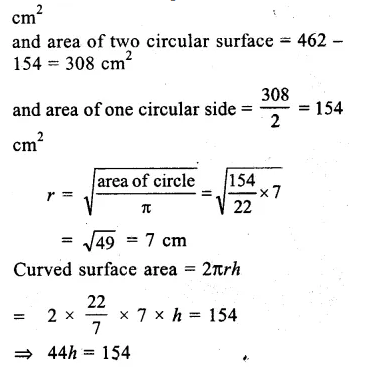
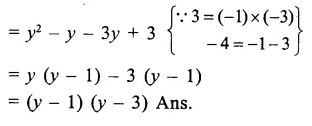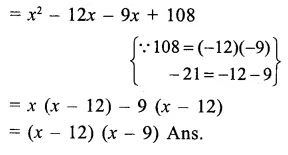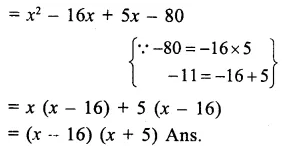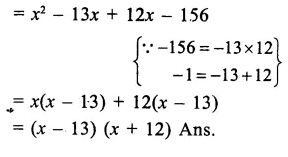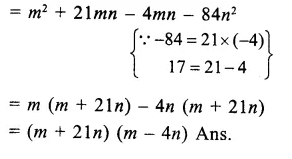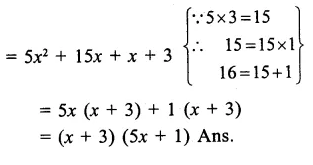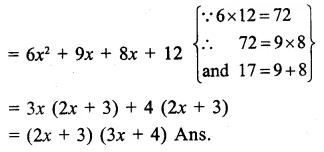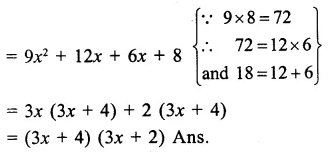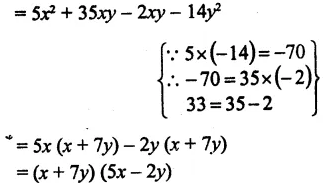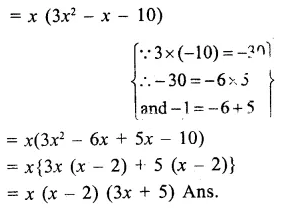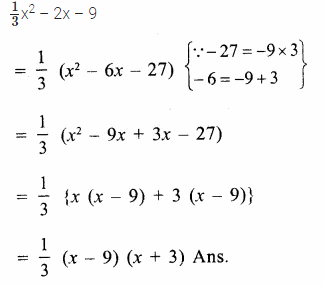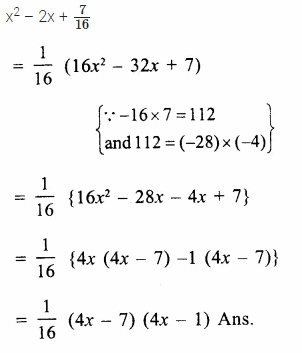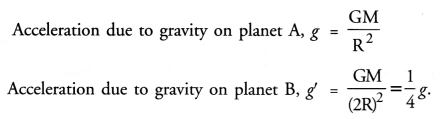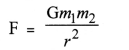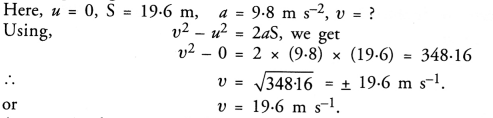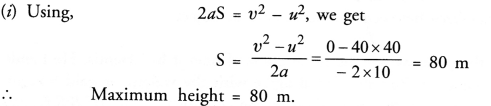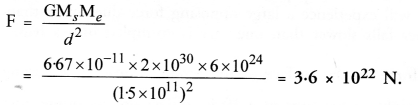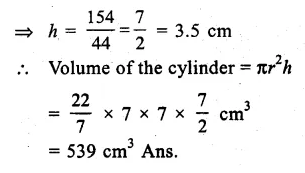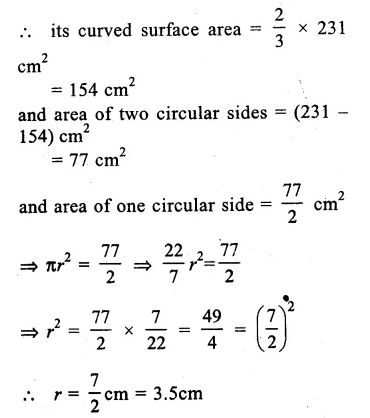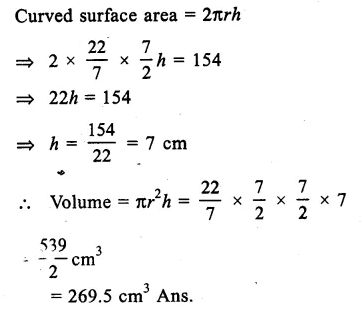Here we are providing Online Education The Dear Departed Extra Questions and Answers Class 10 English Literature Reader, Extra Questions for Class 10 English was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-english/
Online Education for The Dear Departed Extra Questions and Answers Class 10 English Literature
The Dear Departed Extra Questions and Answers Short Answer Type
The Dear Departed Question Answer Question 1.
“Good gracious, that’s never them.” What does Amelia mean?
Answer:
Amelia’s father Abel Merryweather, who stays with her, has died. She wants to take a few things that belong to him for herself before her sister arrives. So she is worried that they may have come already.
The Dear Departed Part 1 Questions And Answers Question 2.
How did Mrs Slater plan to outshine the Jordans? What does it reveal about her character?
Answer:
Mrs Slater is dressed in black, but is not in complete mourning. She has got her husband to wear a black tailcoat, grey trousers, a black tie and a bowler hat. Victoria, her daughter, is wearing a white frock with a black sash. She feels she will outshine the Jordans as Ben and Elizabeth will not yet have thought about mourning.
