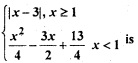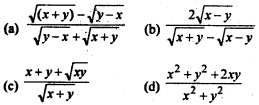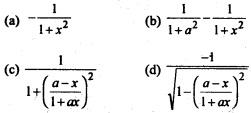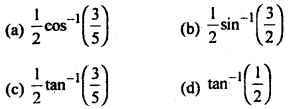Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Application of Derivatives Class 12 Maths MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers
Maths Class 12 Chapter 6 MCQs On Application of Derivatives
Question 1.
The sides of an equilateral triangle are increasing at the rate of 2cm/sec. The rate at which the are increases, when side is 10 cm is
(a) 10 cm²/s
(b) √3 cm²/s
(c) 10√3 cm²/s
(d) \(\frac{10}{3}\) cm²/s
Answer
Answer: (c) 10√3 cm²/s
Question 2.
A ladder, 5 meter long, standing oh a horizontal floor, leans against a vertical wall. If the top of the ladder slides downwards at the rate of 10 cm/sec, then the rate at which the angle between the floor and the ladder is decreasing when lower end of ladder is 2 metres from the wall is
(a) \(\frac{1}{10}\) radian/sec
(b) \(\frac{1}{20}\) radian/sec
(c) 20 radiah/sec
(d) 10 radiah/sec
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{1}{20}\) radian/sec
Question 3.
The curve y – x1/5 at (0, 0) has
(a) a vertical tangent (parallel to y-axis)
(b) a horizontal tangent (parallel to x-axis)
(c) an oblique tangent
(d) no tangent
Answer
Answer: (b) a horizontal tangent (parallel to x-axis)
Question 4.
The equation of normal to the curve 3x² – y² = 8 which is parallel to the line ,x + 3y = 8 is
(a) 3x – y = 8
(b) 3x + y + 8 = 0
(c) x + 3y ± 8 = 0
(d) x + 3y = 0
Answer
Answer: (c) x + 3y ± 8 = 0
Question 5.
If the curve ay + x² = 7 and x³ = y, cut orthogonally at (1, 1) then the value of a is
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) -6
(d) 6
Answer
Answer: (d) 6
Question 6.
If y = x4 – 10 and if x changes from 2 to 1.99 what is the change in y
(a) 0.32
(b) 0.032
(c) 5.68
(d) 5.968
Answer
Answer: (a) 0.32
Question 7.
The equation of tangent to the curve y (1 + x²) = 2 – x, w here it crosses x-axis is:
(a) x + 5y = 2
(b) x – 5y = 2
(c) 5x – y = 2
(d) 5x + y = 2
Answer
Answer: (a) x + 5y = 2
Question 8.
The points at which the tangents to the curve y = x² – 12x +18 are parallel to x-axis are
(a) (2, – 2), (- 2, -34)
(b) (2, 34), (- 2, 0)
(c) (0, 34), (-2, 0)
(d) (2, 2),(-2, 34).
Answer
Answer: (d) (2, 2),(-2, 34).
Question 9.
The tangent to the curve y = e2x at the point (0, 1) meets x-axis at
(a) (0, 1)
(b) (-\(\frac{1}{2}\), 0)
(c) (2, 0)
(d) (0, 2)
Answer
Answer: (b) (-\(\frac{1}{2}\), 0)
Question 10.
The slope of tangent to the curve x = t² + 3t – 8, y = 2t² – 2t – 5 at the point (2, -1) is
(a) \(\frac{22}{7}\)
(b) \(\frac{6}{7}\)
(c) \(\frac{-6}{7}\)
(d) -6
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{-6}{7}\)
Question 11.
The two curves; x³ – 3xy² + 2 = 0 and 3x²y – y³ – 2 = 0 intersect at an angle of
(a) \(\frac{π}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{π}{3}\)
(c) \(\frac{π}{2}\)
(d) \(\frac{π}{6}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{π}{4}\)
Question 12.
