Here we are providing Online Education for The Banyan Tree Extra Questions and Answers Class 6 English Honeysuckle, Extra Questions for Class 6 English was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-6-english/
Online Education for The Banyan Tree Extra Questions and Answers Class 6 English Honeysuckle
The Banyan Tree Extra Questions and Answers Short Answer Type
The Banyan Tree Class 6 Extra Questions And Answers Question 1.
Why did the speaker claim that the old banyan tree was his?
Answer:
The old banyan tree became the narrator’s own property because his grandfather was too old to climb it.
The Banyan Tree Extra Questions Class 6 Question 2.
What did the speaker do on his crude platform?
Answer:
The author used to read story books and watch the world below from his crude platform.
The Banyan Tree Question Answers Class 6 Question 3.
What change did the fig season bring in?
Answer:
The banyan tree became the noisiest place in the garden during the fig season.
The Banyan Tree Class 6 Questions And Answers Class 6 Question 4.
What exciting scene did the author narrate?
Answer:
The author enjoyed the fight between a mongoose and a cobra, a battle of two champions.
Extra Questions Of Chapter The Banyan Tree Class 6 Question 5.
Who won the fight between the mongoose and the snake?
Answer:
The mongoose first bit the snake twice on the back. When the cobra was tired, the mongoose caught it by the snout. He finally dragged the dead snake into the bushes.
The Banyan Tree Class 6 Extra Questions Question 6.
Who were the other two spectators? What did they do? (Did they watch, or did they join in the fight)?
Answer:
The other two spectators were a myna and a jungle crow. They settled on a cactus to watch the outcome joined in the fight off and on.
The Banyan Tree Extra Questions and Answers Long Answer Type
The Banyan Tree Poem Question Answer Class 6 Question 1.
What do you learn from the fight of swift mongoose and venomous snake?
Answer:
One can easily learn that the one with energy and swiftness in action can succeed in life. The snake was a great threat to one as it is filled with deadly venom. The patience and strategic fight plan along with understanding of weakness and strength of the opponent make one a winner. One more thing to be understood here is that various opportunist viable to make use of opportunities.
Banyan Tree Extra Questions Class 6 Question 2.
How does sense of belongingness develop faith?
Answer:
The author describes that the house belongs to his grandfather yet the tree belongs to him. He found a comfort place in the branches and made it a resting place to read various books of his interest. He got a over view of every activity that took place around him. His faith helped him in befriending a squirrel. The child brought food for squirrel. So with time faith was developed and the squirrel could delve into his pockets.
The Banyan Tree Questions And Answers Class 6 Question 3.
What is the significance of the banyan tree in the story of Ruskin Bond’s?
Answer:
The whole story revolves around the tree. The tree was a second home to the author and gave a panoramic view of the world around it. The banyan tree served as a platform for the writer to sit and watch the thrilling fight between a cobra and a wild mongoose. The tree was almost the speaker’s property. The fight started under that tree in sunshine. The other spectators, a myna and a crow also arrived to feed on the dead cobra. But they sat on a cactus plant not the tree.
Question 4.
(i) What happened to the crow in the end?
(ii) What did the myna do finally?
Answer:
(i) In the end the crow flung nearly twenty feet across the garden by a blow from the cobra’s snout. It fluttered about for a while, then lay still.
(ii) Myna finally dropped cautiously to the ground, hopped about, the peered into the bushes from a safe distance and then with a shrill cry of congratulations flew away.
The Banyan Tree Extra Questions and Answers Reference to Context
Question 1.
My first friend was a small grey squirrel. Arching his back and sniffing into the air, he seemed at first to resent my invasion of his privacy. But when he found that I did not arm myself with catapult or air gun, he became friendly, and when I started bringing him pieces of cake and biscuit he grew quite bold and was soon taking morsels from hand. Before long, he was delving into my pockets and helping himself to whatever he could find. He was a very young squirrel, and his friends and relatives probably thought him foolish and headstrong for trusting a human.
(i) Who is the first friend of the writer?
(ii) How did the squirrel become friendly with the child?
(iii) What did the writer bring for the squirrel?
(iv) What could be the opinion of squirrel’s family and friends about human being?
(v) Write antonym of ‘Probably’.
Answer:
(i) A small grey squirrel is the first friend of the writer.
(ii) The squirrel did not see the child with any catapult or gun. So it become friendly with the child.
(iii) The writer brought pieces of cake and biscuits for the squirrel.
(iv) The opinion of squirrel’s family and friends could be that human beings are not trustworthy.
(v) Sure.
Question 2.
Halfway up the tree I had built a crude platform where I would spend the afternoons when it was not too
hot. I could read there ropping myself up against the tree with a cushion from the living room. Treasure Island, Huckleberry Finn and The Story of Dr Dolittle were some of the books that made up my banyan tree library. When I did not feel like reading, I could look down through the leaves at the world below. And on one particular afternoon I had a grandstand view of that classic of the Indian wilds, a fight between a mongoose, and a cobra.
(i) What did the child build on the tree?
(ii) What did the child do on the platform?
(iii) What did the child see one day?
(iv) From where did the narrator arranged a cushion?
(v) Find ‘present participle’ of‘prop’ from the above passage.
Answer:
(i) The child built a crude platform on the tree.
(ii) The child read books on the platform.
(iii) The child saw a grandstand view of wild fights between a mongoose and a cobra.
(iv) The narrator arranged a cushion from his living room.
(v) Propping.
Question 3.
The warm breezes of approaching summer had sent everyone, including the gardener, into the house. I was feeling drowsy myself, wondering if I should go to the pond and have a swim with Ramu and the buffaloes, when I saw a huge black cobra gliding out of a clump of cactus. At the same time a mongoose emerged from the bushes and went straight for the cobra.
(i) What does the ‘warm breezes’ suggest?
(ii) What was he thinking of doing?
(iii) From where did the snake emerge?
(iv) Who went straight to attack cobra?
(v) Find a word from the passage, which means ‘a small group’?
Answer:
(i) The “Warm breezes’ suggest about the approaching summer.
(ii) He was thinking of going for swimming.
(iii) The snake emerged from the clump of cactus.
(iv) A Mongoose went straight to attack cobra.
(v) Clump.
Question 4.
At the same moment that the cobra struck, the crow and the myna hurled themselves at him, only to collide heavily in mid-air. Shrieking insults at each other they returned to the cactus plant. A few drops of blood glistened on the cobra’s back. The cobra struck and missed. Again in the mongoose sprang aside, jumped in and bit. Again the birds dived at the snake, bumped into each other instead, and returned shrieking to the safety of the cactus.
(i) Where did the crow and myna collide each other?
(ii) Where did they myna and the crow land?
(iii) Whose attack was more fierce?
(iv) On whom were the eyes of the birds were focused?
(v) Choose the past participle of strike.
Answer:
(i) The crow and the myna collided with each other in mid-air.
(ii) They landed onto the cactus plant.
(iii) Mongoose attack was more fierce.
(iv) The eyes of the bird were focused on snake.
(v) Struck.


