The Dear Departed Lesson Questions And Answers Question 3.
Why does Mrs Slater decide to shift the bureau from grandfather’s room before the arrival of the Jordans? How does Henry react to the suggestion?
Answer:
Mrs Slater always wanted to have the bureau after grandfather died. She feels she can easily take it before . her sister arrives as it has been bought recently and her sister doesn’t know of it. She says if she leaves it in grandfather’s room, her sister will drive a hard bargain. Henry feels it is not sensitive or becoming to do that.
The Dear Departed Part 2 Questions And Answers Question 4.
“I suppose it’s in the family.” What does Henry mean by that?
Answer:
Amelia calls her sister Elizabeth heartless and insensitive. She also feels that as Elizabeth is selfish and greedy, she will soon arrive for her share of grandfather’s property. Henry implies that both the sisters are similar in nature.
The Dear Departed Part 1 Question And Answers Question 5.
“You must arrange with Elizabeth when you’re dividing things up.” What does this reveal of Henry’s character?
Answer:
This shows that Henry is fair. He does not want to cheat Elizabeth out of her fair share by grabbing things for himself. He feels it should be decided who is to take what, after Elizabeth arrives.
Dear Departed Questions And Answers Question 6.
Why wouldn’t Henry care to bring the bureau downstairs?
Answer:
Henry feels it is not delicate or sensitive to bring the bureau down. Abel Merryweather has just died and instead of mourning him, they were trying to grab his things?Moreover, he feels that it should be decided who is to take what, after Elizabeth arrives.
The Dear Departed Questions And Answers Question 7.
“Elizabeth could have that and welcome.” What does Amelia mean by that?