The interval on which the function f (x) = 2x³ + 9x² + 12x – 1 is decreasing is
(a) [-1, ∞]
(b) [-2, -1]
(c) [-∞, -2]
(d) [-1, 1]
Answer
Answer: (b) [-2, -1]
Question 13.
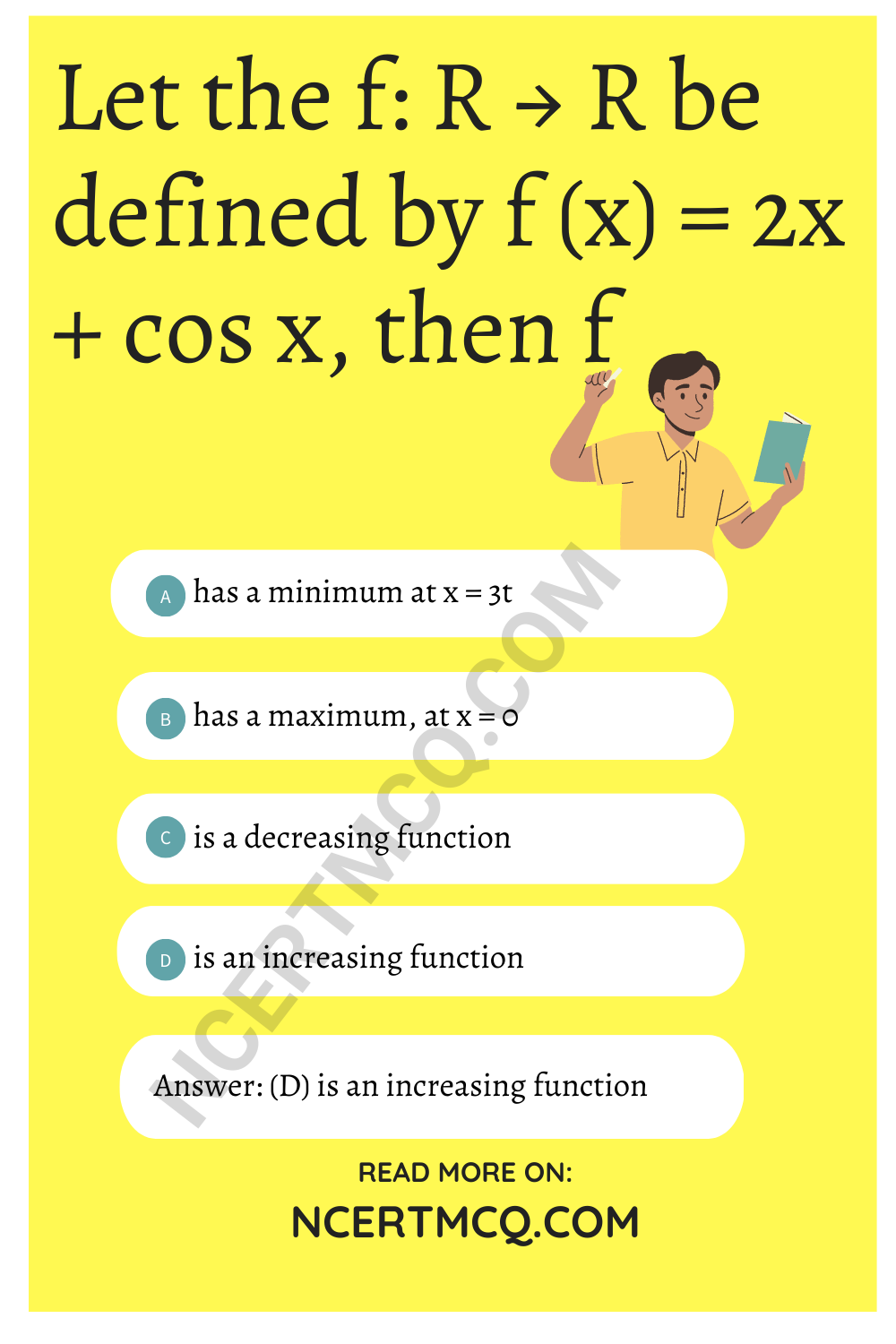
Let the f: R → R be defined by f (x) = 2x + cos x, then f
(a) has a minimum at x = 3t
(b) has a maximum, at x = 0
(c) is a decreasing function
(d) is an increasing function
Answer
Answer: (d) is an increasing function
Question 14.
y = x (x – 3)² decreases for the values of x given by
(a) 1 < x < 3
(b) x < 0
(c) x > 0
(d) 0 < x <\(\frac{3}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 < x < 3
Question 15.
