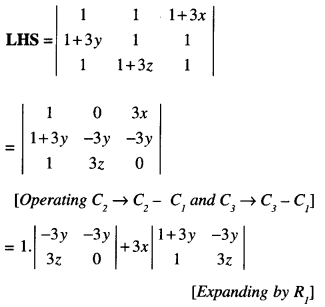
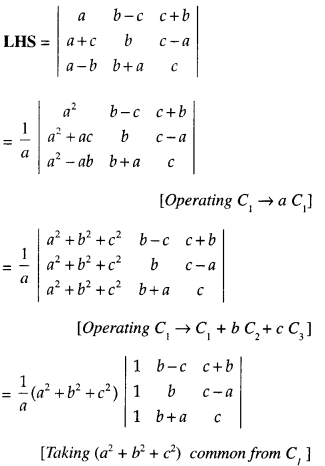
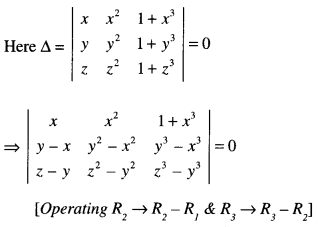
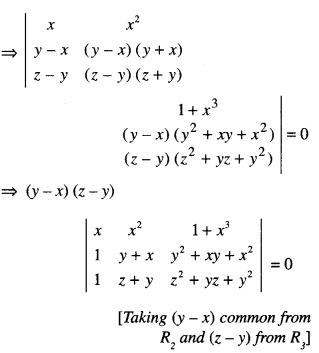
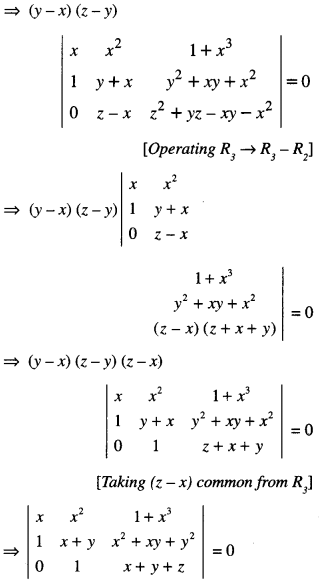
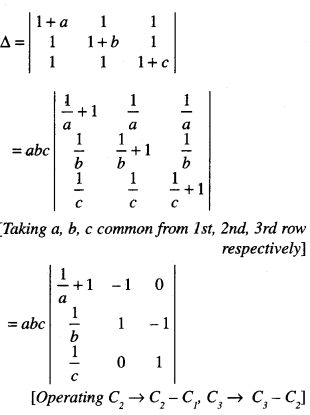
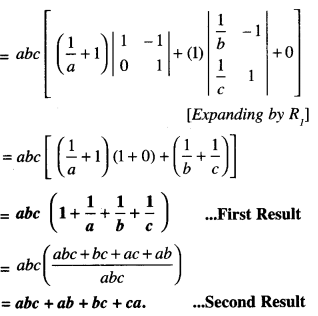
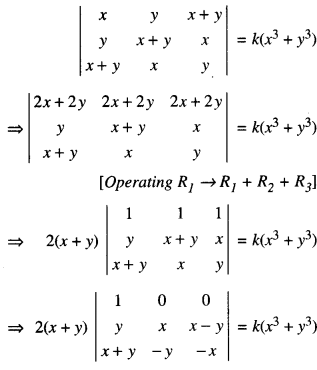
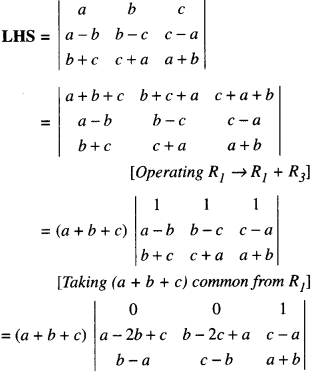
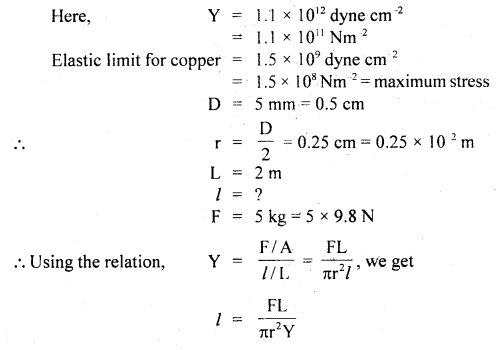
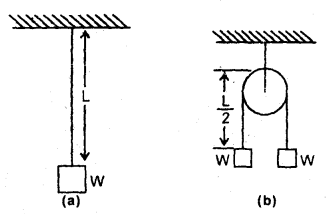
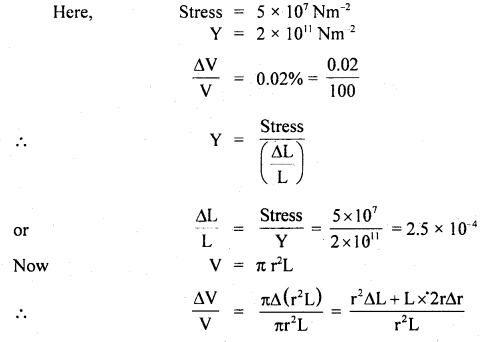
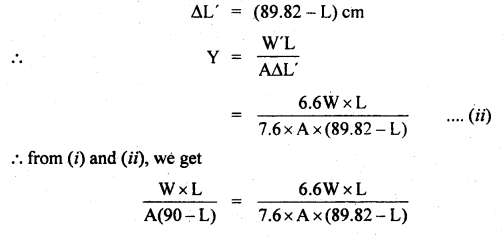
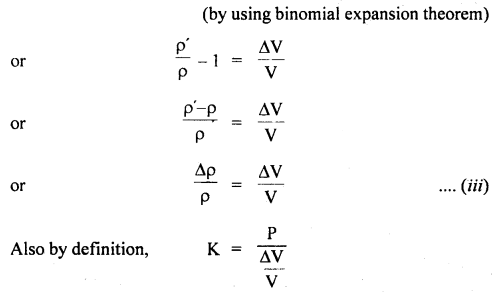
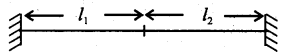
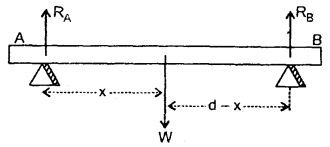
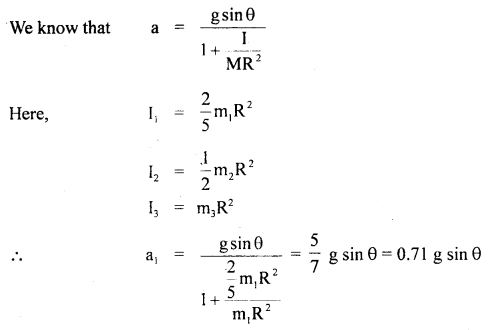
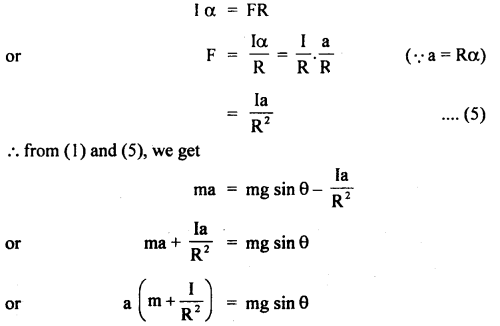
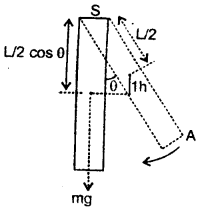
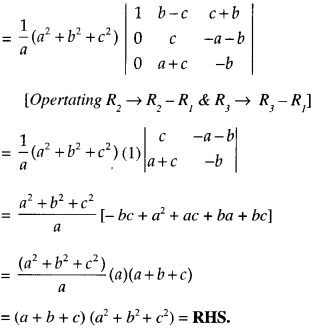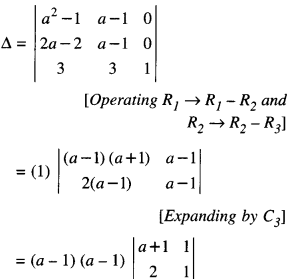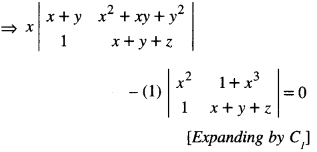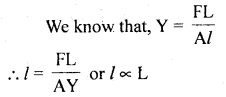