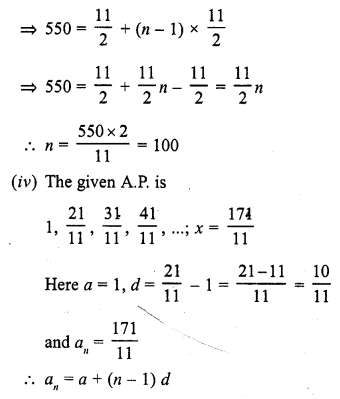
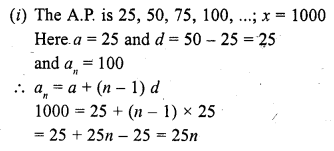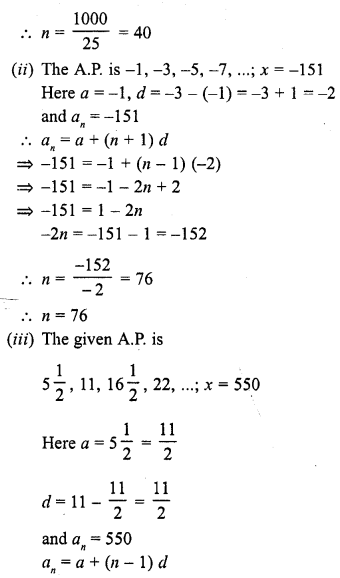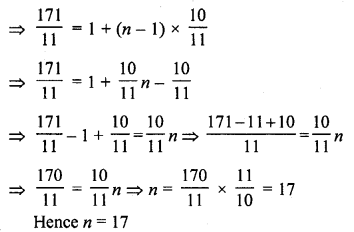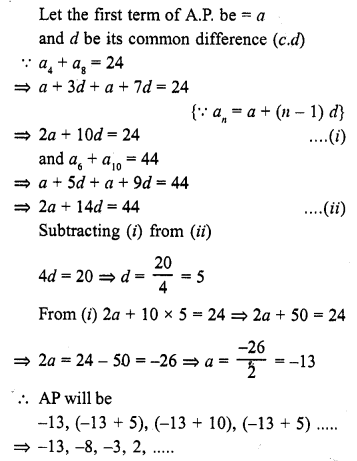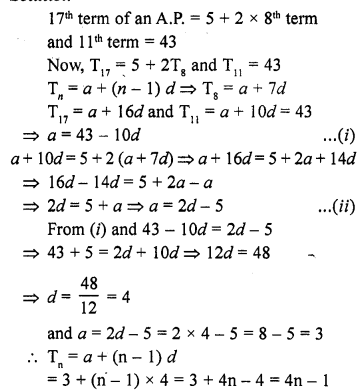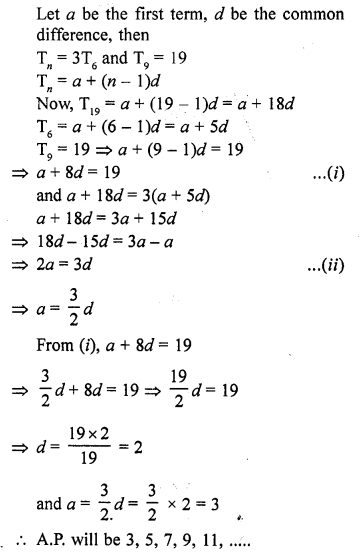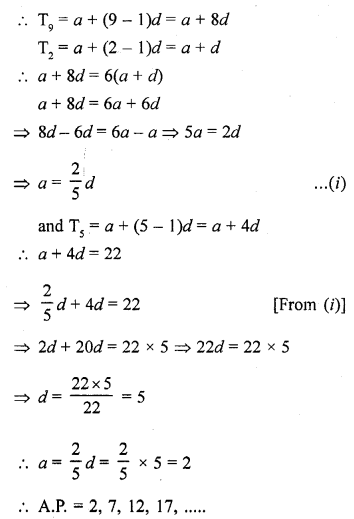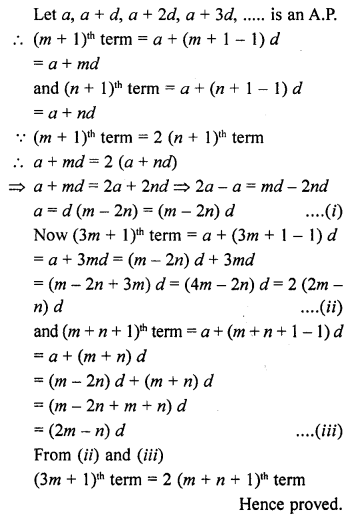Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Kshitij Chapter 17 बच्चे काम पर जा रहे हैं
These Solutions are part of Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Kshitij Chapter 17 बच्चे काम पर जा रहे हैं.
पाठ्य-पुस्तक के प्रश्न-अभ्यास
प्रश्न 1.
कविता की पहली दो पंक्तियों को पढ़ने तथा विचार करने से आपके मन-मस्तिष्क में जो चित्र उभरता है उसे लिखकर व्यक्त कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कविता की पहली दो पंक्तियाँ पढने तथा विचार करने से हमारे मन-मस्तिष्क में आक्रोश, चिंता और सदयता का भाव उमड़ता है। कोहरे से ढंकी सरदी की सुबह में बच्चों का काम पर जाना मन में करुणा भाव पैदा करता है। जिस प्रतिकूल परिस्थिति में हम बिस्तर से भी नहीं निकलना चाहते हैं उन्हीं दशाओं में बच्चे काँपते-ठिठुरते काम पर जा रहे हैं। यह देखकर समाज की संवेदनहीनता एवं स्वार्थी प्रवृत्ति पर क्रोध आता है। ऐसे बच्चों का बचपन नष्ट होता देखकर चिंता होती है।
प्रश्न 2.
कवि का मानना है कि बच्चों के काम पर जाने की भयानक बात को विवरण की तरह न लिखकर सवाल के रूप में पूछा जाना चाहिए कि ‘काम पर क्यों जा रहे हैं बच्चे?’ कवि की दृष्टि में उसे प्रश्न के रूप में क्यों पूछा जाना चाहिए?
उत्तर:
बच्चों का काम पर जाना सामाजिक एवं आर्थिक विडंबना का जीता-जागता उदाहरण है। आज के बच्चे कल के भविष्य हैं। इन बच्चों का अमानवीय दशाओं में मजदूरी करने को सामान्य बात मानकर जानकारी भर नहीं देना चाहिए। इसके प्रति गहरा * लगाव एवं चिंता दिखाई पड़नी चाहिए कि ऐसा क्यों हो रहा है।
प्रश्न 3.
सुविधा और मनोरंजन के उपकरणों से बच्चे वंचित क्यों हैं? [Imp.]
उत्तर:
सुविधा और मनोरंजन के उपकरणों से वंचित होने का सबसे मुख्यकारण गरीबी है। इस कारण गरीब माता-पिता न चाहकर भी अपने बच्चों को काम पर भेजने के लिए विवश हो जाते हैं। गरीबी के कारण जब माता-पिता बच्चों को मूलभूत सुविधाएँ उपलब्ध नहीं करा पाते हैं तो उन्हें खिलौने कहाँ से देंगे। इस स्थिति के लिए समाज में व्याप्त स्वार्थी प्रवृत्ति और शोषण की व्यवस्था भी समान रूप से उत्तरदायी है।
प्रश्न 4.
दिन-प्रतिदिन के जीवन में हर कोई बच्चों को काम पर जाते देख रहा/रही है, फिर भी किसी को कुछ अटपटा नहीं लगता। इस उदासीनता के क्या कारण हो सकते हैं?
उत्तर:
काम पर जाते बच्चों को देख हर कोई उदासीनता का भाव प्रकट नहीं कर रहा है। क्योंकि-
- लोग आत्मकेंद्रित हो गए हैं। वे सोचते है कि चलो मेरा बच्चा तो काम पर नहीं जा रहा है।
- लोग इसके प्रति जागरूकता नहीं दिखाते हैं। वे सोचते हैं कि यह सरकार के सोचने का कार्य है।
- समाज का एक बड़ा वर्ग इन बच्चों से काम कराकर मुनाफा कमाकर अपनी जेब भर रहा है, तो वह इस बारे में क्यों सोचे।
प्रश्न 5.
आपने अपने शहर में बच्चों को कब-कब और कहाँ-कहाँ काम करते हुए देखा है?
उत्तर:
मैंने अपने शहर में बच्चों को चाय की दुकान, ढाबे, किराने की दुकानों, मोमबत्ती, अगरबत्ती बनाने वाले स्थानों, सामानों की पैकिंग करने वाली जगहों, घरों में, प्राइवेट कार्यालयों आदि जगहों पर देखा है। ये बाल-मज़दूर सुबह से देर रात तक प्रायः बारहों महीनों में देखे जा सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
बच्चों का काम पर जाना धरती के एक बड़े हादसे के समान क्यों है? [CBSE][Imp.]
उत्तर:
बच्चों का काम पर जाना हादसे के समान है। क्योंकि बच्चे राष्ट्र का भविष्य हैं। जिस उम्र में बच्चों को पढ़ना-लिखना चाहिए तथा भविष्य का योग्य एवं सुशिक्षित नागरिक बनने की तैयारी करनी चाहिए, वे उस उम्र में बाल-मजदूरी करते हुए अपना भविष्य नष्ट कर रहे हैं। बच्चों का भविष्य नष्ट होना किसी हादसे से कम नहीं है।
रचना और अभिव्यक्ति
प्रश्न 7.
काम पर जाते किसी बच्चे के स्थान पर अपने-आप को रखकर देखिए। आपको जो महसूस होता है उसे लिखिए।
उत्तर:
काम पर जाते हुए किसी बच्चे के स्थान पर स्वयं को रखकर देखने से महसूस होता है कि मुझे काम पर क्यों जाना पड़ रहा है। इस समय तो मित्रों के साथ खेलना-कूदना चाहिए था, रंग-बिरंगी पुस्तकें लेकर बाजार जाना चाहिए था और अपनी इच्छा से घूमना-फिरना था, वर बाल मजदूरी करने की विवशता के कारण बचपन छिना जा रहा है। उन बच्चों की किस्मत कितनी अच्छी है जिन्हें काम पर नहीं जाना पड़ता है।
प्रश्न 8.
आपके विचार से बच्चों को काम पर क्यों नहीं भेजा जाना चाहिए? उन्हें क्या करने के मौके मिलने चाहिए? [CBSE]
उत्तर:
मेरे विचार से बच्चों को काम पर नहीं भेजा जाना चाहिए क्योंकि छोटी उम्र में काम करने पर बच्चों का शारीरिक एवं बौधिक विकास बाधित होता है। वे जिंदगी भर के लिए मजदूर बनकर रह जाते हैं। बच्चों का बौधिक विकास हो इसके लिए उन्हें पढ़ने-लिखने के पर्याप्त अवसर तथा शारीरिक विकास हेतु खेलकूद के उचित अवसर मिलने चाहिए।
पाठेतर सक्रियता
• किसी कामकाजी बच्चे से संवाद कीजिए और पता लगाइए कि-
(क) वह अपने काम करने की बात को किस भाव से लेता/लेती है?
(ख) जब वह अपनी उम्र के बच्चों को खेलने/पढ़ने जाते देखता/देखती है तो कैसा महसूस करता/करती है?
उत्तर:
परीक्षोपयोगी नहीं।
• ‘वर्तमान युग में सभी बच्चों के लिए खेलकूद और शिक्षा के समान अवसर प्राप्त हैं-इस विषय पर वाद-विवाद आयोजित कीजिए।
उत्तर:
पक्ष में विचार –
वर्तमान युग में सभी बच्चों के लिए खेलकूद और शिक्षा के समान अवसर हैं। यह बात बिलकुल ठीक है। सरकार ने अपने शिक्षण-संस्थानों में सब बच्चों को बिना किसी भेद-भाव के छूट दी है। गरीब से गरीब बच्चा भी पढ़ सकता है और खेल-कूद में भाग ले सकता है। आजकल कई राज्यों में तो प्राथमिक शिक्षा मुफ्त है। बड़ी कक्षाओं में भी फीस न के बराबर है। अत: हम कह सकते हैं कि सबके लिए खेलकूद और शिक्षा के समान अवसर हैं।
विपक्ष में विचार –
भारत में सभी बच्चों के लिए खेलकूद और शिक्षा के समान अवसर हैं, यह बात कहना झूठ ही नहीं, एक भद्दा मजाक है। यहाँ करोड़ों बच्चे भूखे रह जाते हैं। उन्हें पढ़ने और खेलने से पहले पेट भरने की चिंता खाने लगती है। उधर लाखों बच्चे बड़े-बड़े स्कूलों में पढ़ते हैं तथा हर खेल का आनंद लेते हैं। किसी गाँव के सरकारी स्कूल की तुलना किसी महानगर के बड़े स्कूल से करें तो पता चलेगा कि दोनों में जमीन-आसमान का अंतर है।
• ‘बाल श्रम की रोकथाम’ पर नाटक तैयार कर उसकी प्रस्तुति कीजिए।
उत्तर:
छात्र प्रस्तुत करें।
• चंद्रकांत देवताले की कविता ‘थोड़े से बच्चे और बाकी बच्चे’ (लकड़बग्घा हँस रहा है) पढ़िए। उस कविता के भाव तथा प्रस्तुत कविता के भावों में क्या साम्य है?
उत्तर:
स्वयं करें।
Hope given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Hindi Kshitij Chapter 17 are helpful to complete your homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online tutoring for you.