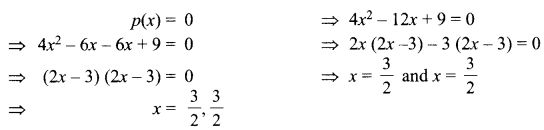
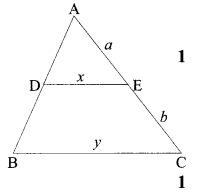
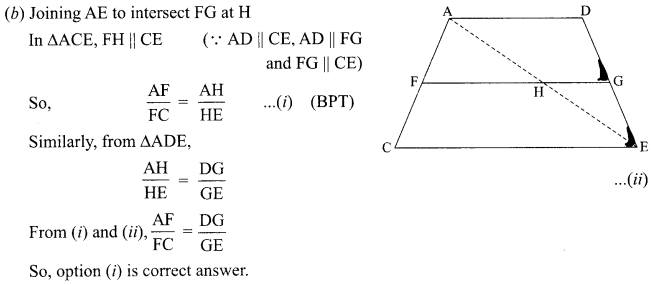
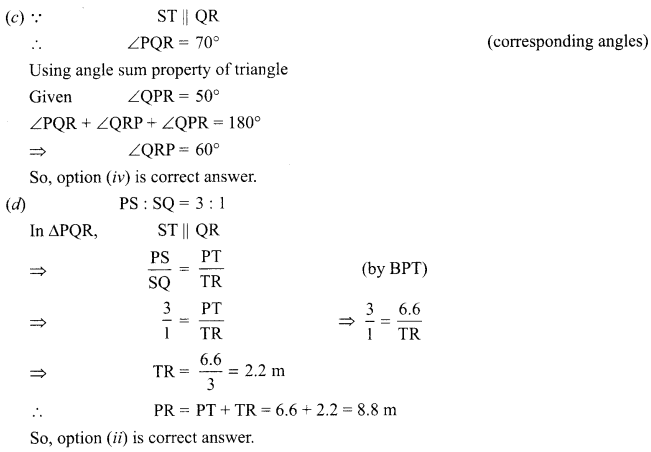
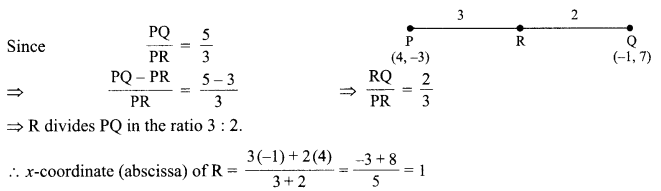
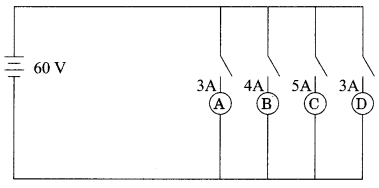
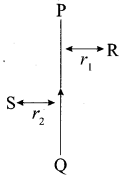
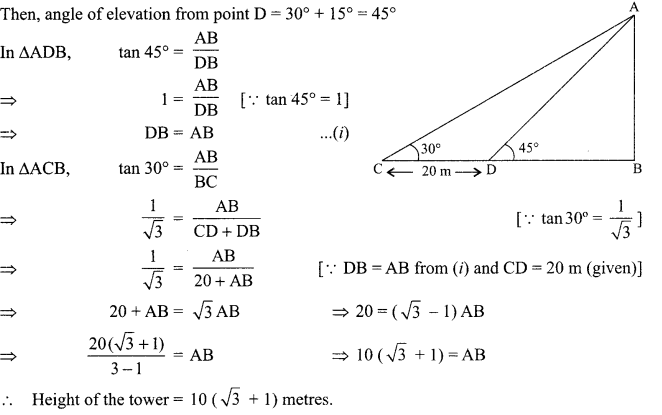
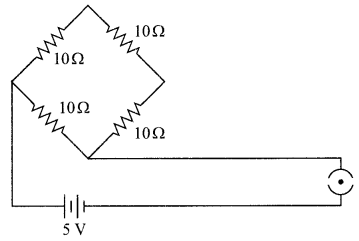
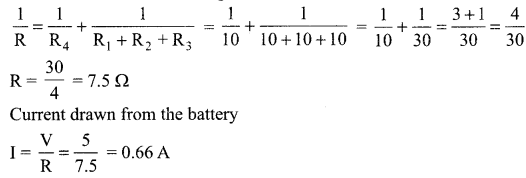
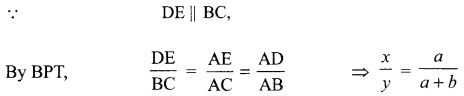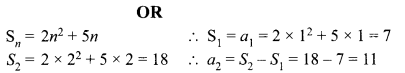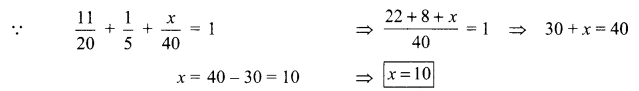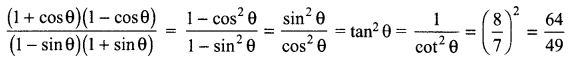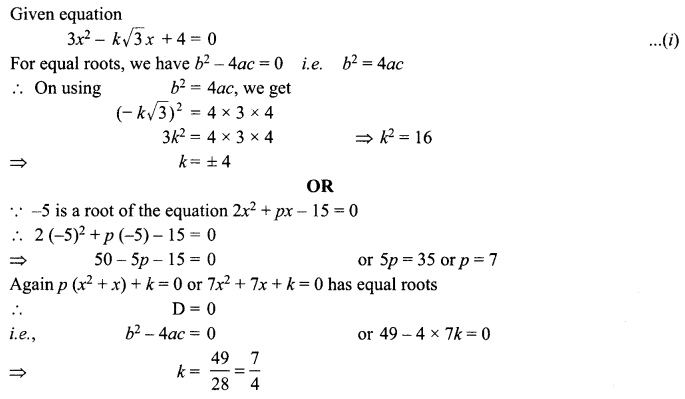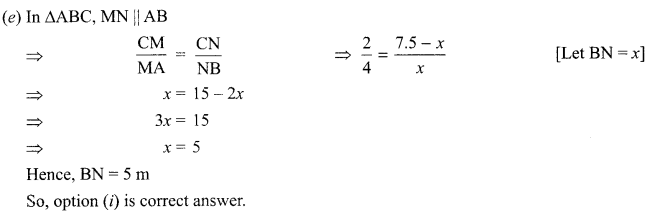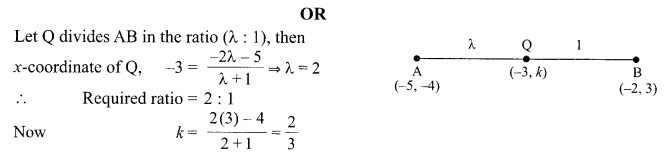