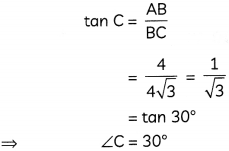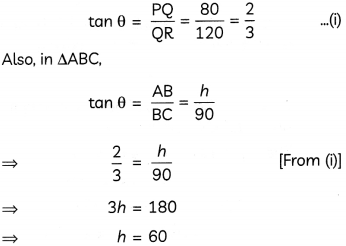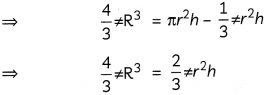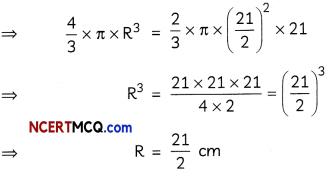Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Maths with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Maths Term 2 Set 5 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains three sections-A. B and C. Each part is compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 short answer type (SA1) questions of 2 marks each.
- Section-B has 4 short answer type (SA2) questions of 3 marks each.
- Section-C has 4 long answer type questions (LA) of 4 marks each.
- There is an Internal choice in some of the questions.
- Q14 is a case-based problem having 2 sub parts of 2 marks each.
Section – A
(Section – A has 6 short answer type (SA-1) questions of 2 marks each.)
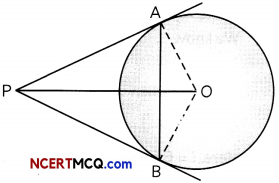
Question 1.
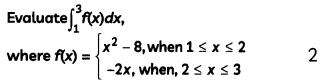
Question 2.
A die is rolled. If the outcome is an odd number, what is the probability that it is a prime number? (2)
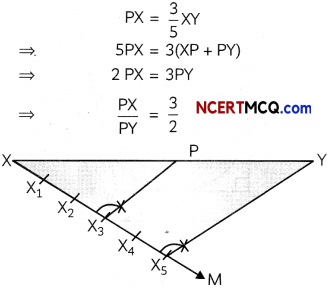
![]()
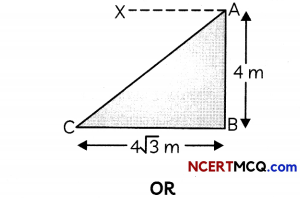
Question 3.
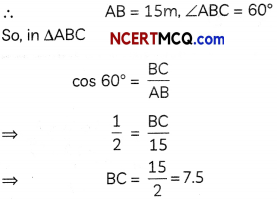
A line makes the same angle θ with x and z-axes. If the angle β which it makes with y-axis is such that sin2β = 3 sin2θ, then find the value of cos2θ.
OR
If the distance of the point (1,1,1) from the origin is half its distance from the plane x + y + z + k = 0, then find k. (2)
Question 4.
Write the probability distribution of the random variable “number of heads” when one coin is tossed. (2)
Question 5.
Find the vector projection of \(\vec{a}\) on \(\vec{b}\), where \(\vec{a}\) = Sj – 3k and \(\vec{b}\) = î + ĵ + k̂. (2)
Question 6.
Show that xdy – (y + 2x2) dx = 0 is a linear differential equation. (2)
Answer:
We have,
x dy – (y + 2x2) dx = 0
or \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{y+2 x^{2}}{x}=\frac{y}{x}+2 x\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}-\frac{1}{x} y\) = 2x
This is of the type \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + P(x)y = Q(x), where P(x)
= \(\frac{1}{x}\) and Q(x) = 2x. x
∴ The given differential equation is a Linear differential equation.
Hence proved.
SECTION – B
(Section – B has 4 short answer type (SA-2) questions of 3 marks each.)
Question 7.
Evaluate \(\int \frac{1}{3 \sin x+4 \cos x}\) dx. (3)
OR
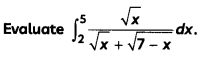
Answer:
Let I = \(\int \frac{1}{3 \sin x+4 \cos x}\) dx
Let r cos α = 3 and r sin α = 4.
Then, r2 = 25, i.e., r = 5 and α = tan-1\(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right)\)
∴ 3 sin x + 4 cos x
= 5 cos α sin x + 5 sin α cos x
= 5 sin (x + α)
Now, I = \(\int \frac{1}{5 \sin (x+\alpha)}\) dx
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) ∫cosec (x + α) dx
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) log |cosec (x + α) – cot (x + α)| + C
= \(\frac{1}{5}\) log |cosec (x + tan-1\(\frac{4}{3}\) – cot (x + tan-1\(\frac{4}{3}\)| + C
OR

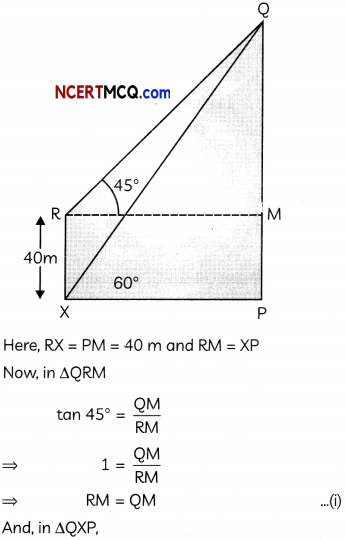
![]()
Question 8.