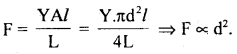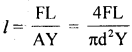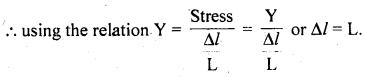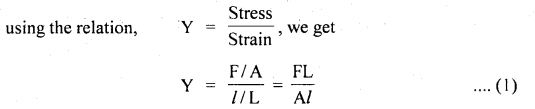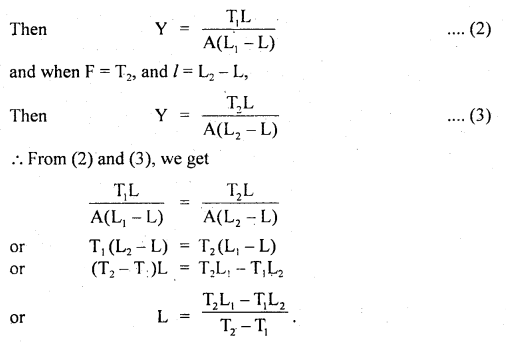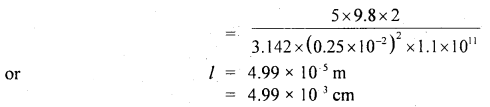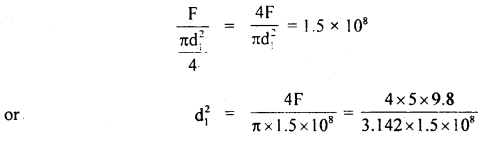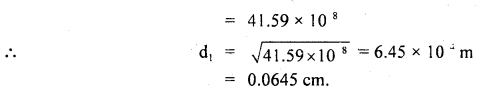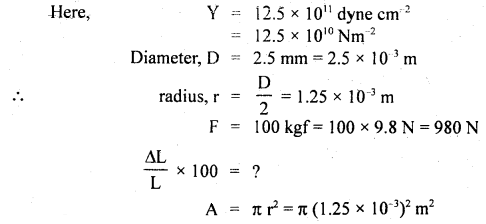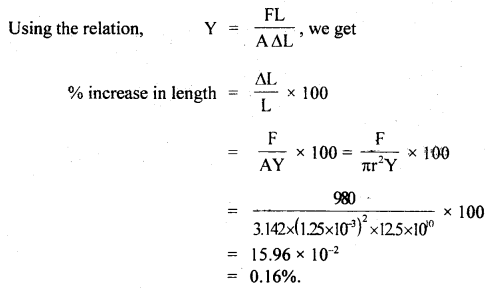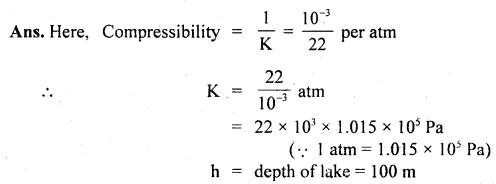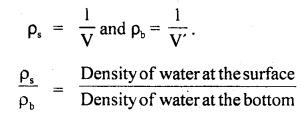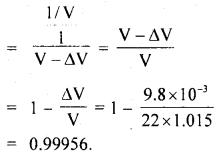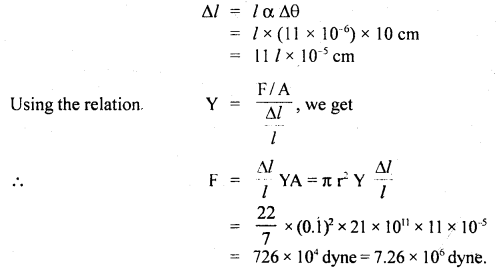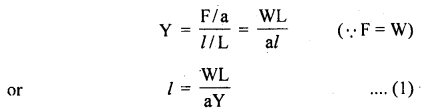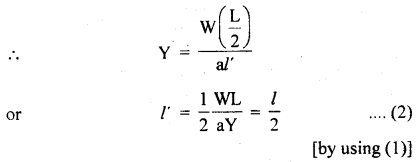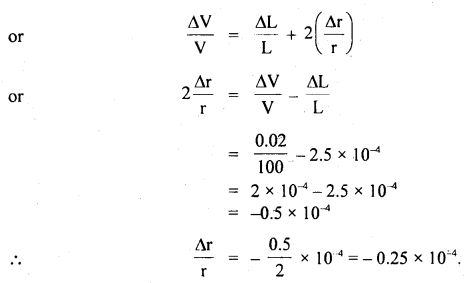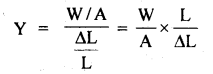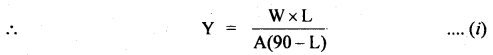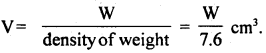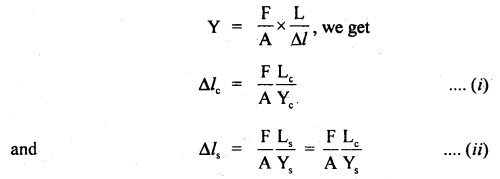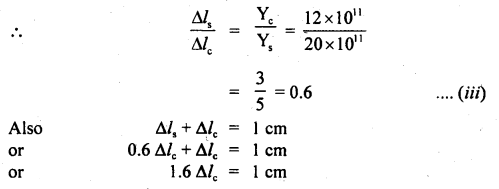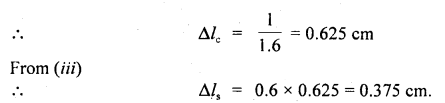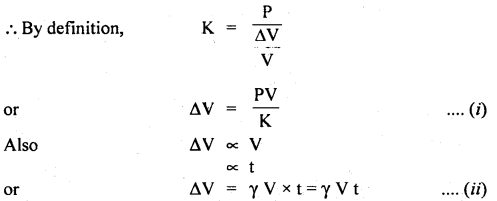