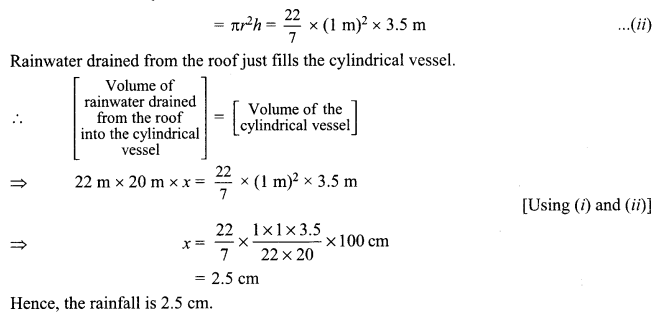
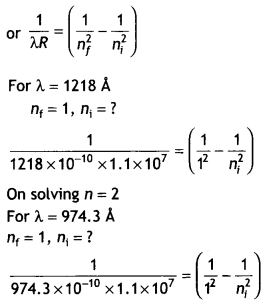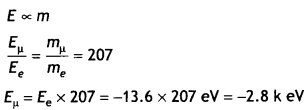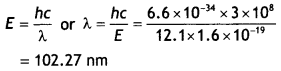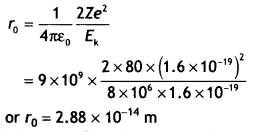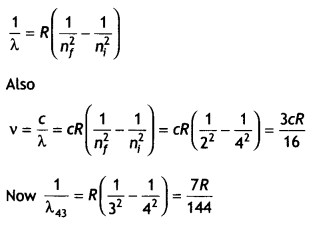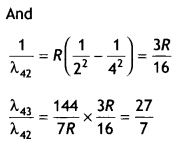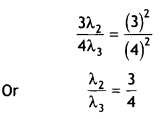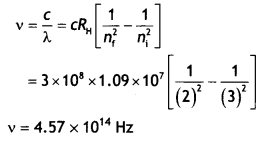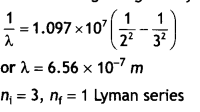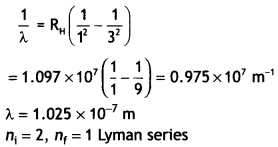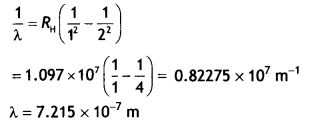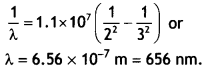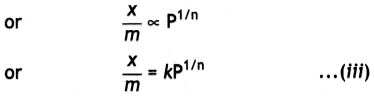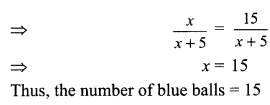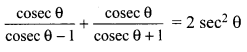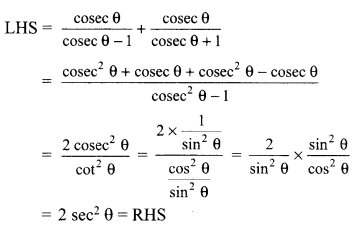Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Sanskrit with Solutions and marking scheme Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Sanskrit Set 1 with Solutions
समयः- होरात्रयम्
सम्पूर्णाङ्काः – 80
सामान्यनिर्देशाः
- कृपया सम्यक्तया परीक्षणं कुर्वन्तु यत् अस्मिन् प्रश्नपत्रे 19 प्रश्नाः सन्ति।
- उत्तरलेखनात् पूर्व प्रश्नस्य क्रमाङ्कः अवश्यं लेखनीयः।
- अस्य प्रश्नपत्रस्य पठनाय 15 निमेषाः निर्धारिताः सन्ति। अस्मिन् अवधौ केवलं प्रश्नपत्रं पठनीयम् उत्तरपुस्तिकायां च किमपि न लेखनीयम्।
प्रश्नपत्रस्वरूपम्
‘अ’-भागः (बहुविकल्पात्मकः) 40 अङ्काः
‘आ’-भागः (वर्णनात्मकः) 40 अङ्काः
(i) अस्मिन् प्रश्नपत्रे द्वौ भागौ स्तः।
(ii) ‘अ’- भागः बहुविकल्पात्मकः अस्ति।
(iii) ‘आ’-भागः वर्णनात्मकः अस्ति।
(iv) प्रश्नसङ्ख्या प्रश्नपत्रानुसारम् अवश्यमेव लेखनीया।
(v) सर्वेषां प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि संस्कृतेन लेखनीयानि।
(vi) प्रश्नानां निर्देशाः ध्यानेन अवश्यं पठनीयाः।
‘अ’-भागः- बहुविकल्पात्मकाः प्रश्नाः (अङ्काः 40)
अनुप्रयुक्त-व्याकरणम् (अङ्काः 25)
प्रश्न 1.
अधोलिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदस्य सन्धिपदं सन्धिच्छेदपदं वा चिनुत-(केवलं प्रश्नचतुष्टयम्) (1 x 4 = 4)
(i) तन्नाम सर्वोच्चं वर्तते।
(क) तन् + नाम
(ख) तत् + नाम
(ग) तद् + नाम
उत्तर
(ख) तत् + नाम
(ii) वाक् + मयम् तपः।
(क) वाग्मयम्
(ख) वाङ्मयम्
(ग) वाकमयम्
उत्तर
(ख) वाङ्मयम्
(iii) सोऽपि पठितुम् वाञ्छति।
(क) सः + अपि
(ख) सो + अपि
(ग) सो + ऽपि
उत्तर
(क) सः + अपि
(iv) रामकथायां रामस्य यशः + गानम् वर्तते।।
(क) यशोऽगानम्
(ख) यशगानम्
(ग) यशो गानम्
उत्तर
(ग) यशो गानम्
(v) कशचौर : गृहं प्राविशत्।
(क) के + चौरम्
(ख) कम् + चौरः
(ग) कः + चौरः
उत्तर
(ग) कः + चौरः
प्रश्न 2.
अधोलिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदानां समासं विग्रहं वा प्रदत्तविकल्पेभ्यः चिनुत। (केवलं प्रश्नचतुष्टयम्) (1 x 4 = 4)
(i) भवान् सपरिवारम् मम गृहम् आगच्छतु।
(क) परिवार सहितम्
(ख) परिवार सहितम्
(ग) परिवारेण सहितम्
उत्तर
(ग) परिवारेण सहितम्
(ii) कार्य समापयितुं स शक्तिम् अनतिक्रम्य परिश्रमं करोति।
(क) यथाशक्तिः
(ख) यथाशक्ति
(ग) यथाशक्तिम्
उत्तर
(ख) यथाशक्ति
(iii) सुरभेः वचनम श्रुत्वा इन्द्रस्य हृदयमद्रवत्।
(क) सुरभीवचनम्
(ख) सुरभेवचनम्
(ग) सुरभिवचनम्
उत्तर
(ग) सुरभिवचनम्
(iv) सीतोर्मिले भगिन्यौ स्तः।
(क) सीता च उर्मिले
(ख) सीता च उर्मिला च
(ग) सीता उर्मिले च
उत्तर
(ख) सीता च उर्मिला च
(v) राजसिंहः नाम राजपुत्रः अवसत्।
(क) राज्ञे पुत्रः
(ख) राज्ञा पुत्रः
(ग) राज्ञः पुत्र
उत्तर
(ग) राज्ञः पुत्र
प्रश्न 3.
अधोलिखितवाक्येषु रेखाकिन्तपदानां प्रकृति-प्रत्ययौ संयोज्य विभन्य वा उचितम् उत्तरं विकल्पेभ्यः चिनुत। (केवलं प्रश्नचतुष्टयम्) (1 x 4 = 4)
(i) माता सदैव पूजनीय + टाप् अस्ति।
(क) पूजनीयः
(ख) पूजनीयम्
(ग) पूजनीया
उत्तर
(ग) पूजनीया
अथवा
पी.टी. उषा एका धावक + टाप् आसीत्।
(क) धावकः
(ख) धाविका
(ग) धाविकाः
उत्तर
(क) धावकः
(ii) वाक्पटुः धैर्य + मतुप् मंत्री सभायाम् अपि अकातरः।
(क) धैर्यवत्
(ख) धैर्यवान्
(ग) धैर्यवन्तः
उत्तर
(ख) धैर्यवान्
(iii) तदेव महात्मानः समत्वम् इति आहु।
(क) सम + त्व
(ख) समत् + त्व
(ग) सम् + त्वम्
उत्तर
(क) सम + त्व
(iv) विद्वांसः एव अस्मिन् लोके चुक्षष् + मतुप सन्ति।
(क) चक्षुःमन्तः
(ख) चक्षुमान्
(ग) चक्षुष्मन्तः
उत्तर
(ग) चक्षुष्मन्तः
प्रश्न 4.
वाच्यस्य नियमानुगुणम् उचितं विकल्पं चिनुत। (केवलं प्रश्नत्रयम्) (1 x 3 = 3)
(i) रमेशः – किम् अशोकः पाठं … ?
