is interconnection between countries.
Extra Questions Of Chapter 4 Economics Class 10 Question 12.
Give an example of trade barrier.
Answer:
Tax on import is an example of trade barrier.
![]()
Globalisation Class 10 Extra Questions And Answers Question 13.
Explain the term ‘Liberalisation’.
Answer:
Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is what is known as liberalisation.
Extra Question Of Globalisation Class 10 Question 14.
What are the implications of fair globalisation?
Answer:
Fair globalisation would imply
- opportunities for all, and
- benefits of globalisation are shared and ensured for all equally.
Globalisation And The Indian Economy Class 10 Important Questions Question 15.
What is WTO?
Answer:
WTO stands for World Trade Organisation.
Question 16.
What is the main task of WTO
Answer:
The main task of WTO is to formulate rules and regulations with regard to trade among the different countries.
Question 17.
What is globalisation?
Answer:
Globalisation means integrating our economy with the world economy. Globalisation makes us economically interdependent at the global or international level. Globalisation also facilitates those who have capital to establish enterprises produce goods for sale and export them.
Question 18.
Define liberalisation?
Answer:
The term liberalisation contains two components
- To allow private sector to run those activities which we restricted earlier only to public sector.
- Realisation of all the rules and regulations which put restrictions in the growth of the private sector.
Thus liberalisation is the process that provides more and more facilities to the private sector so that it can make fast progress.
Question 19.
Define sustainable economic development.
Answer:
Sustainable economic development is meant by the development that takes place without damaging the environment. This kind of development does not compromise on the needs of the future generation. Sustainable economic development, in fact, is an issue that has emerged from rapid industrialisation of the world in the past century. The need for sustainable development stems from the concern for environment.
![]()
Question 20.
What is WTO and when and why was it set up?
Answer:
WTO stands for the World Trade Organisation. It was set up in 1995 by the member countries of the United Nations. The main purpose of its setting up was to promote trade among the countries.
Question 21.
Describe the main steps that have been taken for globalisation of the economy?
Answer:
Following are the steps that have mainly been taken for the globalisation of the economy
- Devaluation of rupee.
- Full convertibility of rupee.
- Long-period trade policy for removal of restrictions.
- Encouragement to open competition.
- Modification of custom and tariff.
Question 22.
Point out the main objectives of new Economic policy.
Answer:
The main objectives of the new economic policy are the following
- Liberalisation of economy.
- Dispensing with too many controls.
- Expansion of private sector.
- Encouragement of foreign direct investment
- Controlling fiscal deficit.
Question 23.
Point out the significant advantage of globalisation?
Answer:
The significant advantages of globalisation are the following
- Globalisation provides scope’ to every nation to special. Specialize in the production of the commodity that it can produce most effectively.
- Commodities produced at low cost are made available at cheap prices to producers and consumers throughout the world.
- Due to the globalisation, consumers can get the commodities produced in any part of the World.
- Globalisation has provided the producers the scope to sell their goods throughout the world.
- Due to globalisation technology has spread fastly towards advancement.
- Globalisation has given scope for formation of multi-national companies and banks.
Question 24.
Explain with example how a MNC functions in another country.
Answer:
MNCs invest to buy up local companies and in turn expands production. MNCs, with huge wealth, can do this easily. To take an example, Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC, has bought over smaller Indian companies such as Parakh Foods.
Parakh Foods had built a large marketing network in parts of India, where its brand was well-reputed. Also, Parakh Foods had four oil refineries, whose control has now shifted to Cargill. Cargill is now the largest producer of edible oil in India, with a capacity to make5 million pouches daily.
![]()
Question 25.
Why do you think the company wants to develop India as a base for manufacturing car components for its global operations? Discuss the following factors:
(a) cost of labour and other resources in India.
(b) the presence of several local manufacturers who supply auto-parts to Ford Motors
(c) closeness to a large number of buyers in India and
Answer:
India provides Ford Motors an opportunity for market in other countries.
(a) Cost of labour and other resources, in India, is relatively very low
(b) Motor raw-material industries in India is very rich industries provide Ford Motors necessary auto parts at low price.
(c) India’s geographical location is good for Ford Motors markets close to other nations in the region.
Question 26.
Nearly all major multinationals are American, Japanese or European, such as Nike, Coca-Coia, Pepsi, Honda, Nokia. Can You guess why?
Answer:
Nearly all MNCs are American, Japanese, Europeans such as Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Honda, Nokia etc. This is because these countries are technologically more advanced. They have had expertise in the field, working at home. Now with a view to capture the world market, these companies are expanding ford Motors, an American company is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 140 plants in 26 countries of the world, Ford Motors came to India.
In 1995 and spent ₹ 1700 crores to set up a large plant near Chennai. This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of jeeps and trucks. By the year 2004, Ford Motors was selling 27,000 cars in the Indian markets. An additional 24,000 cars were exported from India to south Africa, Mexico and Brazil. The company wants to develop ford India as a component supplying base for its global operations.
Question 27.
Write a short essay on WTO in your own words?
Answer:
WTO stands for the World Trade Organisation. It was set p in 1995 by the member countries of the United Nations. The foundation aim of the WTO was to promote trade among the member countries.
The headquarters of WTO is located in Geneva. It has significantly influenced the liberalisation as well as globalization process in most of the developing countries. WTO aims at conducting international trade among countries of the world in an open, uniform and nondiscriminatory manner, while facilitating trade among countries, WTO expects countries to follow what it wants.
WTO deals with three issues
- Bilateral agreements
- import quotas
- export quotas.
All of these three issues are very significant for India as well as for all other developing countries. Bilateral agreements play crucial role in the trade relations among countries. In order to prevent competition from the producers of other countries with local manufacturers, it is common for countries to impose taxes on the imported goods.