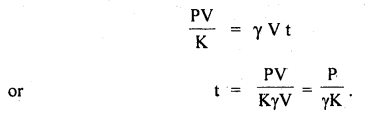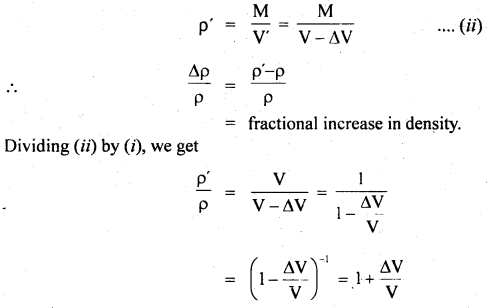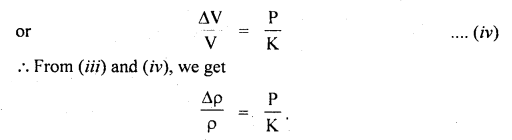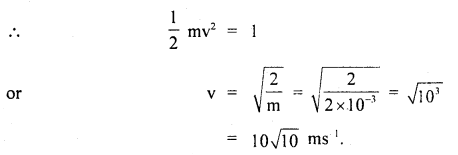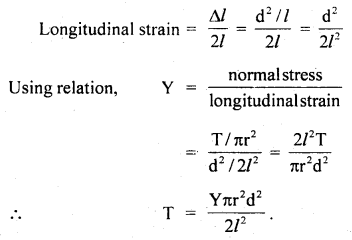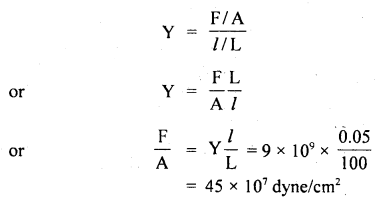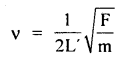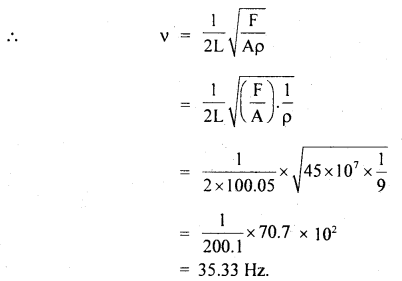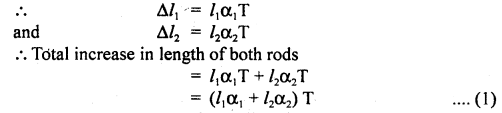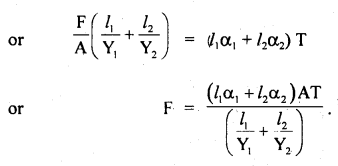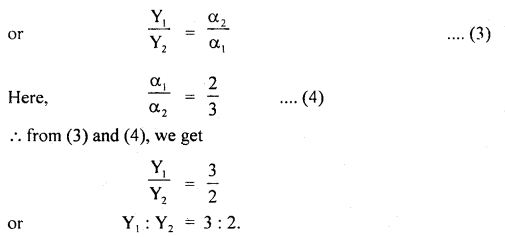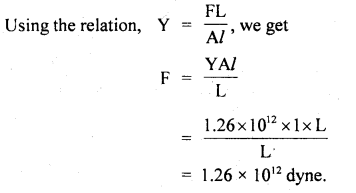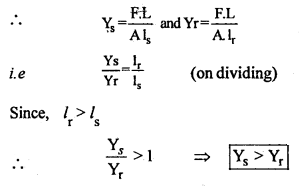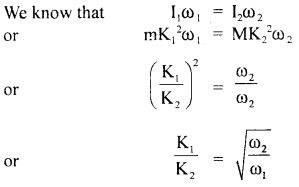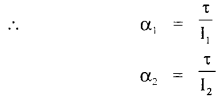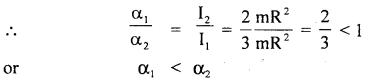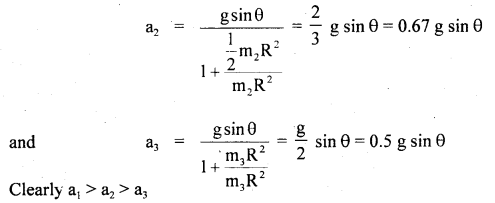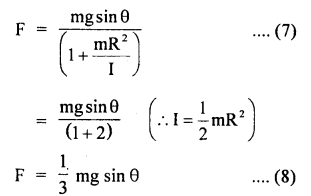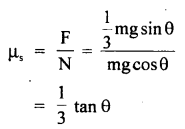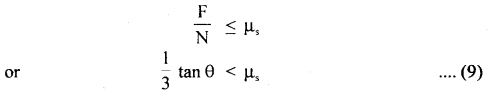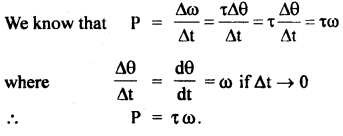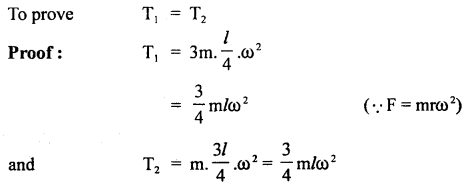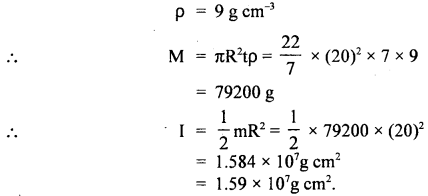