Answer:
Amelia plans to bring grandfather’s new bureau downstairs and put their own chest of drawers in grandfather’s room. This way Elizabeth will look upon it as her father’s property and lay claim to it. Amelia doesn’t mind letting go of it as it is old and shabby and she had always wanted to get rid of it.
The Dear Departed Question Bank Question 8.
What does Henry tell Victoria when she asks if they are pinching grandfather’s bureau?
Why does Henry want to hide the truth from Victoria? How does Mrs Slater handle the same situation?
Answer:
Henry tells Victoria that Grandpa had given it to her mother before he died. He does not want the sensitive young child to think poorly of her parents. So he wishes to hide the truth from her. On the other hand, Mrs Slater who is practical and brusque, tells Victoria to be quiet and not tell her aunt about it.
The Dear Departed Question Answer Degree Question 9.
“I thought I’d fetch this down as well.” What does Mrs Slater bring down? What does ‘as well’ mean in this context?
Answer:
Mrs Slater brought grandfather’s clock downstairs along with his bureau. In this context, ‘as well’ refers to the clock in addition to the bureau.
The Dear Departed 2 Questions And Answers Question 10.
What is the reason for the Jordans taking a long time to get to the house of the Slaters? What does it show about the two sisters’ attitude towards each other?
Answer:
The Jordans came late because they bought new mourning clothes and dressed up in them before reaching the Slaters’ residence. This shows that both the sisters were trying to get the better of each other all the time.
Dear Departed Comprehension Questions Question 11.
What does Mrs Jordan describe as ‘a fatal mistake’? What is the irony in the comment she makes on Mrs Slater’s defense?
Answer:
Mrs Jordan calls not calling in a doctor to see grandfather ‘a fatal mistake’ as the doctor may have saved Abel Merryweather’s life. It turns out that Abel Merryweather was alive. He realized his daughters were selfish and greedy and he decides to change his will.
Dear Departed 2 Comprehension Questions Question 12.
“Your father wasn’t drowned, Elizabeth.” Why does Henry say this?
Answer:
Elizabeth wanted to know why the Slaters had not called in a doctor to see their father when he was supposedly gone. She added that at times people who have been presumed dead were revived by doctors.
Henry tells her that such incidents have occurred only with people who drowned. Therefore, he states that Abel Merryweather had not died of drowning.
Question 13.
“If there was one thing he couldn’t bear it was water.” What does Ben mean by this joke? Whom is he talking about?
Answer:
Ben is talking about his father-in-law, Abel Merryweather. He implies that Abel did not wash as often as he should have and that he drank a lot. He did not drink water.
Question 14.
Ben appreciates grandfather saying “its’ a good thing he did.” Later he calls him a “drunken old beggar.” Why does he change his opinion about grandfather?
Answer:
Ben praises Abel Merryweather when he thinks that the old man has paid his insurance premium that morning and they will inherit his insurance money. But when Victoria Slater tells them that grandfather had not gone to pay the insurance premium that morning but had gone with his friend to the Ring-o’-Bells for drinks, Ben is angry and calls him a drunken old beggar as the insurance policy may have lapsed and there may be no money for them.
Question 15.
What amazing news does Victoria bring as she comes downstairs?
Answer:
Victoria brings the news that her grandfather was getting up and that she had seen him do so.
Question 16.
What makes grandfather ask, “What’s the matter with little Vicky?”
Answer:
As soon as Vicky saw grandfather get up, she was terrified and ran down. Abel Merryweather was puzzled to see his granddaughter run away from him in fear. That is why he asked that.
Question 17.
Why is Mrs Jordan disconcerted when Mrs Slater brings ir^the topic of the gold watch?
Answer:
Mrs Jordan claimed that grandfather had promised his gold watch to her son, Jimmy. She was disconcerted when Mrs Slater brings in the topic of the gold watch because she knew her lie would be out.
Question 18.
How does the truth about the bureau come out?