Show that the points A(- 2, 3, 5), B (1, 2, 3) and C (7, 0, -1) are collinear. (3)
Answer:
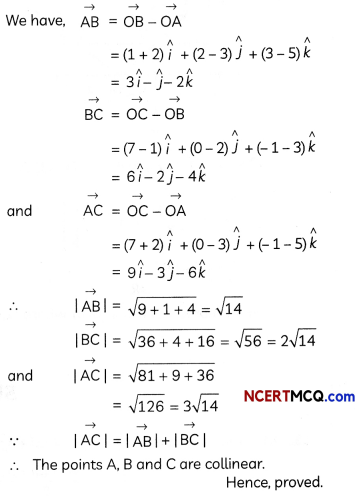
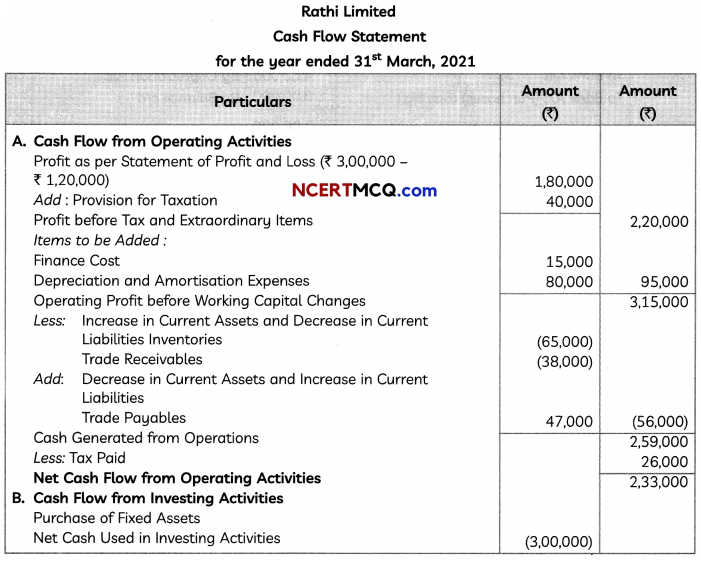
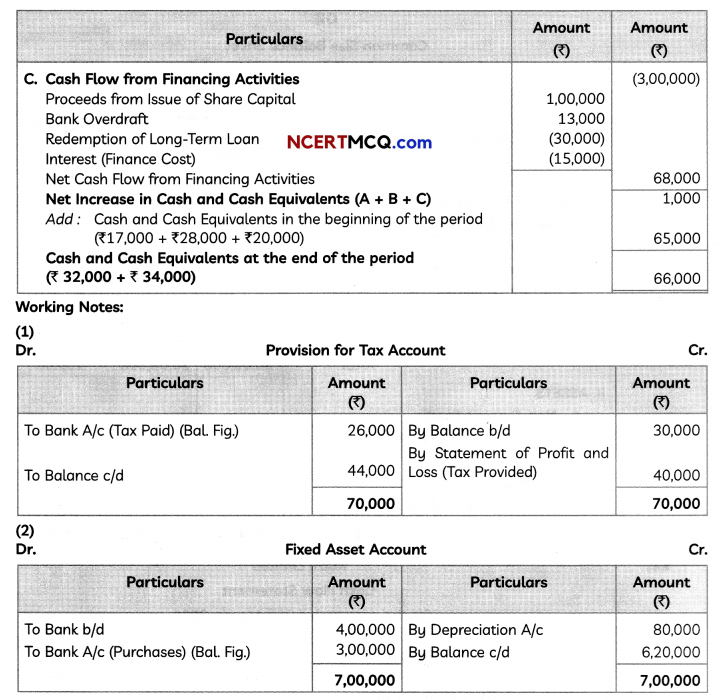
Question 9.
Prove that \(\vec{a} \times(\vec{b}+\vec{c})+\vec{b} \times(\vec{c}+\vec{a})+\vec{c} \times(\vec{a}+\vec{b})\) = 0. (3)
Answer:
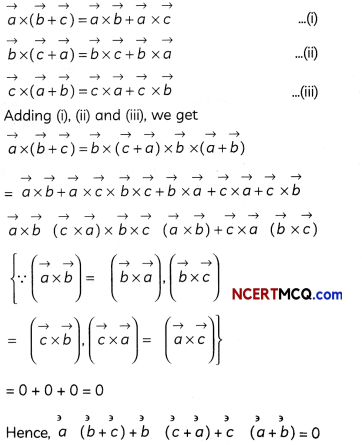
![]()
Question 10.
Sketch the bounded region and find the area of the region bounded by the curve y = |x – 1| and the line y = 1.
OR
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y2 = 4x, the lines x = 1 and x = 4 and the x-axis in the first quadrant. (3)
Answer:
We have, y = |x – 1|
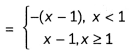
Now, required area = ar(rect OBCD) – ar(∆OAD) – ar(∆ABC)
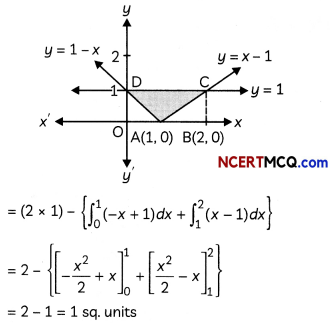
OR
y2 = 4x represents a parabola whose vertex is at the origin, axis of symmetry is x-axis, focus on the positive direction of x-axis and it opens to the right.