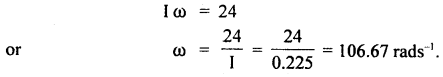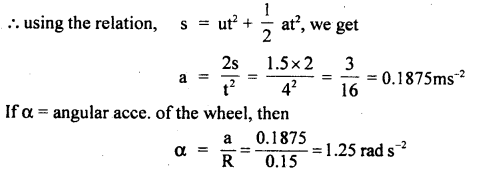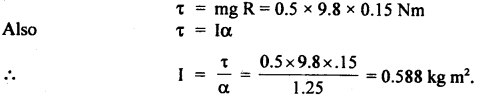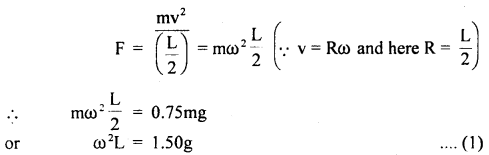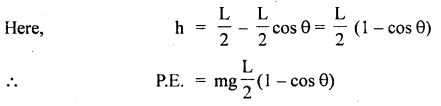We have given detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 12 दशमः त्वम असि Textbook Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 12 दशमः त्वम असि
Class 6th Sanskrit Chapter 12 दशमः त्वम असि Textbook Questions and Answers
अभ्यासः
प्रश्न 1.
उच्चारणं कुरुत- (उच्चारण कीजिए- Pronounce these words.)
उत्तरम्-
छात्र स्वयं उच्चारण करें।
प्रश्न 2.
प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि लिखत- (प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए- Answer the questions.)
(क) कति बालकाः स्नानाय अगच्छन्?
(ख) ते स्नानाय कुत्र अगच्छन्?
(ग) ते कम् निश्चयम् अकुर्वन्?
(घ) मार्गे कः आगच्छत्?
(ङ) पथिकः कम् अवदत्?
उत्तर:
(क) दश बालकाः स्नानाय अगच्छन्।
(ख) ते स्नानाय नदीम् अगच्छन्।
(ग) ते निश्चयम् अकुर्वन् यत् दशमः नद्यां मग्नः।