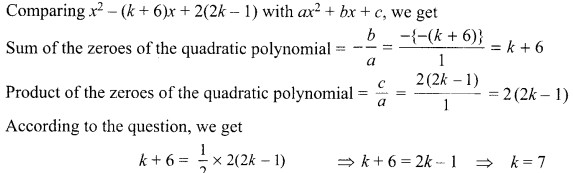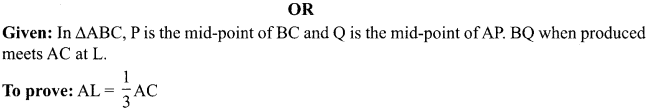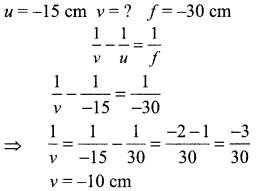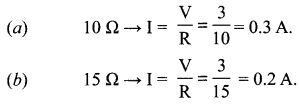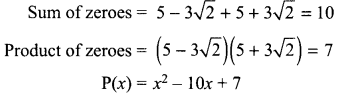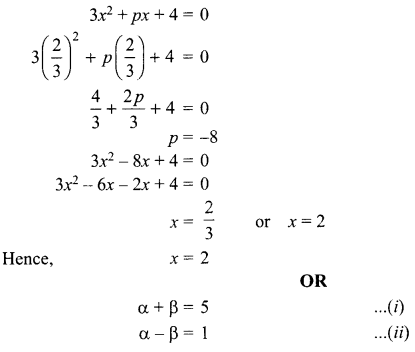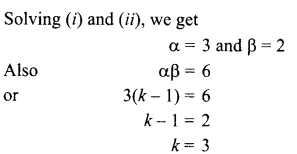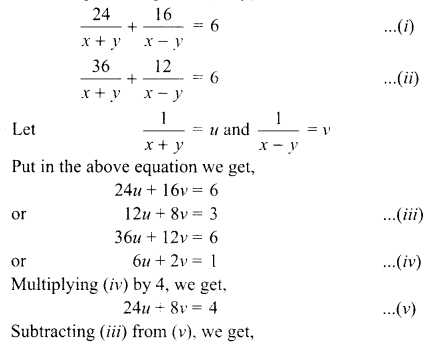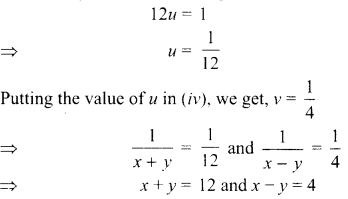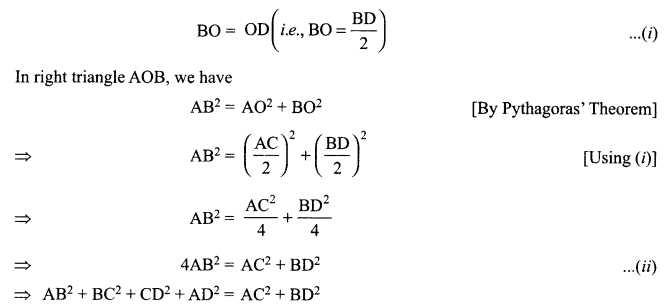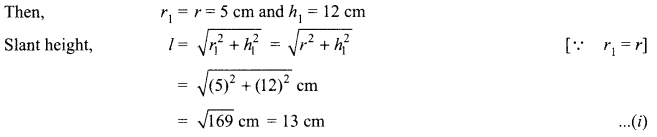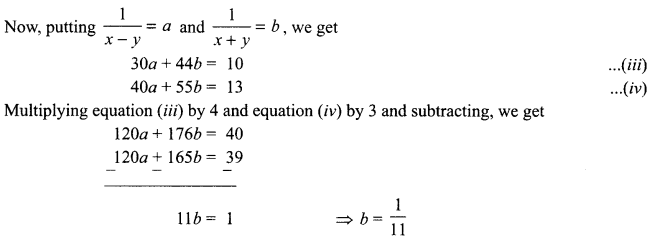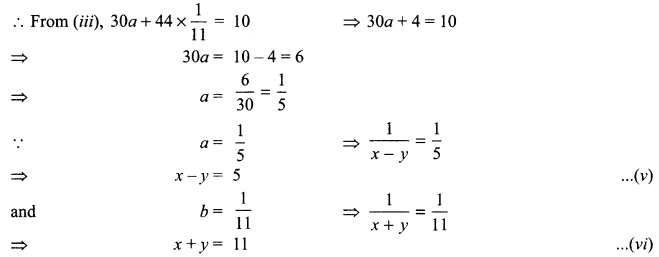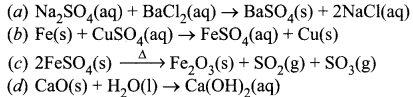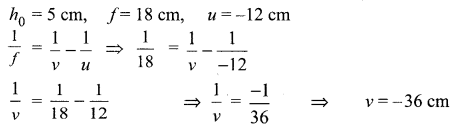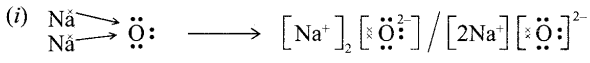Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 4 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 4 for Practice
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
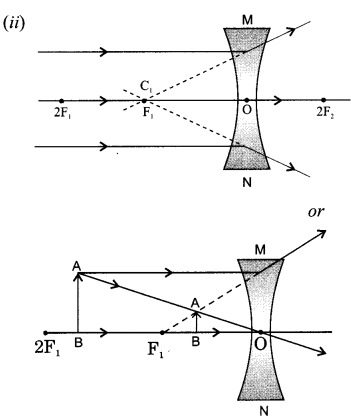
(ii) Section-A – question no. 1 to 20 – all questions and parts there of are of one mark each.
These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion – reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one sentence.
(iii) Section-B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(iv) Section-C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words. :
(v) Section—D – question no. – 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vi) There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