The function f(x) = 4 sin³ x – 6 sin²x + 12 sin x + 100 is strictly
(a) increasing in (π, \(\frac{3π}{2}\))
(b) decreasing in (\(\frac{π}{2}\), π)
(c) decreasing in [\(\frac{-π}{2}\),\(\frac{π}{2}\)]
(d) decreasing in [0, \(\frac{π}{2}\)]
Answer
Answer: (c) decreasing in [\(\frac{-π}{2}\),\(\frac{π}{2}\)]
Question 16.
Which of the following functions is decreasing on(0, \(\frac{π}{2}\))?
(a) sin 2x
(b) tan x
(c) cos x
(d) cos 3x
Answer
Answer: (c) cos x
Question 17.
The function f(x) = tan x – x
(a) always increases
(b) always decreases
(c) sometimes increases and sometimes decreases
(d) never increases
Answer
Answer: (a) always increases
Question 18.
If x is real, the minimum value of x² – 8x + 17 is
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
Answer
Answer: (d) 2
Question 19.
The smallest value of the polynomial x³ – 18x² + 96x in [0, 9] is
(a) 126
(b) 0
(c) 135
(d) 160
Answer
Answer: (b) 0
Question 20.
The function f(x) = 2x³ – 3x² – 12x + 4 has
(a) two points of local maximum
(b) two points of local minimum
(c) one maxima and one minima
(d) no maxima or minima
Answer
Answer: (c) one maxima and one minima
Question 21.
The maximum value of sin x . cos x is
(a) \(\frac{1}{4}\)
(b) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(c) √2
(d) 2√2
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 22.
At x = \(\frac{5π}{6}\), f (x) = 2 sin 3x + 3 cos 3x is
(a) maximum
(b) minimum
(c) zero
(d) neither maximum nor minimum
Answer
Answer: (d) neither maximum nor minimum
Question 23.
Maximum slope of the curve y = -x³ + 3x² + 9x – 27 is
(a) 0
(b) 12
(c) 16
(d) 32
Answer
Answer: (a) 0
Question 24.
f(x) = xx has a stationary point at
(a) x = e
(b) x = \(\frac{1}{e}\)
(c) x = 1
(d) x = √e
Answer
Answer: (b) x = \(\frac{1}{e}\)
Question 25.
The maximum value of (\(\frac{1}{x}\))x is
(a) e
(b) e²
(c) e1/x
(d) (\(\frac{1}{e}\))1/e
Answer
Answer: (d) (\(\frac{1}{e}\))1/e
Question 26.
If the volume of a sphere is increasing at a constant rate, then the rate at which its radius is increasing is
(a) a constant
(b) proportional to the radius
(c) inversely proportional to the radius
(d) inversely proportional to the surface area
Answer
Answer: (d) inversely proportional to the surface area
Question 27.
A particle is moving along the curve x = at² + bt + c. If ac = b², then particle would be moving with uniform
(a) rotation
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) retardation
Answer
Answer: (c) acceleration
Question 28.
The distance Y metres covered by a body in t seconds, is given by s = 3t² – 8t + 5. The body will stop after
(a) 1 s
(b) \(\frac{3}{4}\) s
(c) \(\frac{4}{3}\) s
(d) 4 s
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{4}{3}\) s
Question 29.
The position of a point in time Y is given by x = a + bt + ct², y = at + bt². Its acceleration at timet Y is
(a) b – c
(b) b + c
(c) 2b – 2c
(d) 2\(\sqrt{b^2+c^2}\)
Answer
Answer: (d) 2\(\sqrt{b^2+c^2}\)
Question 30.