(घ) मार्गे पथिकः आगच्छत्।
(ङ) पथिकः अवदत्-दशमः त्वम् असि।
प्रश्न 3.
शुद्धकथनानां समक्षम् (✓) इति अशुद्धकथनानां समक्षं (✗) कुरुत- (शुद्ध कथन के सामने (✓) तथा अशुद्ध कथन के सामने (✗) चिह्न लगाएँ- Put a tick mark (✓) in front of correct statement and a cross (✗) opposite the incorrect one.)
(क) दशबालकाः स्नानाय अगच्छन्। ……………
(ख) सर्वे वाटिकायाम् अभ्रमन्। ……………
(ग) ते वस्तुतः नव बालकाः एव आसन। ……………
(घ) बालकः स्वं न अगणयत्। ……………
(ङ) एक: बालकः नद्यां मग्नः। ……………
(च) ते सुखिताः तूष्णीम् अतिष्ठन्। ……………
(छ) कोऽपि पथिकः न आगच्छत्। ……………
(ज) नायकः अवदत्-दशमः त्वम् असि इति। ……………
(झ) ते सर्वे प्रहृष्टाः भूत्वा च गृहम् अगच्छन्। ……………
उत्तर:
(क) ✓, (ख) ✗ , (ग) ✗ , (घ) ✓, (ङ) ✗, (च) ✗, (छ) ✗, (ज) ✗, (झ) ✓
प्रश्न 4.
मञ्जूषातः शब्दान् चित्वा रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत- (मञ्जूषा से शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थान भरिए Fill in the blanks by taking words from the brackets.)