WTO is in fact not only regulating the international trade of goods but also the services. All the members of WTO have to adopt laws and policies in order to comply with the WTO rules.
Question 28.
Point out the impact of the World Trade Organisation on the Indian Economy?
Answer:
The main impact of the World Trade Organisation on the Indian economy can be described in the following points
- It has provided an opportunity to India for trading with other member countries.
- India is now able to export its goods and services to other countries with less restriction from those countries.
- Thanks to the WTO that it is expected that the technology from developed countries will be available to India at a reduced cost.
- Since a major share of world trade is taking places among the developed countries themselves, the benefit of being a member of WTO to the developing countries, especially to India, is very limited.
- It is feared that once India abides by the rules and regulations of WTO, the prices of many essential and life-saving drugs may go up.
- It is alleged that WTO is being used by the developed countries to support globalisation in areas that are not directly related to trade. These rules often interfere in the management of the domestic economy of a country.
![]()
Question 29.
Point out the advantages as well as disadvantages of globalisation or to what extent globalisation is beneficial for the Indian economy? Give your own arguments.
Answer:
Globalisation means opening up the economic system for the other countries across the world. It provides opportunity for bilateral as well as free trade. It is actually integrating ones economy with the world economy. Globalisation takes place at various levels. It makes an economically interdependent world.
Argument in favour of the Globalisation
- Globalisation is the idea that has a support base from all the leading international organisations like UN, OECD, WTO.
- Because of the globalisation, the growth of trade between the nations increases the wealth of everyone.
- Due to the globalisation, the world prosperity is enhanced by greater exchange between nations and this also makes possible that everyone abides by the rules.
Question 30.
To what extent WTO can be beneficial for India?
Answer:
- WTO can be beneficial for India for the following reasons
- If India succeeds in producing quality goods, its market will naturally expand.
- WTO may help in rooting out the concern of labour. It will provide a high speed to the production process.
- It will make the Indian labourers realise that they have no alternative of hard work.
- In order to boost agricultural exports, India should make effort that the restrictions imposed on the export of agricultural products to developed countries due to domestic subsidies and barriers to trade be removed.
- A proper check on multilateral and multinational companies should also be kept so that they might not harm fabric industry of India.
Question 31.
Explain the various liberalisation measures undertaken by the Government of India.
Answer:
The liberalisation process that has been undertaken by the Indian government since 1991 are as follows
The Indian Government has opened many industrial activities for the private sector which were reserved for the public sector earlier.
Formerly, the private sector had to request to get prior permission from the Government for manufacturing a large number of goods. At present this system was done away with and only for the manufacturing of a few things like alcohol, industrial expertise, hazardous chemicals, cigarettes, electronics, drugs and pharmaceuticals.
The number of industries reserved for public sector has been reduced from 17 to 3.
Because of the liberalisation, the private sector has been freed from many regulations like
- permission to import raw materials
- licensing
- regulation on price and distribution
- restriction on investment by large business companies.
Question 32.
Describe the changes that have occurred in India due to the adoption of the policy of liberalisation and globalisation.
Answer:
Following are the changes which have occurred in India due to the adoption of the policy of liberalisation and globalisation:
- Communication sector has seen much progress.
- Telephone facilities have spread to the far village areas also.
- Colour televisions have become more cheaper.
- Food processing companies like Coca-Cola, Pepsi etc. have entered the country and are providing cold drinks and products as well.
- The share of our country in the world market in the field of goods and services has increased.
- It has provided the scope to do better with better quality.
![]()
Question 33.
Explain with examples that the top Indian companies have benefitted from competition. How has globalisation created new opportunities?
Answer:
Several of the top Indian companies have been able to benefit from the increased competition. They have invested in newer technology and production methods and raised their production standards. Some have gained from successful collaborations with foreign companies. Moreover, globalization has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as multinationals themselves Tata Motors (automobiles), Infosys (l), Ranbaxy (medicines), Asian Paints (paints), Sundaram Fasteners (nuts and bolts) are some Indian companies which are spreading their operations worldwide.
Globalisation has also created new opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving information and communication technologies. The Indian company producing a magazine for the London based company and call centre and some examples. Besides, a host of services such as data entry, accounting, administrative tasks, engineering, etc. are now being done cheaply in countries such as India and are exported to the developed countries.
Question 34.
How can we make globalisation ‘fair?
Answer:
Since globalisation is now a reality, the question is how to make globalisation more fair’ Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all and also ensure that the benefits of globalisation are shared better.
The government can play a major role in making this possible.
Its policies must protect the interests, not only of the rich and the powerful but all the people in the country. For instance, the government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights.
It can support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete. If necessary, the government can use trade and investment barriers. It can negotiate at the WTO for “fairer rules. It can also align with other developing countries with similar interests to fight against the domination of developed countries in the WTO.
In the past few years, massive campaigns and representation by people’s organisations have influenced important decisions relating to trade and investments at the WTO. This has demonstrated that people also can play an important role in the struggle for fair globalisation.
Objective Type Questions
1. Choose true (✓) and false (✗) from the following
Question 1.
Globalisation has been an American phenomenon.
Answer:
Question 2.
Foreign investment is made by the multinational companies.
Answer:
Question 3.
WTO formulates trade rules among the nations.
Answer:
![]()
Question 4.
India has reverted to pre-1991 policies since 2001.
Answer:
2. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Investment includes …………………………… such lands, building etc.
Answer:
assets.
Question 2.
MNCs are private companies, but …………………………… in infrastructure.
Answer:
large
Question 3.
Ford Motors is an American …………………………… .
Answer:
MNC
Question 4.
…………………………… toys are becoming popular in India.
Answer:
Chinese.