The function f(x) = log (1 + x) – \(\frac{2x}{2+x}\) is increasing on
(a) (-1, ∞)
(b) (-∞, 0)
(b) (-∞, ∞)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) (-1, ∞)
Question 31.
f(x) = (\(\frac{e^{2x}-1}{e^{2x}+1}\)) is
(a) an increasing function
(b) a decreasing function
(c) an even function
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) an increasing function
Question 32.
If f (x) = \(\frac{x}{sin x}\) and g (x) = \(\frac{x}{tan x}\), 0 < x ≤ 1, then in the interval
(a) both f (x) and g (x) are increasing functions
(b) both f (x) and g (x) are decreasing functions
(c) f(x) is an increasing function
(d) g (x) is an increasing function
Answer
Answer: (c) f(x) is an increasing function
Question 33.
The function f(x) = cot-1 x + x increases in the interval
(a) (1, ∞)
(b) (-1, ∞)
(c) (0, ∞)
(d) (-∞, ∞)
Answer
Answer: (d) (-∞, ∞)
Question 34.
The function f(x) = \(\frac{x}{log x}\) increases on the interval
(a) (0, ∞)
(b) (0, e)
(c) (e, ∞)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) (e, ∞)
Question 35.
The value of b for which the function f (x) = sin x – bx + c is decreasing for x ∈ R is given by
(a) b < 1
(b) b ≥ 1
(c) b > 1
(d) b ≤ 1
Answer
Answer: (c) b > 1
Question 36.
If f (x) = x³ – 6x² + 9x + 3 be a decreasing function, then x lies in
(a) (-∞, -1) ∩ (3, ∞)
(b) (1, 3)
(c) (3, ∞)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) (1, 3)