गणयित्वा , श्रुत्वा , दृष्ट्वा , कृत्वा , गृहीत्वा , तीर्वा |
(क) ते बालकाः ………………. नद्याः उत्तीर्णाः।
(ख) पथिक: बालकान् दुःखितान् ………………. अपृच्छत्।
(ग) पुस्तकानि ……….. विद्यालयं गच्छ।
(घ) पथिकस्य वचनं …… सर्वे प्रमुदिताः गृहम् अगच्छन्।
(ङ) पथिक : बालकान् ………………. अकथयत् दशमः त्वम् असि।
(च) मोहनः कार्यं ………………. गृहं गच्छति।
उत्तर:
(क) तीर्खा
(ख) दृष्ट्वा
(ग) गृहीत्वा
(घ) श्रुत्वा
(ङ) गणयित्वा
(च) कृत्वा
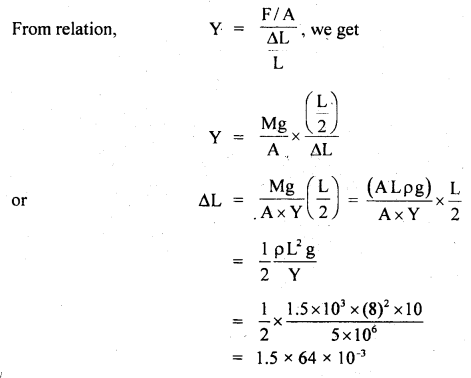
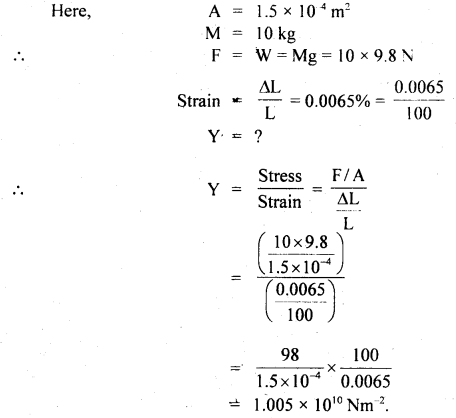
प्रश्न 5.
चित्राणि दृष्ट्वा संख्यां लिखत- (चित्रों को देखकर संख्या लिखिए- Look at the pictures and write the number of objects.)

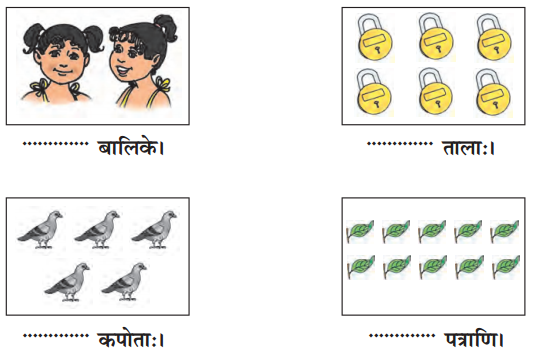
उत्तर:
(क) अष्ट
(ख) तिस्रः
(ग) एकम्
(घ) द्वौ
(ङ) द्वे
(च) षट्
(छ) पञ्च
(ज) दश
Class 6th Sanskrit Chapter 12 दशमः त्वम असि Additional Important Questions and Answers
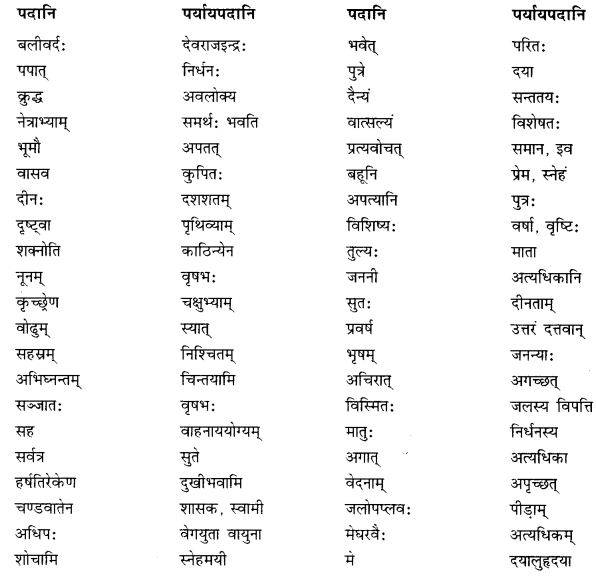
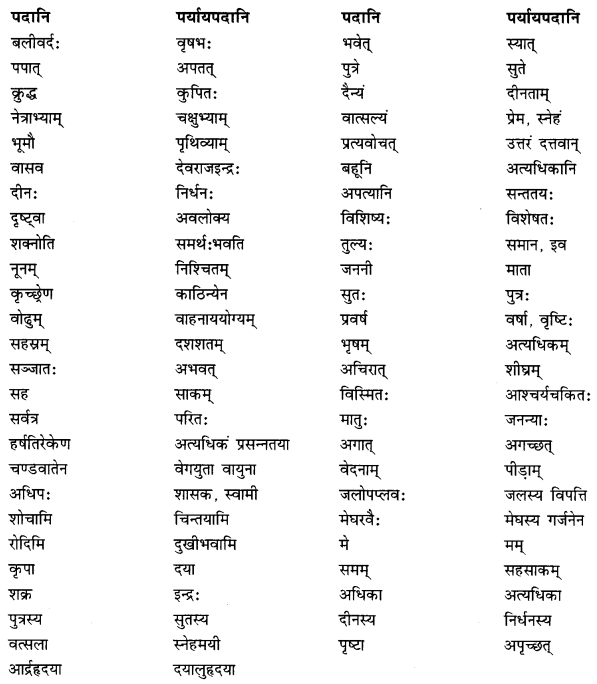
प्रश्न 1.
संस्कृतपर्यायं लिखत- (संस्कृत पर्याय लिखिए- Give the Sanskrit equivalent).