(vii) Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section-A
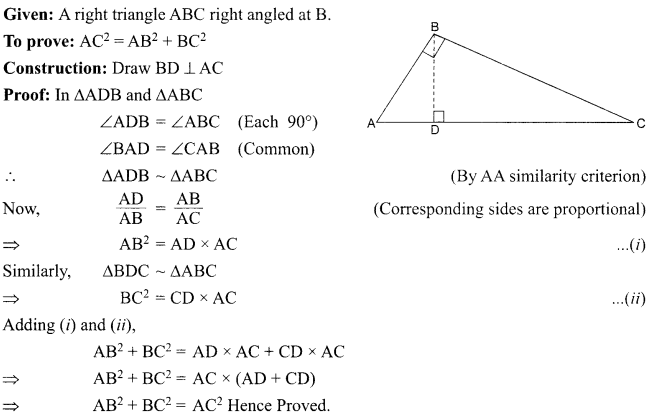
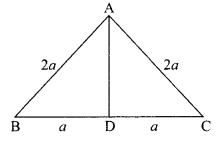
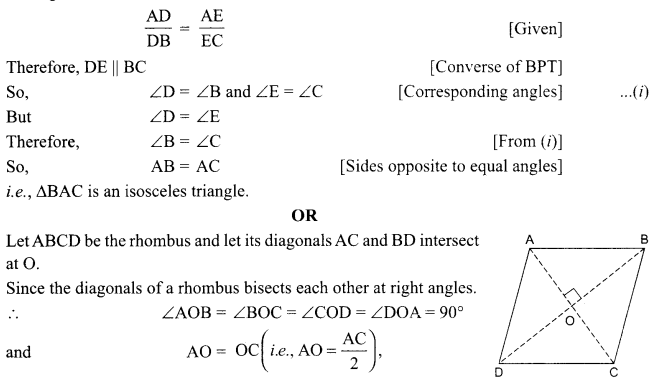
1. What is the radius of curvature of a plane mirror?
2. Why is red colour selected for danger signal lights?
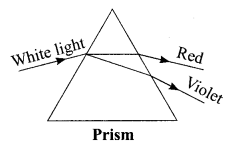
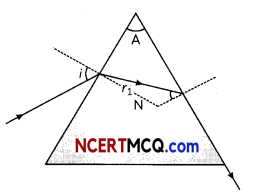
3. What is the cause of dispersion of light by prism.
OR
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
4. Name the components of blood which transport:
(i) Food, carbon dioxide and nitrogeneous wastes
(ii) Oxygen
5. Write the relationship between heat energy produced in a conductor when potential difference V is applied across its terminals and a current, I flows through it for the time ‘F.
6. A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the hole on the other face of the box as shown in the figure. What type of lens could be inside the box?
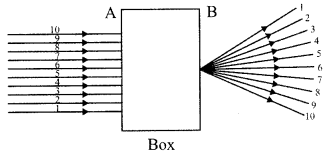
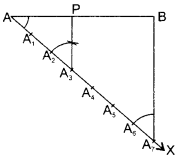
7. Why do stars twinkle?
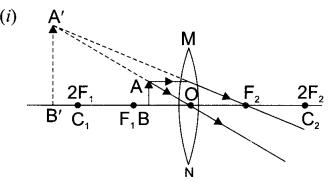
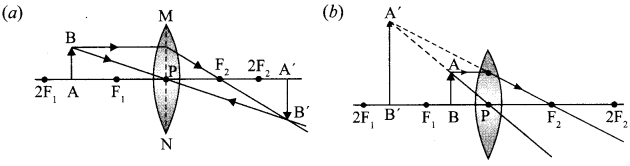
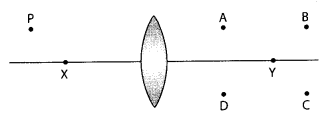
8. A lens forms an image at Y of an object at X. Where does the lens form an image of an object at P?
9. What indication do we get by appearance of dwarf plant in F2 generation?
OR
What is sex of the baby that inherits Y-chromosome from the father?
10. If a women is using copper-T, will it help in protecting against sexually transmitted diseases?
OR
Why is temperature of scrotal sac 2°C less than the body temperature?
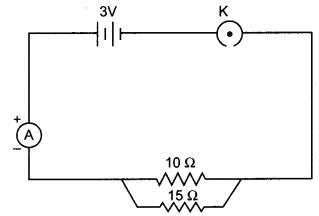
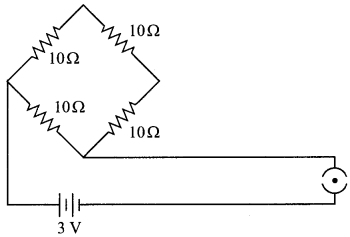
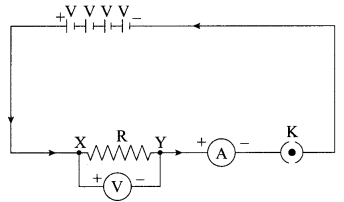
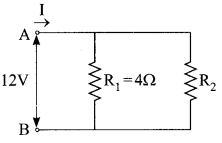
11. Name the intermediate and the end products of glucose breakdown on aerobic respiration.
In the experiment “Chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis’, why does the green part of variegated leaf turns blue black after putting in iodine solution?
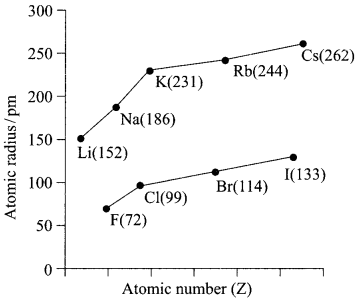
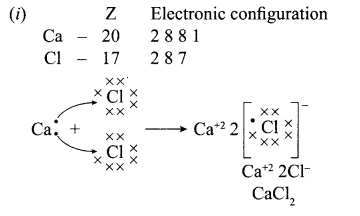
12. Out of Li and K, which one have stronger metallic character and why?
OR
The formula of magnesium oxide is MgO. State the formula of barium nitrate and barium sulphate, if barium belongs to the same group.