Answer:
Grandfather, talking about his condition, says he had been in a daze and not asleep. At that point, he recollects Amelia and Henry had come to his room and shifted his bureau out.
Question 19.
How does Amelia get even with her sister?
Answer:
When Elizabeth tries to convince her father to go and live with her, she tells Abel that she and her sister had quarrelled because Elizabeth had said she wouldn’t take him off their hands at any price. She adds that Elizabeth had said she had enough of him to last a lifetime, and the Slaters would have to keep him.
Question 20.
What change does Abel Merryweather plan to make in his new will? What effect does it have on his daughters?
Answer:
Abel Merryweather said that he will change his will, stating that his money and his bits of things would go to whomever he was living with when he died. His daughters at once began to fight as each wanted to keep him with her, while earlier they had fought over not wanting to keep him.
Question 21.
What were the three things grandfather planned to do on Monday next?
Answer:
On Monday next, grandfather planned to do three things. He planned to go to the lawyer’s and alter his will leaving all he had to the person he was staying with, at the time of his death. He also planned to go to the insurance office and pay his premium. The third thing was to go to St Philip’s Church and get married to Mrs John Shorrocks.
Question 22.
In what way is the play The Dear Departed a satirical comment on the nature of human beings?
Answer:
The play brings out the greed and selfishness of people for whom money is more important than relationships. They are more interested in what they will inherit and try to grab the lion’s share.
The Dear Departed Extra Questions and Answers Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Bring out the irony in the title of the play.
Answer:
The title The Dear Departed refers to the death of a loved one but Abel Merryweather is neither dearly loved nor departed. The daughters do not mourn his death. They wanted to grab whatever belongings they can after his death. He was not dead but merely drunk.
Question 2.
Write a character sketch of Mrs Slater.
Answer:
Mrs Slater is greedy and wants to take some of grandfather’s things she likes before her sister arrives. She is overbearing and gets the reluctant Henry to help her shift the bureau and also put on grandfather’s slippers. She is straight talking, rude and impolite to her sister. She lacks feelings and hurts grandfather by telling him that Elizabeth did not wish to keep him.
Question 3.
Write a character sketch of Mrs Jordan.
Answer:
Mrs Jordan is greedy and arrives to take her share of grandfather’s things though she had vowed never to enter the house. She is bothered by appearances and comes dressed in new mourning. She is overbearing and dominates Ben. She is rude and impolite to her sister and lacks feelings and hurts grandfather by telling him that Amelia had started stealing soon as she had realised he was no more.
Question 4.
How does the spat between his daughters lead to grandfather discovering the truth?
Answer:
He hears about the spat between his daughters when he gets up. Elizabeth shows him the bureau and the clock grabbed by Amelia. Amelia talks about the gold watch supposedly promised to Jimmy. He realises the truth behind the fight. He knows that Amelia wanted to get rid of him two years ago and Elizabeth didn’t want him either.
Question 5.
Compare and contrast Henry’s character with that of his wife. Support your answer with evidences from the play.
Answer:
She is greedy and wants to take some of grandfather’s things she likes before her sister arrives. She is overbearing and gets the reluctant Henry to help her shift the bureau and also put on grandfather’s slippers. She is straight talking, while Henry tells Victoria that grandfather had promised the bureau to them, she just tells Victoria to be quiet and not tell her aunt. She is rude and impolite to her sister and lacks feelings. She hurts grandfather by telling him that Elizabeth did not wish to keep him.
Henry is sensitive and does not wish to take the slippers or the bureau. He has a weaker character and allows himself to be dominated by Amelia. He is evasive and hides from the ugly truth. He tells Victoria that grandfather had promised them the bureau.
Question 6.
In the play the two daughters do not seem to be concerned at their father’s death. Do you think it is proper? If not, why?
(Encourage students to think creatively and formulate their own answers.)
Question 7.
How are the two sisters exposed in the play The Dear Departed?