Question 37.
The function f (x) = 1 – x³ – x5 is decreasing for
(a) 1 < x < 5
(b) x < 1
(c) x > 1
(d) all values of x
Answer
Answer: (d) all values of x
Question 38.
Function, f (x) = \(\frac{λ sin x+ 6 cos x}{2 sin x + 3 cos x}\) is monotonic increasing, if
(a) λ > 1
(b) λ < 1
(c) λ < 4
(d) λ > 4
Answer
Answer: (d) λ > 4
Question 39.
The length of the longest interval, in which the function 3 sin x – 4 sin³ x is increasing is
(a) \(\frac{π}{3}\)
(b) \(\frac{π}{2}\)
(c) \(\frac{3π}{2}\)
(d) π
Answer
Answer: (d) π
Question 40.
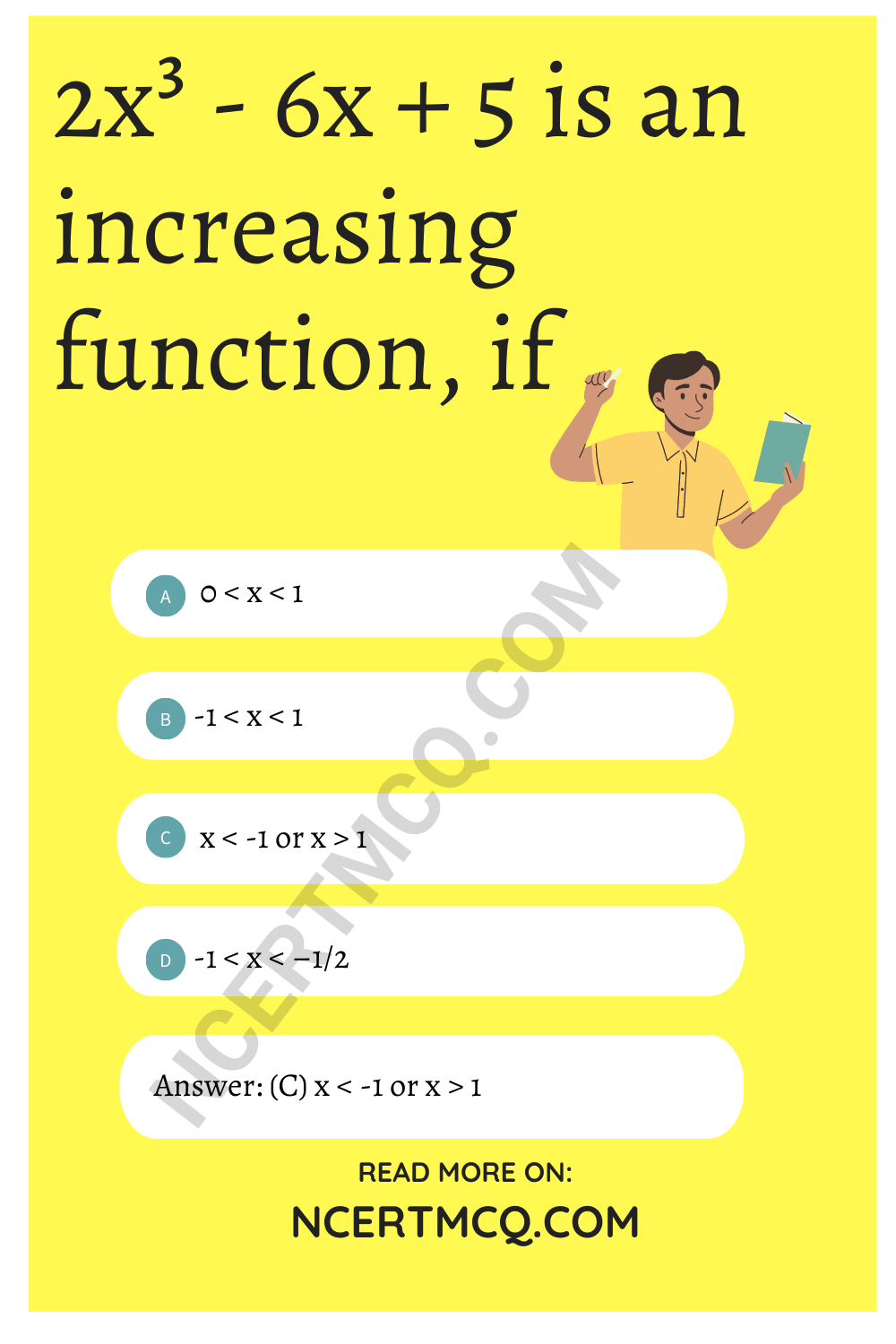
2x³ – 6x + 5 is an increasing function, if
(a) 0 < x < 1
(b) -1 < x < 1
(c) x < -1 or x > 1
(d) -1 < x < –\(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) x < -1 or x > 1
Question 41.
The function f(x) = x + cos x is
(a) always increasing
(b) always decreasing
(c) increasing for certain range of x
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) always increasing
Question 42.
The function which is neither decreasing nor increasing in (\(\frac{π}{2}\), \(\frac{3π}{2}\)) is
(a) cosec x
(b) tan x
(c) x²
(d) |x – 1|
Answer
Answer: (b) tan x
Question 43.
The function /’defined by f(x) = 44 – 2x + 1 is increasing for
(a) x < 1
(b) x > 0
(c) x < \(\frac{1}{2}\)
(d) x > \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer
Answer: (d) x > \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 44.