(क) पठसि
(ख) पठति
(ग) पठ्यते
उत्तर
(ख) पठति
(ii) सुधा – आम्! ……………. पाठः पठ्यते।
(क) अशोकेन
(ख) अशोकम्
(ग) अशोकः
उत्तर
(क) अशोकेन
(iii) रमेशः – किम् तेन ………….. नम्यते?
(क) अध्यापकम्
(ख) अध्यापकः
(ग) अध्यापको
उत्तर
(ख) अध्यापकः
(iv) सुधा – आम् ……………. अध्यापकम् नमति।
(क) ते
(ख) सः
(ग) तेन
उत्तर
(ख) सः
प्रश्न 5.
प्रदत्तेभ्यः विकल्पेभ्यः समुचितं कालबोधकशब्द चिनुत- (केवलं प्रश्नचतुष्टयम्) (1 x 4 = 4)
(i) मम भ्राता प्रातः (5.00) …. ………. वादने भ्रमणार्थं गच्छति।
(क) सार्ध-पञ्च
(ख) सपाद-पञ्च
(ग) पञ्च
उत्तर
(ग) पञ्च
(ii) अहम् प्रातः (8.30) ……………………… वादने कार्यालयं गच्छामि।
(क) सार्ध-अष्ट
(ख) सपाद-अष्ट
(ग) अष्ट
उत्तर
(क) सार्ध-अष्ट
(iii) तव भ्राता मध्याह्न (2.00) …………………. वादने विद्यालयात् आगच्छति।
(क) द्वि-सपाद
(ख) द्वि
(ग) त्रि
उत्तर
(ख) द्वि
(iv) मम जनकः (7.45) ……………… वादने गृहम् आगच्छति।
(क) पदोन-सप्त
(ख) सार्ध-अष्ट
(ग) पादोन-अष्ट
उत्तर
(ग) पादोन-अष्ट
(v) मम माता (8.15) …………… वादने पाकशालाम् गच्छति।
(क) पादोन-अष्ट
(ख) सपाद-अष्ट
(ग) सार्ध-अष्ट
उत्तर
(ख) सपाद-अष्ट
प्रश्न 6.
वाक्यानुगुणम् उचिताव्ययपदं चिनुत- (केवलं प्रश्नत्रयम्) (1 x 3 = 3)
(i) किं त्वम् ……………” वाराणसी गमिष्यसि?
(क) हयः
(ख) श्वः
(ग) पुरा
उत्तर
(ख) श्वः
(ii) ……. एव अहम् मातुलस्य गृहं गच्छामि।
(क) यावत्
(ख) यदा-कदा
(ग) तत्र
उत्तर
(ख) यदा-कदा
(iii) ……………..” अहं पाठं पठामि तावत् त्वम् अभ्यासं कुरु
(क) यावत्
(ख) यत्र
(ग) यदा
उत्तर
(क) यावत्
(iv) यत्र मम विद्यालयः “…………..” एव अहम् वसामि।
(क) तत्र
(ख) कुत्र
(ग) अत्र
उत्तर
(क) तत्र
प्रश्न 7.
अधोलिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदम् अशुद्धम् अस्ति। शुद्ध पदं विकल्पेभ्यः चिनुत- (केवलं प्रश्नत्रयम्) (1 x 3 = 3)
(i) गृहे अनेकानि अतिथयः आगच्छन्।
(क) अनेके
(ख) अनेकम्
(ग) अनेकाः
उत्तर
(क) अनेके
(ii) एतत् दृष्ट्वा बालकाः प्रसन्नाः अभवत्।
(क) अभवताम्
(ख) अभवन्
(ग) अभवत
उत्तर
(ख) अभवन्
(iii) आवाम् नाटकम् द्रक्ष्यामि।
(क) वयम्
(ख) आवाम्
(ग) अहम्
उत्तर
(ग) अहम्
(iv) सा श्वः मम गृहम् आगच्छत्।।
(क) आगमिष्यामि
(ख) आगमिष्यति
(ग) आगच्छन्
उत्तर
(ख) आगमिष्यति
पठितावबोधनम् (अङ्काः 15)
प्रश्न 8.