13. X + YSO4 → XSO4 + Y
Y + XSO4 → No reaction
Out of two elements, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ which is more reactive and why?
Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
For question numbers 14,15 and 16, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (i), (iii) and (iv) as given below:
(i) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(iii) A is true, but R is false.
(iv) A is false, but R is true.
14. A. Copper sulphate solution turns blue litmus red.
R. Copper sulphate is salt of strong acid H2SO4, weak base Cu(OH)2, therefore, acidic in nature.
Answer:
(i)
15. A. The angle of incidence and reflection are equal.
R. The angle between incidence ray and normal is called angle of incidence.
Answer:
(ii)
16. ![]()
R. It is a combination reaction because CO combines with H2 to form CH3OH i.e. two substances combine to form a single compound.
OR
1. The reaction, MnO2 + 4HCl → MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2 is an example of redox reaction.
2. In this reaction, HCl is reduced to Cl2 whereas MnO2 is oxidized to MnCl.
Answer:
(ii) OR (iii)
Answer Q. No 17 – 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four subparts in these questions.
17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on.
Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of population.
(i) Which of the following is not a common sign of sexual maturation in boys and girls.
(a) Pubic hair
(b) Menstrual cycle in females
(c) Broad shoulders in females
(d) Wider chest in males
Answer:
(c) Broad shoulders in females
(ii) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
(a) Condoms
(b) Orals pills
(c) IUCD
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Orals pills
(iii) Sex ratio of females/1000 males in different states are as follows:
| States | 2013-15 | 2012-14 |
| Delhi | 869 | 876 |
| Haryana | 831 | 866 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 879 | 869 |
| Punjab | 889 | 870 |
Name the state which improves the ratio to maximum extent in 2013-15.
(a) Delhi
(b) Haryana
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(d) Punjab
(iv) According to the tabel in above question, which state declines this ratio to maximum extent in 2013-15.
(a) Delhi
(b) Haryana
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(b) Haryana
(v) What is the major cause of less females than males in India?
(a) Males live longer than females
(b) Naturally, male child birth rate is higher than female child
(c) Female foeticide
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Female foeticide
18. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
The data for four elements is given below:
| Element | Carbon | Nitrogen | Fluorine | Neon |
| Symbol | C | N | F | Ne |
| Structure | Macromolecular | Simple molecules N7 | Simple molecules F, | Single atoms Ne |
| Boiling point/°C | 4200 | -196 | -188 | -246 |
(i) Name the element that is solid at room temperature.
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Fluorine
(d) Neon
Answer:
(a) Carbon
(ii) Why is the boiling point of carbon the highest?
(a) Carbon atoms linked through strong ionic bonds to form molecules.
(b) Carbon atoms are close together with strong covalent bonds.
(c) Carbon atoms are small in size thus have more stronger attractions among them.
(d) Carbon atoms are not linked to each other.
Answer:
(b) Carbon atoms are close together with strong covalent bonds.
(iii) Which of the following element is inert?
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Fluorine
(d) Neon
Answer:
(d) Neon
(iv) Carbon has many allotropes with macromolecular structure. Which of the following is not such kind of allotrope of carbon?
(a) Diamond
(b) Fullerene
(c) Graphite
(d) Coke
Answer:
(d) Coke
(v) Which of the following is the most reactive element?
(a) Carbon
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Fluorine
(d) Neon
Answer:
(c) Fluorine
19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
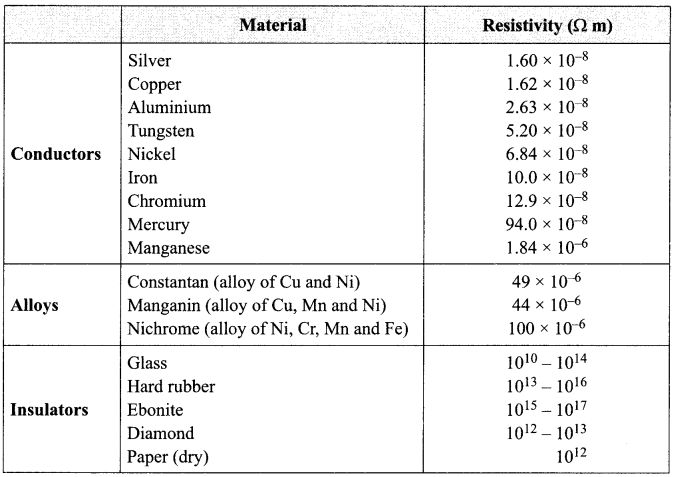
(i) What is the range of resistivity in metals which are conductor of electricity?