(क)
(i) एक छात्र – ……………..
(ii) दो कबूतर – ……………..
(iii) तीन शेर – ……………..
(iv) चार घोड़े – ……………..
(v) पाँच बकरियाँ – ……………..
(vi) छः हाथी – ……………..
(vii) सात लड़कियाँ – ……………..
(viii) आठ पुस्तकें – ……………..
(xi) नौ घर – ……………..
(x) दस पेड़ – ……………..
उत्तर:
(i) एकः छात्रः
(ii) द्वौ कपोतो
(iii) त्रयः सिंहाः
(iv) चत्वारः अश्वाः
(v) पञ्च अजाः
(vi) षट् गजाः
(vii) सप्त बालिकाः
(viii) अष्ट पुस्तकानि
(ix) नव गृहाणि
(x) दश वृक्षाः
(ख)
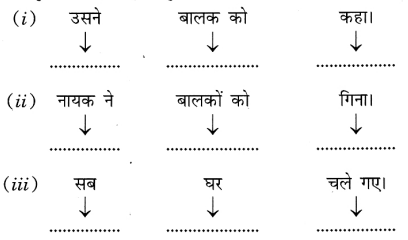
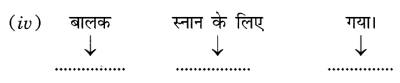
उत्तर:
(i) सः बालकम् अकथयत्।
(ii) नायकः बालकान् अगणयत्।
(iii) ते सर्वे गृहम् अगच्छन्।
(iv) बालकः स्नानाय अगच्छत्।
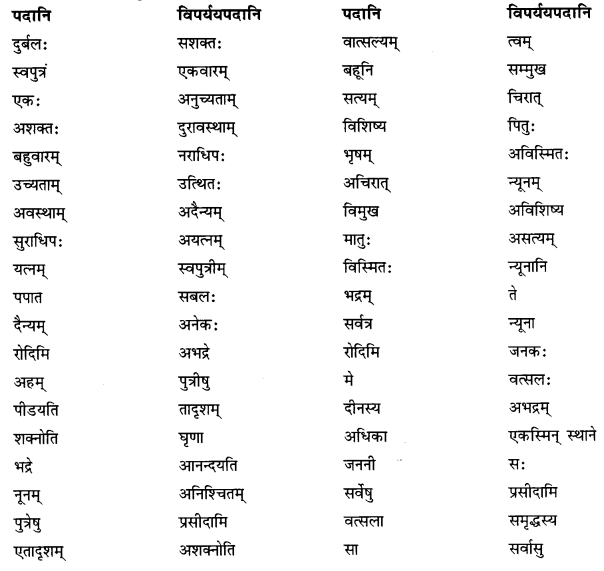
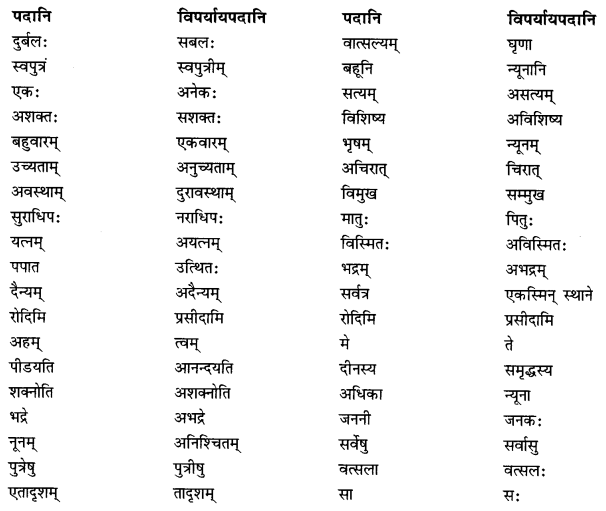
प्रश्न 2.
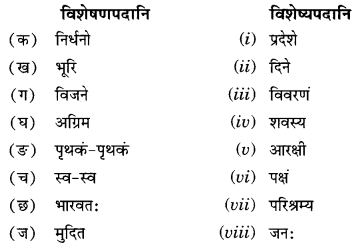
परस्परं मेलयत- (परस्परं मेलयत- Match the following.)
क्त्वा प्रत्ययान्तानि – हिन्दी-पर्यायाः
(क) (i) दृष्ट्वा – सुनकर
(ii) स्नात्वा – गिनती करके
(iii) कृत्वा – लिखकर
(iv) श्रुत्वा – तैरकर
(v) गणयित्वा – देखकर
(vi) लिखित्वा – करके
vii) तीर्वा – स्नान करके
उत्तर:
(i) दृष्ट्वा – देखकर
(ii) स्नात्वा – स्नान करके
(iii) कृत्वा – करके
(iv) श्रुत्वा – सुनकर
(v) गणयित्वा – गिनकर
(vi) लिखित्वा – लिखकर
(vii) ती| – तैरकर।
(ख) ‘क’ खण्डात् उचितम् क्त्वा-प्रत्ययान्तं पदं चित्वा अधोदत्तानि वाक्यानि पूरयत- (खण्ड ‘क’ के अंतर्गत ‘क्त्वा’ प्रत्ययांत पदों में से उचित पद चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए। Pick out the appropriate word ending in suffix ‘क्त्वा’ from sections’ and complete the sentences given below.)