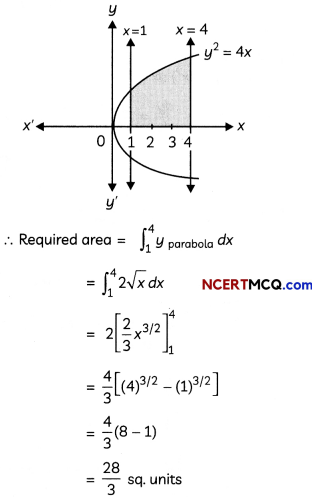
![]()
SECTION – C
(Section – C has 4 long answer type questions (LA) of 4 marks each.)
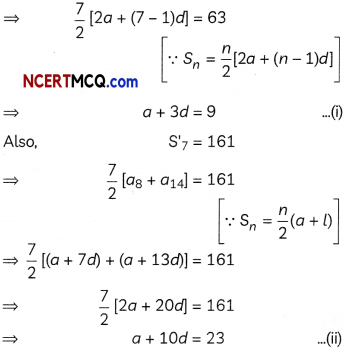
Question 11.
Show that the points (î – ĵ + 3k̂) and 3 (î + ĵ + k̂)are equidistant from the plane \(\vec{r}\). (5î + 2ĵ – 7k̂) + 9 = 0 and lies on opposite side of it.
OR
Find the point(s) on the line through the points A(l, 2, 3) and B (3, 5, 9) which are at a distance of 14 units from the mid-point of AB. (4)
Answer:
Mid-point of vectors (î – ĵ + 3k̂) and (3î + 3ĵ + 3k̂)
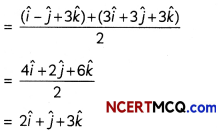
If the vectors (î – ĵ + 3k̂) and (3î + 3ĵ + 3k̂) are equidistant and lies on opposite side of the
plane \(\vec{r}\) . (5î + 2ĵ – 7k̂)+ 9 = 0, then their mid-point must satisfy the equation of the plane.
Since, (2î + ĵ + 3k̂) . (5î + 2ĵ – 7k̂) + 9
= 10 + 2 – 21 + 9
= 0 = R.H.S.
Hence, the vectors (î – ĵ + 3k̂) and (3î + 3ĵ + 3k̂) are equidistant and lies on opposite side of the given plane.
Hence, proved.
The equation of the line AB joining A(1, 2, 3) and B(3, 5, 9) is
\(\frac{x-1}{3-1}=\frac{y-2}{5-2}=\frac{z-3}{9-3}\)
⇒ \(\frac{x-1}{2}=\frac{y-2}{3}=\frac{z-3}{6}\) = λ(say)
∴ Any point on this line is
(2λ + 1, 3λ + 2, 6λ + 3) …(i)
Since, this point is at a distance of 14 units from the mid-point of AB i.e., \(\left(2, \frac{7}{2}, 6\right)\).
∴ \(\sqrt{(2 \lambda+1-2)^{2}+\left(3 \lambda+2-\frac{7}{2}\right)^{2}+(6 \lambda+3-6)^{2}}\) [Using distance formula]
i.e., (2λ – 1)2 + (3λ – \(\frac{1}{2}\))2 + (6λ – 3)2 = 196 [squaring both sides]
⇒ 49λ – 49λ – \(\frac{735}{4}\) = 0
or 4λ – 4λ – 15 = 0
⇒ (2λ + 3) (2λ – 5) = 0
⇒ λ = \(\frac{5}{2}\), – \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Substituting the values of λ in (i), we get the
requirec points as (6, \(\frac{19}{2}\), 18) and (- 2, –\(\frac{5}{2}\), – 6).
![]()
Question 12.
Solve the differential equation: \(\frac{d y}{d x} \sqrt{1+x+y}\) = x + y – 1 (4)
Answer:
Given differential equation is:
\(\frac{d y}{d x} \sqrt{1+x+y}\) = x + y – 1 ……. (i)
Put \(\sqrt{1+x+y}\) = z
or 1 + x + y = z2
Differentiating w.r.t x, we get
0 + 1 + \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2z\(\frac{d z}{d x}\)
Substituting these values in (i), we get
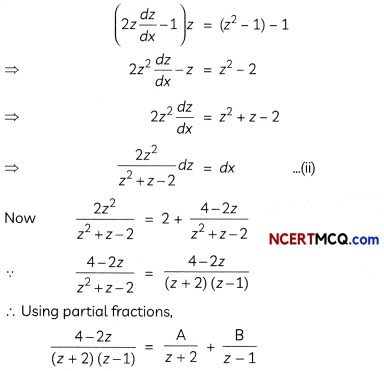
⇒ 4 – 2z = A(z – 1) + B(z + 2)
⇒ 4 – 2z = (A + B)z – A + 2B
Comparing coefficients of z and constant terms both sides, we get
A + B = – 2
and – A + 2B = 4
Solving these equations, we get
B = \(\frac{2}{3}\), A = – \(\frac{8}{3}\)
∴ \(\frac{2 z^{2}}{z^{2}+z-2}\) = 2 + \(\left(-\frac{8}{3}\right) \frac{1}{z+2}+\frac{2}{3} \frac{1}{z-1}\)
Substituting this value in (ii), we get
⇒ \(2\left\{1+\frac{1}{3(z-1)}-\frac{4}{3(z+2)}\right\}\)dz = dx
Integrating on both sides, we have
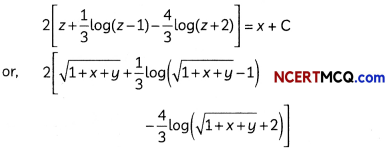
= x + C
Which is the required solution of the given differential equation.