Answer:
They are portrayed as greedy. Amelia is after the bureau and the clock and Elizabeth wants the gold watch. But since grandfather is alive, the truth behind the spat comes out.
Question 8.
Narrate the story of The Dear Departed from the point of view of Abel Merryweather.
Answer:
I went out to the pub and came home and fell asleep. Due to the sudden turn, I couldn’t move or speak. I saw Amelia and Henry come in my room and take the bureau but I couldn’t stop them or ask them why they were doing that. I heard voices and tried to get up but little Vicky came in, saw me and got frightened. Downstairs my daughters and sons-in-law presumed that I was dead and started grabbing my things. I am going to get married and shift out soon, as I do not want to stay with such greedy people.
Question 9.
Victoria in The Dear Departed is very upset by the behaviour of her parents. She expresses her feelings in a diary entry. As Victoria, write the diary entry.
Answer:
My grandfather is dead. The greed shown by my parents as well as by my aunt and uncle under the circumstances is appalling. Each one is more interested in benefits derived from this situation rather than grieving over their father and I am completely saddened by their attitudes.
Question 10.
In what way is the play The Dear Departed a satirical comment on the nature of human beings?
Answer:
In The Dear Departed, the playwright William Stanley Houghton highlights the degradation of moral values and the weakening relationships between the members of the family. He brings out the greed and selfishness of people for whom money is more important than relationships. The drama depicts how present generation is reacting towards the elders. They are more interested in what they will inherit and try to grab the lion’s share.
The Dear Departed Extra Questions and Answers Reference to Context
Read the extracts and answer the questions that follow.
Question 1.
“She’ll come fast enough after her share of what grandfather’s left. You know how hard she can be when she likes. Where she gets it from I can’t tell.”
(a) Who speaks these words and about whom?
(i) Mrs Slater about Victoria
(ii) Victoria about Mrs Jordan
(iii) Mrs Jordan about Mrs Slater
(iv) Mrs Slater about Mrs Jordan
(b) The speaker implies that ‘she’ is:
(i) cruel.
(ii) selfish.
(iii) generous.
(iv) loving.
(c) The literary device used in the above lines is:
(i) irony.
(ii) personification.
(iii) alliteration.
(iv) metaphor.
Question 2.
“Are we pinching it before Aunt Elizabeth comes?”
(a) What does ‘it’ refer to here?
Answer:
It refers to the bureau belonging to Abel Merry weather.
(b) How does Vicky conclude that her parents are ‘pinching it’?
Answer:
Vicky concludes her parents are pinching it because it belonged to grandfather and they are taking it without permission after his death.
(c) Mention the two realsons that Mrs Slater gives for her action.
Answer:
Mrs Slater says that she has always wanted it and if her sister Elizabeth were to see it, she would drive a hard bargain over it.
(d) What does it reveal about the difference between the attitude of the elders and that of Vicky?
Answer:
The elders are out for what they can get while Victoria has more of a sense of what is right.
Question 3.
“Be off now, and change your dress before your Aunt Elizabeth and your Uncle Ben come. It would never do for them to find you in colours.”
(a) Who says these words aind to whom?
Answer:
These words are spoken by Amelia Slater to her daughter Victoria.
(b) Why does she disapprove of the listener being in colours?
Answer:
Abel Merryweather, Amelia’s father, has died and so they should be in mourning and not wearing colours.
(c) Bring out the irony in the above statement.
Answer:
Victoria, the one in colours, is actually the only one who is mourning her grandfather’s death. Herein lies the irony.
Question 4.
“I’m wondering if they’ll come at all. When you and Elizabeth quarrelled she said she’d never set foot in your house again.”
(a) Where will ‘she’ not come?
Answer:
‘She’, that is, Elizabeth, was not expected to come to Amelia and Henry’s house.
(b) Why will she not come?
Answer:
Elizabeth was not expected to come because the two sisters had a quarrel.
(c) Why, according to the listener, will she come?
