Here we are providing Class 7 History Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers Tracing Changes Through A Thousand Years was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-7-social-science/
Tracing Changes Through A Thousand Years Class 7 Extra Questions History Chapter 1
Class 7 History Chapter 1 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
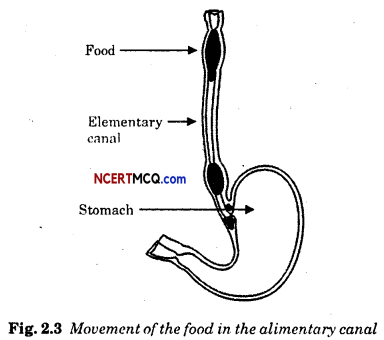
How was paper used?
Answer:
The paper was used to write holy texts, chronicles of rulers, letters and teachings of saints, petitions and judicial records, accounts and taxes.
Class 7 History Chapter 1 Important Questions And Answers Question 2.
Which group of people became important during medieval period?
Answer:
The Rajputs became important during medieval period.
Class 7 History Chapter 1 One Word Questions And Answers Question 3.
What is meant by bhakti?
Answer:
The bhakti means-a love for a personal deity that devotees could reach without the aid of priests or elaborate rituals.
![]()
Class 7 History Chapter 1 Short Questions And Answers Question 4.
Who were Ulemas?
Answer:
In Islam, Ulemas were learned theologians and jurists. Their job was to interpret what was written in the Holy Quran.
Class 7 History Chapter 1 Questions And Answers Question 5.
What were the main features of jatis, during medieval period?
Answer:
- During medieval period, people were grouped into jatis, or sub-castes and ranked on the basis of their backgrounds and occupations.
- Ranks were not fixed permanently and varied according to the power, influence and resources controlled by members of jati.
- The status of the same jati could vary from area to area.
Ncert Solutions For Class 7 History Chapter 1 Extra Questions Question 6.
What were the problems of peasants during medieval period?
Answer:
During the medieval period, peasants had following problems :
- They were influenced by various forces such as – regional markets, chieftains, priests, monasteries and temples.
- They became part of large, complex societies, and were required to pay taxes and offer goods and services to local lords.
- Some peasants possessed more productive land, others also kept cattle while some of them did. artisanal work with agricultural activities during the lean season.
![]()
1. Who of the following made a larger map of the world in 1154 CE?
(а) Ghiyasuddin Balban
(b) Shihabuddin Umari
(c) Al-Idrisi
(d) Aryabhatta.
Answer:
(c) Al-Idrisi.
2. Which of the following terms were used for a ‘foreigner’ in the past?
(a) Pardesi
(b) Ajnabi
(c) Cartographer
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b).
3. Which one of the following groups of people became important during medieval period?
(a) Agricultural labourers
(b) The Rajputs
(c) The Brahmins
(d) The Traders.
Answer:
(b) The Rajputs.
![]()
4. Why did forest dwellers migrate during the medieval period?
(а) Extension of agriculture
(b) Increase in the number of dangerous animals
(c) Law against forest dwellers
(d) Urbanisation.
Answer:
(а) Extension of agriculture.
5. Which one of the following refers to bhakti?
(a) A love for husband or wife
(b) A love for a personal deity
(c) A love for the king
(d) Both (a) and (b).
Answer:
(b) A love for a personal deity.
6. Who of the following refers to Ulemas?
(a) Learned Islamic theologians and jurists
(b) Arab geographers
(c) French cartographers
(d) Parsi religious leaders.
Answer:
(a) Learned Islamic theologians and jurists.
7. Who of the following divided Indian history in the past on the basis of religion?
(a) Arab historians
(b) French geographers
(c) British historians
(d) Gupta rulers.
Answer:
(c) British historians.
![]()
8. Minhaj-i-Siraj was a
(a) twelfth-century Arab geographer
(b) thirteenth-century chronicler
(c) eighteenth-century French cartographer
(d) eleventh-century Indian astronomer.
Answer:
(b) thirteenth-century chronicler.
9. Which one of the following reasons led to the re-emergence of regional states in the eighteenth century?
(a) Declinement of Mughal empire
(b) People struggles
(c) Efficient regional rulers
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer:
(a) Declinement of Mughal empire.
10. Where did Delhi Sultan Ghiyasuddin. Balban stretch in the east and west?
(a) Bihar in the east and Punjab in the west
(b) Bengal in the east and Ghazani in Afghanistan in the west
(c) Uttar Pradesh in the east and Peshawar in the west
(d) Bengal in the east and Peshawar in the west
Answer:
(b) Bengal in the east and Ghazani in Afghanistan in the west
Important Years Or Periods:
1154 CE: Arab Geographer al-Idrisi made a world map.
1720s: French cartographers made a larger world map.
Important Terms:
→ Cartographer: A person who makes maps.
→ Archive: A place where documents and manuscripts are stored. Today, all national and state governments have archives where they keep all their old official records and transcriptions.
→ Habitat: It refers to the environment of a region and the social and economic lifestyle of its residents.
→ Parton: An influential, wealthy individual who supports another person-an artist, a craftsperson, a learned man, or a noble.