![]()
Question 13.
Evaluate (4)
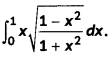
Answer:
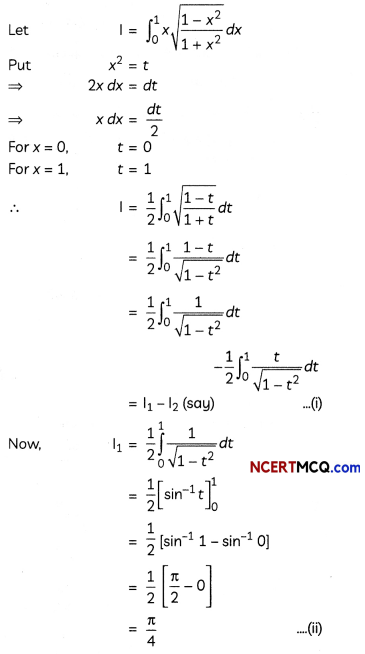
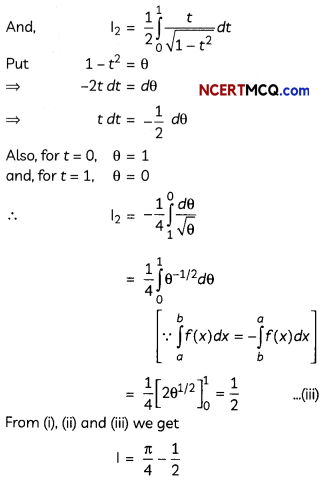
![]()
CASE-BASED/DATA-BASED
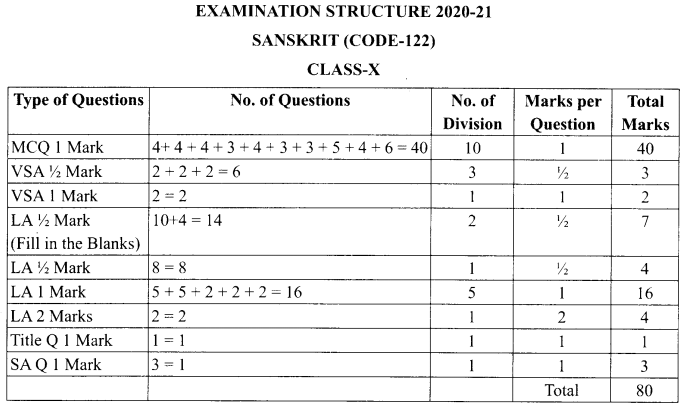
Question 14.
There are two shops in a village market named Vijay General Store and Anand General Store. In Vijay General Store, 30 tin of pure mustard oil, 40 tin of adulterated mustard oil, while in Anand General Store, 50 tin of pure mustard oil 60 tin of adulterated mustard oil are there. Mr. Gautam wants to buy one tin of mustard oil from any store selecting at random.
Based on the above information, answer the following two questions:
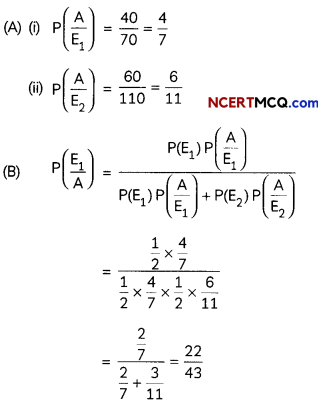
(A) Find the conditional probability than an
adulterated mustard oil tin is bought, given that (i) Vijay General Store is selected at random (ii) Anand General Store is selected at random. (2)
(B) Mr. Gautam wants to know quality of mustard oil Before purchasing, he selected a store at random and then selected a tin of mustard oil at random. If the tin selected at random has adulterated oil, then find the probability that the selected tin is from Vijay General Store. (2)
Answer:
Let E1, E2 and A be the events defined as follows:
E1: Selection of Vijay General Store
E2: Selection of Anond General Store
A: Purchasing of a tin having adulterated mustard oil.