Answer:
Elizabeth would come to claim her share of what their father had left behind, in the opinion of the listener.
Question 5.
“You know how hard she can be when she likes. Where she gets it from I can’t tell.”
(a) Who says this and about whom?
Answer:
Amelia says this about her sister Elizabeth.
(b) Why does the speaker call her hard?
Answer:
Amelia says that Elizabeth will want her share of grandfather’s property and she will not compromise. She will drive a hard bargain because she is seeking to obtain money at every opportunity.
(c) Bring out the irony in the statement ‘Where she gets it from I can’t tell’?
Answer:
The irony in the statement is that even Amelia is hard and greedy like her sister Elizabeth.
Question 6.
They’ll stretch, won’t they? I’m not going to have them wasted.
(a) What is ‘they’?
Answer:
‘They’ refers to Abel Merry weather’s slippers.
(b) What does she want the listener to do? Why?
Answer:
Amelia wants Henry to wear those slippers as they are new and his own slippers are old and worn out.
(c) Why does she say ‘they’ will stretch?
Answer:
The slippers are small for Henry. Amelia says they will stretch once he starts wearing them.
Question 7.
Now, Amelia, you mustn’t give way. We’ve all got to die some time or other. It might have been worse.
(a) Who is the speaker of these lines?
Answer:
The speaker of these lines is Ben Jordan.
(b) What prompts the speaker to say these words?
Answer:
Amelia is giving way to her grief at Abel Merryweather’s death. This prompts Ben to say these words.
(c) What does he mean when he says ‘It might have been worse’?
Answer:
Ben means that it could have been one of them who had died instead of Abel Merryweather.
(d) What does it reveal about the speaker’s character?
Answer:
It shows his callousness at the death of Abel Merryweather.
Question 8.
BEN: You should have gone for another. Eh, Eliza?
MRS JORDAN: Oh, yes. It’s a fatal mistake.
(a) What does Ben mean by ‘another’?
Answer:
Ben means another doctor as Dr Pringle, Abel Merryweather’s doctor was unavailable.
(b) Why does Mrs Jordan call it a fatal mistake?
Answer:
Mrs Jordan calls it a fatal mistake because she feels a doctor may have saved Abel Merryweather’s life.
Question 9.
“He always was thoughtful in that way. He was too honourable to have ‘gone’ without paying his premium.”
(a) Where is Abel Merryweather supposed to have gone that morning?
Answer:
Abel Merryweather was supposed to pay the premium on his insurance.
(b) Why is he said to be thoughtful?
Answer:
Abel Merryweather is said to be thoughtful since he paid the premium so that the two daughters, Amelia and Elizabeth, would get the insurance money.
(c) Bring out the irony in the above statement?
Answer:
Abel Merryweather had not gone to pay the premium on his insurance but to the pub for a drink.
Question 10.
“I don’t call that delicate, stepping into a dead man’s shoes in such haste.”
(a) Who makes this comment?
Answer:
Mrs Jordan makes this comment.
(b) What prompts the speaker to say this?
Answer:
The speaker is prompted to say this when she sees Henry Slater wearing Abel Merryweather’s slippers.
(c) Bring out the significance of this statement.
Answer:
The Slaters and Jordans have started dividing Abel Merryweather’s things among themselves as soon as they presume him to be dead. Herein lies the irony as both the daughters are acting in the same greedy manner.
Question 11.
“And you, too. Are you such a poor creature that you must do every dirty thing she tells you?”
(a) Who is the ‘poor creature’?
Answer:
Henry Slater is the ‘poor creature’.
(b) Why is he being called a ‘poor creature’?
Answer:
Henry is called a ‘poor creature’ since he does not stand up to his wife and does everythinglthat she tells him to do.
(c) What dirty deed had he done at her bidding?
Answer:
At her bidding, Henry had shifted his father-in-law’s bureau and clock to their room in order to keep it to themselves.