रेखाङ्कितपदानि आधृत्य समुचितं प्रश्नवाचकपदं चिनुत। (केवलं प्रश्नपञ्चकम्) (1 x 5 = 5)
(i) कश्चन् धूर्तः शृगालः हसन् आह।
(क) कीदृशी
(ख) कीदृशः
(ग) कीदृशम्
उत्तर
(ख) कीदृशः
(ii) देउलाख्ये ग्रामे राजसिंहः वसति स्म।
(क) के
(ख) कस्मिन्/कुत्र
(ग) कः
उत्तर
(ख) कस्मिन्/कुत्र
(iii) गुणी गुणं वेत्ति।
(क) कः
(ख) को
(ग) का
उत्तर
(क) कः
(iv) कृषिवलः क्रुद्धः अभवत्।
(क) कः
(ख) कीदृशः
(ग) किम्
उत्तर
(क) कः
(v) सः भारवेदनया क्रन्दति स्म।
(क) का
(ख) किम्
(ग) कया
उत्तर
(ग) कया
(vi) पुत्रः पठनाय पाठशाला गच्छति।
(क) किमर्थम्
(ख) कुत्र
(ग) कय
उत्तर
(क) किमर्थम्
प्रश्न 9.
अधोलिखितवाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदानां प्रसङ्गानुकुलम् उचितार्थं चिनुत- (केवलं प्रश्नचतुष्टयम्) (1 x 4 = 4)
(i) अवक्रता चित्ते यथा।
(क) कर्णे
(ख) आत्मनि
(ग) मनसि
उत्तर
(ग) मनसि
(ii) इति एतद् विदुषाम् वचः।
(क) कथितः
(ख) वचनम्
(ग) कार्यम्
उत्तर
(ख) वचनम्
(iii) व्याघ्रं दृष्ट्वा बुद्धिमती उवाच।
(क) अवलोक्य
(ख) पश्य
(ग) दृष्टताः
उत्तर
(क) अवलोक्य
(iv) कृषिवल: वृषभम् तुदति।
(क) अश्वम्
(ख) गर्दभम्
(ग) वलीवर्दम्
उत्तर
(ग) वलीवर्दम्
(v) आरक्षी चौरं न्यायालयं नीतवान्।
(क) सैनिकः
(ख) रक्षी
(ग) आरक्षक:
उत्तर
(ग) आरक्षक:
प्रश्न 10.
भाषिककार्यसम्बद्धानां प्रश्नानां समुचितम् उत्तरं विकल्पेभ्यः चिनुत-(केवलं प्रश्नषट्कम्) (1 x 6 = 6)
(i) “आलस्यं हि मनुष्याणां शरीस्थो महान् रिपुः” अत्र उद्यमम् पदस्य विपर्ययं किम्?
(क) महान्
(ख) रिपुः
(ग) आलस्यम्
उत्तर
(ग) आलस्यम्
(ii) “प्रविष्टः” इति क्रियापदस्य कर्तृपदं किम्?
(क) चौरः
(ख) गृहाभ्यन्तरः
(ग) तस्मिन्
उत्तर
(क) चौरः
(iii) “अहम् तु पुत्रं शोचामि” अत्र शोचामि क्रियापदस्य कर्तृपदं किम्?
(क) तु
(ख) पुत्रम्
(ग) अहम्
उत्तर
(ग) अहम्
(iv) “वायुमण्डलं भृशं दूषितम् नहि निर्मलजलं’ अत्र वायुमण्डलं पदस्य विशेषणं किम्?
(क) भृशम् दूषितम्
(ख) नहि
(ग) जलम्
उत्तर
(क) भृशम् दूषितम्
(v) अनृतम् पदम् वदसि चेत् काकः दशेत्-अत्र असत्यम् पदाय किम् पदं प्रयुक्तम्?
(क) असत्यम्
(ख) अनृतम्
(ग) नृतम्
उत्तर
(ख) अनृतम्
(vi) “तस्य पुच्छम् धुनोति” अत्र तस्य पदं कस्मै प्रयुक्तम्?
(क) पक्षिणे
(ख) सिंहाय
(ग) वानराय
उत्तर
(ख) सिंहाय
(vii) ‘निर्धनः जनः’ अत्र विशेष्यपदं किम्?
(क) निर्धनः
(ख) निधि
(ग) जनः
उत्तर
(ग) जनः
(viii) भाग्यवशात् इति पदस्य पर्यायपदं किम्?
(क) कार्यात्
(ख) दैवात्
(ग) परिश्रमात्
उत्तर
(ख) दैवात्
‘आ’-भागः – वर्णनात्मकाः प्रश्नाः (अङ्काः 40)
अपठितावबोधनम् (अङ्काः 10)
प्रश्न 11.