(a) 10-8 to 10-7 Ωm
(b) 10-7 to 10-6 Ωm
(c) 10 8 to 10-6 Qm
(d) 10 8 to 10 4 Qm
Answer:
(c) 10 8 to 10-6 Qm
(ii) Why are alloys used in heating devices like electric iron, toasters, immersion rods, etc.?
(1) Alloys have high resistivity.
(2) Alloys do not oxidise or bum at high temperature.
(3) Alloys have high conductivity thus allow high current through it
(a) III only
(b) I only
(c) II and III
(d) I and II
Answer:
(d) I and II
(iii) Which of the following is used in transmission wires?
(a) Cu
(b) Al
(c) Zn
(d) Fe
Answer:
(d) Fe
(iv) Which is the best conducting metal?
(a) Cu
(b) Ag
(c) Au
(d) Hg
Answer:
(d) Hg
(v) Based on resistivity, which of the following is better to use as insulation to protect us from electric current.
(a) Glass
(b) Hard rubber
(c) Nichrome
(d) Diamond
Answer:
(c) Nichrome
20. Read the following and answer any four questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
When a single parent is involved in the formation of a new individual, without the fusion of gametes, it is called asexual reproduction. It involves repeated mitotic divisions.
Sexual reproduction is a process of combining DNA from two different individuals during reproduction. This is brought about by the fusion of the male and female gametes.
(i) The type of reproduction taking place is
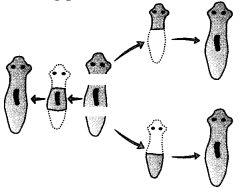
(a) Budding
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Regeneration
(d) Fission
Answer:
(c) Regeneration
(ii) Choose the right option
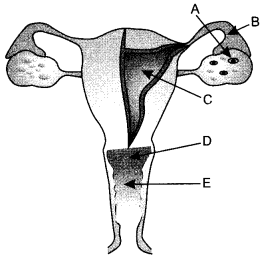
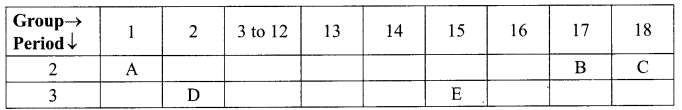
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| (a) | Fallopian tube | Oviduct | Uterus | Cervix | Vagina |
| (b) | Oviduct | Vas deferens | Ovary | Vagina | Cervix |
| (c) | Ovary | Oviduct | Uterus | Cervix | Vagina |
| (d) | Ovary | Fallopian tube | Uterus | Vagina | Cervix |
Answer:
(c)
(iii) Where does fertilisation occur in human females?
(a) Uterus
(b) Cervix
(c) Oviduct
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
(iv) The simple animals like Planaria can be cut into a number of pieces and each piece grows into a complex organism. What is the process known as?
(a) Budding
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Spore formation
(d) Regeneration
Answer:
(d) Regeneration
(v) Spirogyra reproduces by
(a) Fission
(b) Regeneration
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Budding
Answer:
(c) Fragmentation
Section-B
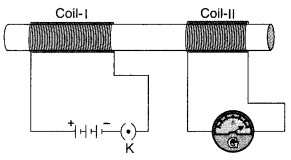
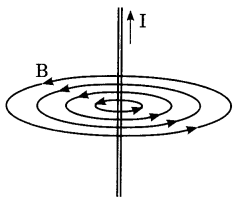
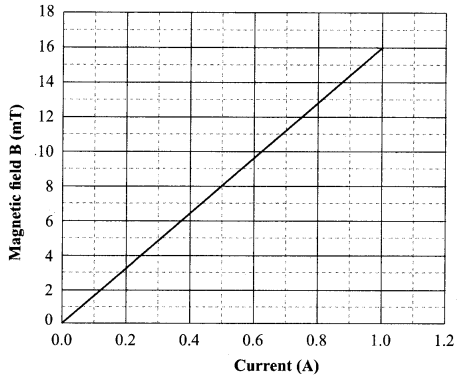
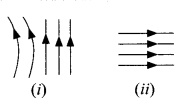
21. Identify the type of magnetic field represented by the magnetic field lines given below and name the type of conductors which can produce them.