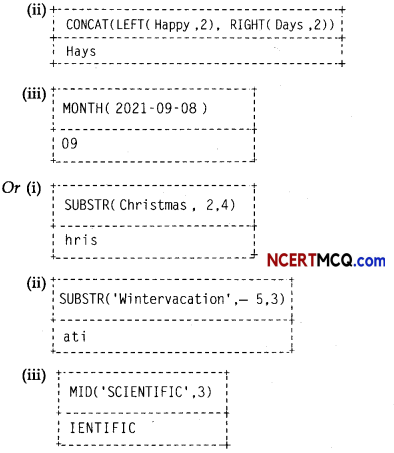
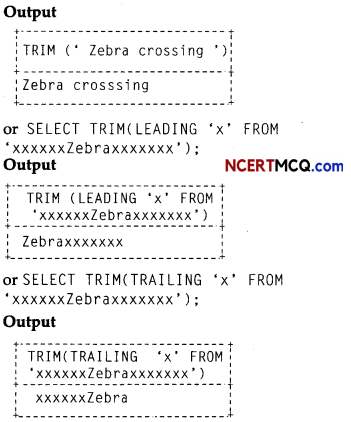


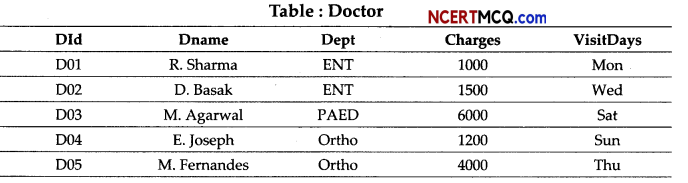
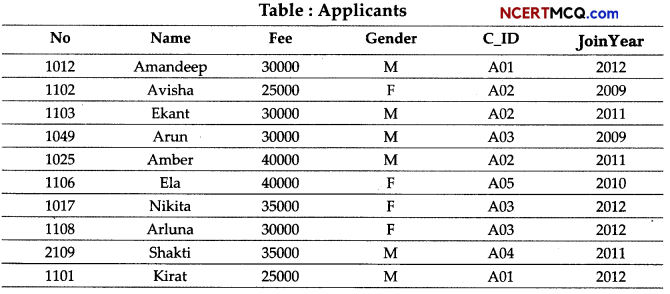
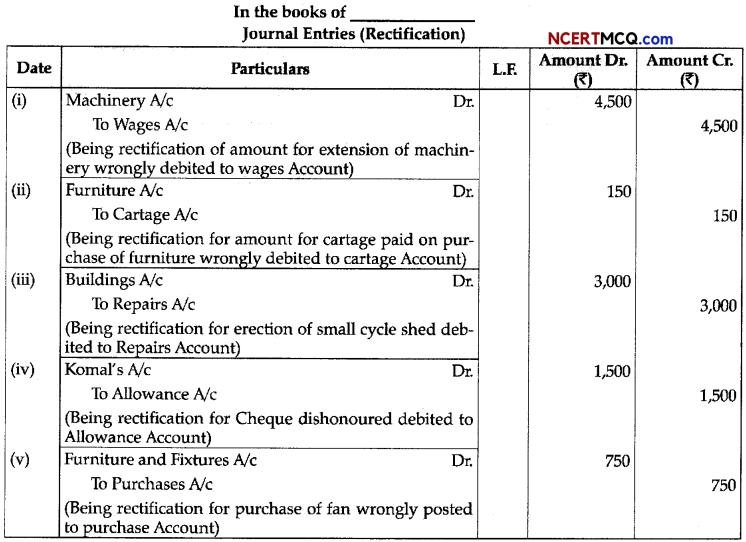
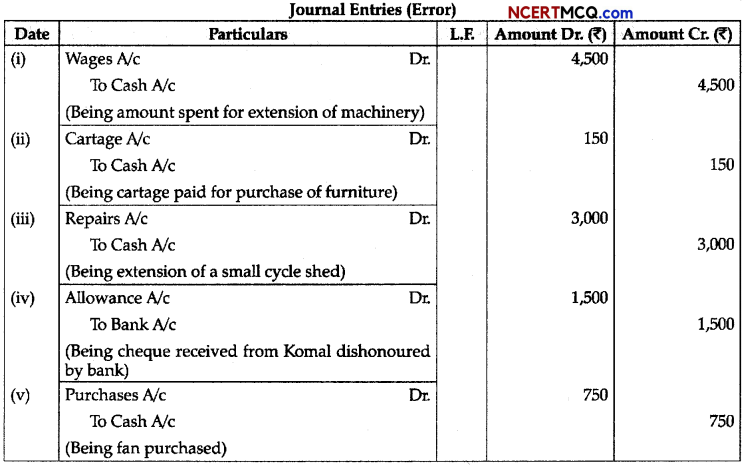

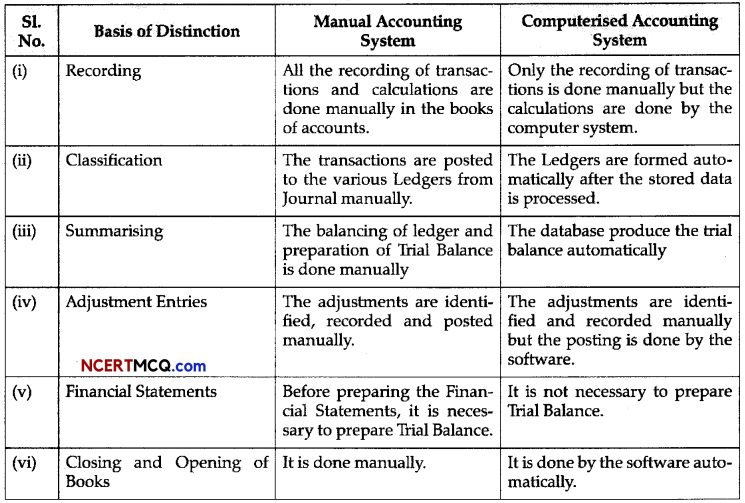