(i) सा ………….. भोजनं करोति।
(ii) चलचित्रं ………….. सर्वे प्रसन्नः सन्ति।
(ii) समाचारं ……… सः दुःखितः आसीत।
(iv) तान् बालकान् …………… पथिकः अवदत्।
(v) अहं विद्यालयकार्यं ………. क्रीडामि।
(vi) बालका: नदी ………… पारं गताः।
(vii) निबंधं ………….. छात्रा अध्यापिकाम् अवदत्।
उत्तर:
(i) स्नात्वा
(ii) दृष्ट्वा
(iii) श्रुत्वा
(iv) गणयित्वा,
(v) कृत्वा
(vi) तीत्वा
(vii) लिखित्वा
प्रश्न 3.
मञ्जूषायाः उचितम् अव्ययं चित्वा वाक्यपूर्तिं कुरुत। (मञ्जूषा से उचित अव्यय पद चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए। Pick out the appropriate indeclinable from the box and complete the sentences.)
अपि , न , अतः , तूष्णीम् , एव , पुनः
सः अवदत्-‘नव ……………. सन्ति। दशमः ……………. अस्ति।’ अपरः अपि बालकः ……………. अन्यान् बालकान् अगणयत्। तदा ……………. नव एव आसन। ……………. ते निश्चयम् अकुर्वन् यत् दशमः नद्यां मग्नः। ते दुःखिताः ……………. अतिष्ठिन।
उत्तर:
(क) एव
(ख) न
(ग) पुनः
(घ) अपि
(ङ) अत
(च) तूष्णीम्।
बहुविकल्पीयप्रश्नाः
प्रश्न 1.
प्रदत्तविकल्पेभ्य उचितं पदं चित्वा वाक्यानि पूरयत। (दिए गए विकल्पों में से उचित विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए। Pick out the correct word from the options given and complete the sentences.)
(क)
(i) …………बलकाः नदीम् अगच्छन्।(अष्ट, नव, दश)
(ii) कश्चित् ………… तत्र आगच्छत्। (बालकः, यात्रिकः, पथिक:)
(iii) एक: नद्यां ……………. । (भग्नः, संलग्नः, मग्नः)
(iv) युष्माकं …………….. कारणं किम्? (हर्षस्य, दुःखस्य, बालकस्य)
(v) ते ……………….. पारं गताः। (दृष्ट्वा, श्रुत्वा, तीर्वा)
उत्तर:
(i) दश
(ii) पथिकः
(iii) मग्नः
(iv) दु:खस्य
(v) तीर्वा।
(ख)
(i) बालकाः …….. अगच्छन्। (स्नानम्, स्नानाय, स्नानेन)
(ii) पथिकः तान् (अगणयन्, अगणयत्, अगणयत्)
(iii) ……………. बालकाः गृहम् अगच्छन्। (सर्वाः, सर्वे, सर्व:)
(iv) ते ……………. स्नानम् अकुर्वन्। (नदीजलम्, नदीजलात्, नदीजले)
(v) तत्र ……………. बालकाः आसन्। (दशाः, दश, दश:)
उत्तर:
(i) स्नानाय
(ii) अगणयत्
(iii) सर्वे
(iv) नदीजले
(v) दश।
(ग)
(i) ………………… (एक, एकः, एकम्)
(ii) …………….. वृक्षौ। (द्वे, द्वौ, त्रयः)
(iii) ………… छात्रा। (एक, एका, एकाः)
(iv) ……….. मित्राणि। (चत्वारः, चतस्त्रः, चत्वारि)
(v) ………….. लते। (द्वौ, द्वे, एकम्)
(vi) …………. पादपाः। (त्रयः, त्रीणि, तिस्त्र)
(vii) …………. बालकाः। (सर्वे, सर्वाः, सर्वम्)
उत्तर:
(i) एकम्
(i) द्वौ ।
(ii) एका
(iv) चत्वारि
(v) द्वे
(vi) त्रयः
(vii) सर्वे।
(घ)
(i) एकः एकः च ………….. भवतः। (द्वि, द्वे, द्वौ)
(ii) त्रयः षट् च ……….. भवन्ति। (अष्ट, नव, दश)
(ii) पञ्च द्वौ च …… भवन्ति। (सप्त, अष्ट, षट)
(iv) चत्वारः चत्वारः च ……. (अष्टः, अष्ट, अष्टा)
(v) द्वौ त्रयः च ………….. भवन्ति। (पञ्चः, पञ्च, पञ्चम)
उत्तर:
(i) द्वौ
(ii) नव.
(iii) सप्त
(iv) अष्ट
(v) पञ्च