अधोलिखितं गद्यांशं पठित्वा प्रदत्तप्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि संस्कृतेन लिखत।
एकस्मिन् ग्रामे मन्थरको नाम तन्तुवायः अवसत्। तन्तु संयोजनं कुर्वतः तस्य सर्वाणि उपकरणानि नष्टानि। अथ सः नवीनानि उपकरणानि निर्मातुं काष्ठानि प्राप्तुं वनगमच्छत्। तत्र एकम् विशाल वृक्षं दृष्ट्वा यावत् सः तस्योपरि कुठाराघातं कर्तुम् उद्यतोऽभवत् तावदेव तवृक्षवासी यक्षः अवदत्-“भो! अयं पादपः मम आश्रयः, एनं मा कर्तय। अहम् तव मनोकामना पूरयिष्यामि, अभीष्टं वरं प्रार्थय इति” एतत् श्रुत्वा तन्तुवायः स्वपत्नी प्रष्टुम् गृहमागच्छत्।
सा तम् अन्यत् बाहुयगलम् द्वितीयं च शिर याचितुम् प्रेरितवती येन सः पुरतः पृष्ठतः च पटान् निर्मातुं समर्थो भवेत्। ततः मन्थरक: वनं गत्वा यक्षं अन्यद् बाहु द्वितीयं शिरः याचितवान्। यक्ष अपि तस्मै तादृशम् वरम् दत्तवान्। अनन्तरम् यावत् सः चतुर्भुजः द्विशिरः भूत्वा गृहमागतवान् तावत् सर्वे तम् राक्षसमत्वा तस्य वधम् अकुर्वन्।
(अ) एकपदेन उत्तरत। (केवलं प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1 × 2 = 2)
(i) तन्तुवायः कुत्र अवसत्?
(ii) तन्तुवायः काम् प्रष्टुम् गृहम् आगच्छत्?
(iii) सर्वे किम् मत्वा मन्थरकस्य वधम् अकुर्वन्?
उत्तर
(i) एकस्मिन् ग्रामे
(ii) स्वपत्नीम्
(iii) राक्षसम्
(आ) पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत। (केवल प्रश्नद्वयम्) (2 × 2 = 4)
(i) मन्थरक: किमर्थम् वनम् अगच्छत्?
(ii) वृक्षवासी यक्षः तन्तुवायम् किम् अवदत्?
(iii) तन्तुवायस्य पत्नी तन्तुवायम् किम् याचितुं प्रेरितवती?
उत्तर
(i) सः नवीनानि उपकरणानि निर्मातुं काष्ठानि प्राप्तुं वनं अगच्छत्।।
(ii) वृक्षवासी यक्षः अवदत् भो अयं पादपः ………… एनं या कर्तय।
(iii) तन्तुवायस्य भार्या अन्यत् ………………… प्रेरितवती।
(इ) अस्य अनुच्छेदस्य कृते उपयुक्तं शीर्षकं संस्कृतेन लिखत। (1)
उत्तर
मूर्खः तन्तुवाय:/मूर्खा भार्या/सहसा क्रियां न विदधीत/लोभस्य परिणामः
(ई) यथानिर्देशम् उत्तरत्-(केवलं प्रश्नत्रयम्) (1 ×3 = 3)
(i) तस्य सर्वाणि उपकरणानि नष्टानि। अत्र विशेष्यपदं किम्?
(क) नष्टानि
(ख) उपकरणानि
(ग) सर्वाणि
उत्तर
(i) उपकरणानि
(ii) सा तम् अन्यत् बाहुयुगलम् … अत्र सा पदम् कस्यै प्रयुक्तम्?
(क) यक्षाय
(ख) तन्तुवायाय
(ग) पत्न्यै
उत्तर
(ग) पत्न्यै
(iii) “यक्षः अपि तस्मै तादृशं वरं दत्तवान्” दत्तवान् क्रियापदस्य कर्तृपदं किम्?
(क) तस्मै
(ख) यक्षः
(ग) वरम्
उत्तर
(ख) यक्षः
(iv) “सः पुरतः पृष्ठतः च पटान् निर्मातुम्” अत्र पटान् इति पदस्य कः अर्थः?
(क) वस्त्राणि
(ख) काष्ठानि
(ग) यन्त्राणि
उत्तर
(क) वस्त्राणि
रचनात्मक कार्यम् (अङ्काः 15)
प्रश्न 12.