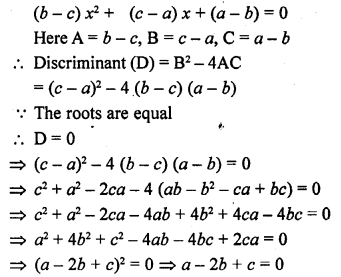

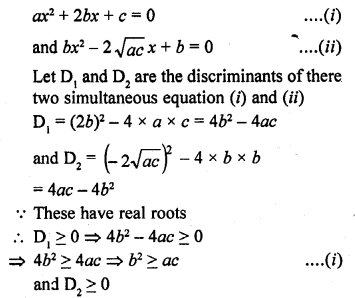
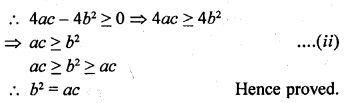

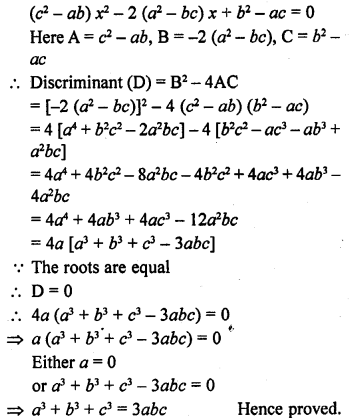




 This grammar section explains Online Education
This grammar section explains Online Education