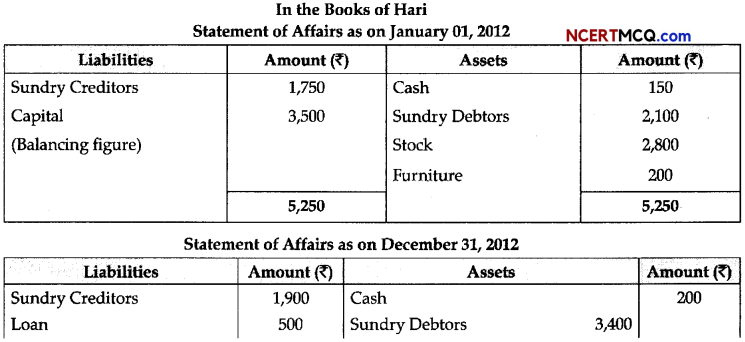
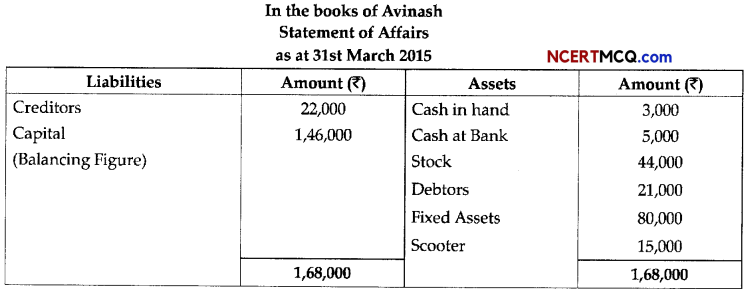
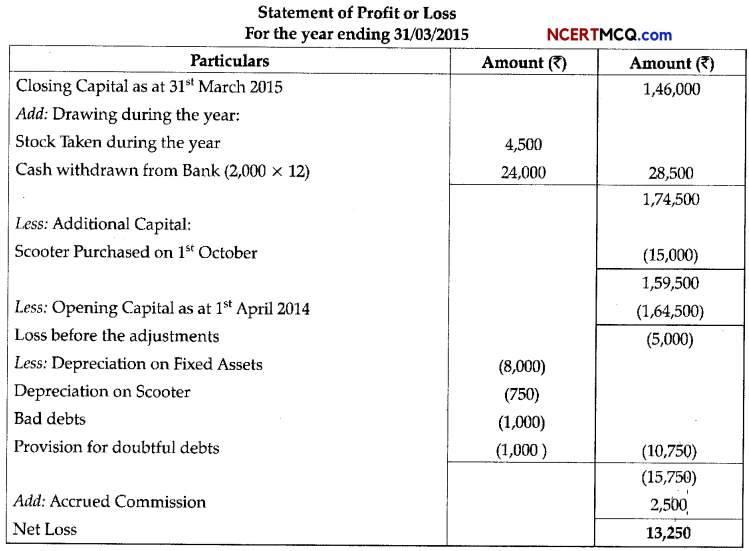
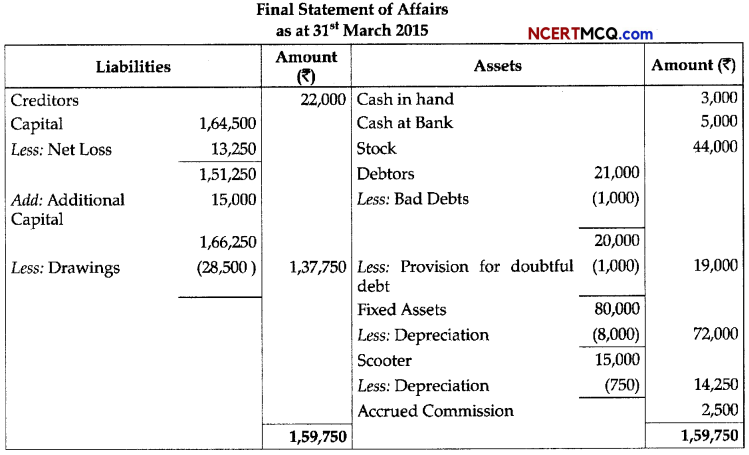

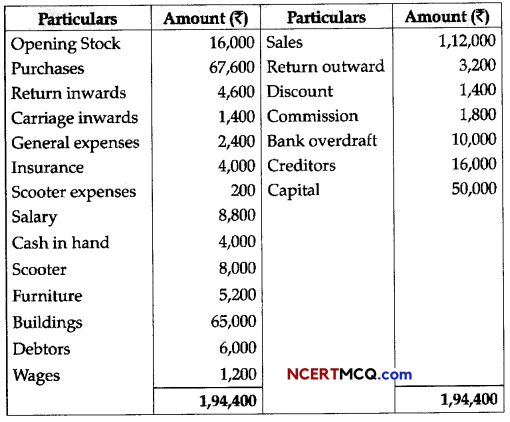
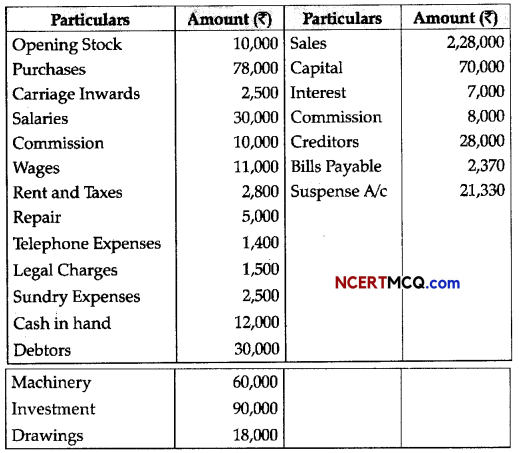
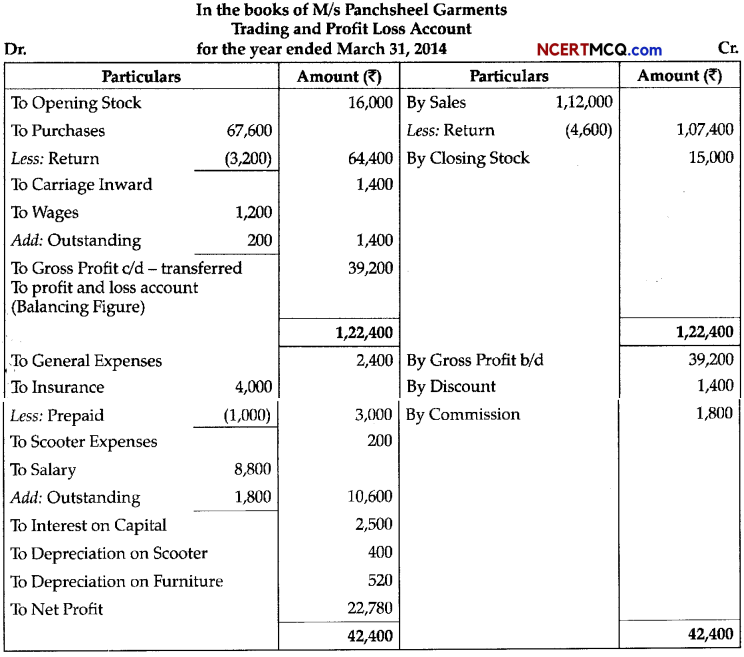