पितामहं प्रति लिखिते पत्रे रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयित्वा पत्रं च पुनः उत्तरपुस्तिकायां लिखतु। छात्रावासतः पूरमपूज्याः पितामहमहोदया:! श्रीमत्-चरणकमलेषु सविनयं प्रणामाः भवतां पत्रं गतदिने मया (i) …………….. पत्रं लब्ध्वा पठित्वा च महान् (ii) …………. जातः। अत्र भवत्कृपया अहं सर्वथा कुशली (iii) ………… अस्मि। अध्ययनम् अपि मम (iv) ………….. प्रचलित। अहं प्रथमश्रेण्याम् उत्तीर्णः इति (v) ………… ज्ञात्वा भवता महती प्रसन्नता प्रकटीकृता पत्रे। परं इदं भवच्चरणकमलयोः एव कृपया फलं वर्तते। (vi) …………… शुभाशीर्वचनैश्च अहं पुनरपि परीक्षासु प्रथमश्रेणी (vii) …………. । काले-काले पत्रप्रदानेन (viii) …………….. मार्गदर्शनेने (ix) ……………… दोषाणाम् निरूपणेन च अहं (x) …………….. अनुग्राह्यः इति पुनः प्रणतिपूर्वकं प्रणामाः। (1/2 × 10 = 5)
उत्तर
(i) प्राप्तम्
(ii) प्रमोदो
(iii) सानन्दश्च
(iv) सम्यक्
(v) समाचारम्
(vi) शुभाशीर्वादैः
(vii) प्राप्स्यामि
(viii) भवताम्
(ix) मम
(x) सर्वदा
भवदङ्कपालितः पौत्रः
कखग मञ्जूषा- सर्वदा, शुभाशीर्वादैः, प्राप्स्यामि, मम, प्रमोदो, समाचार प्राप्तम्, भवताम्, सम्यक्, सानन्दश्च
प्रश्न 13.
प्रदत्तं चित्रं दृष्ट्वा मञ्जूषायां प्रदत्तशब्दानां सहायतया पञ्च वाक्यानि संस्कृतेन लिखत- (1 x 5 = 5)

मञ्जूषा- छात्राः, क्षेत्रे, वृक्षारोपणम्, वनमहोत्सवः पर्यावरणम्, शिक्षकैः, पादपानाम्, रोपणम्, पादपान्, उत्साहपूर्वकम् अनेके वृक्षाः, विशालम्
उत्तर
(1) अस्मिन् चित्रे वनमहोत्सवस्य दृश्यम् अस्ति।
(2) विद्यालयस्य प्राङ्गणे छात्राः वृक्षारोपणम् कुर्वन्ति
(3) पादपान् रोपयित्वा एका बालिका पर्यावरणगीतं गायति।
(4) सर्वे छात्राः उत्साहपूर्वकं वनमहोत्सवम् आचरन्ति।
(5) क्षेत्रे अनेके हरिताः वृक्षाः सन्ति।
अथवा
मञ्जूषा – प्रदत्तशब्दानां साहाय्येन निम्नलिखितं विषयम् अधिकृत्य पञ्चभिः संस्कृतवाक्यैः एकम् अनुच्छेदं लिखत
मञ्जूषा- प्रतिदिनं, सर्वोत्तम् धनम्, सूर्योदयः, संतुलित आहारः, नियमित व्यायामः, स्वास्थ्य, स्वास्थ्यवर्धक, प्राक् ,प्रश्नपत्रम्
उत्तर
(1) स्वास्थ्यम् स्वस्थजीवनस्य आधारस्तम्भः अस्ति।
(2) स्वास्थ्यस्य रक्षायै स्वास्थ्यसंबंधी नियमान् पालयेयुः।
(3) प्रतिदिनं प्रात: व्यायाम कुर्यात्।
(4) सन्तुलितं भोजनं कुर्यात्।
(5) सर्वेषु धनेषु स्वास्थ्यमेव सर्वोत्तमं धनम् अस्ति।
प्रश्न 14.
अधोलिखितानि वाक्यानि संस्कृतभाषया अनूद्य लिखत-(केवलं वाक्यपञ्चकम्) (1 x 5 = 5)
(i) भारत नदियों का देश है। (India is country of Rivers.)
(ii) अरुणाचल प्रदेश की राजधानी इटानगर है। (Capital of Aurmchal Pradesh is Itanagar.)
(iii) सदाचार मनुष्य का पहला धर्म होना चाहिए। (Virtue should be Man’s first religion.)
(iv) सज्जन व्यक्ति सदैव परोपकार करते हैं। (Gentleman always do charity.)
(v) माता और पिता अपने बच्चों का मार्गदर्शन करते है। (Parents always guide their children.)
(vi) जीवन में एक ही लक्ष्य होना चाहिए। (There should be only one goal in life.)
(vii) पिता के साथ पुत्र जाता है। (Son goes with Father.)
उत्तर
(i) भारतम् नदीनाम् देशः अस्ति।
(ii) अरुणाचलप्रदेशस्य राजधानी इटानगरम् अस्ति।
(iii) सदाचारः मनुष्याणां प्रथम धर्मः भवेत्।
(vi) सज्जनाः सदैव परोपकारं कुर्वन्ति।
(v) पितरौ स्वसन्तते:/शिशूनाम् मार्गदर्शनं कुरुतः ।
(vi) जीवने एकमेव लक्ष्यं भवेत्।
(vii) पित्रेण सह पिता गच्छति।
पठितावबोधनम् (अङ्काः 15)
प्रश्न 15.
अधोलिखितं गद्यांशं पठित्वा प्रदत्तप्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि संस्कृतेन लिखत। (3)
विचित्रा दैवगतिः। तस्यामेव रात्रौ तस्मिन् गृहे कश्चन् चौरः गृहाभ्यन्तरं प्रविष्टः। तत्र निहितामेकां मञ्जूषाम् आदाय पलायितः। चौरस्य पादध्वनिना प्रबुद्धोऽतिथिः चौरशङ्कया तमन्वधावत् अगृहणाच्च, परं विचित्रमघटत। चौरः एव उच्चैः क्रोशितुमारभत “चौरोऽयं चौरोऽयम्” इति। तस्य तारस्वरेण प्रबुद्धाः ग्रामवासिनः स्वगृहाद् निष्क्रम्य तत्रागच्छन् वराकमतिथिमेव च चौरं मत्वाऽभर्त्सयन्। यद्यपि ग्रामस्य आरक्षी एव चौर आसीत्। तत्क्षणमेव रक्षापुरुषः तम् अतिथिम् चौरोऽयम् इति प्रख्याप्य कारागृहे प्राक्षितपत्।
(अ) एकपदेन उत्तरत। (केवलं प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1/2 × 2 = 1)
(i) दैवगतिः कीदृशी:?
(ii) गृहाभ्यन्तरं कः प्रविष्ट:?
(iii) अतिथिः केन प्रबुद्ध?
उत्तर
(i) विचित्रा
(ii) चौरः
(iii) पादध्वनिना
(आ) पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत। (केवल प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1 × 2 = 2)
(i) ग्रामवासिनः किम् अकुर्वन्?
(ii) रक्षापुरुषः किम् अकरोत्?
(iii) चौरः किम् आदाय पलायितः?
उत्तर
(i) गृहवासिनः स्वगृहाद् ………………… मत्वा अभय॑न्।
(i) रक्षापुरुषः अतिथिम् ………………… अक्षिपत्।
(iii) गृहे स्थितामेकाम् ………………. पलायितः।
प्रश्न 16.
अधोलिखितं पद्यांशं पठित्वा प्रदत्तप्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि संस्कृतेन लिखत (3)
विनिपातो न वः कश्चिद् दृश्यते त्रिदशाधिपः।
अहं तु पुत्रं शोचामि, तेन रोदिमि कौशकि!।।
(अ) एकपदेन उत्तरत। (केवलं प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1/2 × 2 = 1)
(i) कौशिक! पदं कस्मै प्रयुक्तम्?
(ii) त्रिदशाधिपः कः अस्ति?
(iii) वृषभस्य कः न दृश्यते?
उत्तर
(i) इन्द्राय
(ii) इन्द्रः
(iii) विनिपातः
(आ) पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत। (केवलं प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1 × 2 = 2)
(i) सुरभिः पुत्रस्य चिन्तां कृत्वा किमर्थम् रोदिति?
(ii) सुरभिः इन्द्रम् किम्-किम् कथयित्वा सम्बोधयति?
(iii) सुरभेः चिन्तायाः कारणम् किम् अस्ति?
उत्तर
(i) सुरभि चिन्तयति ………………… दृश्यते।
(ii) कौशिकः च त्रिदशाधिपः ……………. सम्बोधयति।
(iii) सुरभेः पुत्रस्य कोऽपि सहायकः न अस्ति इति सुरभेः चिन्तायाः कारणम्।
प्रश्न 17.
अधोलिखितं नाट्यांशं पठित्वा प्रदत्तानां प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि संस्कृतेन लिखता
काकः रे परभृत! अहं यदि तव संततिं न पालयामि तर्हि कुत्र स्युः पिकाः? अतः अहम् एव करुणापरः पक्षिसम्राट् काकः। (3)
गजः समीपतः एवागच्छन् अरे! सर्वां वार्ता शृण्वन्नेवाहम् अत्रागच्छम्। अहं विशालकायः, बलशाली, पराक्रमी च। सिंहः वा स्यात् अथवा अन्यः कोऽपि। वन्यपशून् तु तुदन्तं जन्तुमहं स्वशुण्डेन पोथयित्वा मारयिष्यामि। किमन्यः कोऽप्यस्ति एतादृशः पराक्रमी। अतः अहम् एव योग्यः वनराजः।
वानरः अरे! अरे! एवं (शीघ्रमेव गजस्यापि पुच्छं विधूय वृक्षोपरि आरोहति)
(अ) एकपदेन उत्तरत। (केवल प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1/2 × 2 = 1)
(i) काकः कम् “रे परिभृत्!” इति कथयति?
(ii) काकः कस्य सन्ततिं पालयति?
(iii) कः विशालकायः बलशाली च?
उत्तर
(i) पिकम्
(ii) पिकस्य
(iii) गजः
(आ) पूर्णवाक्य में उत्तरत। (केवल प्रश्नद्वयम्) (1 × 2 = 2)
(i) गजः आत्मनः विषये किं कथयति?
(ii) काकः आत्मनः विषये किं कथयति?
(iii) गजः कदा वन्यपशून् मारयिष्यति?
उत्तर
(i) अहम् विशालकायः ……………. मारयिष्यामि।
(ii) रे परिभृत! …………… पक्षीसम्राट् काकः।
(iii) वन्य पशून तु तदुन्तं जन्तुम् अहम् …………….. मारयिष्यामि।
प्रश्न 18.
मञ्जूषातः समुचितपदानि चित्वा अधोलिखित-श्लोकस्य अन्वयं पूरयत (1/2 × 4 = 2)
श्लोकः- आलस्यं हि मनुष्याणाम् शरीरस्थो महान् रिपुः।
नास्त्युद्यमसमो बन्धुः कृत्वाः यं नावसीदति।।।
अन्वयः- मनुष्याणाम्
(i) …………………. महान् शत्रुः
(ii) ……………… उद्यमसमः
(iii) …………………. न अस्ति यं
(iv) ……………… (नरः) न अवसीदति। मञ्जूषा- कृत्वा, शरीरस्थः, बन्धुः, आलस्यम्
उत्तर
(i) शरीरस्थः
(ii) आलस्यम्
(iii) बन्धुः
(iv) कुत्वा
अथवा
मञ्जूषायाः साहाय्येन श्लोकस्यभावार्थे रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयित्वा पुनः लिखत।
श्लोकः- यः इच्छत्यात्मनः श्रेयः प्रभूतानि सुखानि च।
न कुर्यादहितं कर्म स परेभ्यः कदापि च।।
भावार्थ:- अस्य श्लोकस्य भावः अस्ति यत् यदि नरः आत्मनः कृते
(i) ………………. बहूनि
(ii) ……….. वाञ्छति सम्मानं च वाञ्छति तर्हि तेन
(iii) ……….. जनेभ्यः
(iv) ……….. कर्म कदापि न कर्तव्यम्।
मञ्जूषा- परेभ्यः, अहितकर, सुखानि, कल्याणं
उत्तर
(i) कल्याणम्
(ii) सुखानि
(iii) परेभ्यः
(iv) अहितकरम्
प्रश्न 19.
अधोलिखित-कथांशं समुचितक्रमेण लिखत। (1/2 x 8 = 4)
(i) एकः कृषकः आसीत्।
(ii) कृषकः तम् दुर्बलम् वृषभ तोदनेन अवर्तत।
(iii) कृषीवलः क्रुद्धः अवभवत्।
(iv) सः जवेन गन्तुम् अशक्तः च आसीत्
(v) तस्य समीपे बलीवौ आस्ताम
(vi) तमुत्थापयितुम् बहुवारं यत्नमकरोत् तथापि सः नोत्थितः।
(vii) सः ऋषभः हलमूढ्वा गन्तुम् अशक्तः क्षेत्रे पपात्।
(viii) तयोः बलीवर्दयोः एकः शरीरेण दुर्बलः आसीत्।
उत्तर
(i) एकः कृषकः आसीत्।
(ii) तस्य समीपे बलीवौ आस्ताम्।
(iii) तयो बलीवर्दयोः एकः शरीरेण दुर्बलः आसीत्।
(iv) सः जवेन गन्तुम् अशक्तः च आसीत्।
(v) कृषकः तम् दुर्बलम् वृषभम् तोदनेन अवर्तत।
(vi) सः ऋषभः हलमूढवा गन्तुम् …….
(vii) कृषीवल क्रुद्धः अभवत्।।
(viii) तमुत्थापयितुम् बहुवारं