The interval in which the function y = x³ + 5x² – 1 is decreasing, is
(a) (0, \(\frac{1}{3}\))
(b) (0, 10)
(c) (\(\frac{-10}{3}\), 0)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) (\(\frac{-10}{3}\), 0)
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Application of Derivatives CBSE Class 12 Maths MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 12 Maths MCQ:
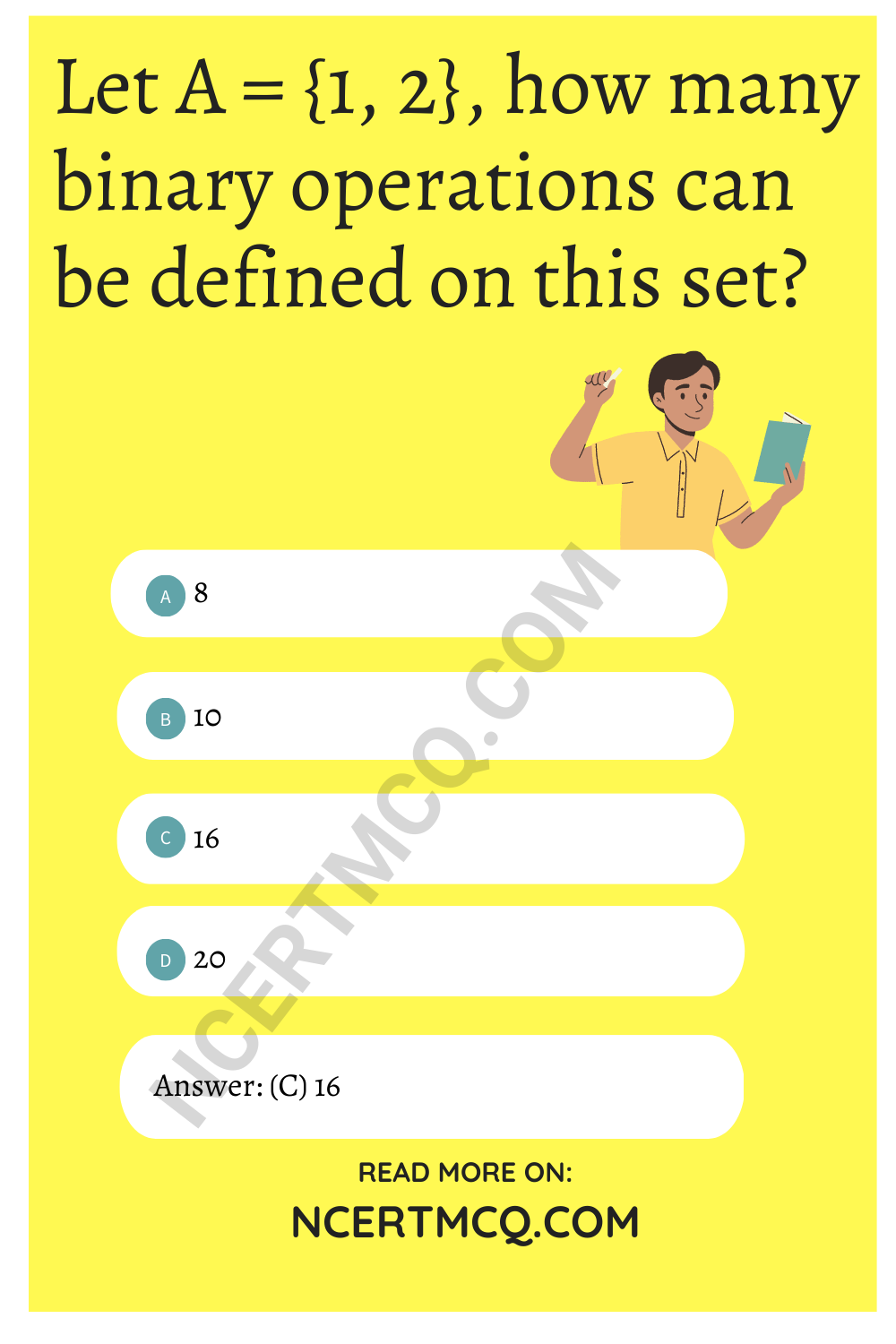
- Relations and Functions Class 12 MCQ
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 MCQ
- Matrices Class 12 MCQ
- Determinants Class 12 MCQ
- Continuity and Differentiability Class 12 MCQ
- Application of Derivatives Class 12 MCQ
- Integrals Class 12 MCQ
- Application of Integrals Class 12 MCQ
- Differential Equations Class 12 MCQ
- Vector Algebra Class 12 MCQ
- Three Dimensional Geometry Class 12 MCQ
- Linear Programming Class 12 MCQ
- Probability Class 12 MCQ


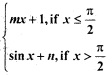 is continuous at x = \(\frac{π}{2}\), then
is continuous at x = \(\frac{π}{2}\), then