Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 Extra Questions and Answers Forest and Wildlife Resources with Answers Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-social-science/
Online Education for Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 Extra Questions Geography Chapter 2
Question 1.
Define an ecosystem.
Answer:
Eco-system is meant as the physical environment of a place formed by all kinds of plants, birds and animals of that area.
Question 2.
What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Answer:
The distribution of plants and animals is mainly determined by the climate of that area. The other determining factors of this distribution are soil, relief and drainage etc.
Question 3.
What is bio-reserve? Give two examples.
Answer:
A bio-reserve is a place which consists of fairly vast wild land and is devoted to the protection and preservation of flora and fauna of the country in the very natural form. Examples : Gulf of Mannar, Nilgiri.
Question 4.
Which was the form of life which appeared on the earth?
Answer:
Plants and vegetation.
Question 5.
What is the importance of the plants for us?
Answer:
Every form of life in the earth is dependent either directly or indirectly on the plants hence these are very significant.
Question 6.
How many flowering plants are there in India?
Answer:
About 15000.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the use of Sarpagandha?
Answer:
Sarpagandha is used for the treatment of the blood pressure.
Question 8.
How many species of the plants have been listed as endangered in India?
Answer:
52.
Question 9.
Which of the international agencies has included Indian plants in the medical list?
Answer:
The World Conservation Union.
Question 10.
Name the Indian regions where Tropical deciduous forests are found.
Answer:
- The north-eastern states,
- The foothills of the Himalays,
- Jharkhand,
- West Orissa,
- Chhattisgarh,
- Eastern slopes of the Western Ghats.
Question 11.
Name two animals having habitat in different types of vegetation.
Answer:
- Tropical Rain Vegetation: Elephant, monkey
- Deciduous Vegetation: Lion, tiger
- Thorn-Scrubs: Fox, Lion.
- Temperate Vegetation: Kashmir Stag, Leopard
- Alpine-Tundra: Yak, Leopard
- Tidal vegetation: Tiger, turtles.
Question 12.
Point out the importance of the biosphere reserves.
Answer:
- The biosphere reserves are very important in reserving the endangered species of animals and plants.
- These are the important source of transmission of the natural heritage to the future generations.
- These inspire the people of the surroundings areas to protect the wildlife.
- These provide opportunities for research.
- These are also important for promoting tourism.
![]()
Question 13.
Name the states where the following biosphere reserves are situated.
(i) Nilgiri
(ii) Nanda Devi
(iii) Manas
(iv) Simlipal
(v) Nokrek
(vi) Sundarban
(vii) Pacha-in
(viii) Dehang Debong
Answer:
Biosphere Reserves:
| (i) Nilgiri | Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala |
| (ii) Nanda Devi | Uttrakhand |
| (iii) Manas | Assam |
| (iv) Simlipal | Orissa |
| (v) Nokrek | Meghalaya |
| (vi) Sundarban | West Bengal |
| (vii) Pachmarhi | Madhya Pradesh |
| (viii) Dehang Debong. | Arunachal Pradesh. |
Question 14.
What is the reason that the tropical deciduous forests shed their leaves during the summer?
Answer:
Tropical deciduous forests are the trees like sal, sandal, shisham etc. All of these trees shed their leaves in summer. The main reason behind this fact is that the leaves get dry by the scorching heat of the summer and as a result, they leave the branches automatically.
Question 15.
What are the main reasons that the evergreen forests are found in the western slopes of the Western Ghats?
Answer:
The evergreen forests are found in the western slopes of the Western Ghats because of the following reasons:
- The western slopes of the Western Ghats get heavy rainfall because they are on the leeward side of the Western Ghats and here the monsoon winds are very active.
- The trees grown here do not have a distinct season of sheding leaves as the region is warm and wet throughout the year.
Question 16.
Why such an importance is given to conserve the natural vegetation?
Or
Describe the importance of the natural vegetation.
Answer:
Natural vegetation is no doubt very important for the environment as well as for human life. Hence, it is very essential to consume it, The main importance of the natural vegetation are the following:
- The natural vegetation adds beauty to nature.
- The natural vegetation provides habitat to the wild life including both birds and animals.
- Without the natural vegetation, the coming generation would be deprived of great variety of fauna.
- Natural vegetation greately helps us attracting the monsoon clouds and making them to rain.
- Natural vegetation also provides us many useful products like wood which gives up material for the construction purposes of domestic as well as furniture and many other things. Many industries are based on the forest products.
- Forests give us fuel.
- The raw material for paper industry, match-making and sports material are also derived from the forests.
- The natural vegetation also gives the sandal, gums, resins, turpine oil etc.
- Many other very useful products like herbs, honey, lac etc. are also taken from natural vegetation whether directly or indirectly.
- The grass form of the natural vegetation provides grazing field for cattle. Hence natural vegetation is undoubtedly one of the most essential elements of life. Hence it must be protected.
Question 17.
Which steps should be taken to preserve the natural vegetation?
Answer:
To preserve the natural vegetation following steps should be taken:
- Cutting of the trees in the forests must be stopped. The government has taken adequate steps in this direction. Forest department has been created for this purpose. Laws have, been implemented to punish die persons found in felling and cutting of the trees. However, awareness among the people is more important Without this awareness desired results cannot be achieved.
- The people must cooperate to check the feeling of trees. They infact must take active part in this regard.
Fortunately, many persons have come forward in this direction. Movement like ‘Chipko Andolan’ has been launched by the people themselves. - Necessary wood for industrial purposes and for other activities must be taken through planned manner. So that purposes-industrial growth and the environment protection-can be achieved.
- Wherever the trees have been cut for whatever reason; new trees must be planted to maintain the ecological balance.
- Function like ‘Vanmahotsava’ should be celebrated everywhere. It would help in growing the awareness.
- 33% of the total land area must be brought under forest area.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Choose the correct answer from the four alternatives given below:
Question 1.
The following is a tree found in tropical rain forests:
(a) mahogany
(b) shisham
(c) palms
(d) spruce.
Answer:
Question 2.
The following is a type of animal found in tropical rain forests:
(a) tiger
(b) elephant
(c) rabbit
(d) snow leopard
Answer:
Question 3.
The following is the type of animal found in the Alpine and Tundra Vegetation:
(a) worms
(b) camels
(c) yaks
(d) turtles
Answer:
Question 4.
The following type of timber is found in deciduous forests:
(a) acacias
(b) silver fir
(c) ebony
(d) sandalwood
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
There are the following number of national parks in India:
(a) 89
(b) 90
(c) 91
(d) 92
Answer:
Question 6.
To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to
(a) Tundra,
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen.
Answer:
Map Skills
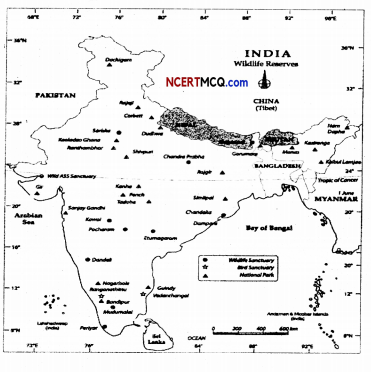
Question 1.
With the help of India’s map, show the following.
(i) Areas of Evergreen Forests
(ii) Areas of Dry Deciduous Forests
Answer:
Question 2.
Show the following in the map of India.
Two National parks each in Northern, Southern, Eastern and Western Parts.
Answer: