Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-9-maths-with-answers/
Students can also refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry for better exam preparation and score more marks.
Online Education for Coordinate Geometry Class 9 MCQs Questions with Answers
Coordinate Geometry Class 9 MCQ Question 1.
Abscissa of a point is positive in
(а) I and II quadrants
(b) I and IV quadrants
(c) I quadrants only
(d) II quadrant only.
Answer
Answer: (b) I and IV quadrants
Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 MCQ Question 2.
The points (-5, 2) and (2, -5) lie in the
(а) same quadrant
(b) II and III quadrant respectively.
(c) II and IV quadrant respectively.
(d) I and IV quadrant respectively.
Answer
Answer: (c) II and IV quadrant respectively.
Coordinate Geometry MCQ Class 9 Question 3.
If (x + 2, 4) = (5, y – 2), then coordinates (x, y) are
(a) (7, 12)
(b) (6, 3)
(c) (3, 6)
(d) (2, 1)
Answer
Answer: (c) (3, 6)
Class 9 Coordinate Geometry MCQ Question 4.
Mirror image of the point (9, -8) in y-axis is
(a) (-9, -8)
(b) (9, 8)
(c) (-9, 8)
(d) (-8, 9)
Answer
Answer: (a) (-9, -8)
Ch 3 Maths Class 9 MCQ Question 5.
The coordinates of the point which lies on y-axis at a distance of 4 units in negative direction of y-axis is
(a) (5, 4)
(b) (4, 0)
(c) (0, -4)
(d) (-4, 0)
Answer
Answer: (c) (0, -4)
Class 9 Maths Ch 3 MCQ Question 6.
If the points A(2, 0), B(-6, 0) and C(3, a – 3) lie on the x-axis, then the value of a is
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) -6
Answer
Answer: (c) 3
MCQ Of Coordinate Geometry Class 9 Question 7.
Which of the following points lies on the negative side of x axis?
(a) (-4, 0)
(b) (3, 2)
(c) (0, -4)
(d) (5, -7)
Answer
Answer: (a) (-4, 0)
MCQ On Coordinate Geometry For Class 9 With Answers Question 8.
The Coordinates of point Q are
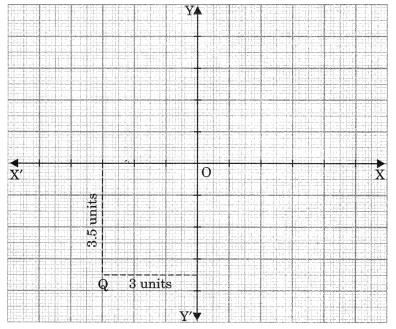
(a) (3, 3.5)
(b) (3.5, 3)
(c) (-3, 3.5)
(d) (-3, -3.5)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-3, -3.5)
Chapter 3 Maths Class 9 MCQ Question 9.
The point M lies in the IV quadrant. The coordinates of point M are
(a) (a, b)
(b) (-a, b)
(c) (a, -b)
(d) (-a, -b)
Answer
Answer: (c) (a, -b)
Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry MCQ Question 10.
Write the name of the quadrant in which the point (-3, -5) lies.
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer
Answer: (c) Third quadrant
Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 MCQ With Answers Question 11.
The number of parts the coordinates axes divide the plane is
(a) Two parts
(b) Four parts
(c) Six parts
(d) Eight parts
Answer
Answer: (b) Four parts
Class 9th Maths Chapter 3 MCQ Question 12.
Point (0, 4) lies
(a) in I quadrant
(b) on x-axis
(c) on y-axis
(a) in IV quadrant
Answer
Answer: (c) on y-axis
MCQ Questions For Class 9 Maths Coordinate Geometry Question 13.
The mirror image of the point (-3, -4) in x-axis is
(a) (-4, -3)
(b) (3, -4)
(c) (3, 4)
(d) (-3, 4)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-3, 4)
Class 9 Chapter 3 Maths MCQ Question 14.
In which quadrant does the point (-1, 2) lies?
(a) First quadrant
(b) Second quadrant
(c) Third quadrant
(d) Fourth quadrant
Answer
Answer: (b) Second quadrant
MCQ Questions For Class 9 Maths Ncert Chapter 3 Question 15.
Abscissa of a point is negative in
(a) I and II quadrant
(b) I and IV quadrant
(c) II and III quadrant
(d) IV quadrant only
Answer
Answer: (c) II and III quadrant
Question 16.
Abscissa of all the points on y-axis is
(a) 1
(b) any number
(c) 0
(d) -1
Answer
Answer: (c) 0
Question 17.
Which is the example of geometrical line?
(a) Blackboard
(b) Sheet of paper
(c) Meeting place of two walls
(d) Tips of sharp pencil.
Answer
Answer: (c) Meeting place of two walls
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Coordinate Geometry CBSE Class 9 Maths MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.