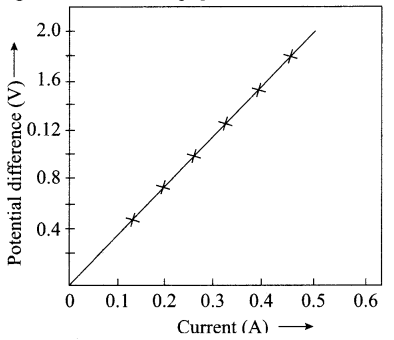
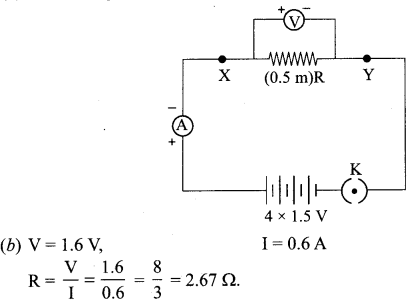
22. The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below:
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Answer:
3.314 Ω
23. You have three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper; how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
OR
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbon are taken in test tubes ‘A’, and ‘B\ Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube ‘A’ while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube ‘B\ In which test tube, will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
24. A solution of potassium chloride when mixed with silver nitrate solution, an insoluble white substance is formed. Write the chemical reaction involved and also mention the type of reaction.
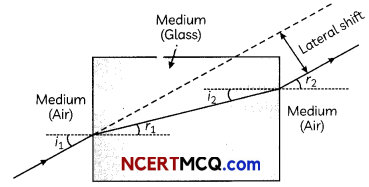
25. A ray of light incident on rectangular glass slab emerges parallel to itself. Draw a labelled diagram to justify this statement.
OR
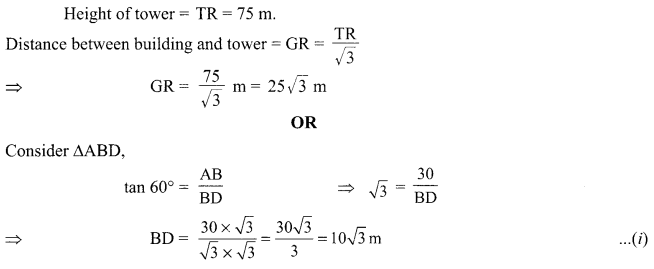
Define absolute refractive index. Mention its unit. Can the value of absolute refractive index be smaller than 1 ? Justify your answer.
26. How does the metallic character of elements changes along a period of the periodic table from left to right and why?
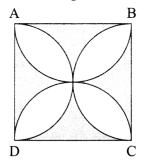
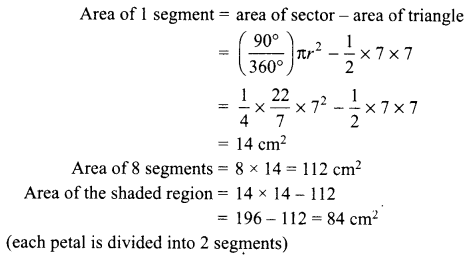
Section – C
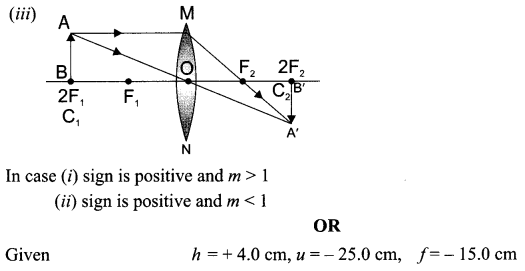
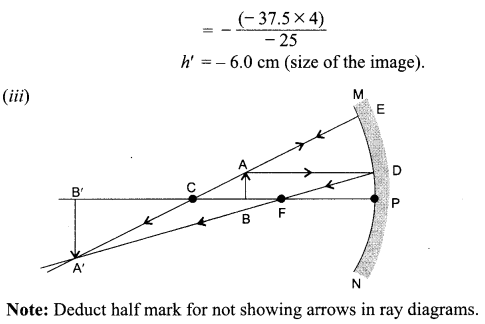
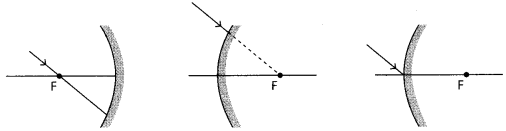
27. Show the path of the reflected ray, after reflection in each case.
(i) Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and label on it:
Oesophagus, Gall bladder, Liver and Pancreas
(ii) Explain the statement, “Bile does not contain any enzyme, but it is essential for digestion.”
OR
How respiration does takes place in plants?
29. Based on the group valency of elements, state the formula of the following, giving justification for each.
(i) Oxides of Group 1 elements.
(ii) Halides of the elements of Group 13.
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of Group 16.