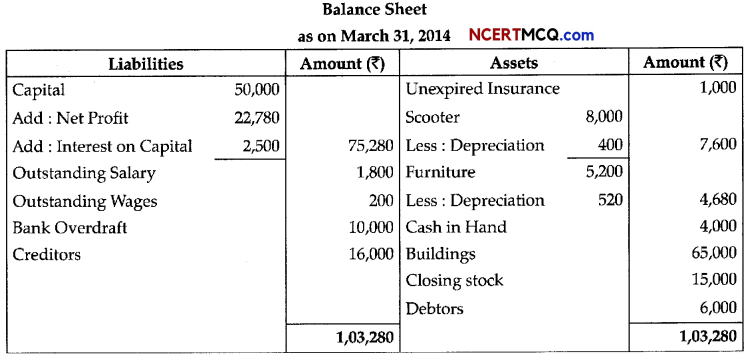
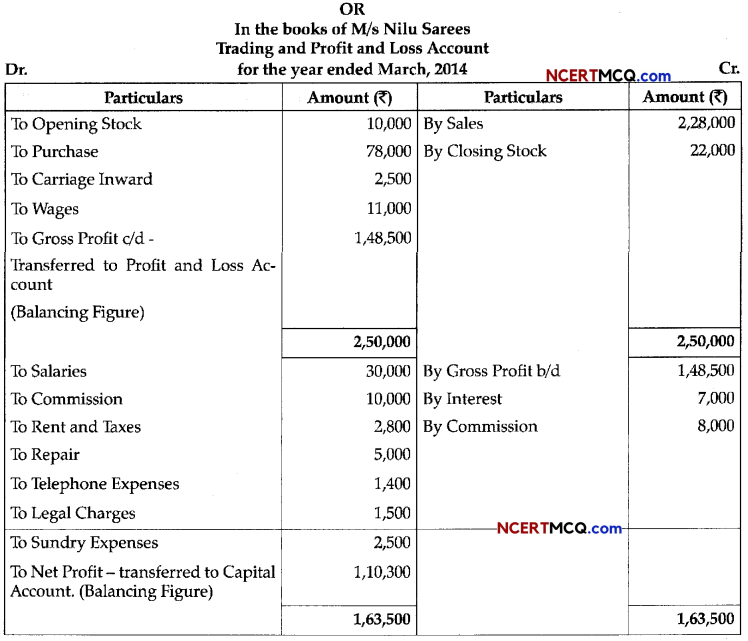
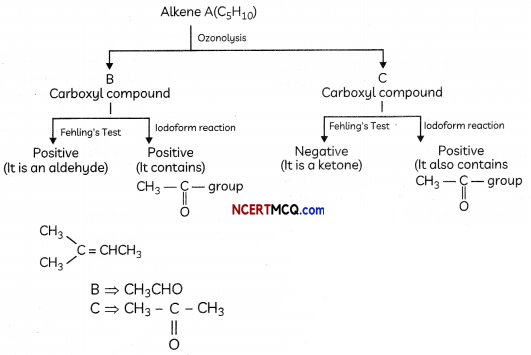
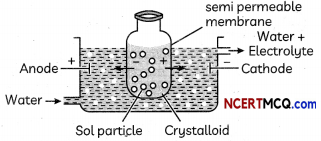
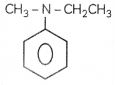
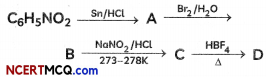

 (3)
(3)


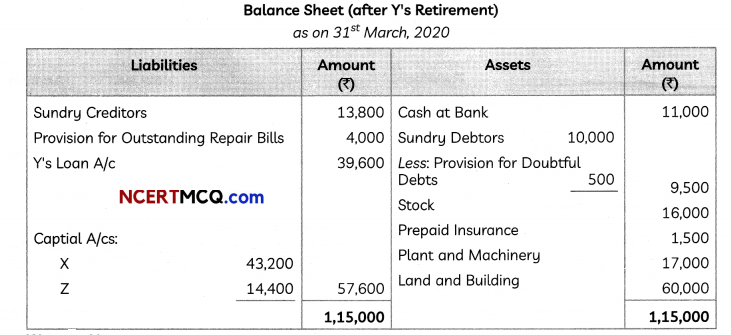