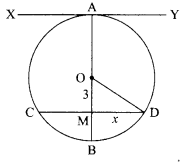
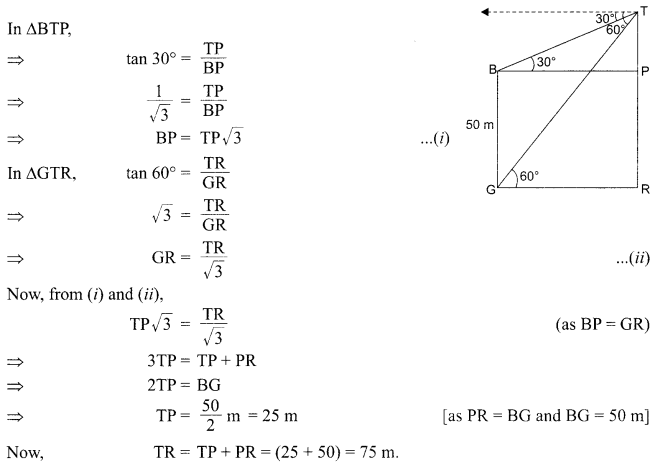
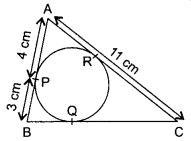
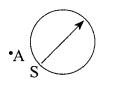
30. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near point A as shown in the figure. In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be placed so that it passes through A and there is no change in the “A deflection of the compass? Under what conditions is the deflection maximum and why?
31. (i) What is the nature of food coming from stomach?
(ii) Mention any two structural modifications in small intestine which helps in absorption of food.
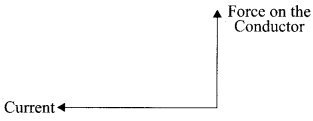
32. An electron enters a magnetic field, at right angle to the field direction.
(i) State the rule to find the direction of force acting on the electron.
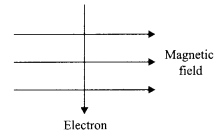
(ii) What will be the direction of force acting on the electron, in the above case?
33. (i) Two conductors A & B of resistance 5 ohms and 10 ohms respectively can be arranged in parallel and later on in series. In each arrangement, the total voltage applied is 120V. In which arrangement will the voltage across A and B be the same and in which case will the current flowing through A and B be the same?
(ii) Calculate the total resistance of each arrangement.
Answer:
(ii) (a) 3.33Ω
(b) 15Ω
Section-D
34. The structural formula of five compounds are given below.
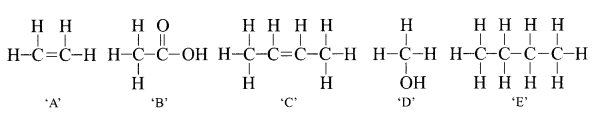
(i) Which two compounds belong to the same homologous series?
(ii) Which compound belongs to the same homologous series as ethanol?
(iii) Which compound on hydrogenation produces E?
(iv) Which compound when dissolved in water turns blue litmus red?
(v) Name the homologous series for compound B.
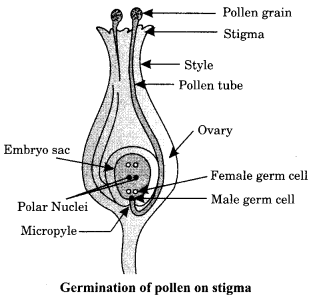
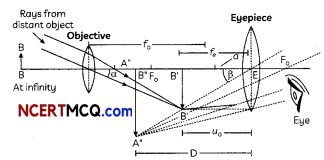
35. (i) Identity A, B, C and D in the given diagram and write their names.
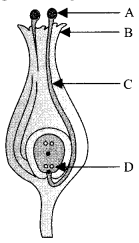
(ii) What is pollination? Explain its significance.
(iii) Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers. Name the parts of the flower that develop after fertilisation into
(a) seed
(b) fruit
OR
(i) Draw the diagram of female reproductive system and match and mark the part (s):
(a) Where block is created surgically to prevent fertilisation.
(b) Where CuT is inserted.
(c) Inside which condom can be placed.
(ii) Why do more and more people prefer to use condoms? What is the principle behind use of condoms?
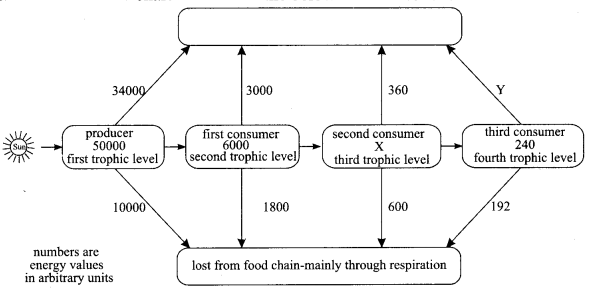
36. (i) Name the organisms which belong to first and third trophic level in food chain comprising of the following:
Insects, birds, frog and grass.
(ii) What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
OR
(i) Give reason to justify the following:
(a) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere.
(b) Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
(ii) Why is improper disposal of waste a curse to environment?