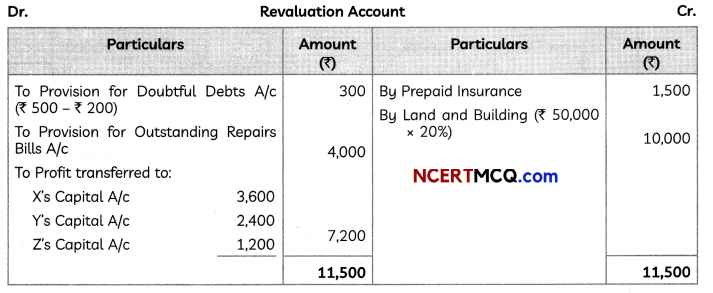
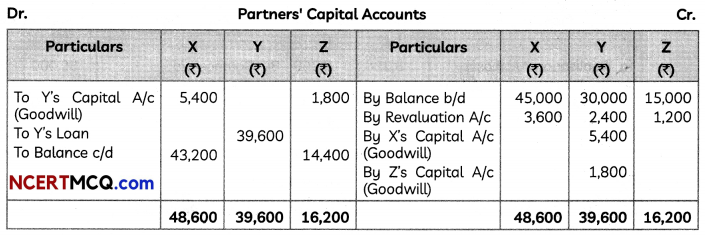
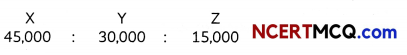
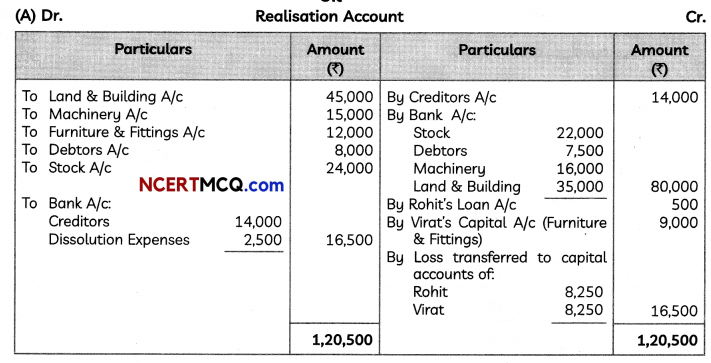
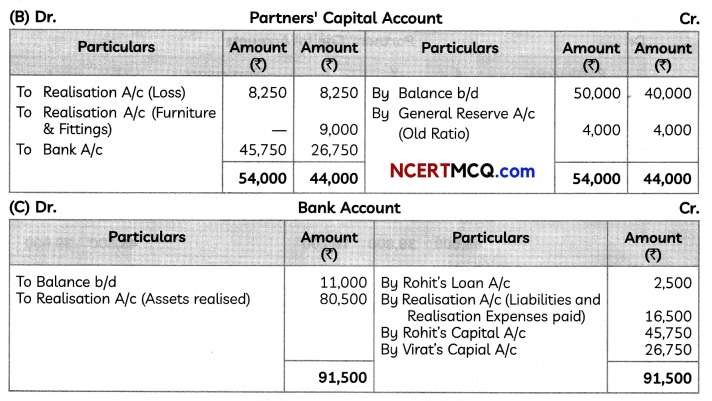
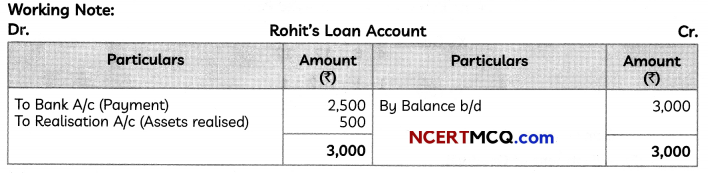

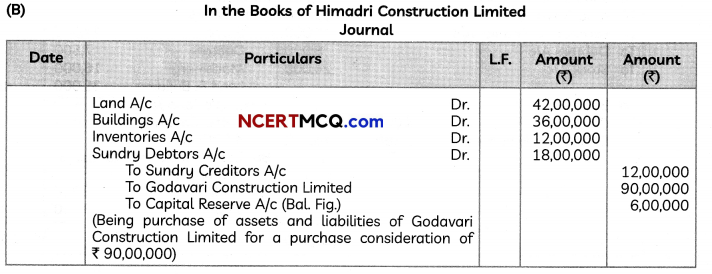



 (5)
(5)